You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science History Solutions Chapter 3 World War II
World War II Textual Exercise
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
When did the Japanese formally sign of their surrender?
(a) 2 September, 1945
(b) 2 October, 1945
(c) 15 August, 1945
(d) 12 October, 1945
Answer:
(a) 2 September, 1945
Question 2.
Who initiated the formation of League of Nations?
(a) Roosevelt
(b) Chamberlain
(c) Woodrow Wilson
(d) Baldwin
Answer:
(c) Woodrow Wilson
![]()
Question 3.
Where was the Japanese Navy defeated by the US Navy?
(a) Battle of Guadalcanal
(b) Battle of Midway
(c) Battle of Leningrad
(d) Battle of El Alamein
Answer:
(b) Battle of Midway
Question 4.
Where did the US drop its first atomic bomb?
(a) Kavashaki
(b) Innoshima
(c) Hiroshima
(d) Nagasaki
Answer:
(c) Hiroshima
Question 5.
Who were mainly persecuted by Hitler?
(a) Russians
(b) Arabs
(c) Turks
(d) Jews
Answer:
(d) Jews
Question 6.
Which Prime Minister of England who signed the Munich Pact with Germany?
(a) Chamberlain
(b) Winston Churchill
(c) Lloyd George
(d) Stanley Baldwin
Answer:
(a) Chamberlain
Question 7.
When was the Charter of the UN signed?
(a) June 26, 1942
(b) June 26, 1945
(c) January 1, 1942
(d) January 1, 1945
Answer:
(b) June 26, 1945
Question 8.
Where is the headquarters of the International Court of Justice located?
(a) New York
(b) Chicago
(c) London
(d) The Hague
Answer:
(d) The Hague
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. Hitler attacked ……… which was a demilitarised zone.
2. The alliance between Italy, Germany and Japan is known as ……..
3. ……… started the Lend Lease programme.
4. Britain Prime Minister …….. resigned in 1940.
5. Saluting the bravery of the ………. Churchill said that “Never was so much owed by so many to so few”.
6. is a device used to find out the enemy aircraft from a distance.
7. ………. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights set forth fundamental human rights in articles.
8. After the World War II ……… was voted into power in Great Britain.
Answers:
1. Rhineland
2. Axis power
3. US – President Roosevelt
4. Chamberlain
5. British Royal airforce
6. Radar
7. 30
8. Labour party
III. Choose the correct statement.
Question 1.
(i) Banking was a major business activity among Jews.
(ii) Hitler persecuted the Jews.
(iii) In the concentration camps Jews were killed.
(iv) The United Nations has currently 129 member countries in it.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (i) and (ii) is correct
(c) (ii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (i) is correct and (ii), (iii) and (iv) are correct
Answer:
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct 2.
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion: President Roosevelt realised that the United States had to change its policy of isolation.
Reason: He started a programme of Lend Lease in 1941.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is right but R is not the correct reason
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) R is right but it has no relevance to A
Answer:
(b) A is right but R is not the correct reason
IV. Match the following.

Answers:
1. (e)
2. (d)
3. (a)
4. (b)
5. (c)
V. Answer the questions briefly.
Question 1.
Mention the important clauses of the Treaty of Versailles relating to Germany.
Answer:
Here are the important clauses of the Treaty of Versailles relating to Germany:
- Germany was forced to give up territories to the west, north and east of the German border;
- Germany had to disarm and was allowed to retain a very restricted armed force (army, navy and air force);
- As reparations for the War, Germany was expected to pay for the military and civilian cost of the War to the Allied nations.
Question 2.
Who were the three prominent dictators of the post World War I ?
Answer:
Mussolini of Italy, Hitler from Germany and Franco from Spain were the three prominent dictators of post-world war I.
Question 3.
How did Hitler get support from the people of Germany?
Answer:
Hitler was well aware of the discontent among the Germans. He used his oratorical skills to sway the common people and promised them to return the glorious military past of Germany. He founded the National Socialist Party, generally known as “the Nazis”. The fundamental platform on which Hitler built his support was the notion of the racial superiority of the Germans as a pure. ‘Aryan’ race and a deep-seated hatred of the Jews.
Hitler came to power in 1933 and ruled Germany for twelve long years.
Question 4.
Describe the Pearl Harbour incident.
Answer:
America had installed strong naval base in Pearl harbour, Hawaii on December 1941, Japan attacked America’s pacific fleet without any warning. Japan’s idea was to cripple America so that they can freely move towards South-east Asian countries. But, when many battle ships and numerous fighter planes were destroyed, the U.S.A. declared war on Japan.
![]()
Question 5.
What do you know of Beveridge Report?
Answer:
In 1942, a report commonly known as the Beveridge Report was published in the United Kingdom. The report proposed a series of measures which the government should adopt to provide citizens with adequate income, health care, education, housing and employment to overcome poverty and disease which were the major impediments to general welfare.
Question 6.
Name the Bretton Woods Twins.
Answer:
The World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) are referred to as the Bretton Woods Twins. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) and International Development Agency (IDA) together often referred as the World Bank.
Question 7.
What are the objectives of IMF?
Answer:
The objectives of the IMF are to:
- foster global monetary cooperation,
- secure financial stability,
- facilitate international trade,
- promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and
- reduce poverty around the world.
VI. Answer the questions given under each caption.
Question 1.
Battle of Stalingrad
(a) When did Germany attack Stalingrad?
Answer:
The Germans attack Stalingrad in August 1942.
(b) What were the main manufactures of Stalingrad?
Answer:
The main manufactures of Stalingrad were armaments and tractors.
(c) What was the name of the plan formulated by Hitler to attack Stalingrad?
Answer:
“Operation Blue” or “Fall Blau” was the name of the plan formulated by ‘ Hitler to attack Stalingrad.
(d) What is the significance of the Battle of Stalingrad?
Answer:
The people of Russia successfully defended the city of Stalingrad. It stopped the German advance into the Soviet Union and favoured the allies. It was a great patriotic war by the Russians.
Question 2.
Japanese Aggression in South-east Asia
(а) Name the South-east Asian countries which fell to the Japanese.
Answer:
Guam, the Philippines, Hong Kong, Singapore, Malaya, the Dutch East Indies (Indonesia) and Burma.
(b) Account for the setback of Allies in the Pacific region?
Answer:
The Allies faced many reverses in the Pacific region because of their inadequate preparations. The colonial rulers, especially the British, withdrew from their territories, leaving the local people to face the atrocities of the Japanese.
(c) What is the significance of Battle of Midway?
Answer:
The US navy defeated the Japanese navy in the Battle of Midway.
(d) What happened to the Indians living in Burma?
Answer:
Many Indians walked all the way from Burma to the Indian border, facing hardships. Many died of disease and exhaustion. Those who remained suffered under the Japanese.
Question 3.
General Assembly and Security Council
(a) List the permanent member countries of the Security Council.
Answer:
The United States, Britain, France, Russia and China are permanent member countries of the Security Council.
(b) What is the Holocaust?
Answer:
Holocaust refers to World’s worst ever genocide of killing nearly six million Jews by the Germans during the Second World War.
(c) Who was the Chairperson of the UN Commission on Human Rights?
Answer:
The widow of the American President Franklin Roosevelt was the chairperson of the UN commission on Human Rights.
(d) What is meant by veto?
Answer:
Veto is an constitutional right to reject a decision or proposal made by a law making body. Each of the permanent members of the UNO has the right of veto.
VII. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
Attempt an essay on the rise and fall of Adolf Hitler.
Answer:
Hitler was great orator. He swayed the people by his impassioned speeches, promising a return to the glorious military past of Germany. He founded the National Socialist Party, known as ‘the Nazis’. He came to power in 1933 and ruled Germany till 1945, with a small group of fanatic followers. He rearmed Germany. He made huge expenditure on the recruitment of armed forces and the manufacture of armaments and machinery for the army, navy and air force. Soon the economic condition of Germany got strengthened and the problem of unemployment came to an end. In 1938, Hitler invaded Austria and Czechoslovakia. Sudetenland in Czechoslovakia was German-speaking, and Hitler’s claim was that the German-speaking people should be united in one nation. Though Hitler gave an assurance in the Munich Pact that Germany would not attack any other country, but this was broken immediately.
In 1939, he invaded Czechoslovakia. Poland was attacked next, and this was the final act which resulted in declaration of war by Britain and France against Germany. In June 1940, Italy joined Germany, and in September 1940, Japan also joined the Axis Powers. The German army followed a tactic of ‘lightning strike’ to storm into various countries and overrun them. In June 1941, German army invaded Russia and remained successful in the initial years. But ultimately got defeated due to the resistance by Soviet army, and the fierce Russian winter. In the Battle of Alamein 1942, the Allied forces counter-attacked and defeated the German and Italian forces in North Africa. The German army was chased across the desert, out of North Africa. The war continued till Hitler’s suicide in April 1945.
![]()
Question 2.
Analyse the effects of World War II.
Answer:
The long term effects of II World War were mostly unpleasant but a little platform of cherishment to the colonies by way of extending them independence. The radiation from the atom bombs were not clearly estimated at the time of war.
New geo-political power alignment: The world got itself split into two new political super powers. One led by the United States with anti-communist ideas and the other one led by Soviet Russia with communist ideas.
Nuclear proliferation: The United States and the Soviet Union built large stock of nuclear powered weapons. This was just like a race between them. Britain and France also joined in the race. More and more resources were spent by the countries for destructive purposes.
International agencies: International agencies like the United Nations Organisation, the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund came into existence.
Independence of the colonies: Colonial powers were forced to give independence.
Empowerment of Women: Women power entered into the labour force in great numbers. There was a change in social relations and more and more women become economically independent.
Question 3.
Assess the structure and activities of the UN.
Answer:
The United Nations came into existence in the year 1945 to achieve lasting peace among all nations which were inter-dependent. It functions like any government, through its principal organs which are similar to the legislative, executive and judicial wings of a state.
- The General Assembly is the body in which each member state is represented. It meets once a year and issues of interest and points of conflict are discussed in the Assembly.
- The Security Council has fifteen members, five of them (the USA, Britain, France, Russia and China) are permanent members. The other ten temporary members are elected in rotation from different parts of the world. Each of the permanent members has the right to veto any decision by the other members of the Security Council.
- The UN Secretariat is headed by the Secretary General, who is elected by the General Assembly on the recommendation of the Security Council.
- The International Court of Justice is the Judicial wing of the United Nations. Its headquarter is at The Hague.
- The fifth organ of the UN is the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC). It is responsible for coordinating all the economic and social work of the United Nations.
Activities of the United Nations
Human rights, the problems of refugees, climate change, gender equality are all within the ambit of the activities of the United Nations. The UN Peace-keeping force has acted in many areas of conflict all over the world.
VIII. Students Activity
Question 1.
Group project involving students to prepare an album with pictures on different phases of the World War II.
Answer:
You can do this activity under the guidance of your teacher.
Question 2.
A debate in the class on the success or failure of the UN in preserving World Peace.
Answer:
You can do this activity by discussing the points in the class under the guidance of your teacher.
![]()
Question 3.
Marking the Allies and Axis countries, as well as important battlefields of World War II in a world map.
Answer:
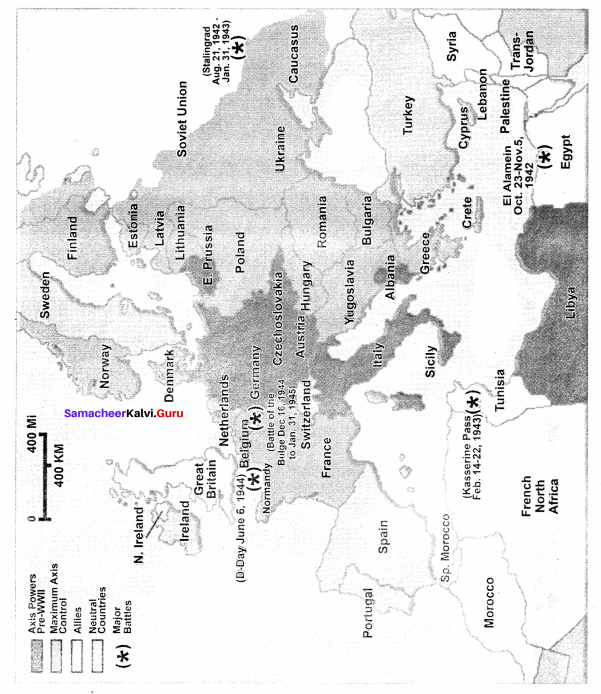
IX. Map Work
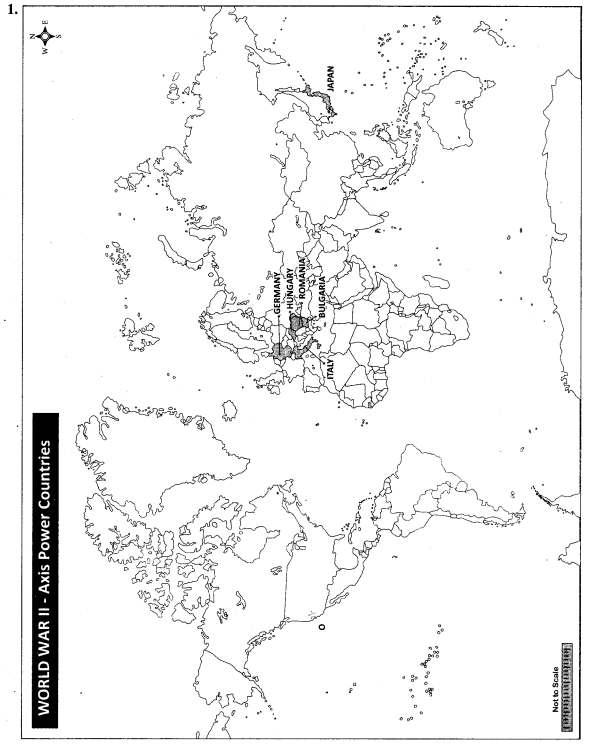
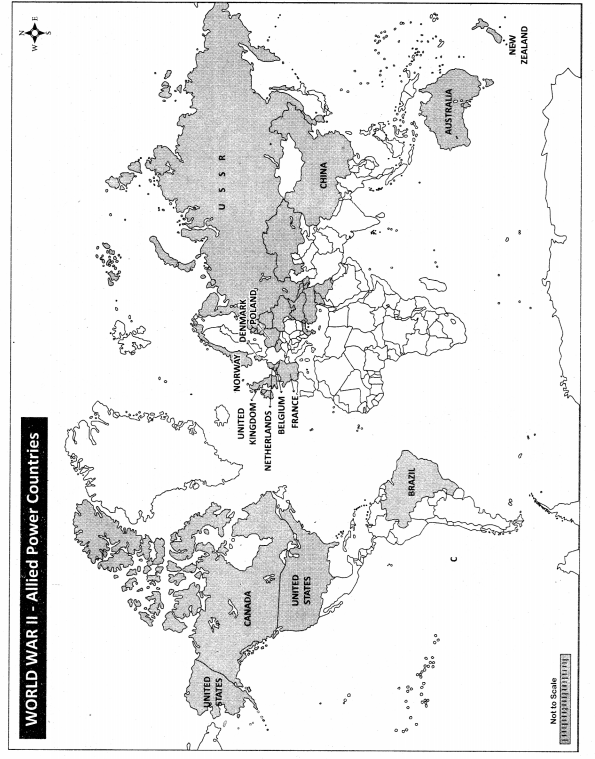
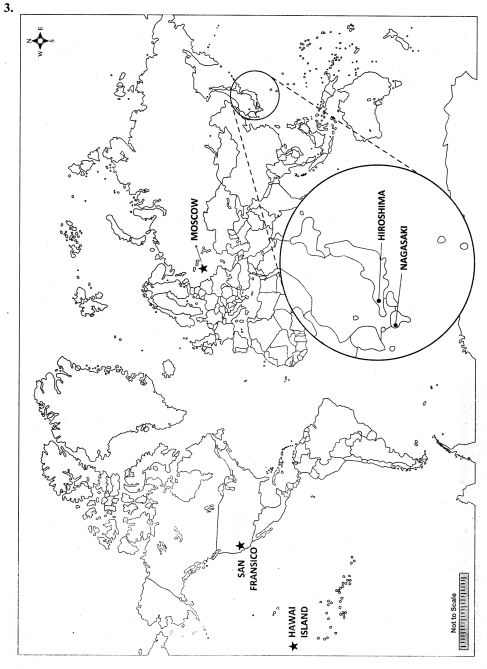
Mark the following on the world map:
1. Axis Power Countries
2. Allied Power Countries
3. Hiroshima, Nagasaki, Hawai Island, Moscow, San Fransico
2.
World War II Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
This treaty contained the seeds of the second world war ………
(a) Treaty of London
(b) Treaty of Rome
(c) Treaty of Versailles
Answer:
(c) Treaty of Versailles
Question 2.
The Dictator of Spain was called:
(a) Mussolini
(b) Franco
(c) Hitler
(d) Edi-Amin
Answer:
(b) Franco
Question 3.
The country emerged as a World power after the First World war was ………
(a) China
(b) India
(c) Japan
Answer:
(c) Japan
Question 4.
Hitler came to power in ……………….. and ruled till 1945.
(a) 1932
(b) 1936
(c) 1934
(d) 1933
Answer:
(d) 1933
Question 5.
In September 1938, Hitler threatened a war on ………
(a) Czechoslovakia
(b) Poland
(c) Finland
Answer:
(a) Czechoslovakia
Question 6.
Italy invaded Ethiopia in ……………….. when they asked help from League of nations, got no help.
(a) 1931
(b) 1935
(c) 1937
(d) 1939
Answer:
(b) 1935
![]()
Question 7.
Blitzkrieg means a ………
(a) Lightning war
(b) Trench warfare
(c) Guerilla warfare
Answer:
(a) Lightning war
Question 8.
World War II was ……………….. war.
(a) Traditional
(b) Modem
(c) Scientific
(d) Alarming
Answer:
(b) Modem
Question 9.
Hitler signed the Non-Aggression pact with ……………
(a) Gorbachev
(b) Stalin
(c) Lenin
Answer:
(b) Stalin
Question 10.
In the year ……………….. Italy and Japan joined the axis powers.
(a) 1939
(b) 1937
(c) 1935
(d) 1940
Answer:
(d) 1940
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. The great powers of the world split up into two opposing groups namely the ……… and the ………
2. ……… was humiliated by the Treaty of Versailles.
3. The dictators ……… and ……… started Nazism and Fascism.
4. The Japanese attacked American fleet stationed at ……… on December 7, 1941.
5. America dropped atom bombs on the cities of ……… and ……… on August 6th and
9th of 1945.
6. The Second World War came to an end in ………
7. The German Air force was known as ………
8. In 1941, Prime Minister Winston Churchill and president F.D.Roosevelt concluded the ………
9. The Munich agreement was signed between Britain and ………
10. In 1945, at the end of the Second World War Hiroshima and Nagasaki were destroyed by ………
11. Hitler sent his airforce to drop bombs on ………
12. The UNO was established in ………
13. The UN charter was signed at ………
14. UNO’s main deliberative body is ………
15. The seat of International Court of Justice is at ………
Answers:
1. Allies and Axis
2. Germany
3. Hitler and Mussolini
4. Pearl Harbour
5. Hiroshima and Nagasaki
6. 1945
7. Luftwaffe
8. Atlantic Charter
9. Germany
10. America
11. Russia
12. 1945
13. San Francisco
14. The General Assembly
15. The Hague
III. Match the following:
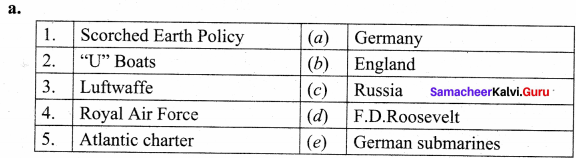
Answers:
1.(c)
2. (e)
3. (a)
4. (b)
5. (d)
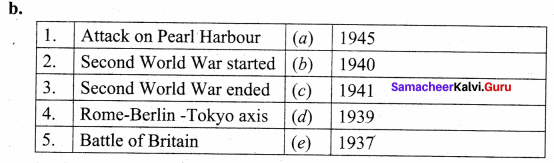
Answers:
1. (c)
2. (d)
3. (a)
4. (e)
5. (b)
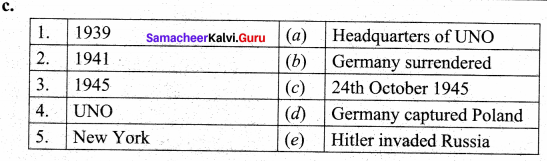
Answers:
1. (d)
2. (e)
3. (b)
4. (c)
5. (a)
IV. Answer briefly:
Question 1.
How did Japan sowed the seeds for Second World War?
Answer:
- Japan emerged as a world power after the First World War.
- The industrial development and economic growth forced Japan to follow the policy of imperialism.
- It signed Rome – Berlin – Tokyo Axis with Italy and Germany and sowed the seeds for the second world war.
Question 2.
List down the important organs of the UN.
Answer:
- FAO – Food and Agricultural organisation
- WHO – World Health Organisation
- UNESCO – United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural organisation
- UNICEF – United Nations Children’s Fund
- UNDP – United Nations Development programme
Question 3.
What was the immediate cause of the Second World War?
Answer:
- In 1939, Hitler demanded from Poland and right to construct a military road connecting East Prussia and Germany through Polish corridor.
- He also demanded the surrender of Danzig.
- When Poland refused, Hitler made a lightning attack on Poland known as Blitzkrieg on 1st September 1939. It was the immediate cause of the second world war.
- Britain and France declared war on Germany in support of Poland and Second World War started.
Question 4.
What are the principal organs of the UNO?
Answer:
- The General Assembly
- The Security Council
- The Secretariat
- The International Court of Justice
- The Economic and Social Council.
![]()
Question 5.
Write a short note on Atlantic charter.
Answer:
- In August 1941, the British prime minister Winston Churchill and U.S. president F.D.Roosevelt met on the board of the battleship Augusta.
- They signed the Atlantic charter and agreed to launch a massive attack against the common enemy Germany.
Question 6.
What is meant by “Lend-Lease”?
Answer:
President Roosevelt of U.S.A. brought the Lend-Lease programme in 1941. Arms, food, military equipment, other supplies were sent to power in the name of loan which would be returned after use.
Question 7.
What were the main objectives of the UNO?
Answer:
- To maintain international peace and security.
- To develop friendly relations among nations.
- To settle International disputes by peaceful means.
- To be a centre for helping nations to achieve these goals.
Question 8.
What is the difference between a ‘Vote’ and a ‘Veto’?
Answer:
Veto: It is the right to block a decision or can be called as Negative vote by law.
Vote: It is the right law that is done infavour of a person/party. This can be called as positive vote.
Question 9.
Mention any two major achievements of the UNO.
Answer:
- The UNO settled disputes between Israel and Palestine, Iran and Iraq, and withdrawal of Soviet troops from Afghanistan.
- It has signed many Nuclear Test Ban Treaties like NTBT in 1963 and CTBT in 1996.
Question 10.
What is meant by the Holocaust?
Answer:
The word ‘Holocaust’ refers to the mass killing of nearly six million jews by the Germans during II World War. This was done because the Nazis completely want to exterminate jews completely from Germany and all other countries where they are.
Question 11.
Name the five permanent members of the security council.
Answer:
The USA, the UK, the France, the Russian Federation and the China.
Question 12.
What are the official languages of the UNO?
Answer:
The official languages of the UNO are Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian and Spanish. However its working languages are English and French.
Question 13.
How does the UNO get its financial aid?
Answer:
UNO gets its financial aid mainly from USA and from other member nations.
![]()
V. Answer all the questions given under each caption:
Question 1.
Aggressive Act of Hitler
(a) When did Hitler came to power?
Answer:
Hitler came to power in 1933.
(b) What did he do to bring back glorious Germany?
Answer:
He began to re-arm Germany. The recruitment of the armed forces, new armaments and machinery for the army, navy and air force.
(c) What was the name of the alliances he had with Japan and Italy?
Answer:
Rome-Berlin-Tokyo axis.
(d) What was his claim for Sudetenland?
Answer:
He claimed that the German-speaking people should be United into one nation and Sudetenland people were German-speaking people.
Question 2.
End of War
(a) Where did a big American and British force land?
Answer:
The American and British force landed in Normandy.
(b) With whom did they join?
Answer:
They joined with the secret underground French forces.
(c) What did Hitler do?
Answer:
He committed suicide.
(d) When did America drop atom bomb on Hiroshima and Nagasaki?
Answer:
America dropped atom bombs on the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki on August 6th and 9th of 1945.
Question 3.
Outbreak Of II World War.
(a) What are the axis powers?
Answer:
Germany, Italy and Japan.
(b) What is the significance of Blitzkrieg?
Answer:
Blitzkrieg means lightning strike which was the tactic followed by Germany to storm into various countries and over run them.
(c) Which country’s naval force was very powerful among the european naval forces?
Answer:
The British Royal Navy was very powerful among the European naval forces.
(d) How did British and French Saved their soldiers at the Battle of Dunkrik?
Answer:
British saved their men by calling all those who had boats/small ship and put them into use.The French formed the nucleus of their army.
VI. Answer the following in detail:
Question 1.
Write and explain any two International agencies of the UNO.
Answer:
The need for international co-operation and achieving peace among the world nations led to the formation of the international agencies of the UNO.
These agencies are:
- The World Bank
- The International Monetary Fund
- The International Labour Office (ILO)
- The International Finance Corporation.
The World Bank:
(i) The World Bank was established in 1945. It is located in Washington, USA. All the members of IMF are also the members of the World Bank.
(ii) The two main organs of the World Bank are the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) and the International Development Agency (IDA). Together they are called “World Bank”.
(iii) Earlier, the IBRD was funding only for the reconstruction activities of the European countries after World War II. Later, its work expanded to promote economic development for poor countries and development projects for developing countries.
(iv) The Bank also works on the key areas like poverty alleviation, and other basic issues of the Societies of the World. The International Development Agency (IDA): It lends money to the governments for developmental activities.
The International Development Agency (IDA): It lends money to the governments for developmental activities.
These loans are given at low rate of interest and for 50 long years. Therefore they are called as soft loans.
The International Finance Corporation (IFC): It mainly functions with private enterprises in developing countries.
The International Labour Office: Is located in Geneva, Switzerland. It works on issues related to Labour and employment.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the major achievements of the UNO?
Answer:
- The UNO has rendered a great service in establishing peace, and security by solving various problems.
- Political disputes are solved by security council, legal disputes by International court of Justice and others by special agencies.
- UNO has solved many International disputes.
- It preserves peace in the world through peaceful negotiations.
- It settled disputes between Israel and Palestine, Iran and Iraq and withdrawal of Soviet troops from Afghanistan.
- In the conference, all countries adopted “Agenda 21”, a blueprint to promote economic development and protect natural resources.
- The UNO established the International Research and Training Institute for the Advancement of Women.
- It has supported many programmes and projects to improve the quality of life for women in over 100 countries.
- The UNO played a vital role in the Suez canal crisis of 1956. It made France, Britain, and Israel to withdraw their troops from Egypt.
- The UNO also settled the Korean war and Vietnam war.
Question 3.
Describe the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Answer:
- The International Monetary Fund was primarily the brainchild of Harry Dexter White and John Maynard Keynes, the famous economist.
- It was formally organized in 1945 with 29 member countries.
- Now it has a membership of 189 countries.
- Its primary objective is to ensure financial stability and development across the world,
- The main agenda is to promote international monetary co-operation, expansion of international trade and exchange stability.
- The Fund lends money from its resources to countries facing balance of payments problems.
- It imposes stringent conditions on the borrowing nations to tighten their budgets, practice fiscal prudence and reduce their expenditure.
- This is often unpopular, especially among the developing countries which may have to cut down on various programmes which provide subsidies to the people.
