You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Solutions Chapter 17 Reproduction in Plants and Animals
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Reproduction in Plants and Animals Textual Evaluation Solved
I. Choose the Correct Answer.
Question 1.
The plant which propagates with the help of its leaves is ______.
(a) Onion
(b) Neem
(c) Ginger
(d) Bryophyllum.
Answer:
(d) Bryophyllum
Question 2.
Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in:
(a) Amoeba
(b) Yeast
(c) Plasmodium
(d) Bacteria
Answer:
(b) Yeast
Question 3.
Syngamy results in the formation of ______.
(a) Zoospores
(b) Conidia
(c) Zygote
(d) Chlamydospores.
Answer:
(c) Zygote
Question 4.
The essential parts of a flower are:
(a) Calyx and Corolla
(b) Calyx and Androecium
(c) Corolla and Gynoecium
(d) Androecium and Gynoecium
Answer:
(d) Androecium and Gynoecium
Question 5.
Anemophilous flowers have ______.
(a) Sessile stigma
(b) Small smooth stigma
(c) Coloured flower
(d) Large feathery stigma.
Answer:
(d) Large feathery stigma.
![]()
Question 6.
Male gametes in angiosperms are formed by the division of:
(a) Generative cell
(b) Vegetative cell
(c) Microspore mother cell
(d) Microspore
Answer:
(a) Generative cell
Question 7.
What is true of gametes?
(a) They are diploid
(b) They give rise to gonads
(c) They produce hormones
(d) They are formed from gonads.
Answer:
(d) They are formed from gonads.
Question 8.
A single highly coiled tube where sperms are stored, get concentrated and mature is known as:
(a) Epididymis
(b) Vasa efferentia
(c) Vas deferens
(d) Seminiferous tubules
Answer:
(a) Epididymis
Question 9.
The large elongated cells that provide nutrition to developing sperms are ______.
(a) Primary germ cells
(b) Sertoli cells
(c) Leydig cells
(d) Spermatogonia.
Answer:
(b) Sertoli cells
Question 10.
Estrogen is secreted by:
(a) Anterior pituitary
(b) Primary follicle
(c) Graffian follicle
(d) Corpus luteum
Answer:
(c) Graffian follicle
Question 11.
Which one of the following is an IUCD?
(a) Copper – T
(b) Oral pills
(c) Diaphragm
(d) Tubectomy.
Answer:
(a) Copper – T
II. Fill in the Blanks.
Question 1.
The embryo sac in a typical dicot at the time of fertilization is ______.
Answer:
Female Gametophyte.
Question 2.
After fertilization the ovary develops into ______.
Answer:
Fruit.
![]()
Question 3.
Planaria reproduces asexually by ______.
Answer:
Regeneration.
Question 4.
Fertilization is ______ in humans.
Answer:
Internal.
Question 5.
The implantation of the embryo occurs at about ______ day of fertilization.
Answer:
6 to 7.
Question 6.
_______ is the first secretion from the mammary gland after childbirth.
Answer:
Colostrum.
Question 7.
Prolactin is a hormone produced by ______.
Answer:
Anterior Pituitary.
III. Match the following.
Question 1.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Fission | (a) Spirogyra |
| 2. Budding | (b) Amoeba |
| 3. Fragmentation | (c) Yeast |
Answer:
1. (b) Amoeba
2. (c) Yeast
3. (a) Spirogyra.
Question 2.
Match the following terms with their respective meanings.
| 1. Parturition | (a) The duration between pregnancy and birth |
| 2. Gestation | (b) Attachment of zygote to the endometrium |
| 3. Ovulation | (c) Delivery of baby from a uterus |
| 4. Implantation | (d) Release of an egg from Graafian follicle |
Answer:
1. (c) Delivery of baby from a uterus
2. (a) Duration between pregnancy and birth
3. (d) Release of the egg from Graafian follicle
4. (b) Attachment of zygote to the endometrium.
IV. State whether the following statements are True or False. Correct the false statement.
Question 1.
The stalk of the ovule is called pedicle.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Stalk of the ovule is called funiculus.
![]()
Question 2.
Seeds are the product of asexual reproduction.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Seeds are the product of Sexual reproduction.
Question 3.
Yeast reproduces asexually by means of multiple fission.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Yeast reproduces asexually by means of budding.
Question 4.
The part of the pistil which serves as a receptive structure for the pollen is called as style.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: The part of the pistil which serves as a receptive structure for the pollen is called as stigma.
Question 5.
Insect pollinated flowers are characterized by dry and smooth pollen.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Insect pollinated flowers are characterized by larger and spiny pollen.
Question 6.
Sex organs produce gametes, which are diploid.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Sex organs produce gametes, which are haploid.
Question 7.
LH is secreted by the posterior pituitary.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: LH is secreted by the anterior pituitary.
Question 8.
Menstrual cycle ceases during pregnancy.
Answer:
True.
Question 9.
Surgical methods of contraception prevent gamete formation.
Answer:
True.
Question 10.
The increased level of estrogen and progesterone is responsible for menstruation.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: The decreased level of estrogen and progesterone is responsible for menstruation.
V. Answer in a word or sentence.
Question 1.
If one pollen grain produces two male gametes, how many pollen grains are needed to fertilize 10 ovules?
Answer:
One sperm fuses with the egg and forms a diploid zygote. So 10 pollen grains are needed to fertilize 10 ovules.
![]()
Question 2.
In which part of the flower germination of pollen grains takes place?
Answer:
Germination of pollen grains takes place in the stigma of the female flower.
Question 3.
Name two organisms which reproduce through budding.
Answer:
Yeast, Hydra.
Question 4.
Mention the function of endosperm.
Answer:
Endosperm provides food to the developing embryo.
Question 5.
Name the hormone responsible for the vigorous contractions of the uterine muscles.
Answer;
Oxytocin, from the posterior pituitary, is responsible for the vigorous contractions of the uterine muscles.
Question 6.
What is the enzyme present in acrosome of sperm?
Answer:
Acrosome contain hyaluronidase an enzyme that help the sperm to enter the ovum during fertilization.
Question 7.
When is World Menstrual Hygiene Day observed?
Answer:
Every year May 28 is observed as World Menstrual Hygiene Day.
Question 8.
What is the need for contraception?
Answer:
Contraception is one of the best birth control measures to check population growth.
Question 9.
Name the part of the human female reproductive system where the following occurs.
- Fertilization
- Implantation
Answer:
- Oviduct of the female genital tract.
- Uterus
VI. Short Answer Questions.
Question 1.
What will happen if you cut Planaria into small fragments?
Answer:
Breaking of fragments of Planaria results into many fragments. Each fragment having one cell will give rise to a new Planaria, by cell division.
![]()
Question 2.
Why is vegetative propagation practiced for growing some type of plants?
Answer:
No gametic fusion is required in vegetative reproduction. In this type, new plantlets are formed from vegetative cells, buds or organ of plant. The vegetative part of plant get detached from the parent body and grows into an Independent daughter plant.
Question 3.
How does binary fission differ from multiple fission?
Answer:
| Binary fission | Multiple fission |
| 1. The nucleus divides into two parts. | 1. The nucleus divides into many parts. |
| 2. It gives rise to new individuals. | 2. It gives rise to many individuals |
| 3. Cytoplasm divides after each nuclear division. | 3. Cytoplasm does not divide after every nuclear division. |
| 4. eg. Amoeba. | 4. eg. Plasmodium. |
Question 4.
Define Triple fusion.
Answer:
The fusion of one male gamete (n) fuses with the secondary nucleus (2n) to produce primary endosperm nucleus (3n) is called Triple fusion.
Question 5.
Write the characteristics of insect-pollinated flowers.
Answer:
Pollination with the help of insects like flies and honey bees are called Entomophily. To attract those insects, these flowers are brightly coloured, have smell and nectar.
Question 6.
Name the secondary sex organs in male.
Answer:
Secondary sex organs in male are seminiferous tubules, epididymis, sperm duct, seminal vesicles, prostrate gland, cowper’s gland and penis.
Question 7.
What is colostrum? How is milk production hormonally regulated?
Answer:
The first fluid which is released from the mammary gland after childbirth is called colostrum. Milk production from alveoli of the mammary gland is stimulated by prolactin secreted from the anterior pituitary. The ejection of milk is stimulated by the posterior pituitary hormone oxytocin.
![]()
Question 8.
How can menstrual hygiene be maintained during menstrual days?
Answer:
Menstrual hygiene to be maintained during menstrual days are:
- Sanitary pads should be changed regularly to avoid infections due to microbes from vagina and sweat from genitals.
- Use of warm water to clean genitals helps to get rid of menstrual cramps.
- Wearing loose clothing rather than tight-fitting clothes will ensure the airflow around the genitals and prevent sweating.
Question 9.
How does developing embryo gets its nourishment inside the mother’s body?
Answer:
The placenta allows the exchange of food materials, diffusion of oxygen, excretion of nitrogenous wastes and elimination of carbon-di-oxide. A cord, containing blood vessels that connect the placenta with the foetus is called the umbilical cord.
Question 10.
Identify the parts A, B, C and D.
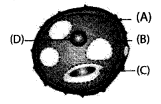
Answer:
The parts A, B, C and D are:
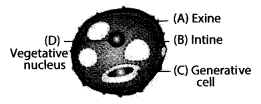
Question 11.
Write the events involved in the sexual reproduction of a flowering plant.
(a) Discuss the first event and write the types.
(b) Mention the advantages and the disadvantages of that event.
Answer:
(a) The first event is pollination. Pollination is the process of transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of a flower. The two types of pollination are self-pollination and cross pollination.
(b) Advantages of self-pollination:
- Self-pollination is possible in certain bisexual flowers.
- Flowers do not depend on agents for pollination.
- There is no wastage of pollen grains.
Disadvantages of self-pollination:
- The seeds are less in numbers.
- The endosperm is minute. Therefore, the seeds produce weak plants.
- New varieties of plants cannot be produced.
Advantages of cross pollination:
- The seeds produced as a result of cross pollination, develop and germinate properly and grow into better plants, i.e., cross pollination leads to the production of new varieties.
- More viable seeds are produced.
Disadvantages of cross-pollination:
- Pollination may fail due to distance barrier.
- More wastage of pollen grains.
- It may introduce some unwanted characters.
- Flowers depend on the external agencies for pollination.
Question 12.
Why are the human testes located outside the abdominal cavity? Name the pouch in which they are present?
Answer:
The testicles, produce sperm and testosterone. The testicles are located outside the body because the sperms develop best at a temperature, several degrees lower than normal body temperature. The pouch, is scrotum, a sac – like structure, in which the testes are present.
Question 13.
Luteal phase of the menstrual cycle is also called the secretory phase. Give reason.
Answer:
In leutal phase LH and FSH decreases, corpus luteum produces progesterone and its level increases followed by a decline progesterone also stimulates the glands in the uterus to secrete substances that maintain the endometrium and keep it from breaking down. For this reason, this phase of menstrual cycle is called secretory phase.
Question 14.
Why are family planning methods not adopted by all the people of our country?
Answer:
- Illiteracy
- Emphasis is in rural areas and not in villages.
- Door to door campaign to encourage families could not be done because of overpopulation.
- Poor economic status and poverty of most of the people in India.
- Age-Old cultural norms continue to cause, poor family planning practices, all across the country.
VII. Long Answer Questions.
Question 1.
With a neat labelled diagram describe the parts of a typical angiosperms ovule.
Answer:
The main part of the ovule is the nucellus which is enclosed by two integuments, leaving an opening called micropyle. The ovule is attached to the ovary wall by a stalk, called funiculus. The basal part is Chalaza.
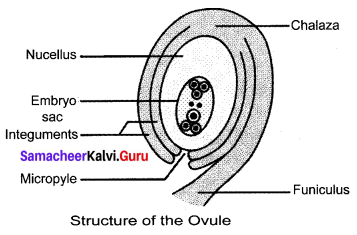
The embryo sac contains seven cells and the eighth nuclei located within the nucellus. Three cells at the micropylar end form the egg apparatus and the three cells at the chalazalnte9uments end are the antipodal cells. The remaining two nuclei are called polar nuclei found in the centre. In the egg apparatus, one is the egg cell (female gamete) and the remaining two cells are the synergids.
Question 2.
What are the phases of the menstrual cycle? Indicate the changes in the ovary and uterus.
Answer:
The four phases of the menstrual cycle are:
- Menstrual or Destructive phase
- Follicular or Proliferative phase
- Ovulatory phase
- Luteal or secretory phase.
Events of the menstrual cycle and changes in ovary and changes in the uterus.
| Phase | Days | Changes in Ovary | Changes in Uterus | Hormonal changes |
| Menstrual phase | 4 – 5 days | Development of primary follicles. | Breakdown of uterine endometrial lining leads to bleeding. | The decrease in progesterone and oestrogen. |
| Follicular phase | 6th – 13th day |
Primary follicles grow to become a fully mature Graafian follicle. | Endometrium regenerates through proliferation. | FSH and Oestrogen increase. |
| Ovulatory phase | 14th day | The Graafian follicle ruptures, and releases the ovum (egg). | Increase in endometrial thickness. | LH peak. |
| Luteal phase | 15th – 28th day | Emptied Graafian follicle develops into corpus luteum. | The endometrium is prepared for implantation if fertilization of the egg takes place if fertilization does not occur corpus luteum degenerates, uterine wall ruptures, bleeding starts and unfertilized egg is expelled. | LH and FSH decrease, Corpus luteum produces progesterone and its level increases followed by a decline, if menstrual bleeding occurs. |
VIII. Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) Questions
Question 1.
In angiosperms the pollen germinates to produce pollen tube that carries two gametes. What is the purpose of carrying two gametes when single gamete can fertilize the egg?
Answer:
In angiosperms, one sperm cell fuses with the egg cell to form the zygote, while the other fuses with the two polar nuclei that form the endosperm which nourishes the developing embryo.
Question 2.
Why the menstrual cycle does not take place before puberty and during pregnancy?
Answer:
The reproducing period of a women’s life starts and becomes functional and an increase in sex hormone production starts only in puberty. So the menstrual cycle does not take place before puberty. The release of a mature egg, maintains the lining of the uterus, during pregnancy. During pregnancy, the placenta produces progesterone. This maintains the lining of the uterus during pregnancy and it means that menstruation does not happen.
Question 3.
Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow.
Rahini and her parents were watching a television programme. An advertisement flashed on the screen which was promoting use of sanitary napkins. Rahini’s parents suddenly changed the channel, but she objected to her parents and explained the need and importance of Such advertisement.
(a) What is first menstruation called? When does it occur?
Answer:
The first menstruation is called Menarche. In human females, the menstrual cycle starts at the age of 11 – 13 years which marks the onset of puberty.
(b) List out the napkin hygiene measures taken during menstruation?
Answer:
- The sanitary pad and tampons should be wrapped properly and discarded because they can spread infections.
- Sanitary pad or tampon should not be flushed down the toilet.
- Napkin incinerators are to be used properly for disposal of used napkins.
(c) Do you think that Rahini’s objection towards her parents was correct? If so, Why?
Answer:
Yes. Awareness to be created in maintaining menstrual hygeine and importance of menstrual hygeine for good health.
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Reproduction in Plants and Animals Additional Questions Solved
I. Fill in the blanks.
Question 1.
The reproduction process is to preserve individual species and is called ______.
Answer:
Self – perpetuation.
Question 2.
The _______ grains are produced in the anther within the pollen sac.
Answer:
Pollen.
Question 3.
The _____ contains the future plant or embryo, which develops into a seedling.
Answer:
Seed.
![]()
Question 4.
Each testis is covered with a layer of fibrous tissue called ______.
Answer:
Tunica albuginea.
Question 5.
The first fluid which is released from the mammary gland after childbirth is called ______.
Answer:
Colostrum.
Question 6.
The organs of the reproductive system are divided into ______ and ____ (accessory) sex organs.
Answer:
Primary, secondary.
Question 7.
The plasma membrane of an ovum is surrounded by inner thin _____ and an outer thick ______.
Answer:
Zona pellucida, Corona Radiata.
Question 8.
______ is the practice of healthy living and personal cleanliness.
Answer:
Hygiene.
Question 9.
Testosterone initiates the process of ______.
Answer:
Spermatogenesis.
Question 10.
The cortex of ovary is composed of a connective tissue called ______.
Answer:
Stroma.
Question 11.
In plants, the fusion of one sperm with the egg is called ______.
Answer:
Syngamy.
Question 12.
The _______ provides energy for the movement of the tail in sperm, causing sperm motility, which is essential for fertilization.
Answer:
Mitochondria.
Question 13.
Self – pollination is also known as ______.
Answer:
Autogamy
![]()
Question 14.
During spore formation, a structure called sporangium develops from the ______.
Answer:
Fungal hyphae.
II. Choose the correct pair from the following.
Question 1.
(a) Chalaza and pollination
(b) Calyx and spores
(c) Anemophily and hydrophily
(d) Stamens and Planaria.
Answer:
(c) Anemophily and hydrophily
Question 2.
(a) Oogenesis and spermatogenesis
(b) Fragmentation and Fertilization
(c) Primary follicle and fission
(d) Micropyle and Regeneration.
Answer:
(a) Oogenesis and spermatogenesis
Question 3.
(a) Scrotum and sporangium
(b) Pollination and population
(c) Spermatogenesis and seminiferous tubules
(d) Diaphragm and Blastocyst.
Answer:
(c) Spermatogenesis and seminiferous tubules
Question 4.
(a) Autogamy and Budding
(b) Funiculus and chalaza
(c) Bulbils and spirogyra
(d) Polar nuclei and pollination.
Answer:
(b) Funiculus and chalaza
Question 5.
(a) Tuberous root and granulosa cells
(b) Corolla and Graafian follicle
(c) Synergids and Regeneration
(d) The vegetative and generative cell.
Answer:
(d) The vegetative and generative cell.
III. Match the following.
Question 1.
| 1. Offsprings | (a) Pollination by insects |
| 2. Anemophily | (b) Pollination by animals |
| 3. Spermatogenesis | (c) Blood vessels |
| 4. Umbilical cord | (d) Expulsion of the young one |
| 5. Entomophily | (e) Seminiferous tubules |
| 6. Parturition | (f) Sexual reproduction |
| 7. Zoophily | (g) Pollination by wind |
Answer:
- (f) Sexual reproduction
- (g) Pollination by wind
- (e) Seminiferous tubules
- (c) Blood vessels
- (a) Pollination by insects
- (d) Expulsion of the young one
- (b) Pollination by animals.
IV. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
The male and the female gametes contain this material on the chromosomes, which transmit the character traits to the next generation.
(a) genes
(b) chromoplast
(c) septum
(d) spores
Answer:
(a) genes
Question 2.
Raphe and hilium in seed represent:
(a) Nucellus
(b) Funiculus
(c) Integument
(d) Micropyle
Answer:
(b) Funiculus
Question 3.
The corona radiata is formed of ______.
(a) Vitelline membrane
(b) Oxytocin
(c) Zygote
(d) Follicle.
Answer:
(d) Follicle.
![]()
Question 4.
Pollination is followed by:
(a) Seed formation
(b) Fragmentation
(c) Fertilization
(d) Budding
Answer:
(c) Fertilization
Question 5.
The membrane forming the surface layer of the ovum is called ______.
(a) Entomophily
(b) Exine
(c) Vitelline membrane
(d) Intine.
Answer:
(c) Vitelline membrane
V. Write True or False for the following statements. Write the correct statement for the incorrect statement.
Question 1.
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of two diploid gametes to form a haploid individual (Zygote).
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of two haploid gametes, to form a diploid individual (Zygote).
Question 2.
Accessory sex organ in man includes the Gonads. (Testes in males and Ovaries in female).
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Primary sex organ in man include the Gonads. (Testes in males and Ovaries in female).
Question 3.
The connective tissue of Cortex called stroma is lined by the germinal epithelium cells called Granulosa cells.
Answer:
True.
Question 4.
The mature ovum or egg in the female is elliptical in shape and has full of yolk.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: The mature ovum or egg is spherical in shape and is always free of yolk.
![]()
Question 5.
The menstrual cycle ceases around 48-50 years of age and this stage is termed as menopause.
Answer:
True.
VI. Answer the following briefly.
Question 1.
What is the role of acrosome in human sperm?
Answer:
The sperm head has a like structure called acrosome. It contain hyaluronidase an enzyme that helps the sperm to enter the ovum during fertilization.
Question 2.
What are the significance of fertilization and the post-fertilization changes?
Answer:
Significance of fertilization:
- It stimulates the ovary to develop into a fruit.
- It helps in the development of new characters from two different individuals.
Post – fertilization changes:
- The ovule develops into a seed.
- The integuments of the ovule develop into the seed coat.
- The ovary enlarges and develops into a fruit.
Question 3.
What is Asexual reproduction? Explain the spore formation in Rfiizoptis with a diagram.
Answer:
Production df an offspring by a single parent without the formation and fusion of gametes is called Asexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction occurs by spore formation. In Rhizopus, during spore formation, a structure called sporangium develops from the fungal hypha. The nucleus divides several times within the sporangium and each nucleus with a small amount of cytoplasm develops into a spore. The spores are liberated and they develop into new hypha after reaching the ground or substratum.
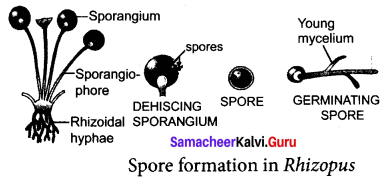
Question 4.
What could be the reasons for adopting contraceptive methods?
Answer:
Contraception is one of the best birth control measures. A number of techniques or method have been developed to prevent pregnancies in women which leads to welfare of the family group and society.
Question 5.
Explain the following:
(a) Toilet Hygiene
(b) Napkin Hygiene
(c) Menstrual Hygiene
Answer:
(a) Toilet Hygiene:
- To reduce the bad odour and infection, the floors of the toilet should be kept clean and dry.
- Toilet flush handles, doorknobs, light switches and walls should be cleaned with disinfectants to kill harmful germs and bacteria.
- Hands should be washed with soap, before and after toilet use.
(b) Napkin Hygiene:
- To prevent infections, the sanitary pad, and tampon should be wrapped and discarded properly.
- Sanitary pad and tampon should not be flushed down the toilet.
- Napkin incinerators are to be used properly for disposal of used napkins.
(c) Menstrual Hygiene:
- Sanitary pads should be changed regularly, to avoid infections due to microbes from vagina and sweat from genitals.
- Use of warm water to clean genitals helps to get rid of menstrual cramps.
- Wear loose clothing, to have airflow around the genitals and prevent sweating.
Question 6.
Explain the structure of the following:
(a) Testes
(b) Ovary
Answer:
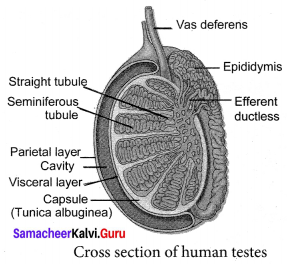
(a) Testes: Testes are the reproductive glands of the male, that are Oval shaped, which lie outside the abdominal cavity of a man, in a sac-like structure called Scrotum. Each testis is covered with a layer of fibrous tissue called tunica albuginea. Septa divides the testes into pyramidal lobules, in which lie seminiferous tubules, cells of Sertoli and the Leydig cells. The process of spermatogenesis takes place in the seminiferous tubules. The Sertoli cells are the supporting cells and provide nutrients to the developing sperms. The Leydig cells lie between the seminiferous tubules and secrete testosterone. It initiates the process of spermatogenesis.
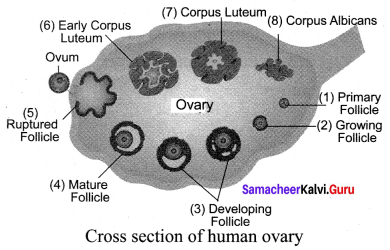
(b) Ovary: Ovaries are located on either side of the lower abdomen, composed of two almond-shaped bodies, each lying near the lateral end of the fallopian tube. Each ovary has an outer cortex and an inner medulla. The cortex is composed of a network of connective tissue called stroma and is lined by the germinal epithelium. The epithelial cells called the granulosa cells to surround each ovum in the ovary together forming the primary follicle. As the egg grows larger, the follicle also enlarges and gets filled with the fluid and is called the Graafian follicle.
Question 7.
What do you know about the National Health Programme?
Answer:
To improve the reproductive health of the people, National Health Programmes such as,
(a) Family Welfare Programme:
- Maternal and Child Health Care (MCH).
- Immunization of mothers, infants and children.
- Nutritional supplement to pregnant women and children.
- Motivate couples to accept contraceptive methods and to have small family norms, which improve economic status, living status and quality of life.
(b) Reproductive and Child Health Care (RCH)
- Pregnancy and childbirth.
- Postnatal care of the mother and child.
- Importance of breastfeeding.
- Prevention of reproductive tract infections and sexually transmitted diseases.
Question 8.
What is gastrulation?
Answer:
The transformation of blastula into gastrula and the formation of primary germ layers (Ectoderm, Mesoderm and Endoderm) by rearrangement of the cells is called gastrulation.
Question 9.
What is implantation?
Answer:
The process of attachment of the blastocyst to the uterine wall (endometrium) is called implantation. The blastocyst (fertilized egg) reaches the uterus and gets implanted in the uterus. The fertilized egg becomes implanted in about 6 to 7 days after fertilization.
VII. Draw a labelled diagram of the following.
Question 1.
Cross Section of:
(a) Human testes
(b) Human ovary
Answer:
(a) Human testes:
(b) Human ovary:
VIII. Write the expansion for the following abbreviations.
Question 1.
- WHO
- RCH
- MCH
- STD
- IUD
- UTI
- LH
- FSH.
Answer:
- WHO – World Health Organization
- RCH – Reproductive and Child Health Care
- MCH – Maternal and Child Health Care
- STD – Sexually Transmitted Diseases
- IUD – Intra-Uterine Device
- UTI – Urinary Tract Infection
- LH – Luteinizing Hormone
- FSH – Follicle Stimulating Hormones.
IX. Answer the following in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Question 1.
With the help of a neat labelled diagram, explain, how does fertilization take place in flowering plants.
Answer:
The mature pollen grain contains two cells, the vegetative and the generative cell. The vegetative cell contains a large nucleus. The generative cell divides mitotically and forms two male gametes.
Pollen grains reach the stigma and begin to germinate. Pollen grain forms a small tube-like structure called pollen tube, which emerges through the germ pore. The contents of the pollen grain move into the tube. The pollen tube grows through the tissues of the stigma and style and finally reaches the ovule through the micropyle.
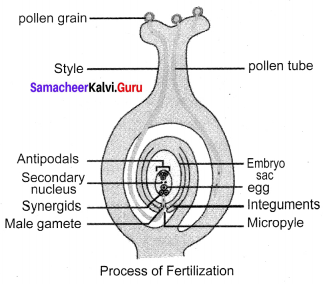
The vegetative cell degenerates and the generative cell divides to form two sperms or male gametes. Tip of pollen tube bursts and the two sperms enter the embryo sac. One sperm fuses with the egg and this process is called Syngamy and forms a diploid zygote. The other sperm fuses with the secondary nucleus, which is called the Triple fusion, to form the primary endosperm nucleus, which is triploid in nature.
Since two types of fusion syngamy and triple fusion take place in an embryo sac, the process is termed as double fertilization. After triple fusion, primary endosperm nucleus develops into an endosperm, which provides food to the developing embryo. Later the synergids and antipodal cells degenerate.
Question 2.
With examples and with the help of a neat labelled diagram, explain the different types of vegetative reproduction of plants.
Answer:
Vegetative reproduction takes place through,
(i) Leaves:
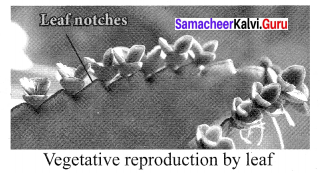
In Bryophyllum, small plants grow at the leaf notches.
(ii) Stem:
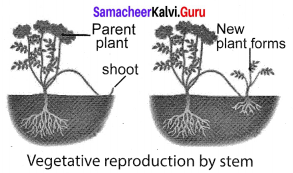
In plants like, strawberry aerial weak stems, touch the ground and give adventitious roots and buds. The offspring becomes an independent plant, when it is detached from the parent plant.
(iii) Root: Tuberous roots are used to develop new plants, eg. Asparagus, Sweet potato.
(iv) Bulbils: In some plants, the flower bud, modifies into the globose bulb, which is called bulbils. When these bulbils fall on the ground they grow into new plants, eg. Agave.
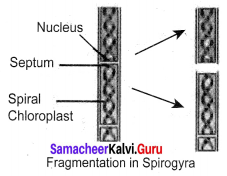
(v) Fragmentation: The breaking of the filament into many fragments is called fragmentation. Each fragment having one cell will give rise to a new filament by cell division, eg. Spirogyra.
(vi) Fission:
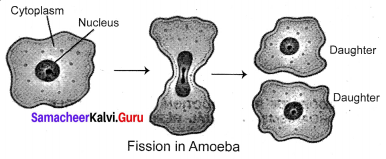
The parent cell divides into two daughter cells and each cell develops into a new adult organism eg. Amoeba.
(vii) Budding:
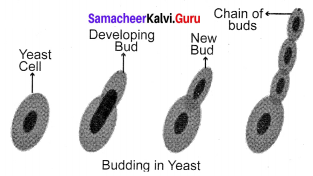
Formation of a daughter individual from a small projection, the bud arising on the parent body is called budding, eg. Yeast.
(viii) Regeneration: The ability of the lost body parts of an individual organism to give rise to a whole new organism is called regeneration. Regeneration takes place by the specialized mass of cells, eg. Hydra and Planaria.
Question 3.
Explain the two types of pollination and write the advantages and disadvantages of the types of pollination.
Answer:
The two types of pollination are
(a) Self – pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or another flower borne on the same plant is called self – pollination.
eg. Hibiscus. Self – pollination is also called Autogamy.
Advantages of self – pollination:
- Self – pollination is possible in certain bisexual flowers.
- Flowers do not depend on agents for pollination.
- There is no wastage of pollen grains.
Disadvantages of self – pollination:
- The seeds are less in numbers.
- The endosperm is minute, so the seeds produce weak plants.
- New varieties of plants cannot be produced.
(b) Cross-pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from the anthers of a flower to the stigma of a flower on another plant of the same species is called Cross-pollination, eg. Apples, Grapes, Plum.
Advantages of Cross-pollination:
- The seeds produced as a result of cross-pollination, develop and germinate properly and grow into better plants.
- Cross-pollination leads to the production of new varieties.
- More viable seeds are produced.
Disadvantages of Cross-pollination:
- Pollination may fail due to the distance barrier.
- More wastage of pollen grains.
- It may introduce some unwanted characters.
- Flowers depend on the external agencies for pollination.
Question 4.
Explain the structure of Human Sperm and Ovum with a neat labelled diagram.
Answer:
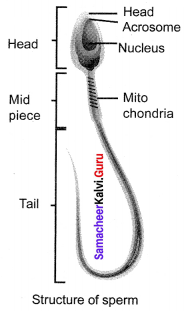
1. Structure of Human sperm:
The spermatozoa consist of a head, middle piece and tail. The sperm head is elongated and formed by the condensation of the nucleus. The anterior portion has a cap-like structure called acrosome, which contains an enzyme hyaluronidase, that helps the sperm to enter the ovum during fertilization. A short neck connects the head and middle piece, which comprises the centrioles. The middle piece contains the mitochondria which provides energy for the movement of tail. It brings about sperm motility, which is essential for fertilization.
2. Structure of Ovum:
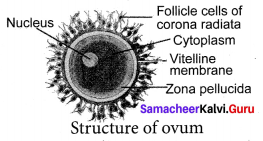
The mature ovum or egg is spherical in shape, free of yolk and contains abundant cytoplasm and the nucleus. The ovum is surrounded by three membranes. The plasma membrane is surrounded by inner thin zona pellucida and an outer thick corona radiata, which is formed of follicle cells. The membrane forming the surface layer of the ovum is called the vitelline membrane. The fluid-filled space between zona pellucida and the surface of the egg is called perivitelline space.
Question 5.
Explain the Agents of cross-pollination.
Answer:
Cross – pollination takes place through the agency of animals, insects, wind and water.
(a) Pollination by the wind: The pollination with the help of wind is called Anemophily. The Anemophilous flowers produce an enormous amount of pollen grains, which are small, smooth, dry and light in weight. This kind of pollen can blow off at a distance of more than 1,000 km. The stigmas are large, protruding and hairy to trap the pollen grains, eg. Grasses and some Cacti.
(b) Pollination by insects: Pollination with the help of insects like honey bees, flies are called entomophily. These flowers are brightly coloured, have the smell and have nectar, to attract insects. The pollen grains are larger in size, and the exine is pitted and spiny, so it can easily adhere firmly on the sticky stigma. About 80% of the pollination by insects is carried by honey bees.
(c) Pollination by water: The pollination with the help of water is called hydrophily. This takes place in aquatic plants. Pollen grains are produced in large numbers. Pollen grains float on the surface of water till they land on the stigma of female flowers, eg. Hydrilla, Vallisneria.
(d) Pollination by Animals: When pollination takes place with the help of animals, it is called Zoophily. The flowers have bright colour, size and scent to attract animals, eg. Sunbird pollinates flowers of Canna, Gladioli etc., Squirrels pollinate flowers of silk cotton tree.
Question 6.
Explain the parts of a flower, with a neat labelled diagram.
Answer:
The flower is the reproductive organ of a flowering plant. A flower is a modified shoot. A flower consists of four whorls borne on the thalamus. The whorls are from outside. The parts of a typical flower are as follows:
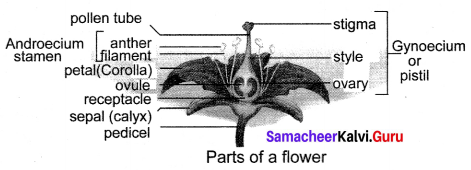
(a) Calyx: Calyx consists of sepals, forms the outermost whorl. They are non-essential or accessory whorls. It protects the flower bud.
(b) Corolla: Corolla consists of petals, which are modified leaves. They are often brightly coloured and in different shapes to attract pollinators. They are non-essential or accessory whorls because they do not directly take part in the reproduction.
(c) Androecium:
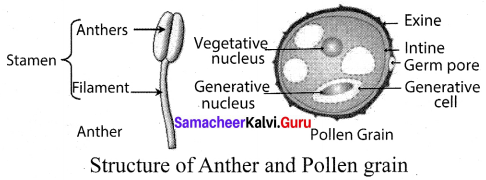
Androecium is the male reproductive part of a flower and is called an essential whorl, as they take part directly in reproduction. The androecium is composed of stamens. Each stamen consists of a stalk called the filament and a small bag like structure called anther at the tip. The pollen grains are produced in the anther within the pollen sac.
Pollen grains are spherical and have a two-layered wall. The hard outer layer is exine, which has apertures, called Germpore. The inner thin layer is intine, which is continuous and made up of cellulose and pectin. Mature pollen grain contain two cells, the vegetative and generative cell. Vegetative cell contains a large nucleus. The generative cell divides, to form two male
gametes.
(d) Gynoecium:
Gynoecium is the female reproductive part of a flower. It is an essential whorl because they take part directly in reproduction. Gynoecium is made up of carpels. It has (a) Ovary (b) Style (c) Stigma. Ovary contains the ovules. The main part of the ovule is the nucellus and is enclosed by two integuments, Jk. leaving an opening called as micropyle. The ovule is attached to the ovary wall, by a stalk called Funiculus.
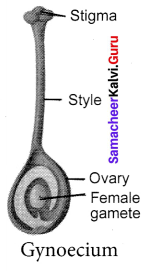
Question 7.
Explain the steps involved from fertilization to foetal development in human.
Answer:
Fertilization in human is internal and occurs in the Oviduct of the female genital tract. It takes place in the ampulla of the fallopian tube. An oocyte is alive for about 24 hours after it is released from follicle. The sperm enters into the ovum, fuses and forms a zygote, which is a fertilized ovum. This process is called fertilization.
(a) Cleavage and formation of Blastula: The first cleavage takes place about 30 hours after fertilization. Cleavage is a series of rapid mitotic divisions of the zygote, to form many-celled blastula (Blastocyst), which comprises an outer layer of smaller cells and inner mass of larger cells.
(b) Implantation: The blastocyst (fertilized egg) reaches the uterus and gets implanted. The process of attachment of the blastocyst to the uterine wall is called Implantation. The fertilized egg, implanted in about 6 to 7 days after fertilization.
(c) Gastrulation: After implantation, the transformation of blastula into Gastrula and the formation of primary germ layers (Ectoderm, Mesoderm and Endoderm) by rearrangement of the cells takes place, which is called Gastrulation.
(d) Organogenesis: The various organs of the foetus are established from the different germ layers, during Organogenesis.
(e) Formation of Placenta: Placenta is a disc-shaped structure, attached to the Uterine wall between the developing embryo and maternal tissues. It allows the exchange of food materials, diffusion of oxygen, excretion of nitrogenous wastes and elimination of carbon-di-oxide. The cord which connects the placenta with the foetus is called the umbilical cord.
(f) Pregnancy (Gestation): Embryo attains its development in the uterus. Gestation period of human is 280 days. During pregnancy the uterus expands up to 500 times of its normal size.
(g) Parturition (Child Birth): Oxytocin from the posterior pituitary stimulates the uterine contractions and provides force to expel the baby from the uterus, causing birth. Parturition is the expulsion of young one from the mother’s Uterus at the end of gestation.
(h) Lactation: The process of milk production after childbirth from the mammary glands of the mother is called lactation. Milk production from the mammary gland is stimulated by prolactin, a hormone secreted by anterior pituitary. The ejection of milk is stimulated by posterior pituitary hormone oxytocin.
Question 8.
What is population explosion? Explain the different ways of family planning.
Answer:
The sudden and rapid rise in the size of the human population is called the Population Explosion. Contraception: Contraception is one of the best birth control measures. The devices used for contraception are called contraceptive devices. The common contraceptive methods used to prevent pregnancy are as follows:
(a) Barrier methods: This method prevents the meeting of an ovum by the sperms. The entry of sperm is prevented into the female reproductive tract by a barrier.
- Condom: Condom is made of thin rubber or latex sheath. Condom prevents deposition of sperms in the vagina. A condom protects against Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) like Syphilis and AIDS.
- Diaphragm (Cervical cap): Vaginal diaphragm fitting into the vagina or a cervical cap fitting over the cervix. This prevents the entry of sperms into the uterus.
(b) Hormonal Methods: Hormonal preparations are in the form of pills or tablets (contraceptive pills). These hormones stop the release of an egg from the ovary.
(c) Intra – Uterine Devices (IUDs): The intrauterine device (IUD) are contraceptive devices, inserted into the uterus. Lippe’s Loop and Copper-T, made of copper and plastic are two synthetic devices, commonly used in India. This can remain for a period of 3 years. This reduces the sperm fertilizing capacity and prevents implantation.
(d) Surgical methods: Surgical contraception or sterilization techniques are terminal methods to prevent any pregnancy. This procedure in males is called as vasectomy (ligation of vas deferens) and in females, it is called tubectomy (ligation of fallopian tube). These are methods of permanent birth control.