You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science History Solutions Chapter 4 The World after World War II
The World after World War II Textual Exercise
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
Who was the first director of Whampoa Military Academy?
(a) Sun Yat-Sen
(b) Chiang Kai-Shek
(c) Michael Borodin
(d) Chou En Lai.
Answer:
(b) Chiang Kai-Shek
Question 2.
Which American President followed the policy of containment of Communism?
(a) Woodrow Wilson
(b) Truman
(c) Theodore Roosevelt
(d) Franklin Roosevelt
Answer:
(b) Truman
Question 3.
When was People’s Political Consultative Conference held in China?
(a) September 1959
(b) September 1948
(c) September 1954
(d) September 1949
Answer:
(d) September 1949
Question 4.
The United States and European allies formed …………. to resist any Soviet aggression in Europe.
(a) SEATO
(b) NATO
(c) SENTO
(d) Warsaw Pact
Answer:
(b) NATO
Question 5.
Who became the Chairman of the PLO’s Executive Committee in 1969?
(a) Hafez al-Assad
(b) Yasser Arafat
(c) Nasser
(d) Saddam Hussein
Answer:
(b) Yasser Arafat
Question 6.
When was North and South Vietnam united?
(a) 1975
(b) 1976
(c) 1973
(d) 1974
Answer:
(b) 1976
Question 7.
Where was Arab League formed?
(a) Cairo
(b) Jordan
(c) Lebanon
(d) Syria
Answer:
(a) Cairo
![]()
Question 8.
When was the Warsaw Pact dissolved?
(a) 1979
(b) 1989
(c) 1990
(d) 1991
Answer:
(d) 1991
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. …….. was known as the “Father of modem China”.
2. In 1918, the society for the study of Marxism was formed in ……… University.
3. After the death of Dr. Sun Yat Sen, the leader of the Kuomintang party was ………..
4. ……….. treaty is open to any Arab nation desiring peace and security in the region.
5. The treaty of ……… provided for mandates in Turkish-Arab Empire.
6. Germany joined the NATO in ……….
7. ……….. was the Headquarters of the Council of Europe.
8. ……….. treaty signed on February 7, 1992 created the European Union.
Answers:
1. Dr. Sun Yat-Sen
2. Peking
3. Chiang Kai-Shek
4. Central
5. Versailles
6. 1955
7. Strasbourg
8. The Maastricht
III. Choose the correct statement/statements.
Question 1.
(i) In China (1898) the young emperor, under the influence of the educated minority, initiated
a series of reforms known as the 100 days of reforms.
(ii) The Kuomintang Party represented the interests of the workers and peasants.
(iii) Yuan Shih-Kai had lost prestige in the eyes of Nationalists, when he agreed to the demand of Japan to have economic control of Manchuria and Shantung.
(iv) Soviet Union refused to recognize the People’s Republic of China for more than two decades.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (ii) and (iii) is correct
(c) (i) and (iii) are correct
(d) (i) and (iv) are correct
Answer:
(c) (i) and (iii) are correct
Question 2.
(i) In 1948, the Soviets had established left wing government in the countries of Eastern
Europe that had been liberated by the Soviet Army.
(ii) The chief objective of NATO was to preserve peace and security in the North Atlantic region.
(iii) The member countries of SEATO were committed to prevent democracy from gaining ground in the region.
(iv) Britain used the atomic bomb against Japan to convey its destructive capability to the USSR.
(a) (ii), (iii) and (iv) are correct
(b) (i) and (ii) are correct
(c) (iii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
Answer:
(b) (i) and (ii) are correct
Question 3.
Assertion (A): America’s Marshall Plan was for reconstruction of the war-ravaged Europe. Reason (R): The US conceived the Marshal Plan to bring the countries in the Western Europe under its influence.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(b) Both (A) and (R) are wrong
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(d) (A) is wrong and (R) is correct
(c) (iii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of A
IV. Match the following.

Answers:
1. (b)
2. (c)
3. (d)
4. (e)
5. (a)
V. Answer briefly.
Question 1.
Write any three causes for the Chinese Revolution of 1911.
Answer:
- The Disintegration of the Manchu dynasty.
- With the death of Empress Dowager, the governors proclaimed their independence.
- The new emperor was too little two years old who cannot take any decision.
Question 2.
Explain how in 1928 Kuomintung and Chiang-Kai Shek established Central Government in China.
Answer:
- Chiang Kai-Shek became the leader of Kuomintang after the death of Sun Yat-Sen in 1925. Being an avowed critic of Communists, he removed all the important position holders in the communist party including Mao Tse Tung and Chou En Lai.
- The communists increased their influence among the peasants and obtained recruits for their army. The Kuominatang represented the interests of the landlords and capitalists.
- Chang Kai-Shek started conquering China. In early 1927 he successfully land siege on Shanghai and Nanking. He removed all communists in the Kuominatang Party. In 1928 he captured Pehung and established control government in China.
Question 3.
Write a note on Mao’s Long March.
Answer:
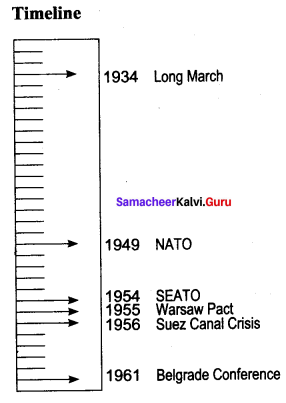
By 1933, Mao had gained full control of the Communist party of China. In 1934, the Communist party army of about 100,000 set out on a long march. The marchers were troubled greatly by Kuomintang forces, unfriendly tribes and local war lords. At last only 20,000 people reached northern Sheni region in 1935, after crossing nearly 6000 miles. By .1937, Mao became the leader of over 10 million people.
Question 4.
What do you know of Baghdad Pact?
Answer:
In 1955, Turkey, Iraq, Great Britain, Pakistan and Iran signed a pact known as Baghdad Pact. In 1958, the United States joined the organisation and therefore it came to be known as the Central Treaty Organisation. The treaty was open to any Arab nation desiring peace and security in the region.
Question 5.
What was Marshall Plan?
Answer:
The Secretary of state of USA George C. Marshall proposed the Marshall plan. The European nations who were affected by World War II will be given administrative and technical assistance, along with shipments of food, fuel and machinery by USA. This would help them for a early recovery and intum help USA to influence them.
![]()
Question 6.
The Suez Canal crisis confirmed that Israel had been created to serve the cause of western interests -Elaborate.
Answer:
In 1956, Nasser, the President of Egypt, nationalised Suez Canal. This measure undermined British interests with the failure of diplomacy, Britain and France decided to use force. Israel saw this as an opportunity to open the Gulf of Aqaba to Israeli shipping and put a stop to Egyptian border roads. On 29 October Israels, forces invaded Egypt, Britain used this opportunity to demand that its troops be allowed to occupy the canal zone to protect the canal. When Egypt refused British demand, it was bombed. Britain and France also attached Suez Canal area.
Question 7.
Write a note on Third World Countries.
Answer:
The term Third World Countries generally refers to the developing countries of the world. Earlier, the former colonies of Africa, Asia and Latin America were called as Third World countries.
Question 8.
How was the Cuban missile crisis defused?
Answer:
The Cuban Missile crisis was a confrontation between the United States and the Soviet Union which initiated by the American discovery of Soviet Ballistic missile deployment in Cuba. Finally, the Soviet President Nikita Khrushchev agreed to with draw the missiles and thus the missile crisis was defused.
VI. Answer all the questions under each caption.
Question 1.
Cold War
(a) Name the two military blocs that emerged in the Post-World War II.
Answer:
- The United States
- The Soviet Union
(b) Who coined the term “Cold War” and who used it first?
Answer:
The term ‘Cold War’ was first coined by the English Writer George Orwell in 1945. Bernard Baruch, the US presidental adviser, was the first to use it in a speech.
(c) What was the response of Soviet Russia to the formation of NATO?
Answer:
Soviet Russia did not welcome the formation of the NATO. To counter it, Soviet Union organised the Soviet-bloc countries for united military actions under the Warsaw Pact in 1955.
(d) What was the context in which Warsaw Pact was dissolved?
Answer:
The Warsaw Pact was dissolved in 1991 following the fall of the Berlin Wall and the reunification of Germany.
Question 2.
Korean War
(a) Who was the President of North Korea during the Korean War?
Answer:
The president of North Korea was KIM II during the Korean War.
(b) Name the southern rival to the President of North Korea.
Answer:
The Southern rival to the President or North Korea was Syngman Rhee.
(c) How long did the Korean War last?
Answer:
The Korean war lasted for three years.
(d) What was the human cost of the War?
Answer:
The human cost of the Korean war was enormous.
Question 3.
Non-Aligned Movement (NAM)
(a) When and where was the first conference on Non-Aligned Movement held?
Answer:
The first conference on NAM was held at Belgrade in 1961.
(b) Who were the prominent personalities present in the first conference?
Answer:
The prominent personalities present in the first conference were Tito (Yugoslavia), Nasser (Egypt), Nehru (India), Nkrumah (Ghana) and Sukarno (Indonesia).
(c) What were the objectives of NAM?
Answer:
To fight all forms of colonialism and imperialism.
(d) List out any two basic principles of Non-Alignment Movement enunciated in the Belgrade
Conference.
Answer:
Two basic principles of NAM eximiated in the Belgrade conference were:
- peaceful cooperation, commitment to peace and security
- no military alliance with any super power.
VII. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
Estimate the role of Mao Tse tung in making China a communist country.
Answer:
- Chinese Revolution broke out in 1911. Mao joined the revolutionary army, but very soon left for his studies.
- Later, Mao went to Peking and worked as an assistant librarian in Peking University.
- Karl Marx and Lenin became very popular those days and in 1918, A society for the study of Marxism was formed in Peking University and Mao attended it.
- The communist party of China was under the leadership of Mao – Tse- tung , But at the same time, Chiang Kai sheik’s Kuomintang party was very strong.
- So, Mao organized the peasantry when the Kuomintang and Communist party rivalry continued, communists led by Mao-Tse-tung stayed for seven years and his army started growing gradually.
- By 1933, he gained full control of the Chinese Communist party.
- He organised a long march with 100,000 people. This legendry march was obstructed very badly by his rival party of Kuomintang.
- Only 20,000 people finally reached safely .
- By 1937, Mao had become the leader of China of over 10 million people.
- By 1948, Communist control had been established over most parts of China.
- In 1949, the people’s political consultative conference met in Peking.
- The conference consisted of 650 delegates from the communist party and other left-wing organisations and elected the central Governing Council with Mao as its chairman.
- Thus, Mao established the people’s Republic of China as a major communist power in the world next to the Soviet Union.
Question 2.
Attempt an essay on the Arab-Israeli wars of 1967 and 1973.
Answer:
The formation of Palestinian Liberation Organisation (PLO) was never friendly to Israel. It came to be attached frequently by Palestinian guerrilla groups based in Syria, Lebanon and Jordan. Israel also made violent retaliation. In November 1966, Israel attacked the village of Al-Sami in the Jordanian West Bank. The death toll in this attack was 18. In April 1967 Israel started air battle with Syria which resulted in the shooting down of six Syrian Mig fighter jet.
In his bid to show Egypt’s support for Syria, Nasser mobilised Egyptian forces in the Sinai, seeking the removal of UN emergency forces stationed there on May 18. On May 22, he closed the Gulf Aqaba to Israeli shifting. On June 5, Israel stoped a sudden pre-emptive air strike that destroyed more than 90 percent of Egypt’s air force on the tarmac. A similar air assault was in capacitated the Syria air force. Within three ways, Israel captured the Gaza Strip and all the Senai Peninsula up to the East Bank of the Suez Canal. On June 7, the Israeli forces drove Jordanian forces out of East Jerusalem and most the West Bank. The War ended when the UN Security Council called for a ceasefire.
Arab-Israel War of 1973
Egypt and Syria made a secret agreement in January 1973 to bring their armies under one command. Hafez al-Assad, the President of Syria was keen on retrieving Golan Heights. As Assad was aware that his country’s weapons were dated, he offered the Israelis a peace deal of they would withdraw from Sinai. Israel rejected the offer. Egypt and Syria then launched a sudden attack on the Yom Kippur religions holiday on 6 October 1973. Though Israel suffered heavy casualties, it could finally push back the Arab forces. But this time, due to UN intervention, Israel was forced to return to 1967 position. Arabs gained nothing out of this war too.
Question 3.
Narrate the history of transformation of Council of Europe into an European Union.
Answer:
- The historical decision taken in the post II World War era was the integration of the States of western Europe.
- In May 1949, ten countries met in London and signed to form a council of Europe, with head quarters at Strasbourg.
- It consisted of a committee with the foreign ministers of the member countries and a Consultative Assembly drawn from the parliaments of foreign countries.
- Initially, the European Defence Community (EDC) and European Coal and Steel community was established with six countries France, West. Germany, Italy, Belgium, Holland and Luxembourg.
- As per the Treaty of Rome signed by the six countries, European Economic Community with headquarters at Brussels was established (EEC).
- The EEC eliminated all types of barriers and made it as a European common market.
- A common Agricultural policy and A common Trade policy was also evolved.
- Throughout 1970’s and 1980’s the EEC kept on expanding.
- The Single European Act (SEA) came into force on July 1, 1987.
- According to the SEA, each member country was given multiple votes, depending on the country’s population.
- The new procedure also increased the role of the European parliament.
- On February 7 1992, The Maastricht Treaty created the European Union.
- In the same year, A common currency Euro was introduced.
- Common monetary policy with common monetary institutions were also planned and implemented.
- At present, the European Union has 28 member states.
- EU established its headquarters at Brussels, Belgium.
- In. 1973, Britain became its member and voted to exit in 2017.
The World after World War II Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The death toll of Taiping Rebellion was ……… million.
(a) 20
(b) 10
(c) 40
Answer:
(a) 20
Question 2.
The Chinese Revolution broke out in the year …………….
(a) 1909
(b) 1906
(c) 1911
(d) 1910
Answer:
(c) 1911
![]()
Question 3.
The unity of China under Yuan Shih – Kai lasted for ………
(a) ten
(b) four
(c) eight
Answer:
(b) four
Question 4.
Kuomintang party was founded in the year …………….
(a) 1906
(b) 1911
(c) 1912
(d) 1905
Answer:
(c) 1912
Question 5.
Soviet Union tested the nuclear bomb in ………
(a) 1944
(b) 1949
(c) 1950
Answer:
(b) 1949
Question 6.
In the year 1928, Chiang-Kai-Sheik captured …………….
(a) Peking
(b) Beijing
(c) Shangai
(d) Nanking
Answer:
(a) Peking
Question 7.
Which European country colonised Vietnam?
(a) England
(b) Spain
(c) France
Answer:
(c) France
Question 8.
Japan’s military base in China was …………….
(a) Manchuria
(b) Mangolia
(c) Port Arthur
(d) Liaotung
Answer:
(a) Manchuria
Question 9.
When did Ho Chi Minh form the Vietnamese Communist party?
(a) 1930
(b) 1931
(c) 1932
Answer:
(a) 1930
Question 10.
Cold war means a war with no …………….
(a) weapons
(b) agreements
(c) Treaties
(d) dominations
Answer:
(a) weapons
Question 11.
European Union traces its origin from the ………
(a) ECSC
(b) EEC
(c) ETC
Answer:
(a) ECSC
Question 12.
……………. was an Inter alliance between the countries of North America and Europe.
(a) NATO
(b) Truman doctrine
(c) Marshall plan
(d) SEATO
Answer:
(a) NATO
![]()
Question 13.
The name of the single European currency ………
(a) Dollar
(b) Yen
(c) Euro
Answer:
(c) Euro
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. The European Union was formed on ………
2. The European parliament meets in ………
3. The main body which drafts proposals for new European laws ………
4. The court of Justice of EU is located in ………
5. The EU’s budgets are managed by the ………
6. The Symbol of the Euro is ………
7. The total number states of European Union ………
8. The cold war period ended with the fall of ………
9. The ……… was a major rebellion.
10. In 1898, the young Emperor, initiated a series of reforms known as the ………
11. The ideas of ……… and Lenin became popular among intellectuals.
12. ……… was the first president of the state of Palestine on April 2, 1989.
13. ……… founded the communist party in Vietnam.
14. ……… occupied Vietnam in 1940.
Answers:
1. 1967
2. Strasbourg
3. The European commission
4. Luxemburg
5. The Court of Auditor
6. €
7. 28
8. Berlin wall
9. Taiping Rebellion
10. Hundred days of reform
11. Marx
12. Yasser Arafat
13. Ho Chi Minh 14. Japan
III. Match the following
| 1. | 1908 | (a) | Chiang Kai Shek captured Hanko |
| 2. | Chiang Kai – Shek | (b) | Baghdad pack |
| 3. | 1925 | (c) | Leader of kuomintang |
| 4. | 1955 | (d) | Geneva conference |
| 5. | 1957 | (e) | Death of Dowager – Empress |
Answers:
1. (e)
2. (c)
3. (a)
4. (b)
5. (d)
| 1. | Euro | (a) | European Union was formed |
| 2. | EU Budgets | (b) | Single European Act |
| 3. | 1967 | (c) | 2002 |
| 4. | July 1, 1987 | (d) | Chancellor of West Germany |
| 5. | Helmut Kohl | (e) | Court of Auditor |
Answers:
1. (c)
2. (e)
3. (a)
4. (b)
5. (d)
IV. Answer briefly:
Question 1.
Write a short note on Mao Tse-tung.
Answer:
Mao was bom in Hunan in South-east China. He came from a wealthy family ,learned man who enrolled himself in teacher’s training college. He supported Manchus. Mao concentrated on strengthening peasants and established People’s Republic of China.
Question 2.
What do you know of Arab nationalism.
Answer:
Since the dawn of the twentieth century, Arab nationalism was growing in Syria and Iraq. Subsequently nationalism became intense in Egypt. In March 1945, the Arab league was formed in Cairo. Its founder members were Egypt, Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, Jordon and Yemen.
![]()
Question 3.
What do you understand by First, Second and Third world countries?
Answer:
The capitalist countries led by the USA were called as First World Countries. The communists led by the Soviet Union came to be known as Second World Countries. The developing countries of the world are called as Third World Countries.
Question 4.
What are the principal objectives of the EU?
Answer:
- To establish European citizenship
- To ensure civil rights of European citizens
- To promote social progress
- To protect European security
- To ensure justice
Question 5.
How did the Soviet Union get disintegrated?
Answer:
The East European Communist states under the Soviet umbrella were in a deep economic and social crisis. The division within the ruling group was growing wider. Gorbachev was put into house arrest. Finally he resigned on 25th Dec. and on 31st Dec 1991. It was dissolved.
Question 6.
What is the significance of the EURO?
Answer:
- The Euro is the name of the single European currency. Its symbol is €.
- The Euro eliminated foreign exchange hurdles encountered by companies doing business across European border.
- It promotes free trade policy.
Question 7.
Write a short note on NAM.
Answer:
The Non-Alignment Movement was called in short as NAM. It emerged at the Bandung conference in 1955. Peaceful co-existence, commitment to peace and security, no military alliances were the principles with which NAM operated.
Question 8.
Write a note on Single European Act.
Answer:
- The Single European Act came into force on July 1, 1987.
- It significantly expanded the EEC’s scope giving the meetings of the EPC a legal basis.
- It also called for more intensive co-ordination of foreign policy among member countries.
- According to the SEA, each member was given multiple votes, depending on the country’s population. Approval of legislation required roughly two-thirds of the votes of all members.
- The new procedure also increased the role of the European parliament.
V. Answer all the questions given under each caption:
Question 1.
Organs of the EU
(a) Which is the Legislative body of the EU?
Answer:
The European Parliament
(b) Where is the seat of the Court of Justice?
Answer:
Luxemburg
(c) What is the function of the European commission?
Answer:
- It is responsible for initiating legislation and the day to day running of the EU.
- It drafts proposals for New European laws and presents to the European parliament and the council.
(d) Who is responsible for the foreign exchange operation?
Answer:
The European central bank.
Question 2.
Palestine Liberation Organisation (PLO)
(a) What type of organisation was PLO?
Answer:
It is a political organisation representing all the Arabs and the descendants who live in Palestine, before the creation of Israel.
(b) What type of war does the PLO engage in?
Answer:
The PLO was engaged in Guerrilla war.
(c) Who was their prominent leader?
Answer:
Yasser Arafat was their prominent leader.
![]()
(d) How did his appearance raised world awareness on the political cause?
Answer:
He was wearing a Harley disguised pistol and carrying an olive branch and dressed in a military uniform.
VI. Answer the following in detail:
Question 1.
Write a detailed report on the formation of the military alliances.
Answer:
The cold war was not a war with weapons. Rather, a war on Political, economical and ideological fronts.
The countries started making military alliances, so that they would have joint commands with standing forces.
North Atlantic Treaty Organisation: In short, it was called as NATO, by the United States and its European allies to resist the Soviet aggression in Europe.
The main aim of the NATO was to maintain peace and security in the North Atlantic region.
Members agreed if any one of them would be attacked, it would be an attack on NATO.
WARSAW PACT: As a counter to the NATO, Soviet Union organised the Soviet bloc countries, under the Warsaw pact, A Joint command of the armed forces with head quarters a Moscow was set up.
SEATO: South East Asia Treaty Organization was organised for the collective security of the South east Asian countries. Their aim is to prevent communism to gain popularity in their region. It was called as Manila pact.
CENTO: Central Treaty organisation was a pact signed by Iran, Iraq, Turkey, Pakistan, Britain. When USA joined it was called CENTO. Prior to that, it was called as Baghdad pact. It was open to any Arab region seeking peace and security in their region.
Question 2.
What are the achievements of the European Union?
Answer:
Single market:-
- The EV has developed a single market through a standarized system of laws, which apply to all member states.
- It ensures the free movement of people, goods, services and capital including the abolition of passport controls.
- It maintains common policies of trade, agriculture, fisheries and regional development.
Common foreign and security policy:-
- The EU is able to conclude treaties with countries and enacts legislation injustice and home affairs.
- It has maintained representation at the World Trade Organisation, G – 8, G – 20 and at the United Nations.
Single Currency:-
- The Euro is the name of the Single European currency
- It was put into circulation on January 1, 2002.
- The symbol of the Euro is €.
- Euro eliminated foreign exchange hurdles encountered by companies doing business across European border and promotes free trade policy.
Enlargement of EU:-
- The Union’s membership has grown from the original six to the present day 28 by successive enlargements.
- The countires acceded to the treaties and by doing so, pooled their sovereignty in exchange for representation in the institutions.
Scientific Research:-
- Scientific development is facilitated through the EUs frame work programmes.
- The independent European Research Council allocates funds to European or national research projects.
![]()
EU’s role in the UNO :-
- The EU has established a strong relationship with the UNO.
- The EU co-operates with the UNO on a broad range of areas.
- It extends financial support to UN programmes and projects.
Other Achievements:-
- The EU is the largest contributor of foreign aid in the world.
- Above all, unity was brought by the EU in the Eurozone.