You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 12 Discrete Mathematics Ex 12.1
Question 1.
Determine whether * is a binary operation on the sets given below
(i) a * b = a.|b| on R ,
(ii) a * b = min (a, b) on A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
(iii) (a * b) = \(a \sqrt{b}\) is binary on R.
Solution:
(i) a * b = a.|b| on R
a, b ∈ R ⇒ a.|b| ∈ R as a ∈ R and |b| ∈ R.
Hence * is a binary operation on R
(ii) a * b = min (a, b) on A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
a * b = min {(a, b)}
Now, 1, 2 ∈ A ⇒1 * 2 = 1 ∈ A
3, 5 ∈ A ⇒ 3 * 5 = 3 ∈ A
Hence * is a binary operation on A
(iii) (a * b) = a√b is binary on R
a√b ∉ R
∴ * is not a binary on R
![]()
Question 2.
![]()
Solution:
(m ⊗ n) = mⁿ + nm ∀ m, n ∈ Z
Let us take – 2, 2 ∈ Z
(m ⊗ n) = (-2 ⊗ 2) = (-2)² + (2)-2
= 4 + \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac { 17 }{ 4}\) ∉ Z
∴ ⊗ is a binary operation on R
Question 3.
Let * be defined on R by (a * b) = a + b + ab – 1 .Is * binary on R ? If so, find \(3 *\left(\frac{-7}{15}\right)\)
Solution:
a * b = a + b + ab – 7.
Now when a, b ∈ R, then ab ∈ R also a + b ∈ R.
So, a + b + ab ∈ R.
We know – 7 ∈ R.
So, a + b + ab – 7 ∈ R.
(ie.) a * b ∈ R.
So, * is a binary operation on R.
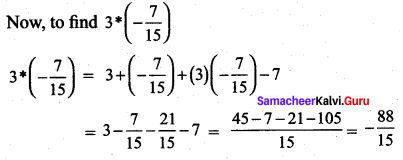
Question 4.
Let A= {a+ \(\sqrt{5}\)b: a, b ∈ Z}. Check whether the usual multiplication is a binary operation on A.
Solution:
A = {a + √5 b: a, b ∈ Z}
Let 1, 2 ∈ Z ⇒ a + √5 b = 1 + 2 √5 ∈ A
and 2, 3 ∈ Z ⇒ a + √5 b = 2 + 3 √5 ∈ A
Taking usual multiplication as binary] operation
(1+2 √5).(2 + 3√5) = (32 + 7 √5) ∈ A
∴ Usual multiplication can be a binary operation on A.
![]()
Question 5.
(i) Define an operation * on Q as follows: a * b = \(\left(\frac{a+b}{2}\right)\); a, b ∈ Q. Examine the closure,
commutative, and associative properties satisfied by * on Q.
(ii) Define an operation * on Q as follows: a*b = \(\left(\frac{a+b}{2}\right)\); a, b ∈ Q. Examine the existence of identity and the existence of inverse for the operation * on Q.
Solution:
(i) 1. Closure property:
Let a, b ∈ Q.
![]()
So, the closure property is satisfied.
2. Commutative property:
Let a, b ∈ Q.
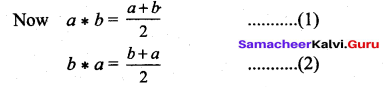
(1) = (2) ⇒ Now a * b = b * a
⇒ Commutative property is satisfied.
3. Associative property:
Let a, b, c ∈ Q
To prove associative property we have to prove that a * (b * c) = (a * b) * c
LHS: a * (b * c)
![]()
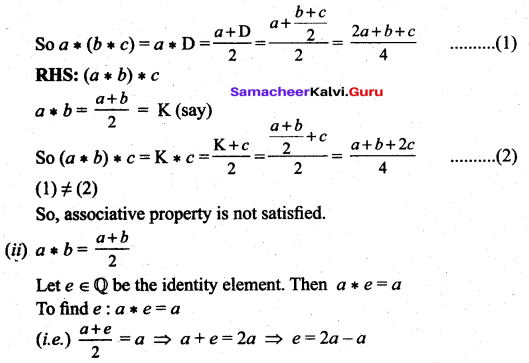
(i.e.) the identity Clement e = a which is not possible.
So, the identity element does not exist and so inverse does not exist.
![]()
Question 6.
Fill In the following table so that the binary operation * on A = {a, b, c} is commutative.
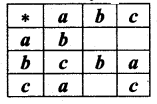
Solution:
Given that the binary operation * is Commutative.
To find a * b :
a * b = b * a (∵ * is a Commutative)
Here b * a = c. So a * b = c
To find a *c:
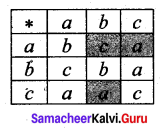
a * c = c * a (∵ * is a Commutative)
c * a = a. (Given)
So a * c = a
To find c * b:
c * b = b * c
Here b * c = a.
So c * b = a
Question 7.
Consider the binary operation * defined on the set A = [a, b, c, d] by the following table:
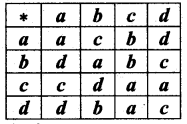
– Is it commutative and associative?
Solution:
From the table
b * c = b
c * b = d
So, the binary operation is not commutative.
To check whether the given operation is associative.
Let a, b, c ∈ A.
To prove the associative property we have to prove that a * (b * c) = (a * b) * c
From the table,
LHS: b * c = b
So, a * (b * c) = a * b = c ……. (1)
RHS: a * b = c
So, (a * b) * c = c * c = a …… (2)
(1) ≠ (2). So, a * (b * c) ≠ (a * b) * c
∴ The binary operation is not associative.
Question 8.
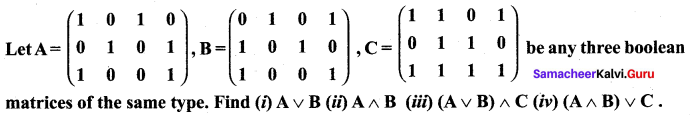
Solution:

Question 9.
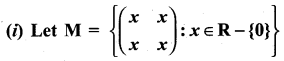 and Let * be the matrix multiplication. Determine whether M is closed under * . If so, examine the commutative and associative properties satisfied by * on M.
and Let * be the matrix multiplication. Determine whether M is closed under * . If so, examine the commutative and associative properties satisfied by * on M.
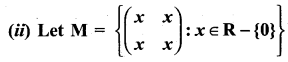 and let * be the matrix multiplication. Determine whether M is closed under *. If so, examine the existence of an identity, the existence of inverse properties for the operation * on M.
and let * be the matrix multiplication. Determine whether M is closed under *. If so, examine the existence of an identity, the existence of inverse properties for the operation * on M.
Solution:
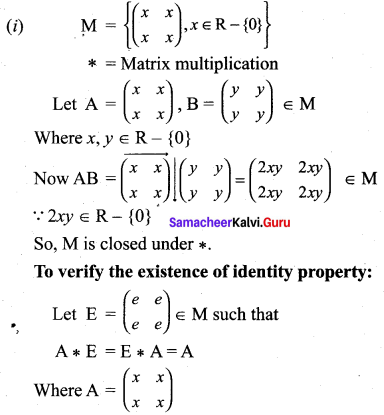

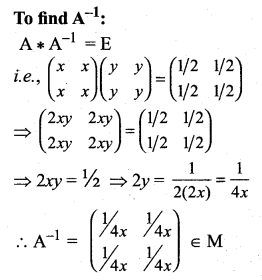
So, inverse property is satisfied.
![]()
Question 10.
(i) Let A be Q\{1). Define * on A by x * y = x + y – xy. Is * binary on A ? If so, examine the commutative and associative properties satisfied by * on A.
(ii) Let A be Q\{1}. Define *on A by x * y = x + y – xy. Is * binary on A ? If so, examine the existence of an identity, the existence of inverse properties for the operation * on A.
Solution:
Let A = Q\{1}
Let x, y ∈ A. Then x and y are rational numbers, and x ≠ 1, y ≠ 1
Closure axiom:
Clearly x * y = x + y – xy is a rational number.
But to prove x * y ∈ A we have to prove that
x * y ≠ 1
Suppose x * y = 1
⇒ x + y – xy = 1
i.e., y – xy = 1 – x
y(1 – x) = 1 – x
y = 1 (as x ≠ 1, 1 – x ≠ 0)
This is impossible as y ≠ 1.
Hence our assumption is wrong. Thus x * y ≠ 1 and hence x, y ∈ A.
This shows that * is binary on A.
Commutative axiom:
For any x, y ∈ A, x * y = x + y – xy
and y * x = y + x – yx
⇒ x * y = y * x for all x, y ∈ A
This shows that * is commutative
Associative axiom:
Now
x * (y * z) = x * (y + z – yz)
= x + y + z – yz – x(y + z – yz)
= x + y + z – xy – yz – xz + xyz
Also (x * y) * z = (x + y – xy) * z
= x + y – xy + z – (x + y – xy)z
= x + y + z – xy – yz – xz + xyz
Thus x * (y * z) = (x * y) * z ∀ x, y, z ∈ A
Hence, the associative axiom is true.
(ii) Identity axiom:
Let ‘e’ be the identity element.
By definition of e, x * e = x
By definition of *, we have x * e = x + e – xe
Thus x + e – xe = x ⇒ e (1 – x) = 0
⇒ e = 0, since x ≠ 1
Since e = 0 ∈ A
The identity element is e = 0 ∈ A
Inverse axiom:
Let x-1 denote the inverse of x ∈ A
By definition of inverse x * x-1 = e = 0
Also, by definition of *, x * x-1 = x + x-1 – x x-1
Thus x + x-1 – x x-1 = 0
x-1 (1 – x) = -x
∴ x-1 = \(\frac { -x }{ 1-x }\) = \(\frac { x }{ x-1 }\)
since x ≠ 1, x – 1 ≠ 0 and
so x-1 = \(\frac { x }{ x-1 }\) ∈ A
as \(\frac { x }{ x-1 }\) ≠ 1
∴ Inverse axiom holds good for A.
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 12 Discrete Mathematics Ex 12.1 Additional Problems
Question 1.
Show that the set G = {a + b\(\sqrt{2}\)/ a, b ∈ Q} is an infinite abelian group with respect to Binary operation addition. Satisfies closure, associative, identity and inverse properties.
Solution:
(i) Closure axiom :
Let x, y ∈ G. Then x = a + b\(\sqrt{2}\), y = c + d\(\sqrt{2}\); a, b, c, d ∈ Q.
x + y = (a + b\(\sqrt{2}\)) + (c + d\(\sqrt{2}\)) = (a + c) + (b + d) \(\sqrt{2}\) ∈ G,
Since (a + c) and (b + d) are rational numbers.
∴ G is closed with respect to addition.
(ii) Associative axiom : Since the elements of G are all real numbers, addition is associative.
(iii) Identity axiom : There exists 0 = 0 + 0 \(\sqrt{2}\) ∈ G
such that for all x = a + b\(\sqrt{2}\) ∈ G.
x + 0 = (a + b\(\sqrt{2}\) ) + (0 + 0\(\sqrt{2}\))
= a + b\(\sqrt{2}\) = x
Similarly, we have 0 + x = x. ∴ 0 is the identity element of G and satisfies the identity axiom.
(iv) Inverse axiom: For each x = a + b\(\sqrt{2}\) ∈ G,
there exists -x = (-a) + (-b) \(\sqrt{2}\) ∈ G
such that x + (-x) = (a + b\(\sqrt{2}\)) + ((-a) + (- b)\(\sqrt{2}\))
= (a + (-a)) + (b + (-b)) \(\sqrt{2}\) = 0
Similarly, we have (- x) + x = 0 .
∴ (- a) + (-b)\(\sqrt{2}\) is the inverse of a + b \(\sqrt{2}\) and satisfies the inverse axiom.
(v) Commutative axiom:
x + y = (a + c) + (b + d) \(\sqrt{2}\) = (c + a) + (d + b) \(\sqrt{2}\)
= (c + d\(\sqrt{2}\)) + (a + b\(\sqrt{2}\))
= y + x, for all x, y ∈ G.
∴ The commutative property is true.
∴ (G, +) is an abelian group. Since G is infinite, we see that (G, +) is an infinite abelian group.
![]()
Question 2.
Show that (Z7 – { [0]}, .7) write to the binary operation multiplication modul07 satisfies closure, associative, identity and inverse properties.
Solution:
Let G = [[1], [2],… [6]]
The Cayley’s table is
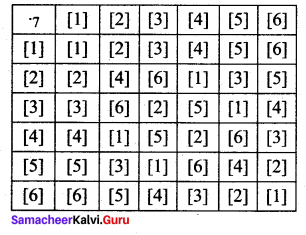
From the table:
(i) all the elements of the composition table are the elements of G.
∴ The closure axiom is true.
(ii) multiplication modulo 7 is always associative.
(iii) the identity element is [1] ∈ G and satisfies the identity axiom.
(iv) the inverse of [1] is [1]; [2] is [4]; [3] is [5]; [4] is [2]; [5] is [3] and [6] is [6] and it satisfies the inverse axiom.
Question 3.
Show that the set G of all positive rationals with respect to composition * defined by ab
a* b = \(\frac{a b}{3}\) for all a, b ∈ G satisfies closure, associative, identity and inverse properties.
Solution:
Let G = Set of all positive rational number and * is defined by,
![]()
(i) Closure axiom: Let a, b ∈ G
![]()
∴ closure axiom is satisfied.
(ii) Associative axiom: Let a, b, c ∈ G.
To prove the associative property, we have to prove that
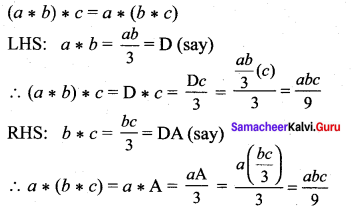
(1) = (2) ⇒ LHS = RHS i.e., associative axiom is satisfied.
(iii) Identity axiom: Let a ∈ G.
Let e be the identity element.
By the definition, a * e = a
![]()
e = 3 ∈ G ⇒ identity axiom is satisfied.
![]()
(iv) Inverse axiom: Let a ∈ G and a’ be the inverse of a * a’ = e = 3.
![]()
Question 4.
Show that the set G of all rational numbers except – 1 satisfies closure, associative, identity, and inverse property with respect to the operation * given by a * b = a + b + ab for all a, b ∈ G
Solution:
G = [Q, -{-l}]
* is defined by a * b = a + b + ab
To prove G is an abelian group.
G1: Closure axiom: Let a, b ∈ G.
i.e., a and b are rational numbers and a ≠ -1, b ≠ -1.
So, a * b = a + b + ab
If a + b + ab = – 1
⇒ a + b + ab + 1 = 0
i.e., (a + ab) + (b + 1) = 0
a (1 + b) + (b + 1) = 0
i.e., (a + 1)(1 + b) = 0
⇒ a = -1, b = -1
But a ≠ -1, b ≠ -1
⇒ a + b + ab ≠ -1
i.e., a + b + ab ∈ G ∀ a, b ∈ G
⇒ The closure axiom is verified.
G2: Associative axiom: Let a, b, c ∈ G.
To prove G2, we have to prove that,
a * {b * c) = (a * b) * c
LHS:
b * c = b + c + bc = D (say)
a * (b * c) = a * D = a + D + aD
= a + (b + c + bc) + a(b + c + bc)
= a + b + c + bc + ab + ac + abc
= a + b + c + ab + bc + ac + abc ……. (1)
RHS:
a * b = a + b + ab = E (say)
∴ (a * b) * c = E * c = E + c + Ec
= a + b + ab + c + (a + b + ab) c
= a + b + ab + c + ac + bc + abc ……. (2)
= a + b + c + ab +be+ ac + abc
(1) = (2) ⇒ Associative axiom is verified.
G3: Identity axiom: Let a ∈ G. To prove G3 we have to prove that there exists an element e ∈ G such that a * e = e * a = a.
To find e: a * e = a
i.e., a + e + ae = a
⇒ e(1 + a) = a – a = 0
![]()
So, e = 0 ∈ G ⇒ Identity axiom is verified.
G4 : Inverse axiom: Let a ∈ G. To prove G4, we have to prove that there exists an element a’ ∈ G such that a * a’ = a’ * a = e.
To find a’: a * a’ = e
i.e., a + a’ + aa’=: 0 {∵ e = 0}
⇒ a'(1 + a) = -a
![]()
Thus, inverse axiom is verified.
![]()
Question 5.
Show that the set { [1], [3], [4], [5], [9]} under multiplication modulo 11 satisfies closure, associative, identity and inverse properties.
Solution:
G = {[1], [3], [4], [5], [9]}
* is defined by multiplication modulo 11.
To prove G is an abelian group with respect to *
Since we are given a finite number of elements i.e., since the given set is finite, we can frame the multiplication table called Cayley’s table.
The Cayle’s table is as follows:
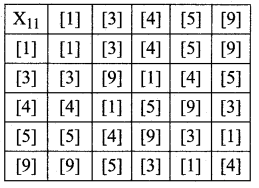
G1: The elements in the above table are [1], [3], [4], [5] and [9] which are elements of G.
∴ closure axiom is verified.
G2: Consider [3], [4], [5] which are elements of G.
{[3] * [4]} * [5] = [1] * [5] = [5] ……. (1)
[3] * {[4] * [5]} = [3] * [9] = [5] …… (2)
(1) = (2) ⇒ (a * b) * c = a * (b * c) i.e., associative axiom is verified.
G3: The first row elements are the same as that of the given elements in the same order. ie., from the table, the identity element is [1] ∈ G. So identity axiom is verified.

G5: From the table * is commutative i.e., the entries equidistant from the leading diagonal on either side are equal ⇒ a * b = b * a