Students can Download Commerce Chapter 5 Hindu Undivided Family and Partnership Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Solutions Chapter 5 Hindu Undivided Family and Partnership
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Hindu Undivided Family and Partnership Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
The firm of Hindu Undivided Family is managed by whom?
(a) Owner
(b) Karta
(c) Manager
(d) Partner
Answer:
(b) Karta
Question 2.
In the firm of Hindu Undivided Family, how one gets the membership?
(a) By Agreement
(b) By Birth
(c) By Investing Capital
(d) By Managing
Answer:
(b) By Birth
Question 3.
The members in the joint Hindu family are known as ………………..
(a) Karta
(b) Coparceners
(c) Generations
(d) Partners
Answer:
(b) Coparceners
![]()
Question 4.
Only the male members in the family get the right of inheritance by birth as ………………..
(a) Hindu law
(b) Mitakshara Law
(c) Dayabhaga law
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Mitakshara Law
Question 5.
partnership is formed by ………………..
(a) Agreement
(b) relationship among partners
(c) The direction of government
(d) Friendship
Answer:
(a) Agreement
Question 6.
Registration of partnership is ………………..
(a) Compulsory
(b) Optional
(c) Not necessary
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Optional
Question 7.
A temporary partnership which is formed to complete a specific job doing a specified period of time is called ………………..
(a) Partnership – at – will
(b) Particular partnership
(c) Limited Partnership
(d) Joint Venture
Answer:
(d) Joint Venture
![]()
Question 8.
The partnership deed is also called ………………..
(a) Articles of Association
(b) Articles of Partnership
(c) Partnership Act
(d) Partnership
Answer:
(b) Articles of Partnership
Question 9.
A partnership is registered with ………………..
(a) Registrar of Companies
(b) Registrar of Co – operatives
(c) Registrar of Firms
(d) District Collector
Answer:
(c) Registrar of Firms
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Who is called KARTA?
Answer:
The head of the Joint Hindu Family whose liabilities are unlimited is known as KARTA. Karta is the senior-most male member of the family.
Question 2.
What are the two schools of Hindu law?
Answer:
- Dayabhaga and
- Mitakshara
Question 3.
Who is called a Partner?
Answer:
A Partner is an owner and member in a partnership business, an entity in which both the profits and losses of a business or other venture are shared between all members.
Question 4.
Who is a Sleeping partner?
Answer:
Such a partner contributes capital and shares in the profits or losses of the firm but does not take part in the management of the business.
![]()
Question 5.
Who is a Minor?
Answer:
Under the Indian Majority Act, the person who has not completed 18 years of age is a minor. He will be continued to be a minor till he completes 21 years if a guardian has been appointed to the minor.
Question 6.
How many types of Dissolution?
Answer:
- Without order of court.
- By order of court.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is the meaning of Joint Hindu Family Business?
Answer:
There are two types of dissolution that arise in partnership, namely Dissolution of Partnership and Dissolution of Firm.
Question 2.
Write any 3 features of HUF?
Answer:
- Governed by Hindu Law: The business of the Joint Hindu Family is controlled and managed under the Hindu law.
- Membership by Birth: The membership of the family can be acquired only by birth. As soon as a male child is born in the family, that child becomes a member.
- Liability: Except the Karta, the liability of all other members is limited to their shares in the business.
Question 3.
Explain the nature of the liability of Karta.
Answer:
In a joint family firm only Karta has the implied authority to enter into a contract for debts and pledge the property of the firm for the ordinary purpose of the businesses of the firm.
![]()
Question 4.
What is the meaning of Coparceners?
Answer:
The members of the Joint Hindu Family business are called Coparceners. It is regulated by the provisions of Hindu Law. According to Hindu Succession Act, 1956, a Coparcener will have a share in the Coparcenaries property after the death of the Co – parcener.
Question 5.
Define Partnership?
Answer:
According to Prof. Haney, “The relations which exist between persons, competent to make contracts, who agree to carry on a lawful business in common with a view to private gain”.
Question 6.
What are the minimum and a maximum number of members in the partnership concern?
Answer:
Since partnership is the outcome of an agreement, the minimum number of persons required to form a partnership is two. Maximum is restricted to 10 in the case of banking business and to 20 in all other cases.
Question 7.
What is the meaning of Partnership Deed?
Answer:
A partnership Deed is an agreement that contains the terms and conditions relating to the partnership.
It defines the rights, Interests, and obligations of partners. It should be properly signed by all the partners and stamped.
Question 8.
Who is called a Secret partner?
Answer:
A secret partner is one whose association is not known to the general public. Other than this distinct feature, he is like rest of the partners in all respects.
Question 9.
What is meant by Joint and Several Liability?
Answer:
Every partner is jointly and severally liable for all acts of the firm. It means that in case the assets are inadequate for meeting the claims of creditors, even their personal properties should be made available. The creditors can recover their claims from all the partners.
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is the implied authority of Karta?
Answer:
1. In a joint family firm, only Karta has the implied authority to enter into a contract for debts and pledge the property of the firm for the ordinary purpose of the business of the firm.
2. The Karta is the senior most male member of the family. The members of the family have full faith and confidence in Karta. Only Karta is entitled to deal with outsiders. But other members can deal with outsiders only with the permission of Karta.
3. Except the Karta, the liability of all other members is limited to their shares in the business. The Karta is not only liable to the extent of his share in the business but his separate property is equally attachable and amount of debt can be recovered from his personal property.
Question 2.
Can a minor be admitted in the Joint Hindu Family business – Why?
Answer:
Yes. A minor can be admitted as a co-parcener in Hindu Family. Because when a baby borns in the family, he/she automatically acquires an interest in the property jointly held by the family. According to Hindu Succession Act, 2005 is applicable to all male and female members of a Hindu undivided family.
Question 3.
What are the contents of the Partnership Deed?
Answer:
- Name Name of the Firm.
- Nature of Business: Nature of the proposed business to be carried on by the partners.
- Duration of Partnership: Duration of the partnership business whether it is to be run for a fixed period of time or whether it is to be dissolved after completing a particular venture.
- Capital Contribution: The capital is to be contributed by the partners. It must be remembered that capital contribution is not necessary to become a partner for, one contributes his organizing power, business acumen, managerial skill etc., instead of capital.
- Withdrawal from the Firm: The amount that can be withdrawn from the firm by each partner.
- Profit/Loss Sharing: The ratio in which the profits or losses are to be shared. If the profit sharing ratio is not specified in the deed, all the partners must share the profits and bear the losses equally.
- Interest on Capital: Whether any interest is to be allowed on capital and if so. the rate of interest.
- Rate of Interest on Drawing: Rate of interest on drawings, if any.
- A loan from Partners: Whether loans can be accepted from the partners and if so the rate of interest payable thereon.
- Account Keeping: Maintenance of accounts and audit.
- Salary and Commission to Partners: Amount of salary or commission payable to partners for their services. (Unless this is specifically provided, no partner is entitled to any salary).
- Retirement: Matters relating to the retirement of a partner. The arrangement to be made for paying out the amount due to a retired or deceased partner must also be stated.
- Goodwill Valuation: Method of valuing goodwill on the admission, death or retirement of a partner.
- Distribution of Responsibility: Distribution of managerial responsibilities. The work that is entrusted to each partner is better stated in the deed itself.
- Dissolution Procedure: Procedure for dissolution of the firm and the mode of settlement of accounts thereafter.
- Arbitration of Dispute: Arbitration in case of disputes among partners. The deed should provide the method for settling disputes or differences of opinion. This clause will avoid costly litigations.
Question 4.
Explain the types of dissolution of the partnership firm.
Answer:
Dissolution of partnership means the termination of the original partnership agreement. A partnership is dissolved by the insolvency, retirement, expiry, or completion of the term of the partnership. The business will continue after the dissolution of the partnership. It takes in the following forms:
- Change in the existing profit-sharing ratio – Admission of a partner.
- Retirement or Death of a partner.
- Insolvency of a partner.
- Expiry of the term of the partnership.
- Completion of the specified venture.
- Dissolution by agreement.
Question 5.
Write any three differences between Dissolution of Partnership and Dissolution of Firm?
Answer:
Dissolution of Partnership:
- In the case of dissolution of the partnership, only one or more of the partners terminate their connections with the firm.
- Dissolution of a partnership may or may not bring the business of the firm to an end.
- In the dissolution of the partnership, the business will continue even after dissolution.
Dissolution of Firm:
- Whereas all the partners terminate their connections with the firms in the case of dissolution of the firm.
- But the dissolution of the firm brings the business of the firm to an end.
- But business cannot be continued in the case of dissolution of the firm.
Question 6.
Write the procedure for Registration of a Firing Procedure for registration:
Answer:
The Indian Partnership Act does not make the registration of a partnership compulsory. Registration is optional. But the disabilities of non-registration virtually make it compulsory.
A statement should be prepared to state the following particulars.
- Name of the firm.
- The principal place of business.
- Name of other places where the firm carried on the business.
- Names and addresses of all the partners.
- The date on which each partner joined the firm.
- The duration of the film.
This statement should be signed by all the partners should be produced to the Registrar of Firms along with the necessary registration fee. Any change in the above particulars must be communicated to the Registrar within 14 days of such alteration.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Hindu Undivided Family and Partnership Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question 1.
……………. is that form of business organisation which is owned and controlled by a single individual.
(a) Sole trading concern
(b) Partnership firm
(c) Joint Hindu family business
(d) Joint-stock companies
Answer:
(a) Sole trading concern
Question 2.
……………… is known as individual entrepreneurship.
(a) Partnership
(b) Sole trader
(c) Joint-stock company
(d) Cooperative
Answer:
(b) Sole trader
Question 3.
When his business assets are not sufficient to pay off the business debts, he has to pay from his personal property.
(a) Unlimited Liability
(b) Flexibility
(c) Small capital
(d) Limited Liability
Answer:
(a) Unlimited Liability
![]()
Question 4.
“He receives all the profits and risks all of his property in the success or failure of the enterprise”- was said by ………………..
(a) Wheeler
(b) J.L. Hansen
(c) H. Haney
(d) O.R. Krishnasamy
Answer:
(a) Wheeler
Question 5.
Which of the following is under non – corporate enterprise?
(a) Government
(b) Cooperative
(c) Company
(d) Sole trading concern
Answer:
(d) Sole trading concern
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write any two examples of Joint Hindu Family business run in India?
Answer:
- Reliance Industries
- Tata Consultancy Services.
Question 2.
Mention any four kinds of Partners?
Answer:
- Active partner
- Sleeping partner
- Nominal partner
- Partner in profits only
Question 3.
What is a partnership firm?
Answer:
The persons who enter into partnership are collectively known as ‘Firm’.
Question 4.
Write any two types of dissolution through court?
Answer:
- When a partner becomes of unsound mind.
- Permanent incapacity observed in its formation, management or in its closure.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is unlimited liability?
Answer:
The liability of a sole trader is unlimited. Since, apart from his business assets, even his private properties are also available for satisfying the claims of creditors. Hence, creditors may give more loans because they can get back the loan from the personal properties of sole traders.
Question 2.
What is a Particular partnership?
Answer:
When a partnership is formed to carry on a particular venture or a business of temporary nature, it is called a particular partnership. In other words, it comes to an end on the completion of the particular venture.
![]()
Question 3.
What is meant by Mitakshara Law?
Answer:
According to Mitakshara law, only the male members in the family get the right of inheritance by birth. It is applied throughout India except for Assam and West Bengal.
Question 4.
What is meant by Dayabhaga Law?
Answer:
According to Dayabhaga Law, the right of property develops on the Coparceners by succession and not by birth. The share in the property is not fluctuating on the basis of births and deaths. The share is specified prior to partition. The coparceners can alienate their share of property given without the concern of their coparceners.
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the rights of a partner? (Any five)
Answer:
- Right to take part in business: Every partner has a right to take part in the management of the business.
- Right to be a consultant: Every partner has the right to be consulted in all matters concerning the firm. The decision of the majority will prevail in all the routine matters.
- Right of access to books, records, and documents: Every partner has the right of access to all records and books of accounts, and to examine and copy them.
- Right to share profit: Every partner is entitled to share the profits in the agreed ratio. If no profit – sharing ratio is specified in the deed, they must be shared equally.
- Right to receive interest: A partner has the right to receive interest on loans advanced by him to the firm at the agreed rate, and where.no rate is stipulated, interest @ 6% p.a. allowed.
Question 2.
What are the circumstances under which a partnership firm is dissolved? (any five)
Answer:
- By agreement or mutual consent: A firm may be dissolved when all the partners agree to close the affairs of the firm. Just as a partnership is created by contract, it can also be terminated by contract.
- By insolvency of all the partners but one: If any of the partners adjudged an insolvent »(or if all the partners become insolvent) it is necessary to dissolve the firm.
- Business becoming unlawful: When the business carried on by the partnership becomes illegal, the partnership firm is automatically dissolved.
- By notice of dissolution: In the case of partnership at will when any partner gives in writing to all the other partners indicating his intention to dissolve the firm, the firm will be dissolved.
- Continued loss: If the business of the firm cannot be continued to expect at a loss, the same may be dissolved by the court on application by a partner.
Case Study
Question a.
A father had self-acquired agricultural land. He transferred the said land in the name of his three sons. The revenue records reflect the names of the three sons with 1/3rd share against each name. Father died recently. However physical partition of the said land amongst the three brothers has not been done as they have mutually decided against it. The eldest son has started managing the land since his father’s demise. Is the land in question ancestral property of the three brothers? Can the three brothers claim to a HUF? If yes, then when are they HUF – after father’s demise or since the date land transferred in their names?
Answer:
Yes, the land is the ancestral property of the three brothers. It is their father’s land. The three brothers can claim to a HUF. After their father’s death, they can get the land transferred in their names.
Question b.
Draw a family tree diagram as you think. Just imagine you are running a business under the Joint Hindu Family system.
Answer:
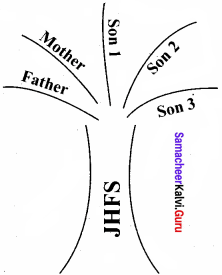
For Future Learning
Question a.
Raman with members of his extended family established a Joint Hindu Family business of Handicrafts. Raman being the head of family-controlled the business as ‘Karta’. He had the authority to make all decisions for the business. Many times, he sold goods for cash without informing other members of the family business. This resulted in lesser profits. He also sold one of the family properties and gave money to his daughter as a wedding gift. What values did Karta ignore in the above case?
Answer:
- Unlimited liability
- No consultation with family members.
- Quick decision making.
- Hasty decision.
![]()
Question b.
Palani is an Electronics Engineer. He has met two businessmen who wish to enter into a partnership with him for the manufacture of tape-recorders. They are prepared to make the investment and offer a fourth share in profits to Palani. Would you have any special words of advice for Palani?
Answer:
Palani is a working partner. He knows the field of product manufacturing of tape – recorders. So he is an expert in the business.