Students can download 12th Business Maths Chapter 3 Integral Calculus II Ex 3.2 Questions and Answers, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Integral Calculus II Ex 3.2
Question 1.
The cost of an overhaul of an engine is ₹ 10,000 The operating cost per hour is at the rate of 2x – 240 where the engine has run x km. Find out the total cost if the engine runs for 300 hours after overhaul.
Solution:
M.C = 2x – 240
Total cost C = ∫(M.C)dx
= ∫(2x – 240)dx
C = 2(\(\frac { x^2 }{2}\)) – 240x + c
Where C = 10000
C = x² – 240x + 10000
Where x = 300
C = (300)² – 240(300) + 10,000
= 90000 – 72000 + 10,000
= 100000 – 72000
C = Rs 28,000
Question 2.
Elasticity of a function \(\frac{\mathbf{E}_{y}}{\mathbf{E}_{x}}\) is given by \(\frac{\mathbf{E}_{y}}{\mathbf{E}_{x}}=\frac{-7 x}{(1-2 x)(2+3 x)}\) Find the function when x = 2, y = \(\frac{3}{8}\)
Solution:
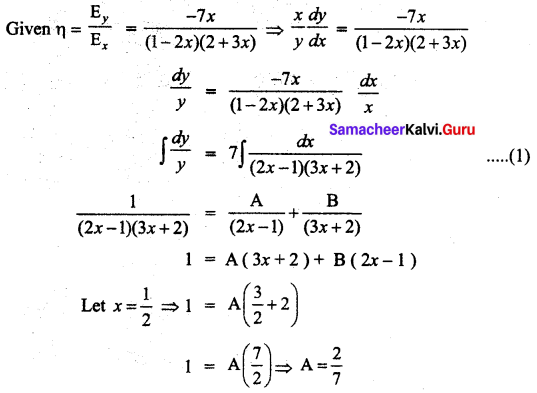
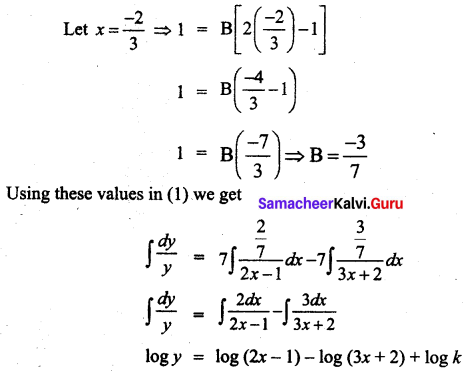
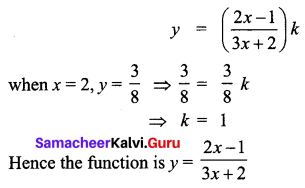
Question 3.
The elasticity of demand with respect to price for a commodity is given by \(\frac{(4-x)}{x}\) where p is the price when demand is x. Find the demand function when the price is 4 and the demand is 2. Also, find the revenue function.
Solution:
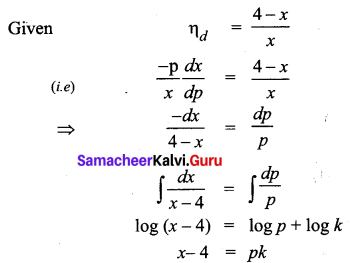
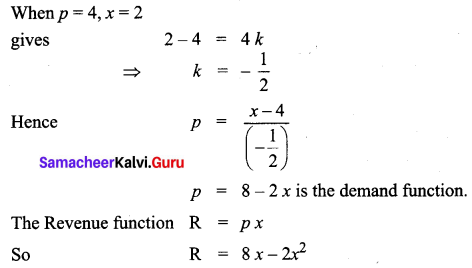
Question 4.
A company receives a shipment of 500 scooters every 30 days. From experience, it is known that the inventory on hand is related to the number of days x. Since the shipment, I(x) = 500 – 0.03x2, the daily holding cost per scooter is ₹0.3. Determine the total cost for maintaining inventory for 30 days.
Solution:
Here inventory I(x) = 500 – 0.03x2
Unit holding cost C1 = ₹0.3
T = 30 days
So total inventory carrying cost
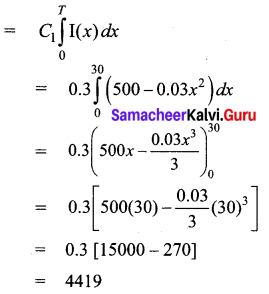
Hence the total cost for maintaining inventory for 30 days is ₹ 4,419.
Question 5.
An account fetches interest at the rate of 5% per annum compounded continuously. An individual deposits ₹ 1,000 each year in his account. How much will be in the account after 5 years. (e0.25 = 1.284)
Solution:
p = 1000, N = 5, r = 5% = 0.05
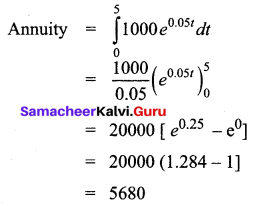
After 5 years ₹ 5680 will be in the account
Question 6.
The marginal cost function of a product is given by \(\frac{d c}{d x}\) = 100 – 10x + 0.1x2 where x is the output. Obtain the total and the average cost function of the firm under the assumption, that its fixed cost is ₹ 500.
Solution:
Given MC = \(\frac{d c}{d x}\) = 100 – 10x + 0.1x2
C = ∫ MC dx + k
C = ∫ (100 – 10x + 0.1x2) dx + k
C = 100x – 5x2 + \(\frac{0.1 x^{3}}{3}\) + k
The fixed cost is 500 ⇒ k = 500
Hence total cost function = 100x – 5x2 + \(\frac{0.1 x^{3}}{3}\) + 500
Average cost function AC = \(\frac{c}{x}\)
\(=100-5 x+\frac{x^{2}}{30}+\frac{500}{x}\)
Question 7.
The marginal cost function is MC = 300 \(x^{\frac{2}{5}}\) and fixed cost is zero. Find out the total cost and average cost functions.
Solution:
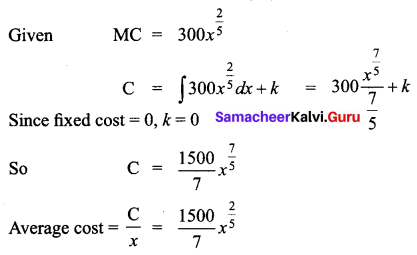
Question 8.
If the marginal cost function of x units of output is \(\frac{a}{\sqrt{a x+b}}\) and if the cost of output is zero. Find the total cost as a function of x.
Solution:
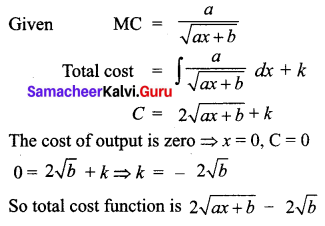
Question 9.
Determine the cost of producing 200 air conditioners if the marginal cost (is per unit) is C'(x) = \(\left(\frac{x^{2}}{200}+4\right)\)
Solution:

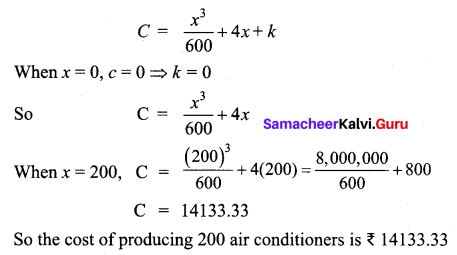
Question 10.
The marginal revenue (in thousands of Rupees) functions for a particular commodity is 5 + 3e-0.03x where x denotes the number of units sold. Determine the total revenue from the sale of 100 units. (Given e-3 = 0.05 approximately)
Solution:
Given, marginal Revenue R'(x) = 5 + 3e-0.03x
Total revenue from the sale of 100 units is
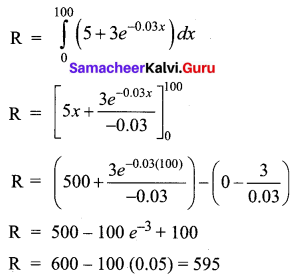
Total revenue = 595 × 1000 = ₹ 5,95,000
Question 11.
If the marginal revenue function for a commodity is MR = 9 – 4x2. Find the demand function.
Solution:
Given, marginal Revenue function MR = 9 – 4x2
Revenue function, R = ∫(MR) dx + k
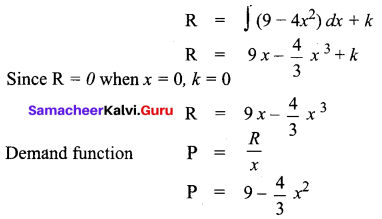
Question 12.
Given the marginal revenue function \(\frac{4}{(2 x+3)^{2}}-1\), show that the average revenue function is P = \(\frac{4}{6 x+9}-1\)
Solution:
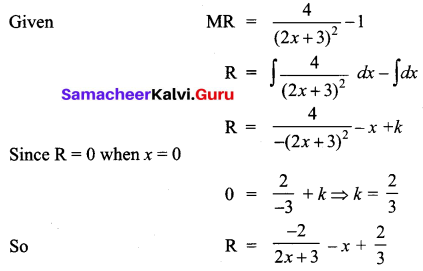
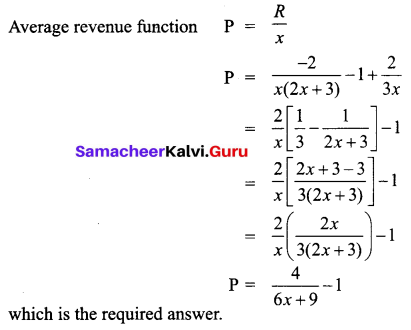
Question 13.
A firm’s marginal revenue function is MR = 20 \(e^{\frac{-x}{10}}\left(1-\frac{x}{10}\right)\). Find the corresponding demand function.
Solution:
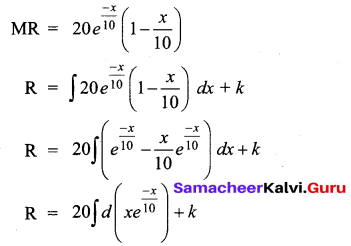

Question 14.
The marginal cost of production of a firm is given by C'(x) = 5 + 0.13x, the marginal revenue is given by R'(x) = 18 and the fixed cost is ₹ 120. Find the profit function.
Solution:
C(x) = ∫C ‘(x) dx = ∫(5 + 0.13x) dx
= 5x + 0.13(\(\frac { x^2 }{2}\)) + k1
C = 5x + 0.065 x² +120 …….. (1)
Total Revenue function
R(x) = ∫R ‘(x) dx = ∫18 dx
R = 18x + k2
when x = 0; R = 0 ⇒ k2 = 0
R = 18x …….. (2)
Profit function p = R – C
= 18x – [5x + 0.065 x² + 120]
= 18x – 5x – 0.065x² – 120
∴ p = 13x – 0.065x² – 120
Question 15.
If the marginal revenue function is R'(x) = 1500 – 4x – 3x2. Find the revenue function and average revenue function.
Solution:
The marginal Revenue function
R'(x) = 1500 – 4x – 3x²
Revenue function
R = ∫R'(x) dx
= ∫(1500 – 4x – 3x²) dx
R = 1500 x – 4(\(\frac { x^2 }{2}\)) – 3(\(\frac { x^3 }{3}\)) + k
R = 1500 x – 2x² – x³ + k
when x = 0; R = 0 ⇒ k = 0
∴ Revenue function
R = 1500 x – 2x² – x³
Average Revenue function A.R = \(\frac { R(x) }{x}\)
\(\frac { 1500x – 2x^2-x^3 }{x}\)
A.R = 1500 – 2x – x²
Question 16.
Find the revenue function and the demand function if the marginal revenue for x units is MR = 10 + 3x – x2
Solution:
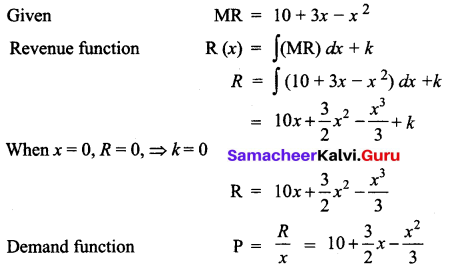
Question 17.
The marginal cost function of a commodity is given by MC = \(\frac{14000}{\sqrt{7 x+4}}\) and the fixed cost is ₹ 18,000. Find the total cost and average cost.
Solution:
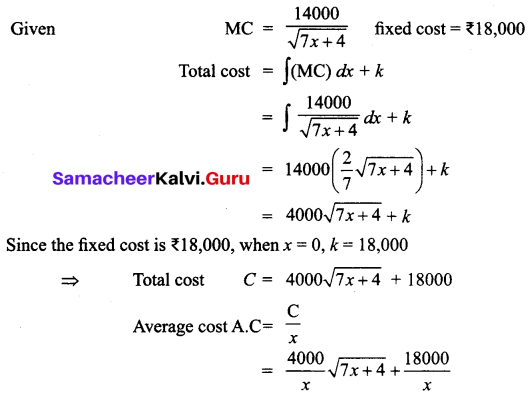
Question 18.
If the marginal cost (MC) of production of the company is directly proportional to the number of units (x) produced, then find the total cost function, when the fixed cost is ₹ 5,000 and the cost of producing 50 units is ₹ 5,625.
Solution:
Given that the marginal cost MC is directly proportional to the number of units x.
That is, MC ∝ x
MC = kx, where k is the constant of proportionality
Total cost C = ∫(MC) dx + c1
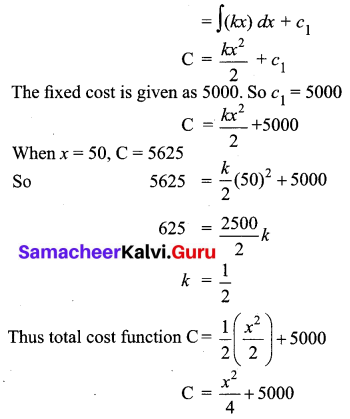
Question 19.
If MR = 20 – 5x + 3x2
Solution:
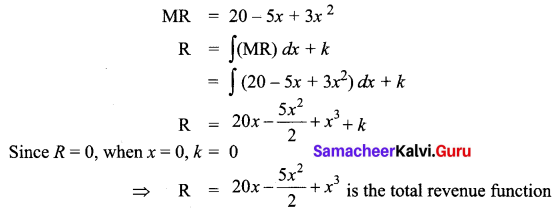
Question 20.
If MR = 14 – 6x + 9x2, find the demand function.
Solution:
MR = 14 – 6x + 9x²
Total Revenue function
R = ∫(MR) dx = ∫(14 – 6x + 9x²) dx
R = 14x – 6(\(\frac { x^2 }{2}\)) + 9(\(\frac { x^3 }{3}\)) + k
R = 14x – 3x² + 3x³ + k
when x = 0; R = 0 ⇒ k =
R = 14x – 3x² + 3x³ + k
⇒ px = 14x – 3x² + 3x³
p = \(\frac { 14x-3x^2+3x^3 }{x}\)
∴ The demand function
p = 14 – 3x + 3x²