You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Solutions Term 2 Chapter 5 Basis of Classification
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Basis of Classification Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The following characteristics are essential for classification.
(a) Similarities
(b) Differences
(c) Both of them
(d) None of them
Answer:
(c) Both of them
Question 2.
Approximately species of living organisms found in the earth.
(a) 8.7 million
(b) 8.6 million
(c) 8.5 million
(d) 8.8 million
Answer:
(a) 8.7 million
Question 3.
The largest division of the living world is
(a) Order
(b) Kingdom
(c) Phylum
(d) Family
Answer:
(b) Kingdom
![]()
Question 4.
Who proposed the five kingdom of classification?
(a) Aristotle
(b) Linnaeus
(c) Whitakar
(d) Plato
Answer:
(c) Whitakar
Question 5.
The binomial name of pigeon is
(a) Homo sapiens
(b) Rattus rattus
(c) Mangifera indica
(d) Columbo livia
Answer:
(d) Columbo livia
II. Fill in the blanks
- ________ in 1623, introduced the binomial nomenclature.
- Species is the ________unit of classification.
- ________ are non- green and non-photosynthetic in nature.
- The binomial name of onion is ________
- Carolus Linnaeus is known as the Father of ________
Answer:
- Gaspard Bauhin
- Basic
- Fungi
- Hum sativum
- Modern Taxonomy
IV. Match the following:
Question 1.
- Monera – Moulds
- Protista – Bacteria
- Fungi – Neem
- Plantae – Butterfly
- Animalia – Euglena
Answer:
- Monera – Bacteria
- Protista – Euglena
- Fungi – Moulds
- Plantae – Neem
- Animalia – Butterfly
V. Assertion and Reason Questions:
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Binomial name is the universal name and contains two names.
Reason (R) : It was first introduced by Carolus Linnaeus.
(a) Assertion is correct, Reasoning is correct
(b) Assertion is correct, Reasoning is incorrect
(c) Assertion is incorrect, Reasoning is correct
(d) Assertion and Reasoning are incorrect
Answer:
(b) Assertion is correct, Reasoning is incorrect
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : Identification, assortment and grouping are essential for classification.
Reason (R) : These are basic steps of taxonomy.
(a) Assertion is correct, Reasoning is correct
(b) Assertion is correct, Reasoning is incorrect
(c) Assertion is incorrect, Reasoning is correct
(d) Assertion & Reasoning is incorrect.
Answer:
(a) Assertion is correct, Reasoning is correct
VI. Give very short answer:
Question 1.
What is classification?
Answer:
The method of arranging the organisms into groups is called classification
Question 2.
List out the five kingdoms classification.
Answer:
- Monera
- Protista
- Fungi
- Plantae
- Animalia
Question 3.
Define – dichotomous key.
Answer:
It is a tool used to classify organisms based on their similarities and differences.
Question 4.
Write two examples of Monera.
Answer:
Bacteria and Blue green algae.
![]()
Question 5.
What is binomial nomenclature?
Answer:
Binomial nomenclature is an universal system of naming organisms. As per this system, each organism has two names – the first is the Genus name and the second is the Species name.
Question 6.
Write the binomial name of
(a) Human being
(b) Paddy
Answer:
Binomial name
(a) Human being – Homo sapiens
(b) Paddy – Oryza sativa
Question 7.
Write two features of protista.
Answer:
- It includes unicellular and few simple multicellular eukaryotes.
- It includes plant like protists (Algae) and animal like protists (protozoans)
VII. Give short Answer :
Question 1.
Write the levels of classification.
Answer:
There are seven main categories of hierarchies namely, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus and Species- Species is the basic unit of classification
![]()
Question 2.
Differentiate plantae and animalia
Answer:
Kingdom plantae
- They are multicellular eukaryotes that can photosynthesize.
- The cells have cell wall.
- The cells can perform specialised functions like photosynthesis.
- Eg. Ferns, cone bearing plants and flowering plants
Kingdom Animalia
- They are multicellular, eukaryotic and heterotrophic animals.
- The cells lack cell wall.
- They cannot photosynthesize but animals move from place to place unlike plants.
- Eg. Invertebrates and Vertebrates
Question 3.
Write any two merits of Five Kingdom classification.
Answer:
- This system of classification is more scientific and natural.
- This system of classification clearly indicates the cellular organization, mode of nutrition, and characters for early evolution of life.
VII. Give answer in Detail:
Question 1.
Explain about five kingdom classification.
Answer:
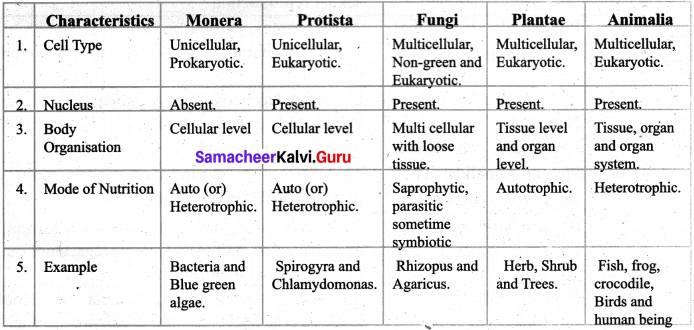
- The five kingdom classification was proposed by R.H.Whittaker in 1969.
- He classified the organisms into five kingdoms on the basis of characteristics like cell structure, mode of Nutrition, Source of Nutrition and body organization.
Question 2.
Write short notes on – Binomial Nomenclature.
Answer:
(i) Gaspard Bauhin jn 1623, introduced naming of organisms with two names which is known as Binomial nomenclature, and it was implemented by Carolus Linnaeas in 1753
(ii) Binomial nomenclature an universal system of naming organisms. As per this system, each organism has two names – the first is the Genusname and the second is the Speciesname.
(iii) Genus name begins with a capital letter and Species name begins with a small letter. Example The nomenclature for onion is Allium sativam. Genus name is Allium, species name is sativam.
(iv) Vernacular name is a local name that is familiar for a particular place. Binomial name is an universal name which never changes.
(v) Binomial nomenclature and classification helps scientists to identify any organisms and to place them at a particular hierarchy.
Question 3.
Give an account on the classification of invertebrates with few general features and examples.
Answer:
Invertebrates are animals without a backbone. The invertebrates have been classified into various phyla as follows:
|
S.No |
Division |
General Characters |
|
1. |
Phylum Protozoa
Eg. Amoeba, Euglena p |
Microscopic unicellular, pseudopodia, flagella and cilia for locomotion, reproduce by fission or conjugation. |
|
2. |
Phylum Porifera
Eg. Leucosolenia, Sycon. |
Multicellular organisms with holes in the body. Skeleton formed of spicules, asexual and sexual reproduction. |
|
3. |
Phylum Coelenterata Eg. Hydra, Jelly fish. |
Multicellular organisms Diploblastic, sessile or free swimming, solitary or colonial, asexual and sexual reproduction |
|
4. |
Phylum Platyhelminthes Eg. Planaria, Liver fuke |
Acoelomates, parasites inside the body of animals and human beings, mostly hermaphrodite (bisexual). |
|
5. |
Phylum Aschelminthes or Nematoda
Eg. Ascaris lumbricoides |
Unsegmented body, mostly parasites in human beings and animals, causing diseases, asexual reproduction. |
|
6. |
Phylum Annelida Eg. Earthworm, Leech. |
Triploblastic, segmented body, mostly hermaphrodite (bisexual and unisexual). |
|
7. |
Phylum Arthropoda Eg. Crab, Prawn |
Segmented body, thick chitinous cuticle forming an exoskeleton, paired and jointed legs, unisexual exhibits sexual dimorphism. |
|
8. |
Phylum Mollusca Eg. Cuttle fish, Snail |
Soft bodied, unsegmented, muscular head, foot and visceral mass, mantle, a calcareous shell, sexual reproduction. |
|
9. |
Phylum Echinodermata Eg. Starfsh, Sea – Urchin |
Exclusively marine, spines and spicules over the body, water vascular system, tube feet, for feeding, respiration and locomotion sexual reproduction. |
IX. HOTS :
Question 1.
Which kingdom has saprophytic, parasitic and symbiotic nutrition. Why?
Answer:
Kingdom Fungi comprises of unicellular to multicellular organisms which are heterotrophic in their mode of nutrition. They do not contain chlorophyll and cannot photosynthesize. Hence they show modes of Nutrition such as:
- Saprophytic – Obtaining nutrition from dead matter Eg. Mucor
- Parasitic – Obtaining nutrition from living organisms Eg. Cercospora
- Symbiotic – Obtaining nutrition through a mutually beneficial relationship with another organism. Eg. Lichens
![]()
X. See the Diagram and write The Kingdom:
Question 1.
Pictures of some living organisms are given below. Identify the kingdom to which each of these belong and write the kingdom name in the blanks provided.
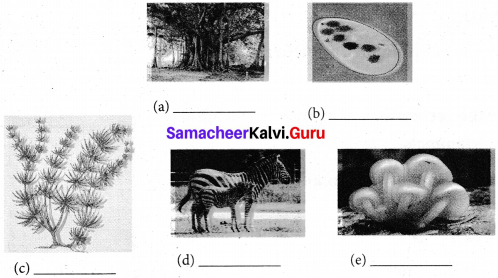
Answer:
(a) Kingdom plantae
(b) Kingdom protista
(c) Kingdom protista
(d) Kingdom Animalia
(e) Kingdom Fungi
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Basis of Classification Intext Activities.
Activity- 2
Question 1.
Fill up the blanks with the suitable organisms
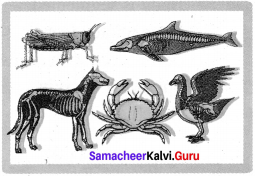
- Vertebrates ________ , ________ and ________
- Invertebrates ________, ________ and ________.
- Name the vertebrates with wings ________, ________.
- Name the invertebrates with wings ________, ________.
- Name the invertebrates with segmented legs ________, ________.
- Name the invertebrates with Jointed legs ________, ________.
- Name the warm blooded vertebrates ________.
- Name the cold blooded vertebrates ________.
- Name the vertebrates with lungs respiration ________, ________.
- Name the animal with beak ________.
Answers:
- Fishes, Amphibians, Mammals.
- Protozoa, Porifera, Annelida.
- Bat, Pigeon.
- Butterfly, Dragon fly.
- Millipedes, Centipedes.
- Crab, Prawn.
- Mammals.
- Fishes.
- Birds, Mammals.
- Birds
Activity – 3
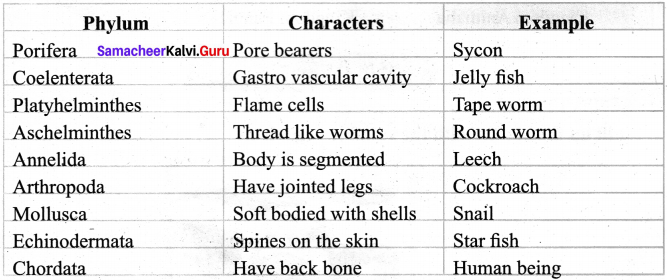
Given table shows the name of the phylum and its characteristic features. Write name of the animals belonging to the respective phylum
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Basis of Classification Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
_______ belongs to Phylum Platyhelminthes.
(a) Ascaris
(b) Liver fluke
(c) Leucosolcnia
(d) Euglena
Answer:
(b) Liver fluke
![]()
Question 2.
_______ are diploblastic.
(a) Protozoa
(b) Annelida
(c) Coelenterata
(d) Echinodermata
Answer:
(c) Coelenterata
Question 3.
_______ is not a characteristic of Phylum Echinodertnata.
(a) Water vascular system
(b) Tube feet
(c) Pores in the body
(d) Spicules
Answer:
(c) Pores in the body
Question 4.
Bones with air cavities ate seen in _______
(a) snail
(b) pigeon
(c) bats
(d) cuttle fish
Answer:
(b) pigeon
Question 5.
_______ is not oviparous.
(a) Snake
(b) Crow
(c) Frog
(d) Human being
Answer:
(d) Human being
Question 6.
Plant is a thallus in _______
(a) Algae
(b) Ferns
(c) Bacteria
(d) Pinus
Answer:
(a) Algae
Question 7.
Naked ovules are seen in _______
(a) Cycas
(b) Funaria
(c) Mango
(d) Chara
Answer:
(a) Cycas
Question 8.
_______ is not a fugus.
(a) Yeast
(b) Chlamydomonas.
(c) Rhizopus
(d) Agaricus
Answer:
(b) Chlamydomonas
![]()
Question 9.
_______ belong to Monera.
(a) Blue green algae
(b) Yeast
(c) Mushrooms
(d) Red algae
Answer:
(a) Blue green algae
Question 10.
_______ are called Amphibious plants.
(a) Ferns
(b) Mosses
(c) Fungi
(d) Gymnosperms
Answer:
(b) Mosses
II. Fill in the Blanks.
Question 1.
- ________ was a greek philosopher who classified animals.
- Paired and jointed legs are seen in phylum ________
- Giving birth to young ones is described as________
- Animals belonging to phylum ________ are mostly parasites.
- Flowering plants belong to________
- ________ are considered to be first land plants,
- ________ are dominant plant forms of present day.
- All prokaryotic belong to kingdom________
- Scientific name for Human being is ________
- Cones are produced by ________
Answer:
- Aristotle
- Arthropoda
- Viviparous
- Aschelminthes
- Angiosperms
- Ferns
- Angiosperms
- Monera
- Homo sapiens
- gymnosperms
III. True or False – if false give the correct statement.
Question 1.
Animals belonging to phylum protozoa reproduce by fission.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Specialised vascular tissues for conduction of food and water are seen in mosses.
Answer:
False. Specialised vascular tissues for conduction of food and water are seen in ferns ‘
Question 3.
Angiosperms are divided into monocots and dicots.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
The angiosperms are evergreen trees.
Answer:
False. The gymnosperms are evergreen trees.
Question 5.
Fungi need water to complete their life cycle.
Answer:
False. Mossesneed water to complete their life cycle
IV. Match the following:
Question 1.
- Protozoa- (a) Spongy bones
- Annelida- (b) Hermaphrodite
- Coelenterata- (c) Soft body
- Aves- (d) Colonial forms
- Mollusca- (e) Conjugation
Answer:
- -e
- -b
- -d
- -a
- -c
Question 2.
- Fungi- (a) Funaria
- Mosses- (b) Cycas
- Gymnosperms- (c) Adiantum
- Flowering Plants- (d) Agaricus
- Ferns- (e) Tamarind
Answer:
- -d
- -a
- -b
- -e
- -c
V. Assertion and Reason.
Mark the correct choice as
(a) Assertion is correct, Reasoning is correct
(b) Assertion is correct, Reasoning is incorrect
(c) Assertion is incorrect Reasoning is correct
(d) Assertion & Reasoning are incorrect
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Angiosperms have ovary in the flower.
Reason (R) : They produce fruits and seeds.
Answer:
(a) Assertion is correct, Reasoning
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : Blue green algae are prokaryotes.
Reason (R) : They do not have a true nucleus.
Answer:
(a) Assertion is correct, Reasoning
Question 3.
Assertion (A) : Xylem does not have vessels in angiosperms.
Reason (R) : They conduct food.
Answer:
(d) Assertion & Reasoning is
Question 4.
Assertion (A) : Reptiles are warm blooded animals.
Reason (R) : They have scales.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is incorrect Reasoning is correct
VI. Give Very short Answers:
Question 1.
Name the following:
- A phylum with diploblastic animals
- A phylum which has hermaphrodite animal
Answer:
- phylum coelenterata.
- Phylum Annelida / Phylum Platyhelminthes.
Question 2.
Mention two features of phylum Echinodermata.
Answer:
Water vascular system, tube feet.
Question 3.
Mention two salient features of class mammalia.
Answer:
Viviparous animals, heterodont dentition.
![]()
Question 4.
What is heterodont dentition?
Answer:
Presence of different kinds of teeth.
Question 5.
Why do Aves have bones with air cavities?
Answer:
It makes the body lighter and helps in flight.
Question 6.
Name the vascular tissues seen in plants.
Answer:
Xylem and phloem.
Question 7.
Gymnosperms do not produce fruits. Give Reason.
Answer:
The ovules are naked, without ovary. Hence gymnosperms do not produce fruits.
VII. Short Answer.
Question 1.
List two demerits of five kingdom system of classification.
Answer:
- In this system of classification, viruses have not been given a proper place
- Multicellular organisms have originated several times from protists.
Question 2.
Write a note on kingdom fungi.
Answer:
- Fungi are eukaryotic, and mostly are multicellular.
- They secrete enzymes to digest the food and absorb the food after digested by the enzymes.
- Fungi saprophytes as decomposes (decay-causing organisms) or as parasites.
- Kingdom Fungi includes molds, mildews, mushrooms and yeast.
![]()
Question 3.
Differentiate Angiosperms and Gymnosperms.
Answer:
Angiosperms
- They produce flowers.
- They produce fruits.
- They are classified into monocots and dicots.
- They possess well developed xylem and phloem.
Gymnosperms
- They produce cones.
- Ovules are naked and no fruit formation occurs.
- They are not classified.
- Xylem lacks vessels and phloem lacks companion cells.
VIII. Give answer in Detail:
Question 1.
Write the merits and demerits of five kingdom classification.
Answer:
Merits:
- This system of classification is more scientific and natural.
- This system of classification clearly indicates the cellular organization, mode of nutrition, and characters for early evolution of life.
- It is the most accepted system of modem classification as the different groups of organisms are placed phylogenetically.
- It indicates gradual evolution of complex organisms from simpler one.
Demerits:
- 1.In this system of classification of viruses have not been given a proper place.
- Multicellular organisms have originated several times from protists.
- This type of classification has drawn back with reference to the lower forms of life.
- Some organisms included under protista are not eukaryotic.
![]()
IX. Creative questions: HOTS
Question 1.
Blue green algae are not placed under kingdom protista whereas other algae are placed under it.
Answer:
Blue green algae has prokaryotic cells like bacteria. The cells lake a proper nucleus, therefore they are placed with bacteria in kingdom monera.
Question 2.
How can you differentiate a Prokaryotic cell from Eukaryotic cell.
Answer:
Prokaryotic
1. Presence of a true nucleus is eukaryotes ,
2. Eg. A nucleus which is covered by a nuclear membrane.
Prokaryotic
1. Presence of a true nucleus is eukaryotes ,
2. Eg. A nucleus which is covered by a nuclear membrane.