You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Geography Solutions Chapter 4 Resources and Industries
Resources and Industries Textual Exercise
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
Manganese is used in …
(a) Storage batteries
(b) Steel Making
(c) Copper smelting
(d) Petroleum Refining
Answer:
(b) Steel Making
![]()
Question 2.
The Anthracite coal has:
(a) 80 to 95% Carbon
(b) Above 70% Carbon
(c) 60 to 70% Carbon
(d) Below 50% Carbon
Answer:
(a) 80 to 95% Carbon
![]()
Question 3.
The most important constituents of petroleum are hydrogen and
(a) Oxygen
(b) Water
(c) Carbon
(d) Nitrogen
Answer:
(c) Carbon
Question 4.
The city which is called as the Manchester of South India is:
(a) Chennai
(b) Salem
(c) Madurai
(d) Coimbatore
Answer:
(d) Coimbatore
Question 5.
The first Jute mill of India was established at
(a) Kolkata
(b) Mumbai
(c) Ahmedabad
(d) Baroda
Answer:
(a) Kolkata
Question 6.
The first Nuclear Power station was commissioned in:
(a) Gujarat
(b) Rajasthan
(c) Maharashtra
(d) Tamil Nadu
Answer:
(c) Maharashtra
Question 7.
The most abundant source of energy is
(a) Biomass
(b) Sun
(c) Coal
(d) Oil
Answer:
(b) Sun
Question 8.
The famous Sindri Fertilizer Plant is located in:
(a) Jharkhand
(b) Bihar
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Assam
Answer:
(a) Jharkhand
Question 9.
The nucleus for the development of the Chotanagpur plateau region is
(a) Transport
(b) Mineral Deposits
(c) Large demand
(d) Power Availability
Answer:
(b) Mineral Deposits
![]()
Question 10.
One of the shore based steel plants of India is located at:
(a) Kolkata
(b) Tuticorin
(c) Goa
(d) Visakhapatnam
Answer:
(d) Visakhapatnam
II. Match the following.

Answer:
a – 2,
b – 1,
c – 4,
d – 5,
e – 3

Answer:
a – 5,
b – 4,
c – 1,
d – 2,
e – 3
III. Answer the following questions briefly.
Question 1.
Define the resource and state its types.
Answer:
Any matter or energy derived from the environment and is used by living things including humans is termed as resource. Based on continued availability classified into Renewable and Non-Renewable Resources.
Question 2.
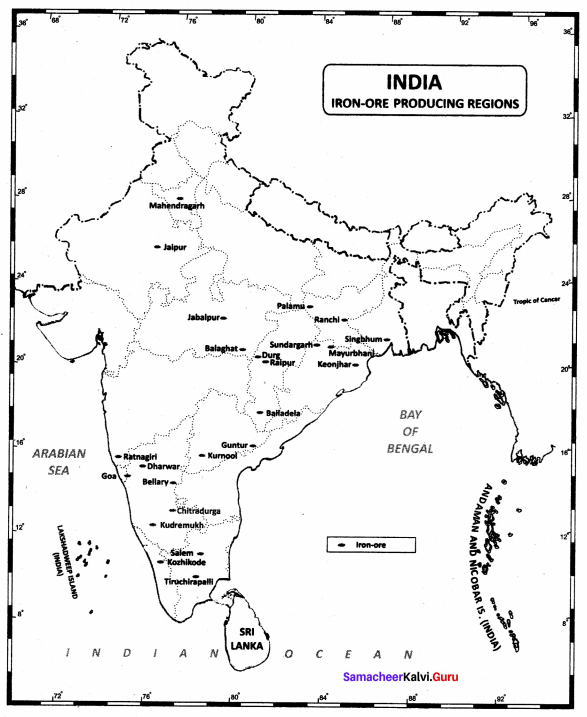
Name the states that lead in the production of Iron ore in India.
Answer:
Jharkhand, Odisha Chhattisgarh, Karnataka, Andhra pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
Question 3.
What are the minerals and its types?
Answer:
Mineral is a natural substance of organic or inorganic origin with definite chemical and physical properties.
Minerals are broadly grouped into two Metallic minerals and Non-Metallic minerals.
![]()
Question 4.
State the uses of magnesium.
Answer:
- It is an important minerals used for making iron and steel and serves as basic raw material for alloying.
- It is also used in manufacturing bleaching powder, insecticides, paints and batteries.
Question 5.
What is natural gas?
Answer:
- Natural gas is a natural hydrocarbon gas mixture primarily consisting of methane.
- Usually accompanies the petroleum accumulations.
- It is formed when layers of decomposed plants and animals are exposed to intense heat and pressure over thousands of years.
Question 6.
Name the different types of coal with their carbon content.
Answer:
- Anthracite: contains 80 to 90% Carbon
- Bituminous: contains 60 to 80% Carbon
- Lignite : 40 to 90% Carbon
- Peat: Contains less than 40% Carbon
Question 7.
Mention the major areas of jute.production in India.
Answer:
- The major Jute producing area are in West Bengal and concentrated along Hoogly river within the radius of six kilometer of Kolkata.
- Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, Chattisgarh and Odisha are other jute producing areas.
Question 8.
Name the important oil producing regions of India.
Answer:
Oil in India is obtained from both from on-shore and off-shore areas.
Western Coast off shore oil fields:
- Mumbai high oil fields
- Gujarat Coast
- Basseim oil field, South of Mumbai high
- Ankleshwar
- Cambay-Luni Region
- Ahemedabad-Kalol Region
- Aliabet oil feild, south of Bhavanagar
Eastern Coast off shore oil fields:
- Brahmaputra valley
- Digboi oil feilds
- Nahoratiya oil fields
- Moran-Hugrijan oil field
- Rudrasagar-Lawa oil feilds
- Surrma valley
- Offshore of Andaman and Nicobar, Gulf of Mannar, Baleshwar coast, Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh.
IV. Distinguish between.
Question 1.
Renewable and Non-renewable resources.
Answer:

Question 2.
Metallic and non-metallic minerals.
Answer:
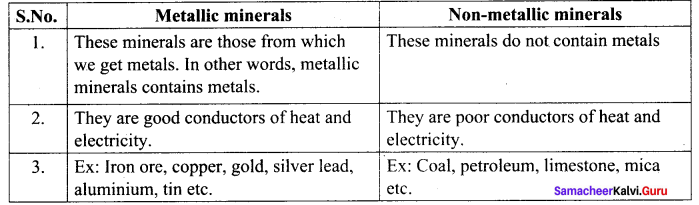
![]()
Question 3.
Agro based industry and mineral based industry.
Answer:
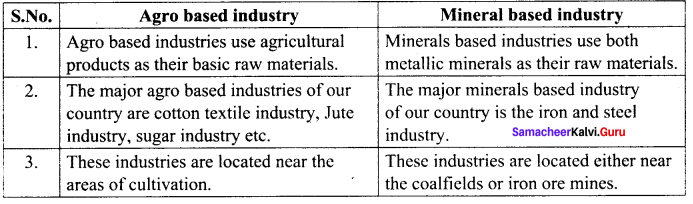
Question 4.
Jute industry and the sugar industry.
Answer:
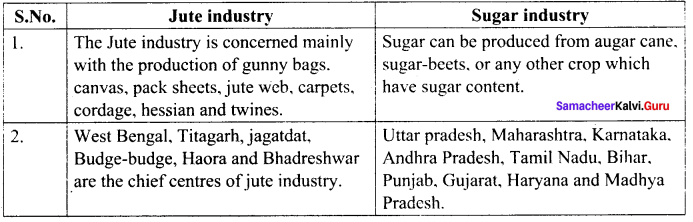
Question 5.
Conventional energy and Non-conventional energy.
Answer:
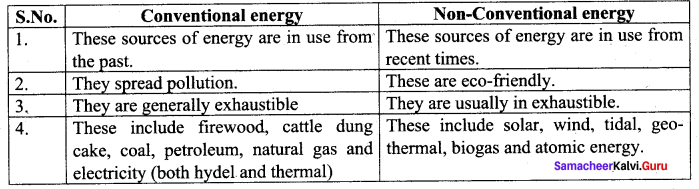
V. Answer the following in a paragraph.
Question 1.
Write about the distribution of cotton textile industries in India.
Answer:
The cotton textile industry is the largest organized modem industry of India.
The major cotton textile industries are concentrated in the States of Maharashtra. Gujarat, West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
The location of cotton textile industries states are due to the presence of black cotton soil, humid climate, cheap labour, availability of capital, transport facilities, port facilities, power supply and good market.
Mumbai: Manchester of India.
Coimbatore: Manchester of South India
Kanpur: Manchester of Uttar Pradesh
The above cities have more number of cotton mills.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the factors responsible for the concentration of jute industries in the hoogly region.
Answer:
Most of the Jute mills of India are centralised in “Hooghly Basin” of the West Bengal. The factors responsible for the concentration of Jute industry in Hooghly Basin region are:
- Ganga, Brahmaputra delta regions grow about 90% of India’s Jute and provides raw materials in jute mills.
- Coal for power is obtained from Raniganj coalfields.
- Hooghly River provides cheap water transport and soft water for washing, processing, retting and dyeing jute.
- Humid climate is favourable for spinning and weaving.
- Cheap labour is available from West Bengal, Bihar and Uttar Pradesh.
- Conductive port facility of Kolkata for export and import at Kolkata.
In addition to West Bengal, Jute mills are also located in Andhra pradesh, Uttar pradesh, Bihar, Madhya pradesh and Odisha.
India exports jute products to Australia, U.K, Thailand, U.S.A, Canada, Argentina, East Africa, New Zealand and Indonesia.
Question 3.
Write an account on the major iron and steel industries of India.
Answer:
1. Mineral based industries:
- The major minerals based industry of our country is the iron and steel industry.
- It is a key or basic industry and lays the foundation for other industries.
- These industries form the economic backbone of a country.
2. Location of Iron and Steel Industries:
Most of our country’s major iron and steel industries are located in the Chotanagpur plateau region.
3. Distribution of Iron and Steel Industries:
India has 11 integrated steel plant and 150 mini steel plants and a large number of rolling and re-rolling mills.
- Tata Iron and Steel Company [TISCO]: In 1911, Tata Iron and Steel Company was setup at Jamshedpur. Its major products are Pig Iron and Crude steel.
- Indian Iron and Steel Company [IISCO]: The Steel plant at Kulti, Bumpur and Hirapur were integrated and the Indian iron and steel company was set up at Bumpur in 1972.
- Visweshwaraya Iron Steel Ltd(VISL): Visweshwaraya Iron Steel Limited was set up in 1923 at Bhadravati in Karnataka. Its major products are alloy and sponge steel.
-
- Hindustan Steel Limited (HSL) – Bhilai: It is located in Durg district of Chattisgarh. It started its production in 1957. Its major products are Railway Equipment and shipbuilding.
- Hindustan Steel Limited (HSL) – Rourkela: It was established in 1965 in Odisha. Its major products include hot and cold rolled sheets, Galvanized sheets and electrical plates.
- Hindustan Steel Limited (HSL) – Durgapur: It was established in 1959 in Durgapur of West Bengal. Its major products are alloy,steel, construction materials and railway equipments.
- Hindustan Steel Limited (HSL) – Bokaro: It is situated in the Hazaribagh district of Jharkhand. It started its operation in 1972. Its major products are sludge and slog.
- Salem Steel Ltd: It is located at salem in Tamil Nadu. It started its production in 1982. The major products are stainless steel.
- Vijayanagar Steel Plant: The Vijayanagar Steel Plant has been set up at Tomagal in Karnataka. It started its production in 1994. The major products are flat steel and long steel.
- The Visakhapatnam Steel Plant(VSP): It started its operation in 1981 at Visakhapatnam in Andhra pradesh. Its major products are Hot metal.
4. Mini Steel Plants:
- Mini steel plants are decentralized secondary units with capacity ranging from 10,000 tonnes to 5 lakh tonnes per year.
- They produce mild steel, alloy steel and stainless steel.
- Most of the mini steel plants are located in areas far away from the major steel plants so that they can meet the local demands.
VI. On the outline map of India mark the following
Question 1.
Iron ore production centres.
Answer:
Question 2.
Centres of Petroleum and Natural Gas production.
Answer:
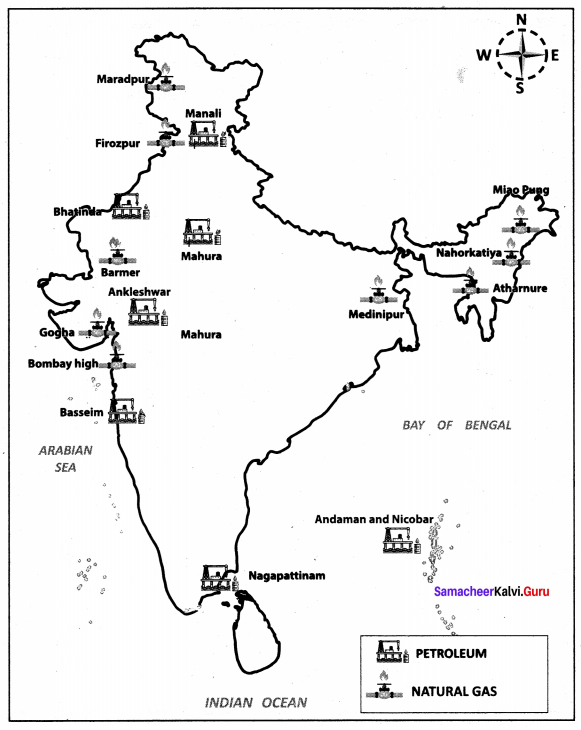
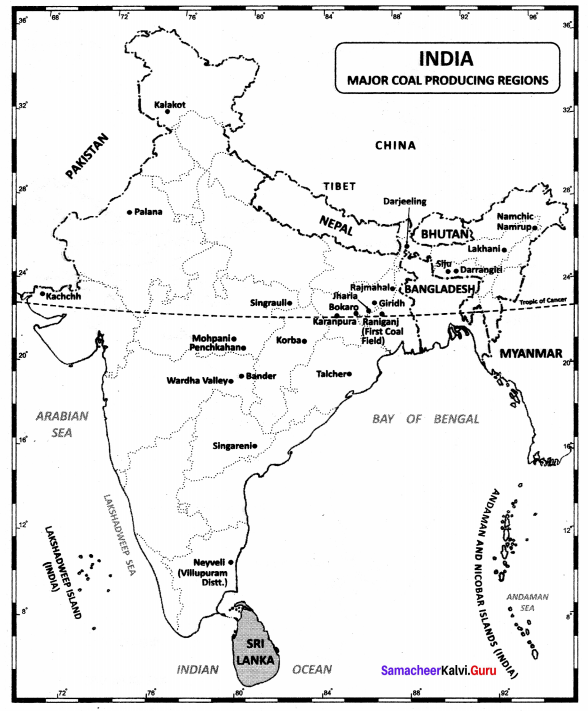
Question 3.
Coal mining centres.
Answer:
Question 4.
Areas of cltivation of cotton.
Answer:
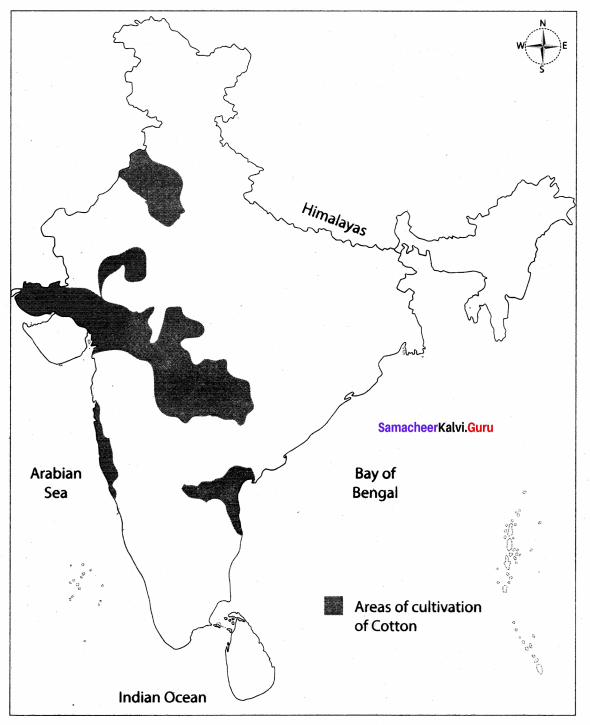
Question 5.
Iron and Steel Industries.
Answer:
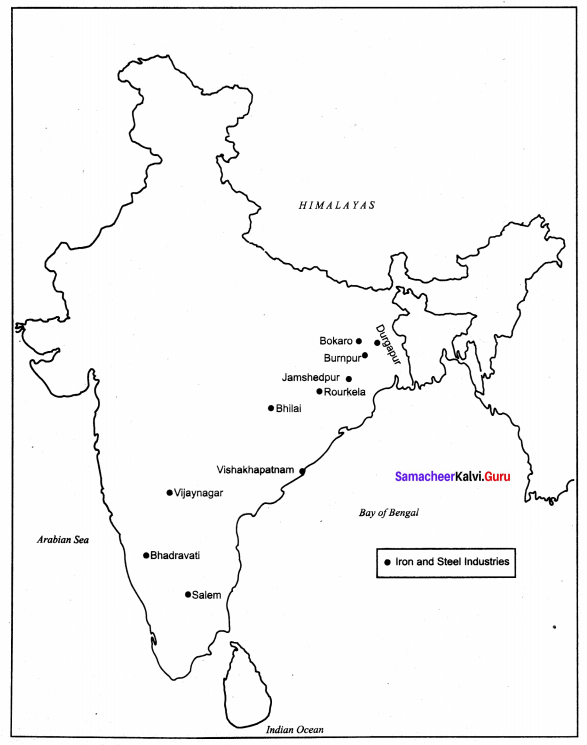
Resources and Industries Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
The cotton textile industry is ……..
(a) Mineral-based industry
(b) Agro-based industry
(c) Forest-based industry
Answer:
(b) Agro-based industry
Question 2.
………………. is the largest coal-producing state in India.
(a) Rajasthan
(b) TamilNadu
(c) Jharkhand
(d) Odisha
Answer:
(c) Jharkhand
![]()
Question 3.
Tata Iron and Steel industry is located at ………
(a) Durgapur
(b) Bhilai
(c) Jamshedpur
Answer:
(c) Jamshedpur
Question 4.
………………. is the oldest oil field in the country.
(a) Gulf of Mannar
(b) Dibrugarh
(c) Digboi
(d) Rudra Sagar
Answer:
(c) Digboi
Question 5.
The City Known as Electronic Capital is ……….
(a) Kanpur
(b) Delhi
(c) Bangalore
Answer:
(c) Bangalore
Question 6.
The flexible mode of power generation is ………………. very quickly adapting to changing demands.
(a) Thermal power
(b) Hydropower
(c) Solar power
(d) Nuclear power
Answer:
(b) Hydropower
Question 7.
…….. is the major exporter of jute.
(a) India
(b) China
(c) Bangladesh
Answer:
(c) Bangladesh
Question 8.
Development of wind power in India began in the year:
(a) 1976
(b) 1966
(c) 1986
(d) 1906
Answer:
(c) 1986
![]()
Question 9.
Petroleum is also known as ……..
(a) Black oil
(b) Mineral oil
(c) Yellow liquid
Answer:
(b) Mineral oil
Question 10.
………………. is the process by which the cotton seeds are removed from the cotton fibre.
(a) Ginning
(b) Relting
(c) Pruning
(d) Tapping
Answer:
(a) Ginning
Question 11.
The first automobile industry was started at ………
(a) Uttar pradesh
(b) Kurla
(c) Lucknow
Answer:
(b) Kurla
Question 12.
Make in India programme was launched in ………………. the year:
(a) 2000
(b) 2004
(c) 2014
(d) 2016
Answer:
(c) 2014
Question 13.
The Oldest and the largest integrated Iron and Steel plant of India is
(a) Tata Iron and Steel Company
(b) Salem Steel Ltd
(c) Indian Iron and Steel Company
Answer:
(a) Tata Iron and Steel Company
![]()
Question 14.
India exports software service to nearly ………………. countries in the world.
(a) 65
(b) 75
(c) 85
(d) 95
Answer:
(d) 95
Question 15.
Jharkhand is the leading producer of
(a) Bauxite
(b) Mica
(c) Indian ore
Answer:
(b) Mica
Question 16.
………. is contained in the Monazite sand.
(a) Oil
(b) Thorium
(c) Coal
Answer:
(b) Thorium
Question 17.
Where are minerals usually found?
(a) On rocks
(b) On earth crust
(c) On ores
Answer:
(c) On ores
Question 18.
Minerals occur igneous and metamorphic rocks in
(a) the veins and the lodes
(b) layers
(c) alluvial deposit
Answer:
(a) the veins and the lodes
![]()
Question 19.
…….. is the basic minerals and the backbone of industrial development.
(a) Coal
(b) Copper
(c) Iron ore
Answer:
(c) Iron ore
Question 20.
…….. metal has a very high content of iron up to 70%.
(a) Magnetic ore
(b) Limonite ore
(c) Hematite ore
Answer:
(a) Magnetic ore
Question 21.
……… is the largest producer of manganese ore in India.
(a) Kudremukh
(b) Odisha
(c) Bailadila
Answer:
(b) Odisha
Question 22.
……… is the basic raw material for the cement industry.
(a) Gypsum
(b) Limestone
(c) Potash salt
Answer:
(b) Limestone
Question 23.
……. is the hardest mineral.
(a) Gold
(b) Diamond
(c) Ruby
Answer:
(b) Diamond
Question 24.
…….. is the softest mineral.
(a) Talc
(b) Salt
(c) Cement
Answer:
(a) Talc
![]()
Question 25.
Which one is not a ferrous mineral?
(a) Iron ore
(b) Copper
(c) Hematite
Answer:
(b) Copper
Question 26.
Which one of the following is not a property of Copper?
(a) It is ductile
(b) It is a good conductor
(c) It is hard
Answer:
(c) It is hard
Question 27.
The mineral ore from which aluminium is mainly obtained.
(a) Copper
(b) bauxite
(c) iron ore
Answer:
(b) bauxite
Question 28.
…….. is the finest iron ore.
(a) Hematite
(b) Magnetite
(c) Lignite
Answer:
(b) Magnetite
Question 29.
……. and …….. are obtained from veins and Nodes.
(a) Zinc and copper
(b) Copper and coal
(c) Coal and Bauxite
Answer:
(a) Zinc and copper
![]()
Question 30.
……. is not a conventional source of energy.
(a) Coal
(b) Biogas
(c) firewood
Answer:
(b) Biogas
Question 31.
The largest solar plant of India is located at …….
(a) Madhapur
(b) Nagarcoil
(c) Madurai
Answer:
(c) Madurai
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. ……… is a silvery grey element.
2. ……… is the first metal used by man.
3. Bauxite is an important one from which …….. is extracted.
4. In ancient time, ……… was used in ayurvedic medicine.
5. ……… is an inflammable organic substance composed mainly of hydrocarbons.
6. …….. usually accompanies petroleum accumulation.
7. India is the second-largest producer of ……..
8. ……… is the largest producer of silk.
9. The first paper mill of India was started in ………
10. The first Jute mill in India was established ……… at near Kolkata.
11. The by-product of the sugar industry are ……. and ……………
12. Most of the jute mills of India are centralized in …….. basin of the West Bengal
13. India is the ……… sugar-producing country in the world.
14. High-grade iron ore is available in …… in Jharkhand.
15. The fast-growing industry of India is …….. industry.
16. The Manchester of Tamil Nadu is ……..
17. The process of rearing silkworm is called ………
18. The first short based integrated steel plant in the country is the …
19. The Electronic capital of India is called ……….
20. Low quality brown coal is called ……..
21. …….. makes our toothpaste white.
22. The first hydro-electric power station in India was established at …….
23. Limestone is found in ………. rocks.
Answers:
1. Manganese
2. Copper
3. aluminium
4. Mica
5. Coal
6. Natural gas
7. raw silk
8. Karnataka
9. West Bengal
10. Rishra
11. Bagasse, Molasses
12. Hooghly
13. second
14. Singbhum
15. automobile
16. Coimbatore
17. Sericulture
18. Vishakhapatnam Steel Plant
19. Bangalore
20. lignite
21. Titanium Oxide
22. Darjeeling
23. Sedimentary
III. Match the following.

Answers
1. (c)
2. (d)
3. (a)
4. (b)
5. (e)

Answers:
1. (b)
2. (e)
3. (a)
4. (c)
5. (d)

Answers:
1. (c)
2. (e)
3. (d)
4. (b)
5. (a)

Answers:
1. (c)
2. (d)
3. (a)
4. (b)
5. (e)

Answers:
1. (c)
2. (a)
3.(e)
4. (b)
5. (e)
IV. Answer in one or two words.
Question 1.
What makes our toothpaste white?
Answer:
Titanium oxide
Question 2.
Name the rock which is made of one mineral.
Answer:
Limestone
![]()
Question 3.
How many minerals have been identified so far in the world?
Answer:
Nearly 2000
Question 4.
Name the mineral which is used to harden steel during manufacturing.
Answer:
Manganese
Question 5.
Which is the most abundantly available fossil fuel?
Answer:
Coal
Question 6.
How many thermal power plants are there in India?
Answer:
310 thermal plants
Question 7.
Which energy can be produced from ocean water?
Answer:
Tidal energy
![]()
Question 8.
What are two categories of minerals?
Answer:
- Metallic
- Non-metallic
Question 9.
Name the two countries which import iron ore from India?
Answer:
Japan and India
Question 10.
In what form ore minerals generally found?
Answer:
In the form of ores.
Question 11.
Name the two important coalfields of India?
Answer:
Jharia and Bokaro
V. Answer in brief.
Question 1.
Give the full form of these abbreviated words:
Answer:
SAIL – Steel Authority of India Limited
MOIL – Manganese Ore India Limited
HCL – Hindustan Copper Limited
NALCO – National Aluminium Company Limited
NLCIL – Neyveli Lignite Corporation of India Limited
![]()
Question 2.
How do we get metals?
Answer:
We get metals by processing minerals ores.
Question 3.
What are the uses of petroleum?
Answer:
Petroleum is used as a source of power and fuel for automobiles, aeroplanes, ships and locomotives.
Question 4.
What are the by products of Jute industry?
Answer:
Gunny bags, canvas, pack sheets, jute webs, lassian, carpets, cordage and twines
Question 5.
What are the by-products of petroleum?
Answer:
The by-products of petroleum are Lubricants, Kerosene, Vaseline, Tar, Soap, Terylene and Wax.
![]()
Question 6.
List out the sugar-producing states of India?
Answer:
Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Punjab, Haryana, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu.
Question 7.
Name some of the Nuclear power stations in India.
Answer:
- Rawatbhatta-Kota in Rajasthan.
- Kalpakkam and Kudankulam in Tamil Nadu.
- Narora in Uttar Pradesh.
- Kaiga in Karnataka and Kakrapara in Gujarat.
Question 8.
List out the leading states of paper production in our country.
Answer:
West Bengal, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
Question 9.
Name some of the major software industries in the country?
Answer:
Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) , L and T Infotech, i-Flex, Accenture, Cognizant, GalexE Solutions India Pvt Limited and ITC Infotech are the major software industries in the country.
Question 10.
How are the industries classified on the basis of raw materials?
Answer:
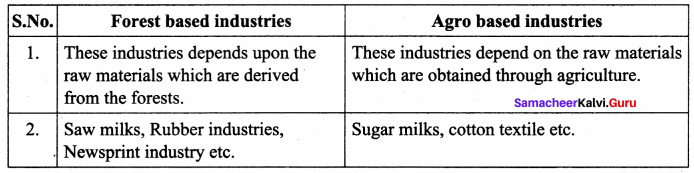
- Agro based industries
- Forest based industries
- Mineral based industries
Question 11.
Define the term ‘ore’.
Answer:
The term ‘ore’ is used to describe an accumulation of any mineral mixed with other elements.
Question 12.
Why is natural gas considered an eco-friendly fuel?
Answer:
Because of low carbon dioxide emissions.
![]()
Question 13.
How is thermal electricity generated?
Answer:
Thermal electricity is generated by using coal, petroleum and natural gas.
Question 14.
How is hydro-electricity generated?
Answer:
Hydro-electricity is generated by fast flowing water.
Question 15.
What is called pruning?
Answer:
Trimming of over grown branches of tea plants is known as pruning.
Question 16.
What is ginning?
Answer:
The seeds are separated from the cotton fibre by means of a process called ginning.
![]()
Question 17.
Name the chief silk weaving centers of India.
Answer:
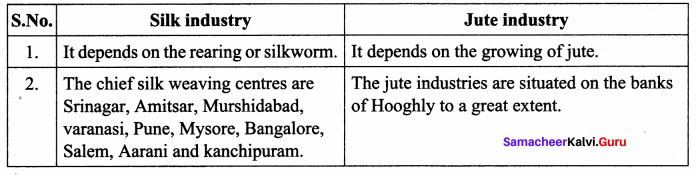
Srinagar, Amritsar, Murshidabad, V aranasi, Pune, Mysore, Bangalore, Arani and Kanchipuram. Karnataka is famous for silk worm rearing.
Question 18.
What is Byssionosis?
Answer:
Byssionosis also called “Brown lung disease” or “Monday fever” ia an occupational lung disease caused dust in inadequately ventilated working environments.
Question 19.
Mention any four activities which require energy.
Answer:
- Cook food
- Provide light and heat
- Propel vehicles
- Drive machinery in industries
Question 20.
How is natural gas used?
Answer:
Natural gas is used as a source of energy as well as an industrial raw material in the petrochemical industry.
![]()
Question 21.
Mention any three major iron ore belts of India.
Answer:
- Odisha – Jharkhand belt
- Durg – Bastar – Chandrapur belt in Chattisgarh and Maharashtra
- Bellary – Chitradurga – Chikmangalur – Tumkur belt in Karnataka
Question 22.
Mention the properties of Mica.
Answer:
- It is made up of a series of plates or leaves.
- It splits easily into thin sheets.
- Mica can be clear, black, green, red, yellow or brown.
- Mica is considered an important mineral used in electric and electronic industries.
Question 23.
What is solar energy?
Answer:
The energy obtained from the sun is known as the solar energy. It does not cause environmental problems as it is pollution free.
![]()
Question 24.
Mention the importance of sugar industry.
Answer:
India is the world’s second largest producer of sugarcane after Brazil. Sugar industry provide employment to 2.86 lakh workers, besides creating extensive indirect employment and income for 25 million cultivators of sugarcane. It is also an important source of excise duty.
Question 25.
Write about Silk industry.
Answer:
India is one of the large producer of raw silk. Sericulture is the process of rearing silkworm. The chief silk weaving centres are Srinagar, Amritsar, Murshidabad, Varanasi, Pune, Mysore, Bangalore, Salem, Arani and Kanchipuram. Karnataka is famous for silkworm rearing.
India exports exclusively silk fabrics like scarves, dress-materials and sarees. The principal buyers of Indian silk are West Germany, Singapore, USA, UK, Russia, Saudi Arabia and Kuwait.
Question 26.
How are deposits of bauxite formed and aluminium obtained?
Answer:
Bauxite deposits are formed due to decomposition of wide variety of rocks rich in aluminium silicates. Ores containing aluminium are obtained from bauxite which is a clay-like substance from which alumina and later aluminium is obtained.
Question 27.
Write the importance of Solar energy.
Answer:
- Solar energy does not cause environmental problems as it is pollution free.
- India has enormous possibilities of tapping solar system.
- It is becoming popular in rural and remote areas of India. Thus, it will be able to minimise the dependence of rural households on firewood and dunk cake.
Question 28.
How is nuclear energy obtained?
Answer:
Nuclear energy is obtained by altering the structure of atoms. When such an alteration is made, much energy is released in the form of heat and this is used to generate electric power. Uranium and thorium, which are available in Jharkhand and the Aravalli ranges of Rajasthan are used for generating atomic or nuclear power. The monazite sands of Kerala is also rich in thorium.
![]()
Question 29.
Give the importance of the Salem Steel Plant.
Answer:
Salem Steel Plant started for commercial production in 1982. It is a major producer of world class stainless steel, which is exported to USA, Mexico, Australia and some other countries of South East Asia.
Question 30.
Give an account of Electronic industry of India.
Answer:
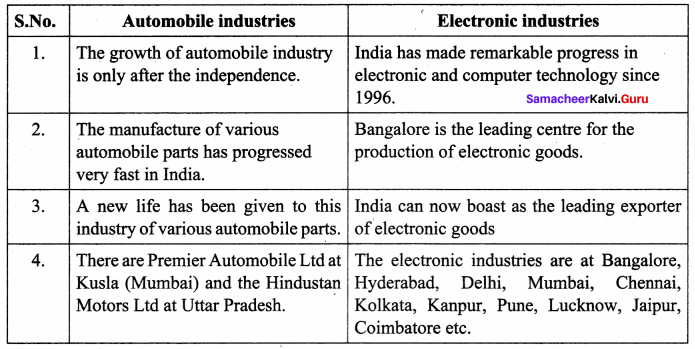
India has made remarkable progress in electronic and computer technology since 1996. “Bangalore” is known as the Electronic Capital of India as it is the leading centre for the production of electronic goods. The other centres are Hyderabad, Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Kanpur, Pune, Lucknow, Jaipur, Coimbatore etc. India can now boast as the leading exporter of electronic goods. It covers a wide range of products including television, transistor, telephone, cellular phones, computer and varied equipment for posts and telegraph, defence, railway and meteorological departments.
VI. Distinguish Between.
Question 1.
Textile industry and Jute industry
Answer:

Question 2.
Solk industry and Jute industry
Answer:
![]()
Question 3.
Automobile industry and Electronic industries
Answer:
Question 4.
Forest based industries and Agro based industries
Answer:
Question 5.
Ginning and Retting
Answer:

Ginning Retting
The seeds are separated from the cotton fibre by the process of Ginning. Retting is a micro-biology process which loosens the outer bark and makes it easier to remove the jute fibres from the stalk.
Question 6.
Iron and steel industry and Software industry
Answer:
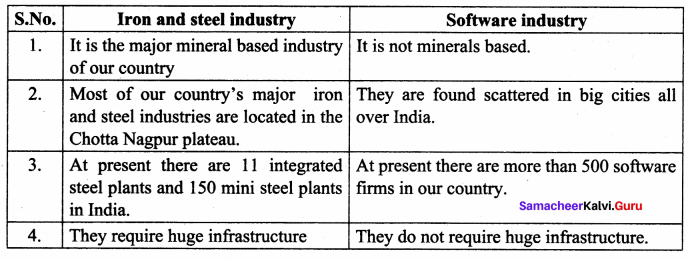
VII. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
What are Resources? How they are classified based on their availability? Give examples.
Answer:
(i) Natural resources are the matter or energy obtained from the environment used by living things including human beings.
(ii) Natural resources include air, water, soil, minerals, fossil, fuels, plants, wild life etc..
(iii) They are classified on several basis. Based on continued availability the resources are classified into two types:
Renewable Resources:
The resources which have natural regeneration after their utilization. Eg: Solar energy, Wind energy, Bio gas, tidal energy, wave energy etc
Non – Renewable Resources:
The resources that cannot be replaced again after utilization.
Eg: Minerals like Coal, Petroleum, Natural gas, Iron ore, Manganese, Bauxite etc.
(iv) Many natural resources are used as raw materials and they play a vital role in the economic development of a region.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe the factors encouraging cotton textile industry in Mumbai.
Answer:
Mumbai in Maharashtra is the leading cotton textile center and it is called the “Manchester of India”.
The following factors favour the cotton industries in Mumbai:
- Location of port facilities for the export of finished goods.
- Well connected to rail and road links with cotton growing area.
- Humid coastal climate favours yarning.
- Availability of capital goods and finance.
- Availability of manpower.
VIII. Expand the following:
1. NFTDC – Non-Ferrous Material Technology Department Centre
2. SAIL – Steel Authority of India Limited
3. MOIL Manganese Ore India Limited
4. HCL – Hindustan Copper Limited
5. NALCO – National Aluminium Company Limited
6. CIL Coal India Limited
7. MOP & NG – The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas
8. GAIL The Gas Authority of India Limited
9. CNG Compressed Natural Gas
10. NPCIL – The Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited
11. DAE – Department of Atomic Energy
12. NHPC National Hydroelectric Power Corporation
13. MNES Ministry of Non-Conventional Energy Source
14. NIWE – The National Institute of Wind Energy
15. CSTRI – Central Silk Technological Research Institute
16. NEPA National Newsprint and Paper Mills
17. BHEL – Bharat Heavy Electrical Limited
18. TCS Tata Consultancy Service
19. NTPC – National Thermal Power Corporation