You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Geography Solutions Term 2 Chapter 2 Hazards
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Geography Hazards Textbook Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
……………. percentage of nitrogen is present in the air.
(a) 78.09%
(b) 74.08%
(c) 80.07%
(d) 76.63%
Answer:
(a) 78.09%
![]()
Question 2.
Tsunami in Indian Ocean took place in the s ear …………….
(a) 1990
(b) 2004
(c) 2005
(d) 2008
Answer:
(b) 2004
Question 3.
The word tsunami is derived from ……………. language.
(a) Hindi
(b) French
(c) Japanese
(d) German
Answer:
(c) Japanese
Question 4.
The example of surface water is –
(a) Artesian well
(b) Groundwater
(c) Subsurface water
(d) Lake
Answer:
(d) Lake
Question 5.
Event that occurs due to the failure of monsoons.
(a) Condensation
(b) Drought
(c) Evaporation
(d) Precipitation
Answer:
(b) Drought
II. Fill in the blanks
- Hazards may lead to ……………..
- Landslide is an example of …………….. hazard.
- On the basis of origin, hazard can be grouped into …………….. categories.
- Terrorism is an example of …………….. hazard.
- Oxides of Nitrogen are …………….. pollutants which affects the human beings.
- Chernobyl nuclear accident took place in ……………..
Answer:
- disaster
- Geologic (or) Seismic
- Eight
- Human – induced
- Primary
- 26th April 1986
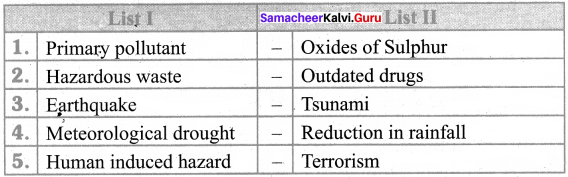
III. Match the following
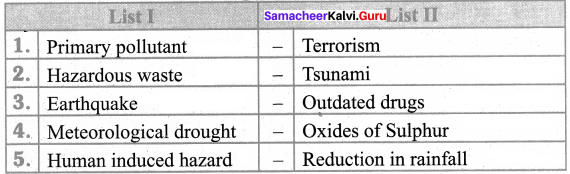
Answer:
IV Answer in brief
Question 1.
Define‘hazard’.
Answer:
Hazards are defined as a thing, person, event, or factor that poses a threat to people, structures, or economic assets and which may cause a disaster.
Question 2.
What are the major types of hazards?
Answer:
- Atmospheric hazard
- Geologic 7 Seismic hazard
- Hydrologic hazard
- Volcanic hazard
- Environmental hazard
- Biological hazard
- Human – induced hazard
- Technological hazard
![]()
Question 3.
Write a brief note on hazardous wastes.
Answer:
The wastes that may or tend to cause adverse health effects on the ecosystem and human beings are called hazardous wastes.
Question 4.
List out the major flood prone areas of our country.
Answer:
- The major flood prone areas in north and northeast India are, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, North Bihar, West Bengal and Brahmaputra valley.
- Coastal Andhra Pradesh, Odisha and Southern Gujarat are the other regions which are also prone to flood often.
Question 5.
Mention the types of drought.
Answer:
The drought is classified into three major types
- Meteorological drought
- Hydrological drought
- Agricultural drought
Question 6.
Why should not we construct houses at foothill areas?
Answer:
We should not construct houses at foothill areas because it has rapid downward movement of rocks and soil and vegetation down the slope under the influence of gravity which leads to landslides.
V. Distinguish the following :
Question 1.
Hazards and disasters.
Answer:
1. Hazard:
A natural hazard is a natural process and event that is a potential threat to human life and property.
2. Disasters:
A disaster is a hazardous event that occurs over a limited time span in a defined area and causes great damage to property / loss of life, also needs assistance from others.
Question 2.
Natural hazard and human-made hazard.
Answer:
Natural Hazards:
- These are the results of natural processes and man has no role to play in such hazards.
- For example: Earthquakes, Floods, Cyclonic storms and volcanic eruption etc.
Human – made – Hazards:
- These are caused by undesirable activities of human. It can be the result of an accident such as an industrial chemical leak or oil spill.
- For example: Hazardous wastes, pollution of air, water and land etc.
![]()
Question 3.
Flood and drought.
Answer:
Flood:
- Flood is an event in which a part of the earth’s surface gets inundated.
- Heavy rainfall and large waves in seas are the common causes of flood.
Drought:
- Any lack of water to satisfy the normal needs of agriculture, livestock, industry or human population may be termed as a drought.
- Droughts in India occur in the event of a failure of monsoon.
Question 4.
Earthquake and tsunami.
Answer:
1. Earthquake:
Earthquake is a violent tremor in the earth’s crust, sending out a series of stock waves in all directions from its place of origin.
2. Tsunami:
Tsunami refers to huge ocean waves caused by an earthquake, landslide or volcanic eruption. It is generally noticed in the coastal regions and travel between 640 and 960 Km/h.
VI. Answer in a paragraph
Question 1.
Write an essay on air pollution.
Answer:
- Air is a mixture of several gases.
- The main gases are Nitrogen (78.09%) for forming products such as fertilizers for plants and for making the air inert, Oxygen (20.95%) for breathing, and Carbon dioxide (0.03%) for Photosynthesis.
- Air pollution is the contamination of the indoor or outdoor air by a range of gases and solids that modify its natural characteristics and percentage.
- It categorized into
- Primary pollutants
- Secondary pollutant.
Primary Pollutants:
- Oxides of Sulphur
- Oxides of Nitrogen
- Oxides of Carbon
- Particulate Matter
- Other Primary Pollutants
Secondary Pollutants:
- Ground-Level Ozone
- Smog
Question 2.
Define earthquake and list out its effects.
Answer:
Earthquakes:
Earthquake is a violent tremor in the earth’s crust, sending out a series of shock waves in all directions from its place of origin.
Effects of Earthquakes:
- The Primary effects of earthquakes are ground shaking, ground rupture, landslides, Tsunamis and soil liquefaction.
- The Secondary effects of earthquakes are fires.
- The effects of earthquakes are terrible and devasting. Thus leads to distraction of buildings, loss of money, property and lines of people. This affects the mental and emotional health of people.
Question 3.
Give a detailed explanation on the causes of landslides.
Answer:
- Landslide is a rapid downward movement of rock, soil, and vegetation down the slope under the influence of gravity. Landslides are generally sudden and infrequent.
- The presence of steep slopes and heavy rainfall are the major causes of landslides.
- Weak ground structure, deforestation, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, mining, construction of roads and railways over the mountains are the other causes of landslides.
- In Tamil Nadu, Kodaikanal and Ooty are frequently affected by landslides.
![]()
Question 4.
Elaborately discuss the effects water pollution.
Answer:
Water Pollution:
- Water pollution may be defined as alteration in the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of water which may cause harmful effects in human and aquatic life.
- In India, water pollution has been taking place on a large scale.
- Some of these waterborne diseases are Typhoid, Cholera, Paratyphoid fever, Dysentery, Jaundice and Malaria.
- Chemicals in the water also have negative effects on our health.
- Pesticides – can damage the nervous system and cause cancer because of the Carbonates and organophosphere that they may contain.
- Both surface and groundwater bodies are polluted to a great extent.
VII. Activities
Question 1.
Name the hazards which you have identified.
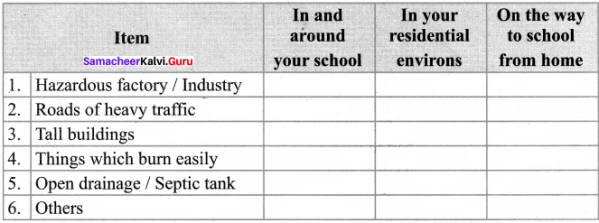
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students.
Question 2.
List out the hazards that occur frequently and occasionally in your place.
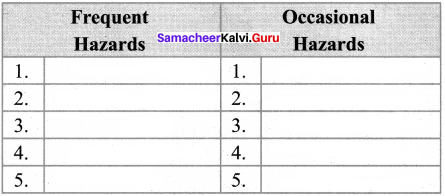
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students.
Question 3.
On the map of Tamilnadu shade the 13 coastal districts in different colors.
Answer:
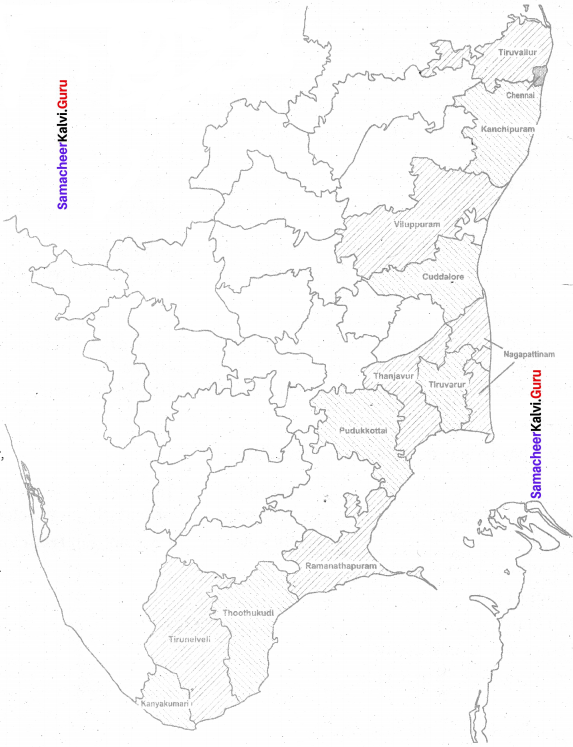
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Geography Hazards Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
…………. is an example of human induced pollutants hazard.
(a) Terrorism
(b) Evaporation
(c) Nuclear accident
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Terrorism
![]()
Question 2.
…………. in Indian ocean took place in the year 2004.
(a) Earthquake
(b) Droughts
(c) Landslide
(d) Tsunami
Answer:
(d) Tsunami
Question 3.
A …………. hazard ¡s a natural process.
(a) Socio natural hazard
(b) Human – made
(c) Natural
(d) All the bove
Answer:
(C) Naturall
Question 4.
…………. can be broadly classified Into three types.
(a) Economics
(b) Hazards
(c) Environment
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Hazards
Question 5.
The main examples of natural hazards are ………….
(a) earthquakes
(b) floods
(c) cyclonic
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Question 6.
…………. hazards are caused by undesirable activities of human.
(a) Human – made
(b) Natural
(c) Socio – natural
(d) Atmospheric
Answer:
(a) Human – made
Question 7.
…………. are caused by natural forces in mountainous areas.
(a) Over populations
(b) Landslides
(c) Socio – natural
(d) Hydrologic hazard
Answer:
(b) Landslides
Question 8.
…………. Is a serious problem In most big Urban.
(a) Storm
(b) Landslides
(c) Smog
(d) Droughts
Answer:
(c) Smog
Question 9.
…………. surge hazards may be worsened by the destruction of mangroves.
(a) Storm
(b) Smog
(c) Flood
(d) Droughts
Answer:
(a) Stormi
![]()
Question 10.
Heavy rainfall and large waves In seas are the common causes of …………..
(a) Droughts
(b) Smog
(c) Tsunami
(d) Flood
Answer:
(d) Flood
Question 11.
…………. storm is a strong wind circulating around a low pressure area in the atmosphere.
(a) Tropical cyclone
(b) Cyclonic
(c) Heavy
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Cyclonic
Question 12.
The west coast of India is …………. vulnerable to storm surges than the east coast.
(a) less
(b) more
(c) great
(d) high
Answer:
(a) less
Question 13.
…………. drought is a reduction in rainfall for a specific period below a specific level.
(a) Agricultural
(b) Hydro – logical
(c) Landslides
(d) Meteorological
Answer:
(d) Meteorological
Question 14.
…………. droughts associated with reduction of water in streams, rivers and reservoirs.
(a) Hydro – logical
(b) Agricultural
(c) Meteorological
(d) Both ‘b’ and ‘c’
Answer:
(a) Hydro – logical
Question 15.
…………. droughts refers to the condition in which the agricultural crops get affected due to lack of rainfall.
(a) Meteorological
(b) Agricultural
(c) Hydro – logical
(d) Both ‘a’ and ‘b’
Answer:
(b) Agricultural
Question 16.
…………. in India occur in the event of a failure of monsoon.
(a) Floods
(b) Landslides
(c) Droughts
(d) Earthquakes
Answer:
(c) Droughts
Question 17.
The dry region lying in the leeward side of the …………..
(a) Western Ghats
(b) Eastern Ghats
(c) Both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Western Ghats
![]()
Question 18.
…………. is a rapid downward movement of rock, soil and vegetation down the slope under the influence of gravity.
(a) Drought
(b) Flood
(c) Landslide
(d) Earthquake
Answer:
(c) Landslide
Question 19.
…………. is a mixture of several gases.
(a) Water
(b) Air
(c) Soil
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) Air
Question 20.
…………. pollutant is an air pollutant emitted directly from a source.
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(a) Primary
II. Fill in the blanks:
- Hazards can be broadly classified into …………. types
- Smog is a serious problem in most …………. areas.
- The beginning of …………. century, the earth supported a human population.
- The meaning of old french “Hazards” ………….
- A catastrophe was recover …………. time.
- …………. can disturb the safety health, welfare of people.
- …………. is a violent tremor in the earth’s crust.
- …………. percentage of carbon di oxide present in the air.
- …………. percentage of oxygen present in the air.
- …………. nuclear accident took place in 26th April 1986.
- …………. hazards are caused by the combined effect forces and misdeeds of human.
- Storm surge hazards may be worsened by the destruction of …………..
- A sudden rise of seawater due to tropical cyclone is called ……………
- In Tamil Nadu coast …………… and …………… districts are frequently affected.
- The drought could be classified into …………… major types.
- Presence of steep slope and heavy rainfall are the major causes of …………….
- The word ‘tsu’ meaning ……………..
- The word ‘nami’ meaning ……………..
- The atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima (Japan) in ………………
- ……………… the wastes resulting from ordnance manufacturing and some industrial gases.
- ……………… refers to huge ocean waves caused by an earthquake, landslide (or) volcanic eruption.
Answer:
- Three
- big urban
- Twenty first
- a game of dice
- long
- Hazards
- Earthquake
- 0.03%
- 20.95%
- Chernobyl
- Socio – natural
- mangroves
- storm surge
- Cuddalore, Nagapattinam
- three
- Landslides
- harbour
- ‘wave’
- 1945
- Explosives
- Tsunami
III. Match the following
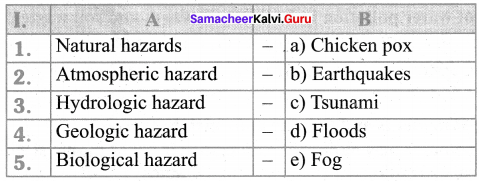
Answer:
- c
- e
- d
- b
- a
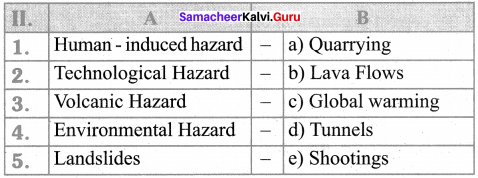
Answer:
- e
- d
- b
- c
- a
IV. State True or False
- Hazards are classified into natural, human – made and socio – natural hazards
- Earthquake is a violent tremor in the earth’s crust, sending out a series of shock waves in all directions from its place of origin.
- Heavy rainfall and large waves in seas are not the common causes of flood.
- The West coast of India is more vulnerable to storm surge than the east coast.
- The coastal belt around the Gulf of Kutch.
- The droughts could be classified into six types.
- Hydro – logical droughts is associated with reduction of water in streams, rivers and reservoirs.
- Agricultural drought refers to the condition in which the agricultural crops get affected due to more of rainfall.
- Weak ground structure, mining, construction of roads and railways over the mountains are the causes of landslides.
- The word ‘Tsunami’ is derived from latin world ‘tsu’ meaning harbour.
Answer:
- True
- True
- False
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
V. Consider the following statements and Tick (✓) the appropriate answer
![]()
Question 1.
Which of the following statements are correct:
(i) Oxides of Nitrogen are primary pollutants which affects the human beings.
(ii) On the basis of origin, hazard can be grouped into eight categories.
(iii) Delayed actions may increase the economic losses.
(iv) The major causes of water pollution in India are sewages and soil wastes,
(a) (i) & (ii) are Correct
(b) (i), (ii) & (iii) are Correct
(c) (i), (ii) and (iv) are Correct
(d) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) are Correct
Answer:
(d) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) are Correct
Question 2.
Consider the following statements and tick the appropriate answer
Statement (A) : Water pollution may be defined as alteration in which the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of water.
Reason (R) : Water pollution cause harmful effects in human and aquatic life.
(a) A is correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) A is correct but R is not correct explanation of A
(c) Both A and R are correct
(d) Both A and Rare wrong
Answer:
(a) A is correct and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 3.
Which one of rthe following is correctly matched?
(a) Secondary Pollutant – Smog
(b)Primary Pollutant – Ground Level Ozone
(c) Water Pollution – Earthquake
(d) 2016 – Tsunami in India
Answer:
(a) Secondary Pollutant – Smog
Question 4.
Which one of the following is not correctly matched?
(a) Ecosystem – Hazardous waste
(b) Chemic1als – Explosives
(c) Carbon di oxide – 0.05%
(d) Oxygen – 20.95%
Answer:
(C) Carbon di oxide – 0.05%
VI. Answer the following one or two sentences
Question 1.
List out any four major causes of water pollution in India.
Answer:
- Urbanization
- Industrial effluents
- Se-wages
- Solid wastes
Question 2.
Define prevention.
Answer:
Prevention is defined as the activities taken to prevent a natural calamity or potential hazard from having harmful effects on either people or economic assets.
![]()
Question 3.
Define Water Pollution.
Answer:
Water Pollution may be defined as alteration in the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of water, which may cause harmful effects in human and aquatic life.
Question 4.
List out any four major hazardous wastes.
Answer:
- Chemicals
- Biomedical wastes
- Flammable wastes
- Explosives
Question 5.
What do you mean by Tsunami?
Answer:
- Tsunami refers to huge ocean waves caused by an earthquake, landslide or volcanic eruption.
- It is generally noticed in the coastal regions and travel between 640 and 960 Km/h.
Question 6.
List out the major drought prone areas of our country.
Answer:
- The arid and semi arid region from Ahmadabad to Kanpur on one side and from Kanpur to Jalandhar on the other.
- The dry region lying in the leeward side of the Western Ghats.
Question 7.
What is earthquake?
Answer:
Earthquake is a violent tremor in the earth’s crust, sending out a series of shock waves in all directions from its place of origin.
Question 8.
List out the Atmospheric hazards.
Answer:
Tropical storms, Thunderstorms, Lightning, Tornadoes, Avalanches, Heat waves, fog and forest fire.
Question 9.
What do you meant by hazard?
Answer:
The word ‘hazard’ owes its origin to the word ‘hazart’ in old French meaning a game of dice (in Arabic-az-zahr; in Spanish – azar).
VII. Answer the following in detail
Question 1
What is flood? What are the Major causes of flood?
Answer:
Meaning of flood :
- Flood is an event in which a part of the earth’s surface gets inundated.
- Heavy rainfall and large waves in seas are the common causes of flood.
Major causes of floods: The Major causes of floods are,
1. Meteorological Factors:
- Heavy rainfall
- Tropical cyclones
- Cloud burst
2. Physical Factors:
- Large catchment area.
- Inadequate drainage arrangement
3. Human Factors:
- Deforestation
- Siltation
- Faulty agricultural practices
- Faulty irrigation practices
- Collapse of dams
- Accelerated urbanization
![]()
Question 2.
What is cyclonic storms? Explain about the cyclonic storms.
Answer:
Cyclonic Storms:
- A Cyclonic storm is a strong wind circulating around a low pressure area in the atmosphere.
- It rotates in anti – clockwise direction in Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the southern Hemisphere.
- Tropical Cyclones are characterized by destructive winds, storms surges and exceptional levels of rainfall, which may cause flooding.
- Wind speed may reach upto 200 Km/h and rainfall may record upto 50 cm/ day for several consecutive days.
- A sudden rise of seawater due to tropical cyclone is called storm surge.
- It is more common in the regions of shallow coastal water.
East Coastal areas vulnerable to storm surges:
- North Odisha and West Bengal coasts. ,
- Andhra Pradesh coast between Ongole and Machilipatnam.
- Tamil Nadu coast (among 13 coastal districts, Nagapattinam and Cuddalore districts are frequently affected).
West Coastal areas vulnerable to storm surges:
- The west coast of India is less vulnerable to storm surges than the east coast.
- Maharashtra coast, North of Hamai and adjoining South Gujarat coast and the coastal belt around the Gulf of Cambay.
- The coastal belt around the Gulf of Kutch.
Question 3.
Give a detailed explanation about droughts.
Answer:
Droughts:
Any lack of water to satisfy the normal needs of agriculture, livestock, industry or human population may be termed as a drought.
Classifications of drought:
The drought could be classified into three major types. They are:
1. Meteorological drought:
ft is a situation where there is a reduction in rainfall for a specific period below ‘ a specific level.
2. Hydrological drought:
It is associated with reduction of water in streams, rivers and reservoirs. It is of two types.
- Surface water and
- Ground water drought
3. Agricultural drought:
- It refers to the condition in which the agricultural crops get affected due to lack of rainfall.
- Droughts in India occur in the event of failure monsoon.
The Major areas highly prone to drought are:
- The arid and semi arid region from Ahmadabad to Kanpur on one side and from Kanpur to Jalandhar on the other.
- The dry region lying in the leeward side of the Western Ghats.