Students can Download Economics Chapter 10 Rural Economy Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Solutions Chapter 10 Rural Economy
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Rural Economy Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part – A
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which is considered as the basic unit for rural areas?
(a) Panchayat
(b) Village
(c) Town
(d) Municipality
Answer:
(b) Village
Question 2.
Which feature is identified with rural areas?
(a) Low population density
(b) High population density
(c) Low natural resources
(d) Low human resources
Answer:
(a) Low population density
Question 3.
Identify the feature of rural economy.
(a) Dependence on agriculture
(b) High population density
(c) Low level of population
(d) Low level of inequality
Answer:
(a) Dependence on agriculture
![]()
Question 4.
What percentage of the total population live in rural area, as per 2011 censes?
(a) 40
(b) 50
(c) 68.84
(d) 70
Answer:
(c) 68.84
Question 5.
How do you term people employed in excess over and above the requirements?
(a) Unemployment
(b) Underemployment or Disguised Unemployment
(c) Full employment
(d) Self-employment
Answer:
(b) Underemployment or Disguised Unemployment
Question 6.
What is the term used to denote the coexistence of two different features in an economy?
(a) Technology
(b) Dependency
(c) Dualism
(d) Inequality
Answer:
(c) Dualism
Question 7.
The process of improving the rural areas, rural people and rural living is defined as
(a) Rural economy
(b) Rural economics
(c) Rural employment
(d) Rural development
Answer:
(d) Rural development
Question 8.
Identify the agriculture related problem of rural economy.
(a) Poor communication
(b) Small size of landholding
(c) Rural poverty
(d) Poor banking network
Answer:
(b) Small size of landholding
Question 9.
The recommended nutritional intake per person in rural areas.
(a) 2100 calories
(b) 2100 calories
(c) 2300 calories
(d) 2400 calories
Answer:
(d) 2400 calories
Question 10.
Indicate the cause for rural poverty.
(a) Lack of non-farm employment
(b) High employment
(c) Low inflation rate
(d) High investment.
Answer:
(a) Lack of non-farm employment
![]()
Question 11.
What is the other name for concealed unemployment?
(a) Open
(b) Disguised
(c) Seasonal
(d) Rural
Answer:
(b) Disguised
Question 12.
How do you term the employment occurring only on a particular season?
(a) Open
(b) Disguised
(c) Seasonal
(d) Rural
Answer:
(c) Seasonal
Question 13.
Identify an example for rural industries?
(a) Sugar factory
(b) Mat making industry
(c) Cement industry
(d) Paper industry
Answer:
(b) Mat making industry
Question 14.
How much share of rural families in India is in debt?
(a) Half
(b) One fourth
(c) Two third
(d) Three fourth
Answer:
(d) Three fourth
Question 15.
Identify the cause for rural indebtedness in India.
(a) Poverty
(b) High population
(c) High productivity
(d) Full employment
Answer:
(a) Poverty
Question 16.
In which year, Regional Rural Banks came into existence?
(a) 1965
(b) 1970
(c) 1975
(d) 1980
Answer:
(c) 1975
Question 17.
Identify the year of the launch of MUDRA Bank?
(a) 1995
(b) 2000
(c) 2010
(d) 2015
Answer:
(d) 2015
Question 18.
Identify the year in which National Rural Health Mission was launched.
(a) 2000
(b) 2005
(c) 2010
(d) 2015
Answer:
(b) 2005
Question 19.
Identify the advantages of rural roads.
(a) Rural marketing
(b) Rural employment
(c) Rural development
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
![]()
Question 20.
“An Indian farmer is born in debt, lives in debt, dies in debt, and bequeaths debt”- who said this?
(a) Adam Smith
(b) Gandhi
(c) Amartya Sen
(d) Sir Malcolm Darling
Answer:
(d) Sir Malcolm Darling
Part – B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences
Question 21.
Define Rural Economy.
Answer:
- Rural Economics deals with the application of economic principles in understanding and developing rural areas.
- Rural areas are geographical areas located outside towns and cities.
- Rural Economy refers to villages and rural community refers to people living in villages.
Question 22.
What do you mean by Rural Development?
Answer:
According to the world bank, “Rural development is a strategy designed to improve the economic and social life of a specific group of people rural poor”
![]()
Question 23.
Rural Poverty – Define.
Answer:
- Rural poverty refers to the existence of poverty in rural areas.
- Poverty in India has been defined as the situation in which an individual fails to earn sufficient income to buy the basic minimum of subsistence.
- On the basis of recommended nutritional intake, persons consuming less than 2400 calories per day in rural areas are treated as they are under rural poverty.
Question 24.
Define Open Unemployment.
Answer:
In open unemployment, unemployed persons are identified as they remain without work. This type of unemployment is found among agricultural labourers, rural artisans, and literate persons.
Question 25.
What is meant by Disguised Unemployment?
Answer:
Disguised unemployment is a situation where many are employed below their productive capacity and even if they are withdrawn from work the output will not diminish.
Question 26.
Define Cottage Industry.
Answer:
Cottage industries are generally associated with agriculture and provide both part-time and full-time jobs in rural areas.
Question 27.
What do you mean by Micro Finance?
Answer:
- Micro Finance is also known as microcredit is a financial service that offers loans, savings, and insurance to entrepreneurs and small business owners who do not have access to traditional sources of capital like banks or investors.
- The goal of micro-financing is to provide individuals with money to invest in themselves or their business.
- Microfinance is available through microfinance institutions, which range from small non-profit organizations to larger banks.
Question 28.
State any two causes of the housing problem in rural areas.
Answer:
- Rapid adaptation of nuclear families.
- Problems in the provision of proper water supply, good sanitation, proper disposal of sewage.
Question 29.
Define Rural Electrification.
Answer:
- Rural Electrification refers to providing electrical power to rural areas.
- The main aims of rural electrification are to provide electricity to agricultural operations and to enhance agricultural productivity.
- To increase cropped area, to promote rural industries, and to lighting the villages.
- In order to improve this facility, the supply of electricity is almost free for agricultural purposes in many states, and the electricity tariff is charged in rural areas is kept very low.
Question 30.
State any two factors hindering Rural Electrification in India.
Answer:
- Lack of funds
- Interstate disputes
- Uneven terrain
Part – C
Answer the following questions in One Paragraph
Question 31.
State the importance of Rural Development.
Answer:
Importance of Rural Development:
- A major share of the population lives in rural areas, and their development and contributions are very much supportive for nation-building activities. India cannot be developed by retaining rural as backward.
- The rural economy supports the urban sectors by way of supplying drinking water, milk, food, and raw materials. Hence, the backwardness of the rural sector would be a major impediment to the overall progress of the economy.
- Improvements in education, health, and sanitation in villages can help avoid many urban problems namely, begging, rag-picking and roadside slumming.
- The development of agriculture and allied activities are necessary for providing gainful employment in rural areas and improving overall food production.
![]()
Question 32.
Explain the causes for Rural Backwardness.
Answer:
- The skewed distribution of land.
- Lack of non-farm employment.
- Lack of public sector investment.
- Inflation.
- Low productivity.
- The unequal benefit of growth.
- Low rate of economic growth.
- More emphasis on large industries.
- Social evils.
Question 33.
Enumerate the remedial measures to Rural Poverty.
Answer:
Remedial measures:
- Since rural unemployment and rural poverty are interrelated, the creation of employment opportunities would support the elimination of poverty.
- Poverty alleviation schemes and programmes have been implemented, modified, consolidated, expanded, and improved over time.
- However, unemployment, begging, rag-picking, and slumming continues.
- Unless employment is given to all the people poverty cannot be eliminated.
Question 34.
What are the remedial measures for Rural Unemployment?
Answer:
- Subsidiary occupation: To reduce seasonal unemployment rural people should be encouraged to adopt subsidiary occupation.
- Rural works programme: Rural works programme should be planned during the offseason to provide gainful employment.
- Irrigation facilities: Irrigation facilities should be expanded to enable the farmers to adopt multiple cropping.
- Rural industrialization: New industries should be set up in rural areas.
- Technical education: Employment oriented courses should be introduced to literate the youth to start their own units.
![]()
Question 35.
Write a note on Regional Rural Banks.
Answer:
- Regional Rural Banks came into existence based on the recommendation made by a working group on rural banks appointed by the Government of India in 1975.
- RRBs are recommended with a view to developing the rural economy by providing credit and other facilities particularly to the small and marginal farmers, agricultural labourers, artisans, and small entrepreneurs.
- RRBs are set up by the joint efforts of the Centre and State Governments and commercial banks.
- At present, there are 64 Regional Rural Banks in India.
- The RRBs confine their lendings only to the weaker sections and their lending rates are at par with the prevailing rate of co-operative societies.
Question 36.
Mention the features of SHGs.
Answer:
- SHG is an economically homogeneous group formed through a process of self-selection based upon the affinity of its members.
- Most SHGs are women’s groups with membership ranging between 10 and 20.
- SHGs have well-defined rules and by-laws, hold regular, meetings and maintain records and savings and credit discipline.
- SHGs are self-managed institutions characterized by participatory and collective decision making.
Question 37.
List out the objectives of MUDRA Bank.
Answer:
- Regulate the lender and the borrower of microfinance and bring stability to the microfinance system.
- Extend finance and credit support to Microfinance Institutions [MFI] and agencies that lend money to small businesses, retailers, self-help groups, and individuals.
- Register all MFIs and introduce a system of performance rating and accreditation for the first time.
- Offer a Credit Guarantee scheme for providing guarantees to loans being offered to micro-businesses.
- Introduce appropriate technologies to assist in the process of efficient lending, borrowing, and monitoring of distributed capital.
Part – D
Answer the following questions in about a page
Question 38.
‘The features of Rural Economy are peculiar’- Argue.
Answer:
The Rural economy has very peculiar features which are :
- The village is an institution: The village is a primary institution and it satisfies almost all the needs of the rural community.
- Dependence on agriculture : Agriculture and allied activities are the main occupations in rural areas.
- Life of rural people: Life styles in villages are very simple. Public services like education, housing, health and sanitation, transport and communication, banking, roads and markets are limited and unavailable.
- Population density : Density of population is very low and houses are scattered in the entire villages.
- Employment: There exists unemployment, seasonal unemployment and underemployment in rural areas.
- Poverty: According to the 2011 – 12 estimates about 22 crores of people in rural areas live below the poverty line.
- Indebtedness: Sir Malcolm Darling stated that an Indian farmer is born in debt, lives in debt, dies in debt and bequeaths debt.
- Rural income: As the rural economy is not sufficiently vibrant to provide them with jobs or self-employment opportunities the income of the rural people is constrained.
- Dependency: Rural households are dependent on social grants and remittances from family members working in urban areas and cities.
- Dualism: Dualism means the co-existence of two extremely different features which is the common characteristics in a rural area.
- Inequality: The distribution of income, wealth, and assets are highly skewed among rural people.
- Migration: Rural people are forced to migrate to urban areas to seek employment which gives rise to the formation of cities. Enmity and lack of basic amenities in rural areas also push the people to migrate. This is called double poisoning by Schumacher.
Question 39.
Discuss the problems of the Rural Economy.
Answer:
Rural areas are facing a number of problems relating to,
- People
- Agriculture
- Infrastructure
- Economy
- Society and Culture
- Leadership and
- Administration.
The problems of the rural economy are discussed below.
1. People Related Problems:
The problems related to individuals and their standard of living consist of illiteracy, lack of technical know-how, low level of confidence, dependence on sentiments and beliefs, etc.
2. Agriculture Related Problems:
The problems related to agriculture include as follows,
- Lack of expected awareness, knowledge, skill, and attitude.
- Unavailability of inputs.
- Poor marketing facility.
3. Infrastructural Related problems:
Poor infrastructure facilities like, water, electricity, transport, educational institutions, communication, health, employment, storage facility, banking, and insurance are found in rural areas.
4. Economics related problems:
The economic problems related to rural areas are,
- Inability to adopt high-cost technology.
- The high cost of inputs.
- Underprivileged rural industries.
- Low income
- Indebtedness
- Existence of inequality in landholdings and assets.
5. Leadership Related Problems:
The Specific leadership-related problems found in rural areas are,
- Leadership among the hands of inactive and incompetent people
- Self-interest of leaders
- Biased political will
- Less bargaining power
- Negation skills and dominance of political leaders
6. Administrative Problems:
The rural administrative problems consist of
- Political interference
- Lack of motivation and interest
- Low wages in villages
- Improper utilization of budget
- Absence of monitoring
- Implementation of the rural development programme.
Question 40.
Analyze the causes for Rural Indebtedness.
Answer:
1. Poverty of farmers: The vicious circle of poverty fore es the farmers to borrow for consumption, cultivation, and celebrations. Thus, poverty’s debt and high rates of interest hold the farmer in the grip of money lenders.
2. Failure of monsoon: Frequent failure of monsoon is a curse to the farmers and they have to suffer due to the failure of nature. Therefore, farmers find it difficult to identify good years to repay their debts.
3. Litigation: Due to land disputes litigation in the court compels them to borrow heavily. Being uneducated and ignorant they are caught in the litigation process and dry away their savings and resources.
4. Moneylenders and high rate of interest: The rate of interest charged by the local money lenders is very high and the compounding of interest leads to perpetuating indebtedness of the farmer.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Rural Economy Additional Questions and Answers
Part-A
Choose the best options
Question 1.
According to the 2011 population census, there are ___________ villages in India.
(a) 6,40,867
(b) 3,40,867
(c) 4,40,867
(d) 5,40,867
Answer:
(a) 6,40,867
![]()
Question 2.
Of 121 crore total population ___________ percent lives in rural areas.
(a) 64.88
(b) 68.84
(c) 68.48
(d) 88.64
Answer:
(b) 68.84
Question 3.
___________ are geographical areas located outside towns and cities.
(a) Townships
(b) Corporations
(c) Rural areas
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Rural areas
Question 4.
Total percentage of poverty in 2009-2010
(a) 33.80
(b) 38.30
(c) 33.08
(d) 80.33
Answer:
(a) 33.80
Question 5.
In 2009, the total number of micro finance institutions in India was around ___________
(a) 140
(b) 150
(c) 160
(d) 170
Answer:
(b) 150
Question 6.
SHG Bank Linked Programme (SBLP) was started in ___________
(a) 1991
(b) 1990
(c) 1992
(d) 1993
Answer:
(c) 1992
Question 7.
Micro Units Development and Refinance Agency is ___________
(a) IRDB
(b) MUDRA
(c) BUNDAN
(d) ICICI
Answer:
(b) MUDRA
Question 8.
MUDRA Bank was started in the year ___________
(a) 2011
(b) 2012
(c) 2015
(d) 2013
Answer:
(c) 2015
![]()
Question 9.
___________ was the first professor of economics at Madras University
(a) Gilbert Slater
(b) Samuelson
(c) Marshall
(d) Manmohan Singh
Answer:
(a) Gilbert Slater
Question 10.
National Rural Health Mission was launched on ___________
(a) 2001
(b) 1991
(c) 2005
(d) 2000
Answer:
(c) 2005
Question 11.
___________ are set up with a view to developing the rural economy by providing credit and other facilities to small and marginal farmers.
(a) MUDRA Bank
(b) RRB
(c) SHG
(d) NABARD
Answer:
(b) RRB
Match the following and choose the answer using the codes given below
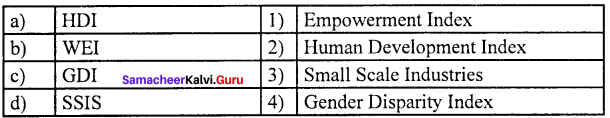
Question 1.
(a) 1 2 3 4
(b) 2 1 3 4
(c) 4 3 2 1
(d) 3 4 1 2
Answer:
(b) 2 1 3 4
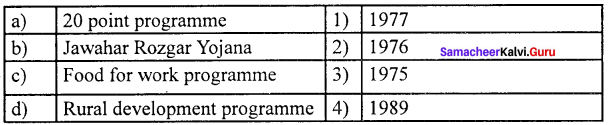
Question 2.
(a) 4 3 2 1
(b) 2 1 4 3
(c) 3 4 1 2
(d) 1 2 3 4
Answer:
(c) 3 4 1 2
Choose the correct option
Question 3.
The national rural health mission was established in
(a) March 12, 2005
(b) June 12, 2005
(c) April 12, 2005
(d) June 13, 2005
Answer:
(c) April 12, 2005
![]()
Question 4.
The gross national happiness index is
(a) GDP
(b) HDF
(c) WEI
(d) GNHI
Answer:
(d) GNHI
Question 5.
The poverty line is calculated on the basis of
(a) Based on inflation
(b) Based on poverty
(c) Based on income or consumption
(d) Based on unemployment
Answer:
(c) Based on income or consumption
Fill in the blanks with the suitable option given below
Question 6.
Microcredit is also known as
(a) Microfinance
(b) Small finance
(c) Large finance
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Microfinance
Question 7.
The co-existence of two extremely different features is called as
(a) Unity
(b) Dualism
(c) Trism
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Dualism
Question 8.
The first economics professor of madras university was
(a) A.K. Sen
(b) Charan Singh
(c) Manmohan Singh
(d) Gilbert Slater
Answer:
(d) Gilbert Slater
Choose the incorrect statement
Question 9.
(a) Physical quality of life index is PQLI
(b) The existence of poverty in rural areas is called rural poverty
(c) SSI s are also known as micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs)
(d) Petter diamond was the first economics professor of madras university
Answer:
(d) Petter diamond was the first economics professor of madras university
Question 10.
(a) MUDRA is micro units development and Refinance Agency Bank
(b) NRHM is National Rural Health Mission.
(c) The length of roads in India as of 2018 is 24 lakh kms.
(d) PURA is the provision of urban facilities for rural areas.
Answer:
(c) The length of roads in India as of 2018 is 24 lakh kms.
Choose the incorrect pair
Question 11.
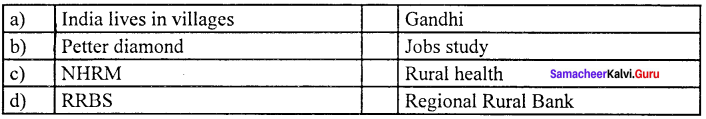
Answer:
(c) NHRM (iii) Rural health
Question 12.
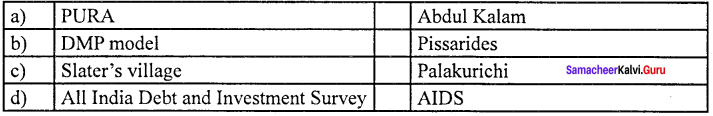
Answer:
(d) All Indian Debt and Investment Survey (iv) AIDS
Question 13.
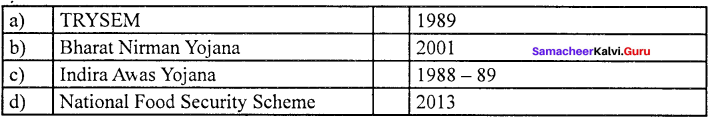
Answer:
(d) National Food Security (iv) 2013
![]()
Question 14.
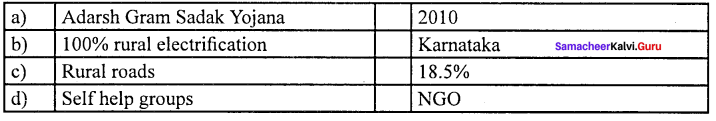
Answer:
(a) Adarsh Gram Sadak Yojana (i) 2010
Choose the correct statement
Question 15.
(a) Unemployment is a situation in which a person who is unwilling to work employed,
(b) According to 2011 12 estimates 42 crore village population list below the poverty line.
(c) In 2015, 60 crore people lived in villages.
(d) Sir Malcolm Darling stated that ‘An Indian farmer is a bom in debt, lives in debt, dies in debt and bequeaths debt’
Answer:
(d) Sir Malcolm Darling stated that ‘An Indian farmer is a bom in debt, lives in debt, dies in debt and bequeaths debt’
Question 16.
(a) Number of people living per sq. km is called population scarcity.
(b) There are 5,40,867 villages in India.
(c) The concept of ‘Double poisoning’ was coined by Schumacher.
(d) In 2009-10, the total percentage of poverty in India is 54.10
Answer:
(c) The concept of ‘Double poisoning’ was coined by Schumacher.
Pick the odd one out
Question 17.
(a) Petter Diamond
(b) A.K.Sen
(c) Dale Mortensen
(d) Christopher Pissarides
Answer:
(b) A.K.Sen
Question 18.
(a) NCC
(b) IRDP
(c) TRYSEM
(d) MGNREGS
Answer:
(a) NCC
Analyze the reason for the following
Question 19.
Assertion (A) : Creation of employment opportunities eliminate poverty in rural areas.
Reason (R) : Rural unemployment and rural poverty are interrelated.
(a) (A) is true; but (R) is false
(b) Both (A) and (R) are false
(c) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(d) Both (A) and (R) are true (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
Answer:
(d) Both (A) and (R) are true (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
Question 20.
Assertion (A) : Agricultural operations are seasonal in nature.
Reason (R) : To reduce seasonal unemployment rural people should be encouraged to adopt subsidiary occupations.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(c) Both (A) and (R) are false.
(d) (A) is false but (R) is true.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Part – B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences
Question 1.
Name some of the economic indicators?
Answer:
Human Development Index (HDI), Women Empowerment Index (WEI), Gender Disparity Index (GDI), Physical Quality of Life Index (PQLI), and Gross National Happiness Index (GNHI).
Question 2.
How can you measure poverty by nutritional index?
Answer:
On the basis of recommended nutritional intake, persons consuming less than 2400 calories per day is rural areas are considered as rural poor.
![]()
Question 3.
What is unemployment?
Answer:
Unemployment is a situation in which a person actively searching for employment but unable to find work at the prevailing wage rate.
Question 4.
Write a note on seasonal unemployment?
Answer:
In seasonal unemployment, employment occurs only in a particular season and workers remain unemployed in the remaining period of a year.
Question 5.
Write a note on NRHM.
Answer:
The National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) was launched on 12th April 2005, to provide accessible, affordable and quality health care to the vulnerable groups in rural areas.
Question 6.
What is population density?
Answer:
Population density is the number of persons living per square kilometer.
Part – C
Answer the following questions in One Paragraph
Question 1.
What are the types of rural unemployment?
Answer:
- Open unemployment: Unemployed persons are identified as they remain without work.
- Concealed unemployment: Many are employed below their productive capacity and even if they are withdrawn from work the output will not diminish. It is also called disguised unemployment or underemployment.
- Seasonal unemployment: Employment occurs only during a particular season and the remaining period of a year the rural people are unemployed or partially employed.
Question 2.
Explain about village industries.
Answer:
Village industries are traditional in nature and depend on the local raw material. They cater to the needs of the local population.
(Eg.) Gur and Khandsari, Cane and Bamboo basket, Shoemaking, Pottery, and Leather tanning.
Question 3.
Write a note on rural indebtedness.
Answer:
Rural indebtedness refers to the situation of the rural people who are unable to repay the loan accumulated over a period. Existence of the rural indebtedness indicates the weak financial infrastructure of our country in reaching the needy farmer’s landless people and agricultural labourers.
![]()
Question 4.
Write a note on rural roads.
Answer:
Rural roads constitute the very lifeline of the rural economy. A well-constructed road network in rural areas would bring several benefits including the linking of remote villages with urban centres, reduction in the cost of transportation of agricultural inputs, and promotion of marketing for rural produces.
Part – D
Answer the following questions in about a page
Question 1.
Explain the causes for rural unemployment.
Answer:
1. Absence of skill development and employment generation: Lack of Government initiatives to give required training and then to generate employment opportunities.
2. Seasonal nature of agriculture: Agricultural operations are seasonal in nature, so non-farm employment opportunities must be created to reduce seasonal unemployment.
3. Lack of subsidiary occupation: Rural people are not able to start subsidiary occupations due to shortages of funds for investment and lack of proper marketing arrangements.
4. Mechanization of agriculture: Mechanization of agricultural operations reduces employment opportunities for farm labour.
5. Capital – Intensive technology: The expanding private industrial sector in urban areas do not create additional employment opportunities due to the application of capital intensive technologies.
6. Defective system of education: The present system of education has also aggravated the rural unemployment problem. Students want to get degrees only, not any skill. Degrees should be awarded only on the basis of skills acquired.