Students can Download Bio Zoology Chapter 1 The Living World Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 1 The Living World
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology The Living World Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Question and Answers
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
A living organism is differentiated from non-living structure based on
(a) Reproduction
(b) Growth
(c) Metabolism
(d) AH the above
Answer:
(c) Metabolism
Question 2.
A group of organisms having similar traits of a rank is
(a) Species
(b) Taxon
(c) Genus
(d) Family
Answer:
(a) Species
Question 3.
Every unit of classification regardless of its rank is
(a) Taxon
(b) Variety
(c) Species
(d) Strain
Answer:
(a) Taxon
Question 4.
Which of the following is not present in same rank?
(a) Primata
(b) Orthoptera
(c) Diptera
(d) Insecta
Answer:
(a) Primata
![]()
Question 5.
What taxonomie aid gives comprehensive information about a taxon?
(a) Taxonomic Key
(b) Herbarium
(c) Flora
(d) Monograph
Answer:
(a) Taxonomic Key
Question 6.
Who coined the term biodiversity?
(a) Walter Rosen
(b) AG Tansley
(c) Aristotle
(d) AP de Candole
Answer:
(a) Walter Rosen
Question 7.
Cladogram considers the following characters –
(a) Physiological and Biochemical
(b) Evolutionary and Phylogenetic
(c) Taxonomie and systematic
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Evolutionary and Phylogenetic
Question 8.
Molecular taxonomic tool consists of –
(a) DNA and RNA
(b) Mitochondria and Endoplasmic reticulum
(c) Cell wall and Membrane proteins
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) DNA and RNA
![]()
Question 9.
Differentiate between probiotic and pathogenic bacteria.
| Probiotic bacteria | Pathogenic bacteria | ||
| 1. | Probiotic bacteria are beneficial bacteria. | 1. | Pathogenic bacteria are harmful bacteria. |
| 2. | The bacteria which cause fermentation are examples of probiotic bacteria. | 2. | The disease causing bacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis are pathogenic. |
Question 10.
Why mule is sterile in nature?
Answer:
The male donkey is crossed with the female horse the mule can be produced, As the donkey is not crossed with its same species the offsprings are sterile.
List any five salient features of the family Felidae.
- They have sharp claws to catch the prey and to eat.
- They have cutting incisors and large sharp canines to cut the meat.
- They are free living.
- They come out at night for searching for prey.
- They have a strongly built body.
- They have sharp sensory organs. (Eg.) Flaring, Smell, Vision, Touch
- Its weight may range from 2 kg to 300 kgs.
Question 11.
List any five salient features of the family Felidae.
Answer:
- The species in the Felidae family are carnivores or omnivores.
- Felids are generally solitary with a few exceptions.
- They have sharp vision, hearing and a strong sense of smell.
- They have short faces and their paws have toes in the 5 forefeet and 4 toes in the hind feet.
- Most Felids live in the wild e.g. cat, tiger, lion, cheetah.
Question 12.
What is the role of Charles Darwin in relation to concept of species?
Answer:
Charles Darwin has written the book “Origin of Species” in 1859. In this book, he has explained the relationship between evolution and the origin of species through natural selection.
Question 13.
Why elephants and other wild animals are entering into human living area?
Answer:
Elephants and other wild animals enter into human living area because of the loss of their habitat, deforestation, mono-culture vegetation by destroying forests
![]()
Question 14.
What is the difference between a Zoo and a wildlife sanctuary?
Answer:
|
Zoo |
Wild Life Sanctuary |
||
| 1. | Zoo is a place where animals and birds are in captivity of artificially created habitat. | 1. | The wildlife sanctuary is the natural habitat of wild animals and birds. |
| 2. | Public can have easy access to the zoo. | 2. | Public does not have easy access to the wildlife sanctuaries. |
| 3. | Zoo is based on commercial aspects. | 3. | Sanctuaries are non-commercial. |
| 4. | Animals are caged and hence they are not free to roam about. | 4. | In a sanctuary, animals can roam about freely. |
Question 15.
Can we use recent molecular tools to identify and classify organisms?
Answer:
- The short genetic marker in an organism’s DNA is used to identify the organism belonging to a particular species – For this molecular technique DNA, bar-coding is used.
- By the degree of genetic similarity between pools of DNA sequences is measured.
- To identify an individual from a sample of DNA by looking at unique patterns in their DNA is used.
- The difference in homologous DNA sequences that can be detected by the presence of fragments of different lengths after digestion of DNA samples is called Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms analysis (RFLP)
- To amplify a specific gene on a portion of a gene by using polymerase chain reaction are used as taxonomical tools.
![]()
Question 16.
Explain the role of Latin and Greek names in Biology.
Answer:
- Before the modern period of the early modem period, learning is done in Greek and Latin.
- Educated people (scientists) knew Greek and Latin.
- Other’s simply borrowed the coined words and terms of educated people or scientists.
- Greek and Latin were the primary languages taught everywhere uniquely it is the common language of Western Europe that too is used and approved as the language of science.
- Greek is more of the language of science than Latin.
- Plants and Animals had local popular names in many other languages. So a system is needed to be devised so that they were to be recognized everywhere universally.
- When Carious Linnaeus (1707 -1778) formulated his binomial system of naming plants he did it in Greek and Latin continued this practice and made it universally acceptable as binomial nomenclature.
- ICBN and ICZN – Indian Code of Botanical and Zoological nomenclature specify that not only the name and its description should be translated in Latin.
In-Text Questions Solved
Question 1.
If you find an animal with four legs, with two eyes, paired ear pinna, covered with fur, possessing mammary gland, which class will you position it? How will you give a binomial name, if you are the first person to discover and report that animal.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Question 2.
What may be the reasons for the extinction of Dinosaurs? If you know the reasons for their extinction, why Sparrows are listed as endangered species?
Answer:
The extinction of the dinosaurs is an enigma that has captivated scientists for well over a century. We find the fossilized remains of giant reptiles all over the earth.
Yet we do not see any of the creatures alive today. If sparrows are not there the population of birds of prey may also be affected. Apart from this, every constitute of an ecosystem is important from an ant to an elephant. We are eliminating species by species which are important links which make the web of life. Today it’s these species which are getting extinct.
![]()
Textbook Activity Solved
The main objective of this activity is to check the students understanding about animals and its characteristics before learning the lesson. Observe the picture given below, identify the animals and classify them according to you own understanding write one character about each class of animals.
Take the students to the school ground and ask them to observe and identify few invertebrates (insects, earthworm, spiders etc). Ask the students to write few characteristics of each animal which they have observed.

| SI. No | Name of the Animal | Known Character | Class | Habitat |
|
1 |
Elephant |
Terrestrial | Mammalia | Land |
| 2 | Bird | Flying | Aves |
Aerial |
|
3 |
Crocodile | Ammotic egg | Reptilia |
Water |
|
4 |
Fish | Cold blooded | Pisces | Sea |
Entrance Examination Questions Solved
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The smallest taxon among the following is ………. (PMT-94)
(a) class
(b) order
(c) species
(d) genus
Answer:
(c) species
Question 2.
Taxonomically a species is ……….. (PMT-94)
(a) A group of evolutionary related population
(b) A fundamental unit in the phylogeny of organisms
(c) Classical evolutionary taxonomy
(d) A community taken into consideration. An evolutionary base.
Answer:
(b) A fundamental unit in the phylogeny of organisms
Question 3.
Species is
(a) not related to evolution
(b) specific class of evolution
(c) specific unit of evolution
(d) fertile specific unit in the evolutionary history of a race
Answer:
(d) fertile specific unit in the evolutionary history of a race
![]()
Question 4.
Two words comprising the binomial nomenclature are ………… (DPMT-96)
(a) Family & genus
(b) order & family
(c) genus & species
(d) species & variety
Answer:
(c) genus & species
Question 5.
A group of plants or animals with similar traits of any rank is kept under ………. (PMT-96)
(a) species
(b) genus
(c) order
(d) taxon
Answer:
(d) taxon
Question 6.
Which of the following is the correct sequence in the increasing order of complexity? (PMT-97)
(a) molecules, tissues, community, population
(b) cell, tissues, community, population
(c) tissues, organisms, population, community
(d) molecules, tissues, community, cells
Answer:
(c) tissues, organisms, population, community
Question 7.
New systematic and the concept of life was given by ……….. (BHU-98)
(a) Huxley
(b) Odom
(c) Elton
(d) Linnaeus
Answer:
(c) Elton
Question 8.
Two organisms of same class but different families will be kept under the same ……… (CET-98)
(a) genera
(b) species
(c) order
(d) family
Answer:
(c) order
Question 9.
Which of the following will form a new species? (PMT-98)
(a) inter breeding
(b) variations
(c) differential reproduction
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) variations
![]()
Question 10.
A community includes ……….. (CET-98)
(a) a group of same genera
(b) a group of same population
(c) a group of individuals from same species
(d) different populations interacting with each other
Answer:
(d) different populations interacting with each other
Question 11.
Binomial nomenclature was given by …………(BHU-97)
(a) Huxley
(b) Ray
(c) Darwin
(d) Linnaeus
Answer:
(d) Linnaeus
Question 12.
In classification the category below the level of family is ……….. (CET-98)
(a) class
(b) species
(c) phylum
(d) genus
Answer:
(d) genus
Question 13.
Taxon is …………. (CET-2000)
(a) species
(b) unit of classification
(c) highest rank in classification
(d) group of closely related
Answer:
(b) unit of classification
Question 14.
One of the following includes most closely linked organisms ………… (PMT-2001)
(a) species
(b) genus
(c) family
(d) class
Answer:
(a) species
Question 15.
Which of the following taxons cover a greater number of organisms?(PMT-2001)
(a) order
(b) family
(c) genus
(d) phylum
Answer:
(d) phylum
Question 16.
Inbreeding is possible between two members of ………… (AMU-2005)
(a) order
(b) family
(c) genus
(d) species
Answer:
(d) species
![]()
Question 17.
Which of these is correct order of hierarchy? (WARDHA-2002)
(a) kingdom, division, phylum, genus & species
(b) phylum, division, genus & class
(c) kingdom, genus, class, phylum & division
(d) phylum, kingdom, genus, species &class
Answer:
(a) kingdom, division, phylum, genus & species
Question 18.
Which is not a unit of taxonomic category? (BVP-2002)
(a) series
(b) glumaceae
(c) class
(d) phylum
Answer:
(b) glum aceae
Question 19.
Which is the first step of taxonomy? (MGIMS-2002)
(a) nomenclature
(b) classification
(c) identification
(d) hierarchical arrangement
Answer:
(c) identification
Question 20.
The five kingdom classification was given by ………… (BYP-2002)
(a) Whittaker
(b) Linnacus
(c) Copeland
(d) Haeckel
Answer:
(a) Whittaker
Question 21.
Taxon includes ………… (PMT-2002)
(a) Genus and species
(b) kingdom and division
(c) all ranks of hierarchy
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) all ranks of the hierarchy
Question 22.
Binomial nomenclature refers to …………. (CET – 2000)
(a) Two names of a species
(b) one specific and one local name of a species
(c) two words for the name of a species
(d) two life cycles of a organism
Answer:
(c) two words for the name of a species
Question 23.
Carl Linnaeus is famous for ………… (GGSPU-2002)
(a) coining the term ‘systematics’
(b) introducing binomial nomenclature
(c) giving all natural system of classification
(d) all of these
Answer:
(b) introducing binomial nomenclature
![]()
Question 24.
True species are …………
(a) interbreeding
(b) sharing the same niche
(c) feeding on the same food
(d) reproductively isolated
Answer:
(d) reproductively isolated
Question 25.
The smallest unit of classification is ………… (GGSPU-2002)
(a) species
(b) sub – species
(c) class
(d) genus
Answer:
(a) species
Question 26.
Who coined the term ‘taxonomy’? (BVP-2003)
(a) Candolle
(b) Waksman
(c) Leuwenhoek
(d) Louis Pasteur
Answer:
(a) Candolle
Question 27.
The basic unit of classification of organisms is ………… (CET-2003)
(a) species
(b) population
(c) class
(d) family
Answer:
(a) species
Question 28.
The unit of classification containing concrete biological entities is ……….. (WARDHA-2003)
(a) taxon
(b) species
(c) category
(d) order
Answer:
(a) taxon
Question 29.
Species are considered as …………..
(a) real basic units of classification
(b) the lowest units of classification
(c) artificial concept of human mind which cannot be defined in absolute terms
(d) real units of classification devised by taxonomists
Answer:
(a) real basic units of classification
Question 30.
The living organisms can be unexceptionally distinguished from the non-living things on the basis of their ability for …………
(a) interaction with the environment and progressive evolution
(b) reproduction
(c) growth and movement
(d) responsiveness to touch
Answer:
(b) reproduction
![]()
Question 31.
Taxonomic category arrange in descending order ……….. (MH-01)
(a) key
(b) hierarchy
(c) taxon
(d) taxonomic category
Answer:
(d) taxonomic category
Question 32.
In which of the animal dimorphic nucleus is found? (PMT 2002).
(a) Amoebaproteus
(b) Trypanosoma gambiense
(c) Plasmodium vivax
(d) Paramecium caudatum
Answer:
(d) Paramecium caudatum
Question 33.
When a fresh-water protozoan possessing a contractile vacuole, is placed in a glass containing marine water, the vacuole will ………. (PMT 2004)
(a) increase in number
(b) disappear
(c) increase in size
(d) decrease in size
Answer:
(d) decrease in size
Question 34.
Which form of reproduction is correctly matched? (AIIMS 2007)
(a) Euglena transvers binary fission
(b) Paramecium longitudinal binary fission
(c) Amoeba multiple fission
(d) Plasmodium binary fission
Answer:
(c) Amoeba multiple fission
Question 35.
The presence of two types of nuclei, a macronucleus and a micronucleus, is characteristic of protozoans are grouped under the class ……….. (BHU 1994, 1999)
(a) sporozoa
(b) flagellate
(c) sarcodina
(d) ciliata
Answer:
(d) ciliata
![]()
Question 36.
Which class of protozoa is totally parasitic? (BHU 1994)
(a) Sporozoa
(b) Mastigophora
(c) Ciliate
(d) Sarcodina
Answer:
(a) Sporozoa
Question 37.
Reproduction in Paramecium is controlled by ………. (BHU 1999).
(a) flagella
(b) cell wall
(c) micronucleus
(d) macronucleus
Answer:
(c) micronucleus
Question 38.
In the life cycle of Plasmodium exflagellation occurs in ……….. (BHU 2007)
(a) sporozoties
(b) microgametes
(c) macrogametes
(d) signet ring
Answer:
(b) microgametes
Question 39.
Excretion in Amoeba occurs through ………… (DPMT 1997)
(a) lobopodia
(b) plasma membrane
(c) uroid portion
(d) contractile vacuole
Answer:
(d) contractile vacuole
Question 40.
Method of dispersal in Amoeba is ……….. (DPMT 1995)
(a) locomotion
(b) encystment
(c) sporulation
(d) binary fission
Answer:
(b) encystment
Question 41.
The Mode of feeding in free living protozoans is …………. (DPMT 2007).
(a) holozoic
(b) saprozoic
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) both (a) and (b)
Question 42.
Infection of Entamoeba is caused ………… (UP- CPMT 1996, 1999).
(a) by kissing
(b) by wearing clothes of patient
(c) by contaminated food
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) by contaminated food
![]()
Question 43.
Choose the correct statement.
(a) All reptiles have a three chambered heart.
(b) All Pisces have gills covered by a operculum
(c) All mammals are viviparous
(d) All cyclostomes do not posses jaws and paired fin
Answer:
(d) All cyclostomes do not posses jaws and paired fin
Question 44.
Which of the following characteristics is mainly responsible for the diversification of insects on land?
(a) Segmentation
(b) Bilateral symmetry
(c) Exoskeleton
(d) Eyes
Answer:
(c) Exoskeleton
Question 45.
The primitive prokaryotes responsible for the production of biogas from the ruminant animals. Include the …………. (2016)
(a) Thermoacidophiles
(b) methanogens
(c) Eubacteria
(d) Halophiles.
Answer:
(b) methanogens
Question 46.
Methanogens belong to ………. (2016)
(a) Dinoflagellates
(b) Slime moulds
(c) Eubacteria
(d) Archaebacteria
Answer:
(d) Archaebacteria
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology The Living World Additional Questions Solved
Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Which of the following is not correct with regard to the ecosystem?
(a) It includes living and non-living things.
(b) It shows interrelationship among living things.
(c) It shows interrelationships among the living and non-living things.
(d) It has a large number of species.
Answer:
(b) It shows interrelationship among living things.
Question 2.
Who was known as the father of Botany?
(a) Aristotle
(b) Carolus Linnaeus
(c) John Ray
(d) Theophrastus
Answer:
(d) Theophrastus
![]()
Question 3.
Who developed the scientific system of Taxonomy and Binomial nomenclature?
(a) R.H. Whittaker
(b) Carolus Linnaeus
(c) John Ray
(d) Charles Darwin
Answer:
(b) Carolus Linnaeus
Question 4.
The system of classification of organisms based on evolutionary and genetic relationship among organisms is called as –
(a) Natural system of classification
(b) Phylogenetic system of classification
(c) Binomial classification
(d) Trinomial classification
Answer:
(b) Phylogenetic system of classification
Question 5.
The bacteria which live in salty environment are called –
(a) Theromoacidophiles
(b) Methanogens
(c) Halophiles
(d) Pathogens
Answer:
(c) Halophiles
Question 6.
Which of the following is the characteristics of the domain Bacteria?
(a) They are eukaryotic organisms
(b) They have true nucleus and membrane bound organelles
(c) The ribosomes are of 80 s type in the cytoplasm
(d) They have membrane bound 70 s type ribosomes.
Answer:
(d) They have membrane bound 70 s type ribosomes.
![]()
Question 7.
Which of the following is not correct with regard to species?
(a) They have similar morphological features
(b) They are reproductively isolated
(c) They produce viable young ones
(d) They have similar anatomical features
Answer:
(b) They are reproductively isolated
Question 8.
The cross between male lion and female tiger results in the production of –
(a) Mule
(b) Tigon
(c) Liger
(d) Hinny
Answer:
(c) Liger
Question 9.
The related families constitute-
(a) Clans
(b) Phylum
(c) Genus
(d) Order
Answer:
(d) Order
Question 10.
Which of the following is not related to scientific names of organisms?
(a) There is only one name for a species.
(b) They are universally accepted.
(c) They are named based on the guidelines of the ICZN.
(d) They are not unique to an organism.
Answer:
(d) They are not unique to an organism.
Question 11.
Naja naja is the zoological name of –
(a) Indian house crow
(b) Indian cobra
(c) Emerald dove
(d) Indian pea fowl
Answer:
(b) Indian cobra
![]()
Question 12.
Origin of species is the book written by –
(a) John Ray
(b) Charles Darwin
(c) Linnaeus
(d) Aristotle
Answer:
(b) Charles Darwin
Question 13.
Taxonomical keys are useful to study –
(a) Similarities and dissimilarities of animals
(b) Preserved plants and animals
(c) Animals kept in protected environments
(d) Plant taxonomy
Answer:
(a) Similarities and dissimilarities of animals
Question 14.
DNA hybridization is helpful to –
(a) Identify an individual from a sample of DNA
(b) Detect difference in homologous DNA sequences
(c) Measure the degree of genetic similarity between pools of DNA sequences
(d) Amplify a specific gene
Answer:
(c) Measure the degree of genetic similarity between pools of DNA sequences
Question 15.
DAISY, the cyber tool is –
(a) Digital automated identification system
(b) Digital automated information system
(c) Direct automated identification system
(d) Digital automated identification science
Answer:
(a) Digital automated identification system
![]()
Question 16.
INOTAXA is an e-Taxonomic resource useful for –
(a) Studying electron microscopic images to study molecular structures of cell organelles.
(b) Digital images and description about the species.
(c) Studying behaviour of organisms
(d) Identifying digital resources of animals.
Answer:
(b) Digital images and description about the species.
II. Give Reasons
Question 1.
What is an ecosystem?
Answer:
The ecosystem is a community of living organisms like plants and animals, non-living environments like minerals, climate soil water sunlight, and their relationships.
Question 2.
Extremophiles inhabiting volcanic vents prepare food.
Answer:
Extremophiles inhabiting volcanic vents prepare food without sunlight and oxygen by utilizing hydrogen peroxide and other chemicals through chemosynthesis.
Question 3.
What are taxa (or) taxon?
Answer:
Classification is a process by which things are grouped in convenient categories based on easily observable characters. The scientific term used for these categories is taxa.
![]()
Question 4.
Nomenclature of organisms is necessary.
Answer:
The unique nomenclature for each organisms is necessary as it is uniform in all countries and in all languages. A scientific name refers to only one organism.
Question 5.
What is taxonomy?
Answer:
Taxonomy is a theoretical study of classification with well-defined principles rules and procedures.
III. Match the following.
Question 1.
| 1. | Ecosystem | (a) Walter Rosen |
| 2. | Taxonomy | (b) Carolus Linnaeus |
| 3. | Biodiversity | (c) AP de Candolle |
| 4. | Species | (d) A.G. Tansley |
| 5. | Binomial nomenclature | (e) John Ray |
Answer:
- (d) A.G. Tansley
- (c) AP de Candolle
- (a) Walter Rosen
- (e) John Ray
- (b) Carolus Linnaeus
Question 2.
| 1. | Extremophiles | (a) Beneficial |
| 2. | Probiotic bacteria | (b) 70s type of ribosomes |
| 3. | Pathogenic bacteria | (c) membrane bound organelles |
| 4. | Eukarya | (d) Extreme conditions |
| 5. | Bacteria | (e) disease causing (f) 80s type of ribosomes |
Answer:
- (d) Extreme conditions
- (a) Beneficial
- (e) disease causing
- (c) membrane bound organelles
- (b) 70 s type of ribosomes
Question 3.
| 1. | Felis margarita | (a) Pea fowl |
| 2. | Chalcophaps indica | (b) Red Panda |
| 3. | Pavo cristatus | (c) Tiger |
| 4. | Ailurus fulgens | (d) Jungle cat |
| 5. | Panthera Tigris | (e) Emerald dove |
Answer:
- (d) Jungle cat
- (e) Emerald dove
- (a) Pea fowl
- (b) Red Panda
- (c) Tiger
![]()
Question 4.
| 1. | Historia Animalium | (a) Charles Darwin |
| 2. | Methodus plantarum | (b) R.H. Whittaker |
| 3 | Origin of species | (c) John Ray |
| 4 | Three Domain classification | (d) Aristotle |
| 5 | Five kingdom classification | (e) Carl Woese |
Answer:
- (d) Aristotle
- (c) John Ray
- (a) Charles Darwin
- (e) Carl Woese
- (b) R.H. Whittaker
Question 5.
| 1. | Museum | (a) Analysis of DNA |
| 2. | Taxonomical keys | (b) Similarities and dissimilarities of organisms. |
| 3. | Herbarium | (c) Difference in homologous DNA sequence |
| 4. | RFLP Analysis | (d) Preserved plants and animals |
| 5. | DNA fingerprinting | (e) Plant Taxonomy |
Answer:
- (d) Preserved plants and animals
- (b) Similarities and dissimilarities of organisms.
- (e) Plant Taxonomy
- (c) Difference in homologous DNA sequence
- (a) Analysis of DNA
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the significances of taxonomy?
Answer:
- It helps in identifying and differentiate closely related species.
- It helps in knowing the variation among the species.
- It helps in understanding the evolution of the species.
- It helps in creating a phylogenetic tree among the different groups.
- It helps in conveniently study living organisms.
Question 2.
What is biodiversity?
Answer:
The presence of a large number of species in a particular ecosystem is called biodiversity.
Question 3.
Distinguish between living and non-living things.
Answer:
|
Living things |
Non-living things |
||
| 1. | Living things exhibit life processes such as nutrition, respiration, excretion, metabolism, growth and movement. | 1. | Non-living things do not exhibit life processes. |
| 2. | These are biotic component of ecosystem. | 2. | These are abiotic component of ecosystem. |
Question 4.
What is the need for classification?
Answer:
The basic need for classification are:
- To identify and differentiate closely related species.
- To know the variation among the species.
- To understand the evolution of the species.
- To create a phylogenetic tree among the different groups.
- To conveniently study living organisms.
Question 5.
Define Taxonomy.
Answer:
It is the branch of science of identifying, describing, naming and classifying organisms.
Question 6.
What are the features of systematics?
Answer:
- Identifying, describing, naming, arranging, preserving and documenting the organisms.
- Investigating evolutionary history of the species, their adaptations to the environment and the interrelationship among species.
Question 7.
How did Aristotle classify organisms?
Answer:
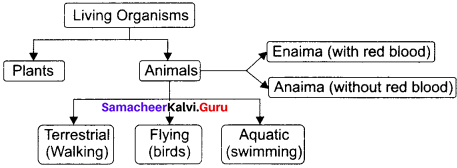
Aristotle classified living organisms into plants and animals. Animals were classified into walking (terrestrial), flying (birds) and swimming (aquatic) based on their locomotion. Based on the presence or absence of red blood animals were classified into Enaima and Anaima.
Question 8.
Give short notes on tautonymy.
Answer:
The practice of naming the animals in which the generic name and species name are the same is called tautonymy.
Name some tools for automated species identification.
- Digital automated identification system – DAISY.
- Automated leaf hopper identification system – ALIS.
- Automatic bee identification system – ABIS.
Question 9.
What is natural system of classification?
Answer:
Linnaeus considered a few characters of organisms for classifying them. Later many characters were considered for classifying organisms. Morphological, anatomical and embryological characters were considered.
![]()
Question 10.
What is numerical taxonomy?
Answer:
The evaluation of resemblances and differences of organisms through statistical methods followed by computer analysis to establish the numerical degree of relationship among them is known as numerical taxonomy.
Question 11.
What is phylogenetic classification or cladistics?
Answer:
The classification of organisms based on evolutionary and genetic relationship among them is known as phylogenetic classification.
Question 12.
What is cladogram?
Answer:
A tree diagram which represents the evolutionary relationship among organisms is known as cladogram.
Question 13.
What is cladistic classification?
Answer:
Cladistic classification is the method of classifying organisms based on genetic differences among all species in a phylogenetic tree.
Question 14.
What is special about Eukarya?
Answer:
- Eukaryotes have true nuclei and membrane-bound organelles.
- DNA in the nucleus is arranged as a linear chromosome with histone proteins.
- In mitochondria 70s ribosome and in the cytosol 80s ribosome is present.
- Animals in this domain are classified under the kingdom namely Protista, Fungi Plantae, and Animalia.
Question 15.
Explain five kingdom classification of Whittaker.
Answer:
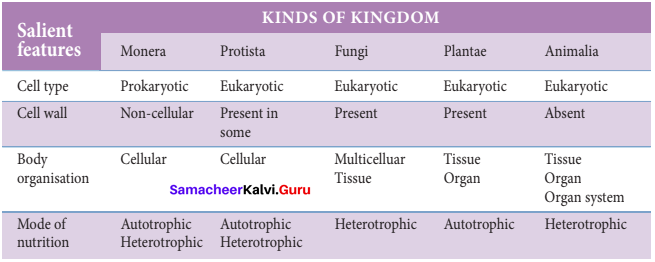
R.H. Whittaker (1969) proposed the Five kingdom classification. They included Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia. He classified organisms based on cell structure, nutrition, reproduction and phylogenetic relationships.
Kinds of kingdom:
Question 16.
Describe three-domain classification.
Answer:
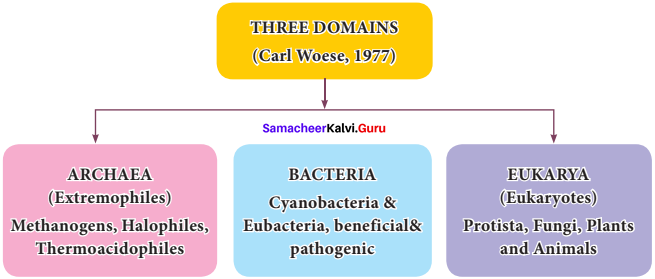
Three domain classification was proposed by Carl Woese (1977) and his co-workers. They classified organisms based on the difference in 16s rRNA genes. This adds the taxon domain higher than the kingdom. In this system, prokaryotes are divided into two domains-bacteria and Arachaea.
All eukaryotes are placed under the domain Eukarya. Archae appears to have common features with Eukarya. Archaea differ from bacteria in cell wall composition and differ from bacteria and eukaryotes in membrane composition and RNA types.
Question 17.
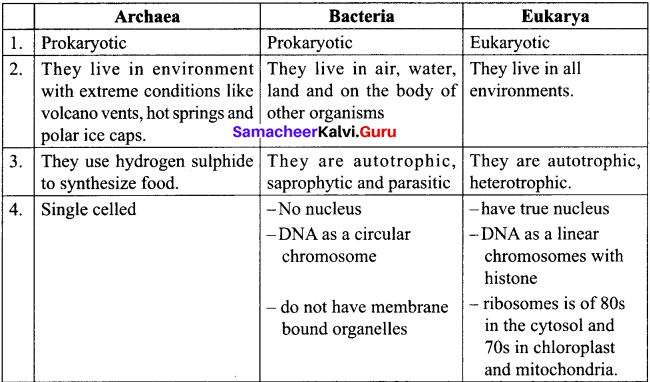
Distinguish Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya.
Answer:
Question 18.
Classify organisms on the basis of seven kingdom system.
Answer:
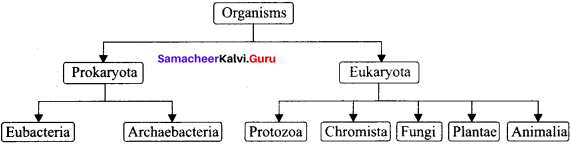
Question 19.
Define species.
Answer:
Species is a group of organisms that have similar morphological and physiological characters which can interbreed to produce fertile off springs.
Question 20.
Show the mating with closely related species.
Answer:
- Male Donkey – Female Horse – Mule
- Male Horse – Female donkey – Hinny
- Male lion – female tiger – Liger
- Male tiger – Female lion – Tiger
Question 21.
Distinguish between species and genus.
Answer:
Species:
- Species is a group of interbreeding population having similar characters.
- It is the basic unit of classification e.g. Felis Domestica, genus species.
Genus:
- Genus is a group of related species.
- It is the second level in classification, e.g., Felis margarita genus species.
Question 22.
Distinguish between Family and Order.
Answer:
Family:
- Family is a group of related genera.
- It is the lower taxon e.g. Felidae
Order:
- Order is a group of related families.
- It is the higher taxon e.g. Carnivora
Question 23.
Distinguish between Class and Phylum.
Answer:
Class:
- The one or more related orders with some common characters is the class
- It is the lower taxon e.g. Mammalia.
Phylum:
- The related orders constitute the phylum.
- It is the higher taxon, e.g. Chordata.
Question 24
What are the advantages of assigning nomenclature to organisms?
Answer:
Assigning nomenclature or scientific name to organisms have advantages.
- They are universally accepted.
- Each organism has unique nomenclature.
- It avoids confusion in naming the organisms.
Question 25.
What is binomial system of nomenclature?
Answer:
The system of naming the organism with two names, generic name and specific (species) name is known as binomial system of nomenclature, e.g. Pavo cristatus – Indian pea fowl.
Question 26.
What is trinomial system of nomenclature?
Answer:
The system of naming the organism with three names, generic name, specific name (species) and sub-species name is known as the trinomial system of nomenclature, e.g. Corvus splendens -Indian house crow.
![]()
Question 27.
Explain the Taxonomic hierarchy It is a group of animals having similar morphological features and is reproductively isolated to produce fertile offspring.
Answer:
The organism formed from closely related animals, which have evolved from a common ancestor. It is a taxonomic category which includes a group of related genera with less similarity as compared to genus and species. Order is an assemblage of one or more related families which show few common features. Eg. Family candidates and Felidae are placed in the order Carnivora.
Class includes one or more related orders with some common characters. The group of classes with similar distinctive characteristics constitute phylum. All living animals belonging to various phyla are included in the kingdom.
Question 28.
What are the taxonomical tools used for the study of plants and animals?
Answer:
Herbarium and Botanical garden may be used as tools for the plant taxonomy. Museum, Taxonomical keys and Zoological parks are classical tools for animal studies. Field visits, survey, identification, classification, preservation and documentation are the important components of taxonomical tools.
Question 29.
Explain the classical taxonomical tools.
Answer:
Taxonomical tools are the tools for the study of classification of organisms. They include- Taxonomical keys: Keys are based on comparative analysis of the similarities and dissimilarities of organisms. There are separate keys for different taxonomic categories. Museum: Biological Museums have collection of preserved plants and animals for study and ready reference. Specimens of both extinct and living organisms can be studied.
Zoological parks:
These are places where wild animals are kept in protected environments under human care. It enables us to study their food habits and behavior.
Marine parks:
- Marine organisms are maintained in protected environments.
- Printed taxonomical tools: It consist of identification cards, description, field guides and manuals.
Question 30.
Name some Automated species identification tools or cyber tools.
Answer:
ALIS: Automated Leafhopper Identification System.
DAISY: Digital Automated Identification System.
ABIS: Automatic Bee Identification System.
SPIDA: Species Identified Automatically (spiders, wasp, bee wing characters).
Draw wing: Honey bee wing identification.
Question 31.
What are neo – taxonomical tools?
Answer:
The new taxonomical tools which are based on electron microscopic images to study the molecular structure of cell organelles are neo-taxonomical tools.
Question 32.
What is INOTAXA?
Answer:
INOTAXA is an electronic resource for digital images and description about species. It was developed by Natural History Museum, London. INOTAXA means Integrated Open Taxonomic Access.
![]()
Question 33.
Scientists and their contribution for taxonomy.
Answer:
- Ecosystem – A.G. Tansley, 1935
- Biodiversity – Walter Rosen, 1985
- Taxonomy – AP de Candolle
- Father of Taxonomy (classical) – Aristotle
- Father of modem taxonomy, Founder of modem systematics – Carolus Linnaeus
- Aristotle – Historia Animalium
- Theophrastus – Father of Botany
- Species – John Ray (1627 – 1708)
- Five kingdom classification – R.H. Whittaker (1969)
- Three domain classification – Carl Woese (1977)
- Seven kingdom classification – Cavalier- Smith (1987)
- Binomial nomenclature – Carolus Linnaeus
- John Ray – Methodus Plantarum Nova and Historia Generalis Plantarum
- Trinomial nomenclature – Huxley and Stricklandt
- Charles Darwin – Origin of species
- Ernst Haeckel – Cladogram
Question 34.
Distinguish between Monotypic genus and polytypic genus
Answer:
Monotypic genus:
- If a genus has only one species, it is called a monotypic genus.
- e.g. Ailurus fulgens (red panda)
Polytypic genus:
- If a genus has more than one species, it is called polytypic genus.
- e.g. Felis domestica Felis margarita