Students can Download Computer Science Chapter 17 Computer Ethics and Cyber Security Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Solutions Chapter 17 Computer Ethics and Cyber Security
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Computer Ethics and Cyber Security Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – 1
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
Which of the following deals with procedures, practices and values?
(a) piracy
(b) programs
(c) virus
(d) computer ethics
Answer:
(d) computer ethics
Question 2.
Commercial programs made available to the public illegally are known as ……………….
(a) freeware
(b) warez
(c) free software
(d) software
Answer:
(b) warez
![]()
Question 3.
Which one of the following are self – repeating and do not require a computer program to attach themselves?
(a) viruses
(b) worms
(c) spyware
(d) Trojans
Answer:
(b) worms
Question 4.
Which one of the following tracks a user visiting a website?
(a) spyware
(b) cookies
(c) worms
(d) Trojans
Answer:
(b) cookies
Question 5.
Which of the following is not a malicious program on computer systems?
(a) worms
(b) Trojans
(c) spyware
(d) cookies
Answer:
(d) cookies
Question 6.
A computer network security that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic is ……………….
(a) cookies
(b) virus
(c) firewall
(d) worms
Answer:
(c) firewall
Question 7.
The process of converting cipher text to plain text is called ……………….
(a) Encryption
(b) Decryption
(c) key
(d) proxy server
Answer:
(b) Decryption
Question 8.
e – commerce means ……………….
(a) electronic commerce
(b) electronic data exchange
(c) electric data exchange
(d) electronic commercialization
Answer:
(a) electronic commerce
Question 9.
Distributing unwanted e-mail to others is called.
(a) scam
(b) spam
(c) fraud
(d) spoofing
Answer:
(b) spam
![]()
Question 10.
Legal recognition for transactions are carried out by ……………….
(a) Electronic Data Interchange
(b) Electronic Data Exchange
(c) Electronic Data Transfer
(d) Electrical Data Interchange
Answer:
(a) Electronic Data Interchange
PART – 2
II. Answers to all the questions
Question 1.
What is harvesting?
Answer:
A person or program collects login and password information from a legitimate user to illegally gain access to others account(s).
Question 2.
What are Warez?
Answer:
Shareware publishers encourage users to give copies of programs to friends and colleagues but ask everyone who uses that program regularly to pay a registration fee to the program’s author directly. Commercial programs that are made available to the public illegally are often called warez.
Question 3.
Write a short note on cracking.
Answer:
Cracking is where someone edits a program source so that the code can be exploited or modified. “Cracking” means trying to get into computer systems in order to steal, corrupt, or illegitimately view data.
Question 4.
Write two types of cyber attacks.
Answer:
Cyber Attack:
- Virus
- Worms
Function:
- A virus is a small piece of computer code that can repeat itself and spreads from one computer to another by attaching itself to another computer file. One of the most common virus is Trojan.
- Worms are self – repeating and do not require a computer program to attach themselves. Worms continually look for vulnerabilities and report back to the author of the worm when weaknesses are discovered.
Question 5.
What is a Cookie?
Answer:
A cookie (also called HTTP cookie, web cookie, Internet cookie, browser cookie, or simply cookie) is a small piece of data sent from a website and stored on the user’s computer memory (Hard drive) by the user’s web browser while the user is browsing internet.
PART – 3
III. Answers to all the questions
Question 1.
What is the role of firewalls?
Answer:
A firewall is a computer network security based system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules. A firewall commonly establishes a block between a trusted internal computer network and entrusted computer outside the network. They are generally categorized as network – based or host – based. Network based firewalls are positioned on the gateway computers of LANs [local area Network], WANs [Wide Area Network] and intranets.
![]()
Question 2.
Write about encryption and decryption.
Answer:
Encryption and decryption are processes that ensure confidentiality that only authorized persons can access the information. Encryption is the process of translating the plain text data (plaintext) into random and mangled data (called cipher – text). Decryption is the reverse process of converting the cipher – text back to plaintext. Encryption and decryption are done by cryptography. In cryptography a key is a piece of information (parameter) that determines the functional output of a cryptographic algorithm.
Question 3.
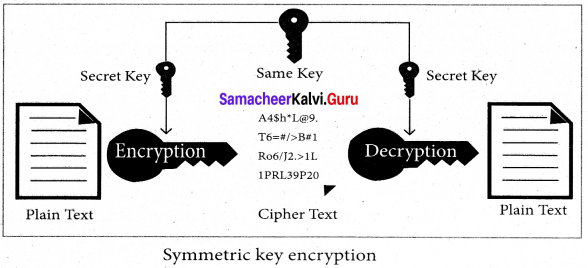
Explain symmetric key encryption.
Answer:
Symmetric encryption is a technique to use the same key for both encryption and decryption. The main disadvantage of the symmetric key encryption is that all authorized persons involved, have to exchange the key used to encrypt the data before they can decrypt it. If anybody intercepts the key information, they may read all messages.
Question 4.
What are the guidelines to be followed by any computer user?
Answer:
Generally, the following guidelines should be observed by computer users:
- Honesty : Users should be truthful while using the internet.
- Confidentiality : Users should not share any important information with unauthorized people.
- Respect : Each user should respect the privacy of other users.
- Professionalism : Each user should maintain professional conduct.
- Obey The Law : Users should strictly obey the cyber law in computer usage.
- Responsibility : Each user should take ownership and responsibility for their actions.
Question 5.
What are ethical issues? Name some.
Answer:
An Ethical issue is a problem or issue that requires a person or organization to choose between alternatives that must be evaluated as right (ethical) or wrong (unethical). These issues must be addressed and resolved to have a positive influence in society.
Some of the common ethical issues are listed below:
- Cyber crime
- Software Piracy
- Unauthorized Access
- Hacking
- Use of computers to commit fraud.
- Sabotage in the form of viruses.
PART – 4
IV. Answers to all the questions
Question 1.
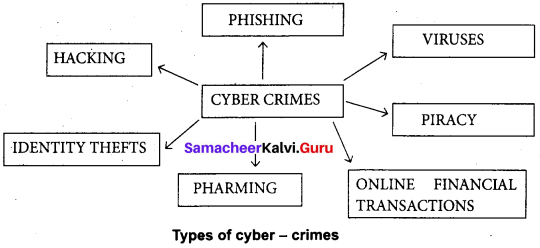
What are the various crimes happening using computer?
Answer:
Crime:
- Crime Function
- Cyber stalking
- Malware
- Harvesting
- Identity theft
- Intellectual property theft
- Salami slicing
Function:
- Hacking, threats, and blackmailing towards a business or a person.
- Harassing through online.
- Malicious programs that can perform a variety of functions including stealing, encrypting or deleting sensitive data, altering or hijacking core computing functions and monitoring user’s computer activity without their permission.
- A person or program collects login and password information from a legitimate user to illegally gain access to others’ account(s).
- It is a crime where the criminals impersonate individuals, usually for financial gain.
- Stealing practical or conceptual information developed by another person or company.
- Stealing tiny amounts of money from each transaction.
![]()
Question 2.
What is piracy? Mention the types of piracy? How can it be prevented?
Answer:
Software Piracy is about the copyright violation of software created originally by an individual or an institution. It includes:
1. stealing of codes / programs and other information illegally and creating duplicate copies by unauthorized means and utilizing this data either for one’s own benefit or for commercial profit.
2. Downloading software from illegal network sources.
An entirely different approach to software piracy is called shareware, acknowledges the futility of trying to stop people from copying software and instead relies on people’s honesty.
Shareware publishers encourage users to give copies of programs to friends and colleagues but ask everyone who uses that program regularly to pay a registration fee to the program’s author directly. To prevent unauthorized access, Firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), Virus and Content Scanners, Patches and Hot fixes are used.
Question 3.
Write the different types of cyber attacks.
Answer:
Cyber Attack:
- Virus
- Worms
- Spyware
- Ransomware
Function:
- A virus is a small piece of computer code that can repeat itself and spreads from one computer to another by attaching itself to another computer file. One of the most common virus is Trojan.
- Worms are self – repeating and do not require a computer program to attach themselves. Worms continually look for vulnerabilities and report back to the author of the worm when weaknesses are discovered.
- Spyware can be installed on the computer automatically when the attachments are open, by clicking on links or by downloading infected software.
- Ransomware is a type of malicious program that demands payment after launching a cyber – attack on a computer system. This type of malware has become increasingly popular among criminals and costs the organizations millions each year.
Samacheer kalvi 11th Computer Science Computer Ethics and Cyber Security Additional Questions and Answers
PART – 1
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
A moral code that is evaluated as right is ………………..
(a) piracy
(b) viruses
(c) cracking
(d) ethics
Answer:
(d) ethics
Question 2.
……………….. is a crime where the criminals impersonate individuals for financial gain.
(a) intellectual property theft
(b) Identity theft
(c) Salami slicing
(d) Spoofing
Answer:
(b) Identity theft
Question 3.
Stealing data from a computer system without the knowledge or permission is called ………………..
(a) warez
(b) hacking
(c) cracking
(d) phishing
Answer:
(b) hacking
![]()
Question 4.
One of the most common virus is ………………..
(a) Ransomware
(b) Spyware
(c) worms
(d) Trojan
Answer:
(d) Trojan
Question 5.
……………….. is the intermediary between the end users and a web browser.
(a) Firewall
(b) Proxy server
(c) Cookies
(d) Warez
Answer:
(b) Proxy server
PART – 2
II. Short Answers
Question 1.
What is hacking?
Answer:
Hacking is intruding into a computer system to steal personal data without the owner’s permission or knowledge (like to steal a password). It is also gaining unauthorized access to a computer system, and altering its contents.
Question 2.
What is proxy server? Explain its working.
Answer:
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between the end users and a web server. A client connects to the proxy server, requesting some service, such as a file, connection, web page, or other resources available from a different server. The proxy server examines the request, checks authenticity and grants the request based on that. Proxy servers typically keep the frequently visited site addresses in its cache which leads to improved response time.
![]()
Question 3.
Mention any 2 reasons as to why the websites use cookies?
Answer:
- To collect demographic information about who has visited the Web site.
- It helps to personalize the user’s experience on the Website.
Question 4.
What is meant by MITM?
Answer:
Man – in – the – middle attack (MITM; also Janus attack) is an attack where the attacker secretly relays and possibly alters the communication between two parties who believe they are directly communicating with each other.
Question 5.
Define software piracy.
Answer:
Software Piracy is about the copyright violation of software created originally by an individual or an institution. It includes stealing of codes / programs and other information illegally and creating duplicate copies by unauthorized means and utilizing this data either for one’s own benefit or for commercial profit.
PART – 3
III. Short Answers
Question 1.
What is cyber crime?
Answer:
A cyber – crime is a crime which involves computer and network. This is becoming a growing threat to society and is caused by criminals or irresponsible action of individuals who are exploiting the widespread use of Internet. It presents a major challenge to the ethical use. of information technologies. Cyber – crime also poses threats to the integrity, safety and survival of most business systems.
Question 2.
Write a short note on ethics.
Answer:
Ethics means “What is wrong and What is Right”. It is a set of moral principles that rule the behavior of individuals who use computers. An individual gains knowledge to follow the right behavior, using morals that are also known as ethics. Morals refer to the generally accepted standards of right and wrong in the society. Similarly, in cyber – world, there are certain standards such as
- Do not use pirated software.
- Do not use unauthorized user accounts.
- Do not steal others’ passwords.
- Do not hack.
![]()
Question 3.
Differentiate Spyware and Ransomware.
Answer:
Spyware:
Spyware can be installed on the computer automatically when the attachments are open, by clicking on links or by downloading infected software.
Ransomware:
Ransomware is a type of malicious program that demands payment after launching a cyber-attack on a computer system. This type of malware has become increasingly popular among criminals and costs the organizations millions each year.
Question 4.
What are the types of encryption?
Answer:
There are two types of encryption schemes as listed below:
1. Symmetric Key encryption : Symmetric encryption is a technique to use the same key for both encryption and decryption.
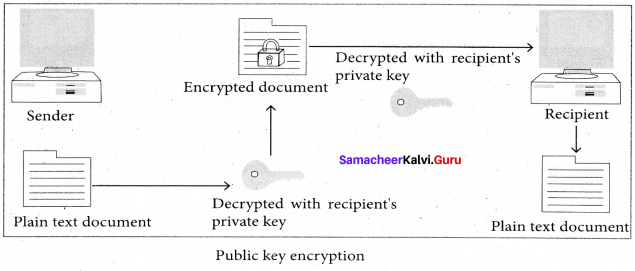
2. Public Key encryption : Public key encryption is also called Asymmetric encryption. It uses the concept of a key value pair, a different key is used for the encryption and decryption
Question 5.
Write down the points to be noted to be safe from cyber crime.
Answer:
To protect the information the following points to be noted:
- Complex password setting can make your surfing secured.
- When the internet is not in use, disconnect it.
- Do NOT open spam mail or emails that have an unfamiliar sender.
- When using anti – virus software, keep it up – to – date.
PART – 4
IV. Explain in Detail
Question 1.
Explain public key encryption and asymetric encryption in digital certificate.
Answer:
Public key encryption is also called Asymmetric encryption. It uses the concept of a key value pair, a different key is used for the encryption and decryption process. One of the keys is typically known as the private key and the other is known as the public key. The private key is kept secret by the owner and the public key is either shared amongst authorized recipients or made available to the public at large.
The data encrypted with the recipient’s public key can only be decrypted with the corresponding private key. A digital certificate in a client – server model of communication is one of the example of Asymmetric Encryption. A certificate is a package of information that identifies a user and a server.
It contains information such as an organization’s name, the organization that issued the certificate, the users’ email address and country, and user’s public key. When a server and a client require a secure encrypted communication, they send a query over . the network to the other party, which sends back a copy of the certificate. The other party’s public key can be extracted from the certificate. A certificate can also be used to uniquely identify the holder.
![]()
Question 2.
Write short notes on:
- Spam
- Fraud
- Cyber stalking
- Spoofing
- Virus
- Worms
Answer:
- Spam : Distribute unwanted e – mail to a large number of internet users.
- Fraud : Manipulating data, for example changing the banking records to transfer money to an unauthorized account.
- Cyber stalking : Harassing through online.
- Spoofing : It is a malicious practice in which communication is send from unknown source disguised as a source known to the receiver.
- Virus : A virus is a small piece of computer code that can repeat itself and spreads from one computer to another by attaching itself to another computer file. One of the most common virus is Trojan.
- Worms : Worms are self – repeating and do not require a computer program to attach themselves. Worms continually look for vulnerabilities and report back to the author of the worm when weaknesses are discovered.
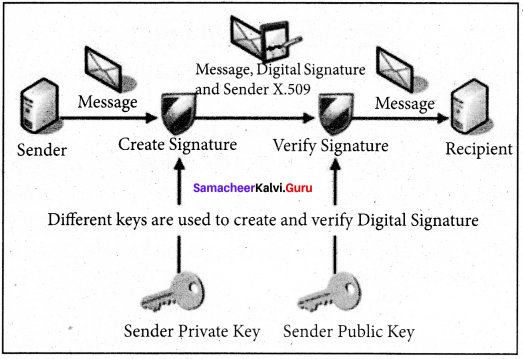
Question 3.
Explain digital signature with a functional diagram.
Answer:
Digital signatures are based on asymmetric cryptography and can provide assurances of evidence to origin, identity and status of an electronic document, transaction or message, as well as acknowledging information given by the signer. To create a digital signature, signing software (email) creates a one – way hash of the electronic data to be signed.
The user’s private key to encrypt the hash, returning a value that is unique to the hashed data. The encrypted hash, along with other information such as the hashing algorithm, forms the digital signature. Any change in the data, even to a single bit, results in a different hash value. This attribute enables others to validate the integrity of the data by using the signer’s public key to decrypt the hash.
If the decrypted hash matches a second computed hash of the same data, it proves that the data hasn’t changed since it was signed. If the two hashes don’t match, the data has either been tampered with in some way (indicating a failure of integrity) or the signature was created with a private key that doesn’t correspond to the public key presented by the signer (indicating a failure of authentication).