You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Civics Solutions Term 2 Chapter 1 Understanding Secularism
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Civics Understanding Secularism Textbook Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Secularism means
(a) State is against to all religions
(b) State accepts only one religion
(c) An attitude of tolerance and peaceful co-existence on the part of citizen belonging any religion
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) An attitude of tolerance and peaceful co-existence on the part of citizen belonging any religion
![]()
Question 2.
India is a land of ………..
(a) multi – religious faith
(b) multi – cultural beliefs
(c) Both (a) & (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Both (a) & (b)
Question 3.
The Preamble of the Constitution was amended in …………..
(a) 1951
(b) 1976
(c) 1974
(d) 1967
Answer:
(b) 1976
Question 4.
Which one of the following describes India as a secular state?
(a) Fundamental Rights
(b) Fundamental Duty
(c) Directive Principles of State Policy
(d) Preamble of the Constitution
Answer:
(d) Preamble of the Constitution
Question 5.
Right to freedom of religion is related to –
(a) Judiciary
(b) Parliament
(c) Directive principles of State Policy
(d) Fundamental rights
Answer:
(d) Fundamental rights
Question 6.
According to Article 28, which type of education is restricted in state aided educational institutions?
(a) Religious instruction
(b) Moral education
(c) Physical education
(d) None above these
Answer:
(a) Religious instruction
Question 7.
The country will be considered as a secular country, if it ………….
(a) gives importance to a particular religion
(b) bans religious instructions in the state – aided educational institutions.
(c) does not give importance to a particular religion
(d) bans the propagation of any religious belief.
Answer:
(b) bans religious instructions in the state – aided educational institutions.
![]()
II. Fill in the Blanks:
- Religion does not teach us……..
- Secularism is a part of democracy which grants ………..
- …………….. is a lack of belief in god and gods.
- The basic aim of our constitution is to promote and ……………..
- Article 15 prohibits …………….. on the grounds of religion, caste, sex or place of birth.
Answer:
- animosity
- equal rights to people
- Atheism
- unity and integrity of the nation
- discrimination
III. Match the following
- Atheism – coined the word secularism
- Children – social reformer
- Din-i-Illahi – lack of belief in god
- Constitution – future citizen
- Holvoake – Divine faith
- Raiaram Mohan Rov – 1950
Answer:
- Atheism – lack of belief in god
- Children – future citizen
- Din-i-Illahi – Divine faith
- Constitution – 1950
- Holvoake – coined the word .secularism
- Raiaram Mohan Rov – social reformer
IV. State true or false:
- There is state religion in India
- The term secularism has been derived from the Greek word.
- The Mughal emperor Akbar followed the policy of religious toleration.
- Jainism originated in China.
- Government of India declares holidays for all religious festivals.
Answer:
- False
- False
- True
- False
- True
V. Consider the following statements and tick the appropriate answer
Question 1.
(i) Secularism is invaluable for a society like India which is characterized by religious diversity.
(ii) The word secularism was not mentioned in the Constitution when it was adopted in 1950.
(iii) Article 26 deals with payment of taxes for the promotion of any particular religion.
(iv) Akbar’s tomb situated at Sikandara near Agra.
(a) i, ii only
(b) ii, iii only
(c) iv only
(d) i, ii and iv only
Answer:
(d) i, ii and iv only
Question 2.
Assertion (A): A foreigner can practice his own religious faith in India.
Reason (R): The freedom of religion is guaranteed by the constitution not only for Indians but also for the aliens also.
(a) A is true but R is false.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is the cdrrect explanation of A.
(c) A is false but R is true.
(d) Both A and R are true. R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answewr:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
![]()
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Secularism is invaluable in India.
Reason (R): India is a multi – religious and multi – cultural country.
(a) A is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) A is correct and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is wrong and R is correct.
(d) Both are wrong.
Answer:
(a) A is correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 4.
Find out the wrong pair.
(a) Din-i-Illahi – A book
(b) Khajuraho – Hindu temple
(c) Ashoka – Rock Edict
(d) Iqbal – Poet
Answer:
(a) Din-i-Illahi – A book
VI. Answer the following in one or two sentences
Question 1.
Name some of the Indians who contributed to the spreading of secularism.
Answer:
Rajaram Mohan Roy, Sir Syed Ahmad Khan, Rabindranath Tagore, Mahatma Gandhi, and B.R. Ambedkar.
![]()
Question 2.
What does secularism mean?
Answer:
- Secularism means an attitude of tolerance towards other religions and peaceful co – existence of citizens belonging to different faiths.
- It is a policy of neutrality and equality by the states towards all religious communities
Question 3.
State the objectives of secularism.
Answer:
- One religious group does not dominate another.
- Some members don’t dominate other members of the same religious community.
Question 4.
Why is it important to separate religion from the state?
Answer:’
It is important to separate religion from state because, a secular state is one in which the state does not officially promote any one religion as state religion.
Question 5.
What are the characteristic features of a secular state?
Answer:
- Principle of Liberty – the state permits the practice of any religion.
- Principle of Equality – the state does not give preference to any religion over another.
- Principle of Neutrality – the state remains neutral in religious matters.
Question 6.
Mention any three Constitutional provisions related to secularism.
Answer:
- Article 15 – Prohibition of discrimination on grounds of religion, caste, sex, or place of birth etc.
- Article 16 – Equality, of opportunity in public employment.
- Article 29(2) – A ban on discrimination in state-aided educational institution.
VII. Answer the following in detail:
![]()
Question 1.
Why we need secular education?
Answer:
- To remove narrow mindedness and makes the dynamic and enlightened view.
- To develop moral and humanistic outlook.
- To train the youth to be good citizen.
- To strengthen democratic values like liberty, equality and fraternity and co-operative living.
- To give wider vision towards life.
- To develop an attitude of appreciation and understanding of others’ point of view.
- To develop the spirit of love, tolerance, co – operation, equality and sympathy.
- To synthesis materialism and spiritualism.
Question 2.
Secularism is necessary for a country like India. Justify.
Answer:
India is a secular country because:
- The word secular has been included into the preamble to the constitution (through 42nd Amendment).
- It has no state religion.
- It remains neutral in religious matters.
- Freedom to religion is offered to all citizens.
- There is no discrimination on the basis of religion.
VIII. HOTs
Question 1.
Will the Government intervene if some religious group says that their religion allows them to practice human sacrifice?
Answer:
If some religious group says that their religion allows them to practice human sacrifice, the government will not allow this.
IX. Project and Activity
Question 1.
Look at the holidays of your school calendar. How many of them pertain to different religions? List them based on religions. What does it indicate?
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students.
Question 2.
How can you develop religious tolerance?
Answer:
- At home – In your locality
- At school – National level
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Civics Understanding Secularism Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
…………….. is a land of multi-religious faith.
(a) Japan
(b) China
(c) India
(d) England
Answer:
(c) India
![]()
Question 2.
…………….. of religion is related to fundamental rights.
(a) Right to freedom
(b) Right to equality
(c) Right to liberty
(d) Right to ideology
Answer:
(a) Right to freedom
Question 3.
In Article 26, which type of freedom is discussed?
(a) religions instructions
(b) moral education
(c) freedom to manage religious affairs
(d) freedom of secularism
Answer:
(c) freedom to manage religious affairs]
Question 4.
…………….. is a part of democracy that grants equal rights to people.
(a) Socialism
(b) Freedom
(c) Constitution
(d) Secularism
Answer:
(d) Secularism
Question 5.
Secularism is ……………. in India.
(a) Valuable
(b) Invaluable
(c) Both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Invaluable
![]()
Question 6.
The Mughal emperor ……………. followed the policy of religious toleration.
(a) Babar
(b) Shah Alam
(c) Akbar
(d) Shahjahan
Answer:
(c) Akbar
Question 7.
Government of India declares ……………. for all religious festivals.
(a) Money
(b) Gifts
(c) Bonus
(d) Holidays
Answer:
(d) Holidays
Question 8.
The term secularism has been driven from the ……………. word.
(a) Greek
(b) British
(c) Tamil
(d) Latin
Answer:
(d) Latin
Question 9.
British newspaper editor coined the term ‘secularism’.
(a) George Jacob Holyoake
(b) Gandhi
(c) Nethaji
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) George Jacob Holyoake
Question 10.
The word ‘speculum’ meaning ……………..
(a) ‘an age’
(b) the spirit of an age
(c) both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) both ‘a’ and ‘b’
![]()
Question 11.
……………. is the principle of separation-of state and religion.
(a) Secularism
(b) Socialism
(c) Liberalisation
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Secularism
Question 12.
“Religion does not teach us animosity; we are Indians and India is our home”, who quoted this statement?
(a) Akbar
(b) Iqbal
(c) Babar
(d) George Jacob Holyoake
Answer:
(b) Iqbal
Question 13.
Akbar’s tomb is situated at Sikandara near ……………. in India.
(a) Delhi
(b) Jaipur
(c) Agra
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(c) Agra
Question 14.
Secularism is the part of Indian …………….
(a) constitution
(b) equal rights
(c) principle of liberty
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) constitution
![]()
Question 15.
Principle of ……………. the state remains neutral in religious matter.
(a) equality
(b) liberty
(c) neutrality
(d) all of these
Answer:
(c) neutrality
Question 16.
Principle of ……………. the state permits the practice of any religion.
(a) equality
(b) liberty
(c) neutrality
(d) both‘a’and‘b’
Answer:
(b) liberty
Question 17.
The word secularism was not mentioned in our constitution when it was adopted in ……………..
(a) 1947
(b) 1948
(c) 1949
(d) 1950
Answer:
(d) 1950
![]()
Question 18.
The word secular was incorporated in the preamble through the ……………. Amendment of the Indian Constitution.
(a) 21st
(b) 26th
(c) 42nd
(d) 29th
Answer:
(c) 42 nd
Question 19.
Secularism in education means making public education ……………. religious dominance.
(a) Free
(b) Liberty
(c) Both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) Faith
Question 20.
Separation of religion from the state means ……………..
(a) Socialism
(b) Democracy
(c) Secularism
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) Secularism
II. Fill in the blanks:
- India is a land of …………… faith and multi – cultural beliefs.
- Secularism is invaluable for a …………
- …………. a British newspaper editor coined a term secularism.
- Secularism is a part of …………. which grants equal rights.
- ………… and ………… were advocated for religious toleration.
- Din-i-illahi means ……………
- Sulh-e-Kul means …………….
- ……………instructed for his mausoleum.
- The Indian state works in various ways to prevent ……………
- ……………the state permits the practice of any religion.
- According to Article ………….. freedom to manage religious affairs.
- Children as future …………… must get education which should aim at their development of character and moral behavior.
- Secular education develop …………… and …………… outlook.
- The basic aim of our ……………is to promote unity and integrity of the nation along with individual dignity.
- According to Article 16 equality of opportunity in public ……………
- ……………allows us to live in civility.
- Secularism grants equal rights to the people in respect of their …………
- The Indian constitution guarantees fundamental rights that are based on ……….. principles.
- Secular education need to train the youth to be good ………..
- …………….. give wider vision towards life.
- Secular education need to synthesis ……….. and …………..
Answer:
- Niulti religious
- Socict
- George Jacob Holyoake
- democrac
- Din-i-illahi and Suih-c-Kul
- Divine faith
- Peace and harmonvi
- Akbar
- religious
- Principle of Liberty
- 26
- citizens
- moral and humanistic
- constitution
- employment
- Secularism
- religious faith
- Secular
- Citizen
- Secular education
- materialism and spiritualism
III Match the following:
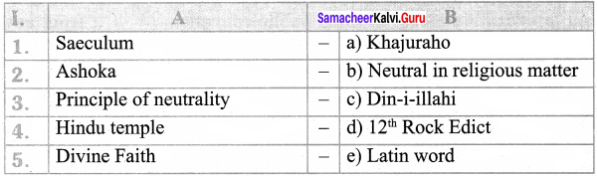
Answer:
- e
- d
- b
- a
- c

Answer:
- c
- a
- e
- b
- d
![]()
IV. State True or False
- Akbar’s tomb is situated at Sikandara near Agra, India.
- Secularism is the principle of-separation of state and country.
- Atheism is a lack of belief in men and women.
- Article 26 defines freedom to manage religious affairs.
- Secularism is non-interference of the state in religious affairs and vice-versa.
- “India will be a land of many faith, equally honored and respected, but of one national outlook” was said by Mahatma Gandhi.
- The State will identify itself with or controlled by any religion.
- Secularism was accepted as one of the fundamental tenets for the development of democracy in India.
- Secular education is need to develop moral and humanistic outlook.
- Secularism compels people to respect other religion.
Answer:
- True
- False
- False
- True
- True
- False
- False
- True
- True
- True
V. Consider the following statements and Tick (✓) the appropriate answer
Question 1.
(i) The Indian state works in various ways to prevent religious domination.
(ii) Secularism is the belief that no one should be discriminated on the basis of religion.
(iii) Article 26 equality of opportunity in public employment.
(iv) Secular education is needed to give a wider vision towards life.
(a) (i), (ii) & (iii) are Correct
(b) (i), (ii) & (iv) are Correct
(c) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) are Correct
(d) (iv) and (ii) are Correct
Answer:
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv) are Correct
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : India is a land of Multi-religions faith and Multi-cultural beliefs.
Reason (R) : India is the birth place of four major religions, Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism and Sikhism.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation A
Question 3.
Which of the following is correctly matched?
(a) The Mughal Emperor – Ashoka
(b) 12th Rock Edict – Akbar
(c) Atheism – Lack of belief in god and gods
(d) Secularism – Divine faith
Answer:
(c) Atheism – Lack of belief in god and gods.
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following is not correctly matched?
(a) Poet labal – “Religion does not teach us animosity; we are Indians and India is our home”.
(b) Principle of Equality – Give preference to any religion over another
(c) Secularism – Tolerance towards other religious and peaceful
(d) Article – 25(1) – Neutral in religious matters
Answer:
(d) Article – 25(1) – Neutral in religious matters
VI. Answer in one or two sentences:
Question 1.
Why do we need secular education?
Answer:
- Secularism in education means making public education free from any religious dominance.
- Children as future citizens must get education which should aim at their development of character and moral behavior irrespective of religious affiliation.
Question 2.
Write a short note on Article 27.
Answer:
The state shall not compel any citizen to pay any taxes for the promotion of any particular religion.
Question 3.
Write about Akbar’s instruction for mausoleum.
Answer:
Akbar’s instruction for his mausoleum was that it would incorporate elements from different religions including Islam and Hinduism.
Question 4.
What is the basic aim of our Indian constitution?
Answer:
The basic aim of our constitution is to promote unity and integrity of the nation along with individual dignity.
Question 5.
What is the religious toleration of Akbar?
Answer:
The Mughal emperor Akbar followed the policy of religious toleration. His propagation of Din-i-Illahi (Divine Faith) and Sulh-e-Kul (Peace and harmony among religions) were advocated for religious toleration.
Question 6.
Write a short note on King Ashoka’s 12th Rock Edict.
Answer:
In his 12th Rock Edict, Ashoka made an appeal not only for the tolerance of all religious sects but also to develop a spirit of great respect towards them.
VII. Answer the following in detail
Question 1.
Distinguish between constitution and secularism.
Answer:
Secularism :
- Secularism is the part of Indian constitution.
- Secularism was accepted as one of the fundamental tenets for the development of democracy in India.
- The word secularism was not mentioned in our constitution when it was adopted in 1950.
- Later on in 1976, the word secular was incorporated in the Preamble through the 42nd Amendment of the Indian Constitution.
Constitution :
- The makers of the Indian constitution were aware that a strong and united nation could be built only when all sections of people had the freedom to practice their religion.
- The basic aim of our constitution is to promote unity and integrity of the nation along with individual dignity.
- The freedom of religion guaranteed under the Indian constitution is not confined to its citizen alone but extends to aliens also.
![]()
Question 2.
Bring out the features of the constitution of India.
Answer:
- The state will not identify itself with or be controlled by any religion.
- The state guarantees to everyone the right to profess any religion of their own.
- The state will not accord any preferential treatment any of them.
- No discrimination will be shown by the state against any person on account of his religious faith.
- It creates fraternity of the Indian people and gives assurance the dignity of the individual and unity of the nation.