You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 10 Matter Around Us
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Matter Around Us Textbook Exercises
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
The separation of denser particles from lighter particles done by rotation at high speed is called ………………..
(a) Filtration
(b) sedimentation
(c) decantation
(d) centrifugation
Answer:
(d) centrifugation
Question 2.
Among the following ………………… is a mixture.
(a) Common salt
(b) Juice
(c) Carbon dioxide
(d) Pure silver
Answer:
(b) Juice
![]()
Question 3.
When we mix a drop of ink in the water we get a …………………..
(a) Heterogeneous Mixture
(b) Homogeneous Mixture
(c) Compound
(d) Suspension
Answer:
(b) Homogeneous Mixture
Question 4.
…………… is essential to perform separation by solvent extraction method.
(a) Separating funnel
(b) Centrifuge machine
(c) Filter paper
(d) Sieves
Answer:
(a) Separating funnel
Question 5
…………… has the same properties throughout the sample.
(a) Pure substance
(b) Mixture
(c) Colloid
(d) Suspension
Answer:
(a) Pure substance
II. State whether the following statements are true or false. If false give the correct statement.
- Oil and water-immiscible in each other – True
- A compound cannot be broken, into simpler substances chemically – False.
Correct Statement: A compound can be broken into simpler substances chemically. - Liquid-liquid colloids are called gels – False
Correct Statement: Liquid – solid colloids are called gels. - Buttermilk is an example of the heterogeneous mixture – True
- Aspirin is composed of 60% Carbon, 4.5% Hydrogen, and 35.5% Oxygen by mass. Aspirin is a mixture – False.
Correct Statement: The constituents of Aspirin are present in a fixed ratio by mass. So it is a Compound.
III. Match the following.
| S.No. | A | B |
| 1. | Element | (a) Settles down on standing |
| 2. | Compound | (b) Impure substance |
| 3. | Colloid | (c) Made up of molecules |
| 4. | Suspension | (d) Pure substances |
| 5. | Mixture | (e) Made up of atoms |
Answer:
- (c) Made up of molecules
- (b) Impure substance
- (a) Settles down on standing
- (d) Pure substances
- (e) Made up of atoms
IV. Fill in the blanks.
- A ____________ mixture has no distinguishable boundary between its components.
- An example of a substance that sublimes is ______________
- Alcohol can be separated from water by ___________
- In petroleum refining, the method of separation used is ___________
- Chromatography is based on the principle of ____________
Answer:
- homogeneous
- Naphthalene
- distillation
- fractional distillation
- absorptions
V. Very Short Answers.
Question 1.
Differentiate between absorption and adsorption.
Answer:
| Absorption | Adsorption |
| It is the process by which atoms, molecules, or ions enter a bulk phase (liquid, gas, solid) | It is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface |
![]()
Question 2.
Define sublimation.
Answer:
Some solids changes directly to vapours on heating. This is called sublimation.
Question 3.
A few drops of ‘Dettol’ when added to water the mixture turns turbid. Why?
Answer:
The mixture turns turbid, because of emulsion,
(Disperse phase and Dispersion medium are liquid).
Question 4.
Name the apparatus that you will use to separate the components of mixtures containing two,
- Miscible liquids,
- Immiscible liquids
Answer:
- miscible liquids: Distillation flask, fractionating column.
- immiscible liquids: Separating funnel.
Question 5.
Name the components in each of the following mixtures.
- Ice cream
- Lemonade
- Air
- Soil
Answer:
- The main constituents of ice cream are fat, milk solids (skim-milk powder), sugar, gelatin, egg and flavouring.
- Lemonade is a mixture of lemon juice, sugar and water.
- Air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour and other gases.
- Soil is a mixture of clay, sand and various salts.
VI. Short Answers.
Question 1.
Which of the following are pure substances?
Ice, Milk, Iron, Hydrochloric acid, Mercury, Brick and Water.
Answer:
Ice, Iron, Hydrochloric acid, mercury, brick, water.
Question 2.
Oxygen is very essential for us to live. It forms 21% of air by volume. Is it an element or a compound?
Answer:
Oxygen is an element. It contains the atoms of oxygen of the same kind.
![]()
Question 3.
You have just won a medal made of 22-carat gold. Have you just procured a pure substance or impure substance?
Answer:
lt is a mixture – so it is an impure substance.
Question 4.
How will you separate a mixture containing sawdust, naphthalene and iron filings?
Answer:
When a magnet is brought near the mixture containing sawdust naphthalene and iron filings, it attracts the iron filings. Thus iron filings are separated.
The mixture of naphthalene and sawdust are put in a china dish and covered with a perforated asbestos sheet. An inverted funnel is placed over the asbestos sheet.
The open end of the stem of the funnel is closed, using cotton wool. The china dish is heated. The pure vapours of naphthalene solid pass through the holes in the asbestos sheet and condense on the inner side of the funnel. The sawdust is left in the china dish.
Question 5.
How are homogenous solutions different from heterogeneous solution? Explain with examples.
Answer:
| S.No. | Homogeneous solutions | Heterogeneous solutions |
| 1. | Components are uniformly mixed. | Components arc not uniformly mixed. |
| 2. | It has single phase. | It has two or more distinct phases. |
| 3. | No boundaries of separation between the components. | There are visible boundaries between the components. |
| 4. | Components are invisible to naked eye. | Components are visible to naked eye. |
| 5. | Examples of Homogeneous solutions are salt solution, lemonade, petrol etc. | Examples of Heterogeneous solutions are chalk in water, petrol in water, and sand in water. |
VII. Long Answer.
Question 1.
Write the differences between elements and compounds and give an example for each.
Answer:
| S.No. | Elements | Compounds |
| 1. | Contains only one kind of atoms. | Contains more than one kind of atoms. |
| 2. | It is a pure substance. | It is not a pure substance. |
| 3 | Elements cannot be broken down further into simpler substances by chemical methods. | Compounds can be broken down further into simpler substances by chemical methods. |
| 4 | Elements have definite physical and chemical properties. | Compounds have definite physical and chemical properties. |
| 5 | Examples for elements: oxygen 07, hydrogen H7, sodium Na. | Examples for compounds, water H70, cane sugar Cp |
Question 2.
Explain the Tyndall effect and Brownian movement with suitable diagram.
A. Tyndall Effect:
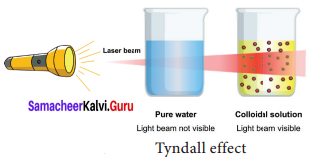
When a strong beam of light is focused on a colloidal solution the path of the beam becomes visible.
This phenomenon is called a Tyndall effect. The illuminated path is called the Tyndall cone. This phenomenon is due to scattering of light by colloidal particles.
B. Brownian movement:
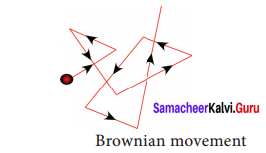
It is a kinetic property. When colloidal solution are viewed under powerful microscope, it can be seen that colloidal particles are moving constantly and rapidly in zig-zag directions. The Brownian movement of particles is due to the unbalanced bombardment of the particles by the molecules of dispersion medium.
![]()
Question 3.
How is a mixture of common salt, oil and water separated?
You can use a combination of different methods.
Answer:
The mixture of common salt, oil and water are taken in a beaker. The salt dissolves in water. Allow it to stand for a few minutes. The mixture of two immiscible liquids is separated by a separating funnel. The oil floats on top. The water can carefully be separated by opening the stopcock in the separating funnel. The oil is left behind in the separating funnel.
The saltwater is heated slowly, in a distillation flask with a water condenser. The pure water vapour passes through the inner tube of the condenser.
The vapours on cooling condense into pure water and are collected in a receiver. The salt is left behind in the flask as a residue.
Activity
Question 1.
Make models of the molecules of compounds by using match sticks and clay balls as shown below,
| Items for identification | Matters | Non-matters |
| Flowers, bee, cloud, rainbow, leaf, fire, baby, torchlight, sky, smoke, heat coming from glowing coals, fog, the sound coming from a drum, a laser beam |
Answer:
| Items for identification | Matters | Non matters |
| Flowers, bee, cloud, rainbow, leaf, fire, baby, torch light, sky, smoke, heat coming from glowing coals, fog, sound coming from a drum, laser beam | Flowers | rainbow |
| bee | torchlight | |
| cloud, | the sound coming from a drum | |
| leaf | laser beam | |
| baby | the heat coming from glowing coals | |
| fog | ||
| fire |
Question 2.
Take some powdered iron filings and mix them with sulphur.
- Divide the mixture into two equal halves.
- Keep the first half of the mixture as it is, but heat the second half of the mixture.
- You will get a grey brittle compound.
Answer:
Iron + Sulphur \(\stackrel{\Delta}{\longrightarrow}\) Iron sulphide
We cannot separate iron from iron sulphide. So, it is a compound, whereas Iron and Sulphur are mixtures. We can separate it by magnetic separation method.
![]()
Question 3.
Identify whether the given substance is mixture or compound and justify your answer.
| S.No. | Substance | Mixture / Compound |
| 1. | Sand and water | |
| 2. | Sand and iron filings | |
| 3. | Concrete | |
| 4. | Water and oil | |
| 5. | Salad | |
| 6. | Water | |
| 7. | Carbon dioxide | |
| 8. | Cement | |
| 9. | Alcohol |
Answer:
| S.No. | Substance | Mixture / Compound | Justification |
| 1. | Sand and water | Mixture | Can be separated by filtration. |
| 2. | Sand and iron filings | Mixture | Can be separated by a magnet. |
| 3. | Concrete | Mixture | Ingredients are mixed together and it can be separated. |
| 4. | Water and oil | Mixture | Oil is less dense. So floats in water and it can be separated. |
| 5. | Salad | Mixture | Vegetable are mixed. Can be separated easily. |
| 6. | Water | Compound | Hydrogen and oxygen are combined chemically in a fixed proportion. |
| 7. | Carbon dioxide | Compound | Two oxygen atoms are bonded or chemically combine with carbon atom. |
| 8. | Cement | Compound | Different elements are combined together in a fixed proportion. |
| 9. | Alcohol | Mixture | Two or more liquids, whose proportion can be altered by distillation. |
II. Match the following.

Answer:
- (c) Hidden heat
- (f) Colloid
- (g) Flows freely
- (e) Homogenous mixture
- (b) Heterogeneous mixture
- (d) Fractional distillation
- (a) Separating funnel
III. State which the following statements are true or false. If false give the correct statement.
- Supernatant denotes the heterogeneous mixture, lying above a solid residue, after crystallization, precipitation, centrifugation or another process – False.
Correct Statement: Supernatant denotes the liquid lying above a solid residue after crystallization, precipitation, centrifugation or other processes. - Liquids cannot be compressed and they have fixed volume – True
- The intensity of scattered light depends on the type of colloidal solution and the size of the colloidal particles – True
- In Aerosol the dispersed phase is liquid and the dispersion medium is gas – False.
Correct Statement: In Aerosol, The dispersed phase is solid and the dispersion medium is gas. - When the solid (Solute) dissolves in a liquid (Solvent), it becomes a solution – True
- Solids possess very high kinetic energy – False.
Correct Statement: Gases possess very high kinetic energy. - Celsius scale is a scale of temperature in which zero represents the melting point of ice and 100 represents the boiling point of water – True
IV. Answer very shortly.
Question 1.
What is a matter?
Answer:
Anything which has mass and occupies space (volume) is called matter.
![]()
Question 2.
What is dry ice or cardice?
Answer:
Frozen carbon dioxide, is dry ice or cardice.
Question 3.
What are the uses of dry ice?
Answer:
- Act as a cooling agent
- Industrial refrigeration
- Transporting frozen food.
- It does not leave any liquid behind, as it directly changes into gas.
Question 4.
When does the pressure of the gas increase?
Answer:
When the volume of the gas decreases, the gas gets compressed. The particles of the gas have only lesser space to move around. So the particles start hitting on the walls of the container and the pressure of the gas increases.
Question 5.
Complete the following table:
| S.No. | CELSIUS | KELVIN |
| 1. | 90°C | 363 K |
| 2. | ? | 283 K |
| 3. | 63 °C | ? |
| 4. | 250°C | ? |
| 5. | ? | 303 K |
Solution:
| S.No. | CELSIUS | KELVIN |
| 1. | 90°C | 363 K |
| 2. | 9.85°C | 283 K |
| 3. | 63 °C | 336.15K |
| 4. | 250°C | 523.15 K |
| 5. | 29.85°C | 303 K |
Question 6.
What does the LPG (Liquefied petroleum gas) contain?
Answer:
LPG is a highly inflammable hydrocarbon. It contains a mixture of butane and propane gases.
![]()
Question 7.
What are pure substances? Give examples.
Answer:
Pure substances contain only one kind of particles.
Eg: 1. Element (Sodium, Bromine, and Hydrogen)
2. Compound (Sodium chloride, water, carbon dioxide)
Question 8.
What are impure substances? Give examples.
Answer:
Impure substances contain more than one kind of particles.
Eg: Mixtures (Gun powder, which is a mixture of sulphur potassium nitrate and charcoal)
Question 9.
Classify the pure substance on the basis of chemical composition.
Answer:
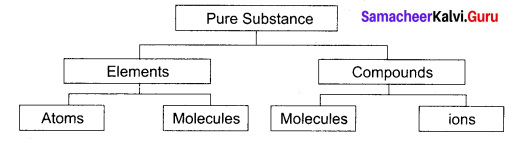
Question 10.
Classify the types of mixtures.
Answer:
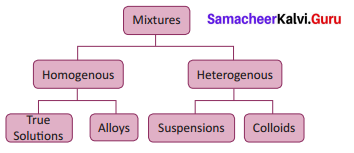
Question 11.
Write a few examples for the following colloids.
Answer:
- Gels – Hair cream, tooth paste
- Foam – Soap bubbles, carbonated beverages.
- Solid foam – Bread, Mattresses
- Emulsion – Milk, butter, paints, facial cream, pesticides
Question 12.
Name the two phases in separation of the mixtures in chromatography.
Answer:
- Mobile phase
- Stationary phase
Question 13.
What is absorption? Give example.
Answer:
Absorption is the process in which the substance is dissolved throughout the bulk of another substance.
Eg: Paper soaks up or absorbs water.
Question 14.
What is adsorption? Give example.
Answer:
Adsorption is the process in which particles of a substances, adhere to a surface of another substance.
Eg: Charcoal adsorbs gases on its surface.
V. Answer the following in detail.
Question 1.
Explain the factors, which will affect the rate of evaporation, taking examples from our daily life experiences.
Answer:
- Temperature: Warmer the evaporation surface, the higher the rate of evaporation. In ponds, lakes and rivers, the rate of evaporation is more in sunny days.
- Surface area: The evaporation increase, with the increase of surface area. Eg: The water kept in a saucer evaporates faster than the water kept in a glass.
- Humidity: The amount of water vapour is high during rainy season. The air can hold little water. So it slows down the evaporation. So we sweat and perspire.
- Wind: The evaporation is slow at low wind. Evaporation is faster at high wind. The particles of water move away, along with the particles of air at high wind. So the wet clothes dry faster on a windy day.
Question 2.
Compare boiling and evaporation.
Answer:
| S.No. | Boiling | Evaporation |
| 1. | Vaporization process. | Natural process. |
| 2. | Turns liquid into gas when it is heated. | The liquid changes into gas without heating. |
| 3. | Fast process. | Slow process. |
| 4. | Occurs only at boiling point. | Occurs at any temperature. |
| 5. | It forms bubbles. | It does not form bubbles. |
| 6. | Energy is required. | Energy is supplied by surrounding. |
| 7. | Temperature of the liquid remains constant. | Temperature of liquid decreases. |
Question 3.
Classify colloids based on physical state of dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
Answer:
| S.No. | Dispersed Phase |
Dispersion Medium |
Name | Examples |
| 1. | Solid | Solid | Solid Sol | Alloys, gems, coloured glass |
| 2. | Solid | Liquid | •Sol | Paints, inks, eggs white |
| 3. | Solid | Gas | Aerosol | Smoke, dust |
| 4. | Liquid | Solid | Gel | Curd, Cheese, Jelly |
| 5. | Liquid | Liquid | Emulsion | Milk, Butter, oil in water |
| 6. | Liquid | Gas | Aerosol | Mist, fog, clouds |
| 7. | Gas | Solid | Solid foam | Cake, bread |
| 8. | Gas | Liquid | Foam ‘ | Soap lather, Aerated water |
Question 4.
Write the methods of separation for the following:
Answer:
- Separation of insoluble solids from liquids
Filtration and Decantation - The separation of fine and tiny particles of solid which do not settle at the bottom.
Centrifugation - Separation of soluble solids from liquids
Evaporation and crystallization - Separation of miscible liquids which do not differ much in their boiling points
Fractional distillation - Separation of two immiscible liquids
Separating funnel - Separation of different fractions of petroleum
Fractional distillation with fractionating column - Separation of mixture containing volatile and non-volatile solids.
Sublimation.
Question 5.
Write the differences between mixture and compounds.
Answer:
| S. No. | MIXTURE | COMPOUND | Name | Examples |
| 1. | Mixture can be separated into its constituents by physical process. | Compounds can be separated into its constituents by chemical process. | Solid Sol | Alloys, gems, coloured glass |
| 2. | Mixture shows the properties of its constituents. | The properties of a compound are entirely different from its constituent elements . | Sol | Paints, inks, eggs white |
| 3. | Energy in the form of heat and light is neither given out nor absorbed in. | Energy in the form of heat and light is given out or absorbed. | Aerosol | Smoke, dust |
| 4. | The composition or proportion of a mixture does not have a definite formula. | The composition of a compound is fixed. The constituents have a fixed ratio by mass. | Gel
. |
Curd, Cheese, Jelly |
| 5. | A mixture does not have fixed boiling point or melting point. | A compound has a fixed boiling or melting point. | Emulsion | Milk, Butter, oil in water |