Samacheer Kalvi 6th English Solutions Term 1 Prose Chapter 1 Sea Turtles
Students can Download English Lesson 1 Sea Turtles Questions and Answers, Summary, Activity, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th English Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th English Solutions Term 1 Prose Chapter 1 Sea Turtles
Talk about
Question 1.
Have you seen turtles? Where do they live?
Answer:
Yes, I have seen turtles. They live in the sea.
Question 2.
What do you know about turtles?
Answer:
I know that turtles live long.
Question 3.
Why do you think the turtles in the picture have names such as Leatherback and Hawksbill?
Answer:
There are reasons why they are called such names. The turtle called leatherback has its back like leather. It has a strong and rough back. The turtle called hawksbill has a long neck like the peak of a hill or mountain.
Put (✓) for the correct and a (×) for the incorrect statements.
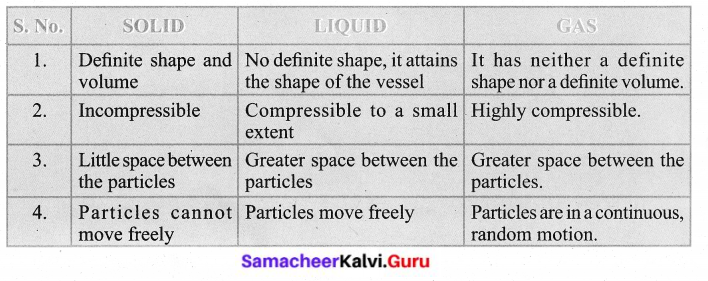
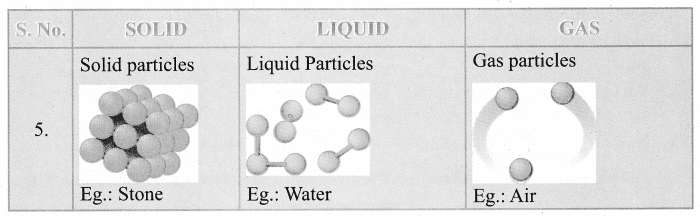
- Turtles are different from tortoises. (✓)
- Turtles are sea animals. (✓)
- There are seven kinds of sea turtles in the world. (✓)
- Sea turtles are very small. (×)
- Turtles come ashore to lay eggs. (✓)
- Sea turtles come to rest on land. (×)
- Olive Ridleys are the only sea turtles seen on Indian shores. (✓)
Are these statements right? Discuss with your partner and (✓) them if they are correct. Correct them if they are wrong. Share your answers in class.
- Female Olive Ridleys come ashore at night to lay eggs. (✓)
- The eggs of an Olive Ridley are in the shape and size of a cricket ball. (×)
- Ridleys come to lay their eggs in the month of January. (✓)
- The turtles use their flippers and make a hollow for their nests. (✓)
- The hatchlings use a tiny egg-tooth to come out of the eggs. (✓)
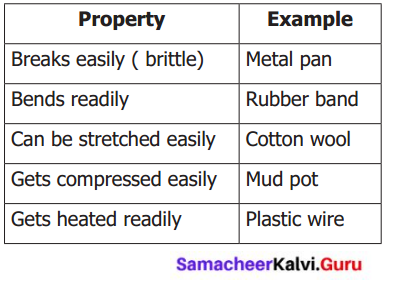
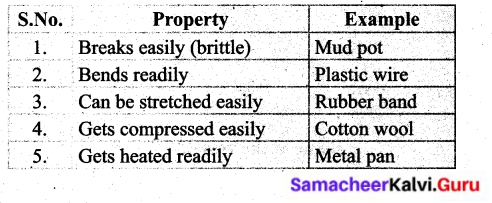
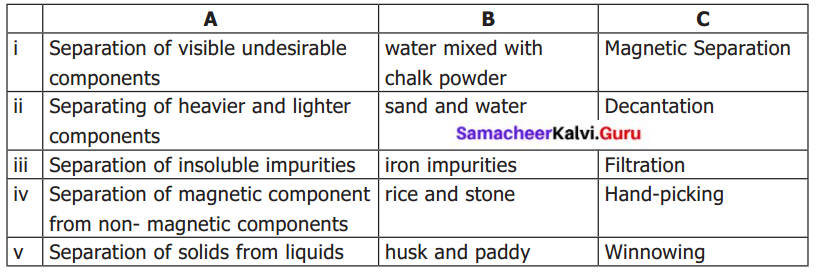
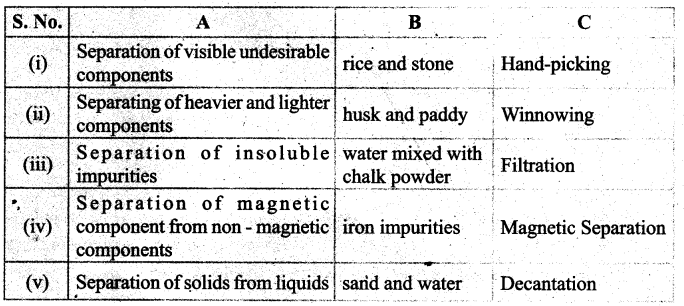
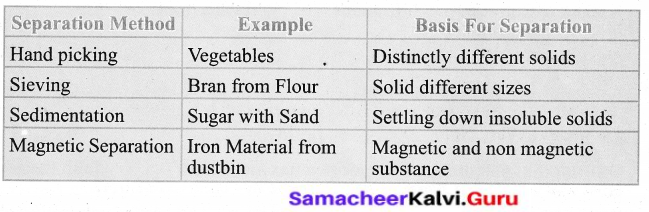
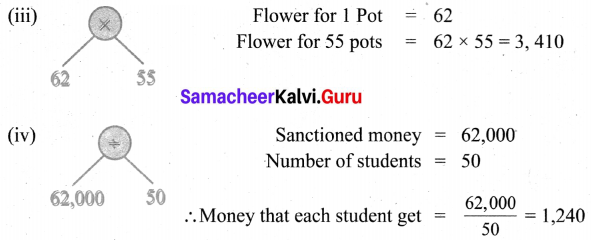
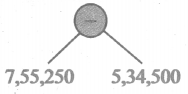
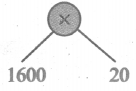
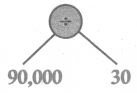
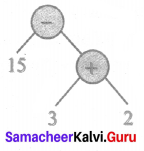
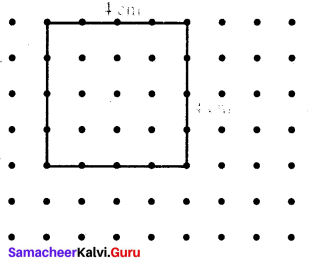
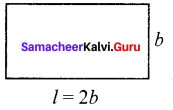
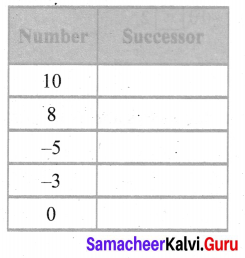
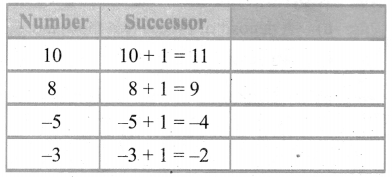
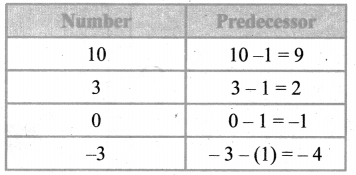
Fill in the table given below

Answer:

![]()
Read and Understand
A. Choose the correct answers. You may choose more than one answer If needed.
Question 1.
The _______ is a biological relative of tortoises.
(a) sea turtle
(b) fish
(c) reptile
Answer.
(a) sea turtle
Question 2.
In India’s coastal waters we can see a species of _______
(a) tortoises
(b) sea turtles
(c) dolphin
Answer:
(b) sea turtles
Question 3.
Sea turtles come to the shore to
(a) visit their birthplace
(b) lay eggs
(c) go back to sea
Answer:
(b) lay eggs
Question 4.
It is a problem for sea turtles to come ashore because _______
(a) they find it difficult to walk on the sand
(b) they don’t know their way to the shore
(c) animals and people hunt them
Answer:
(a) they find it difficult to walk on the sand
Question 5.
A turtle’s flippers help it to _______
(a) swim
(b) dig a nest
(c) climb
Answer:
(a) swim
Question 6.
A sea turtle camouflages its nest by tossing sand on it to _______
(a) hide its eggs from predators
(b) incubate eggs in the warmth of the sun
(c) keep the hatchlings safe
Answer:
(b) incubate eggs in the warmth of the sun
![]()
Vocabulary
B. Find any five words related to sea from the text (Sections I & II). Write them below. Then use the words to frame sentences of your own.
eg: beach – We like to play On the sandy beach.
Swimming – I like swimming
Motorboat – We went on a motorboat
Crabs – People eat crabs as seafood
Sand – Children play on the sand
Cavity – There are cavities on the beach
C. Fill in the blanks with words that convey the correct meaning of the sentences.
- Tiny hatchlings fall _______ (pray / prey) to many predators.
- Sea turtles live their (hole/whole) life in the sea.
- The turtles come ashore only during the _______ (night/knight).
- The predators follow the _______ (sent / scent) of the turtles to eat their eggs.
- The female turtles lay eggs and go back to the _______ (see / sea)
Answers:
- prey
- whole
- night
- scent
- sea
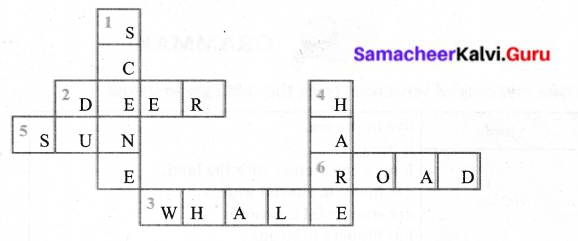
D. Use the dues and fill In the crossword puzzle.


- This word rhymes with seen.
- This animal has two horns and a spotted coat.
- This is a huge sea animal.
- Sounds like hair
- Shines brightly
- Rhymes with load
Answer:
![]()
Listening
E. Listen to the flash news. Read the questions given below, then listen to the flash news again and complete the responses.
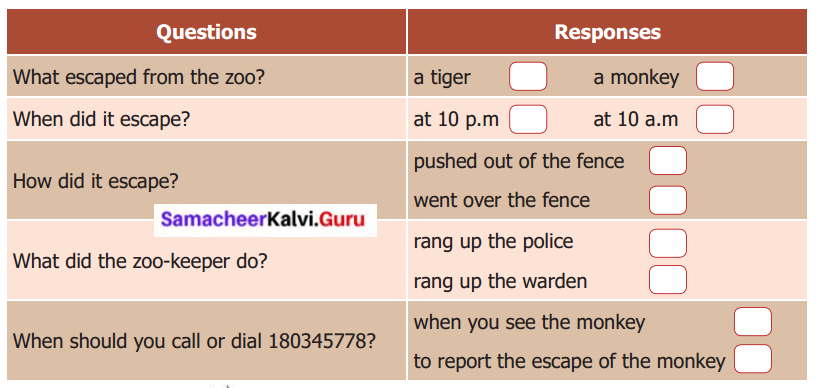
Answer:
![]()
Speaking
F. Look at the picture. Work in groups and give a short Wk about it using the words given below.

Good morning to one and all. I am going to speak about the Students’ Sea Turtle Conservation Network and its activities. This voluntary group protects the Olive Ridley turtles. The boys collect many eggs and incubate in a hatchery. Thus they enjoy doing this service. As soon as the hatchlings come out, they safely take them in a basket of sand. After that they leave them near the sea at night. The little turtles rush into the sea waves. However, rough sea conditions affect the turtles.
![]()
Grammar
G. Make meaningful sentences from the table given below.

A turtle – is huge.
– has flippers to swim.
Turtles – live in the sea.
– have a connection with the land.
– are found in coastal waters.
– are wonderful creatures.
H. Write a suitable sentence for the pictures given below.
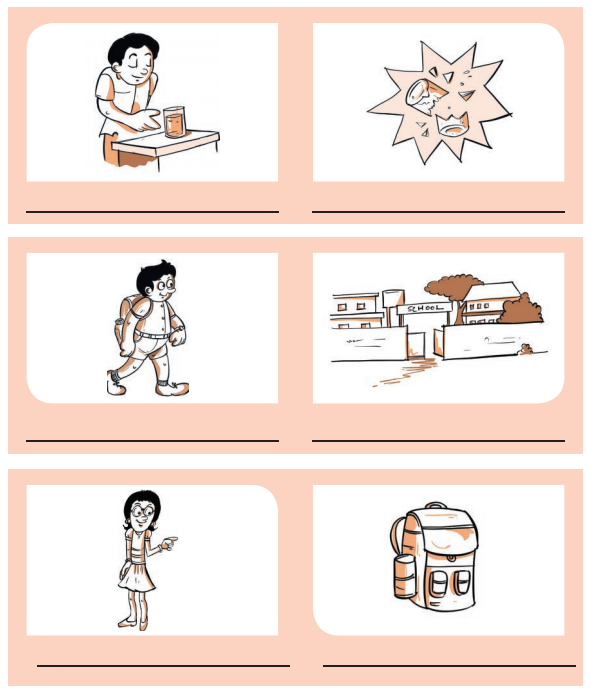
Answer:

I. Match the two halves of the sentences and read them.
- Sea turtles – a. threaten the survival of sea turtles.
- Hatchlings – b. uses its front flippers to swim.
- A turtle – c. come ashore to lay eggs.
- Many factors – a. cut open the leathery eggshell.
Answer:
- c
- d
- b
- a
![]()
Writing
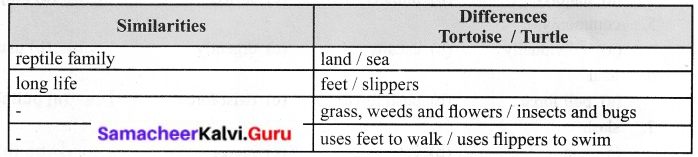
J. Tortoises and Turtles are not the same. Read the facts given below.
List the similarities and differences between them.
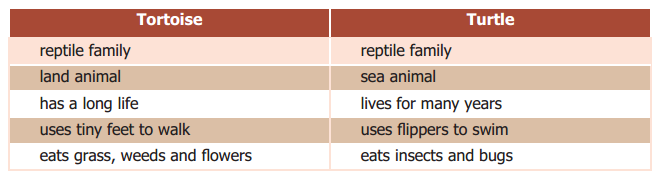
Answer:
K. Write a paragraph from the contents of the table given above. Frame sentences with these words – but as well as, whereas.
eg. A turtle, as well as a tortoise, belongs to the reptile family.
Answer:
A turtle as well as a tortoise belongs to the reptile family. A tortoise is a land animal whereas a turtle is a sea animal. Both a tortoise and a turtle lives long for many years. A tortoise uses its tiny feet to walk but a turtle uses flippers to swim. A tortoise feeds on grass, weeds, and flowers but a turtle eats insects and bugs.
![]()
Creative Writing
L. Describe the picture in about fifty words and give a suitable title. Make use of the words/phrases given below.

Answer:
There are many sea animals in the ocean. They are beautiful and wonderful in varied sizes, shapes, and structures. The fishes are in different colours and are of different varieties. Many rare species of fishes are found in the deep sea. Most corals and exotic species are under the sea.
![]()
Sea Turtles Additional Questions
I. Select the Suitable Synonyms.
1. entire
(a) small
(b) partial
(c) whole
Answer:
(c) whole
2. huge
(a) large
(b) little
(c) dwarfed
Answer
(a) large
3. connection
(a) separation
(b) link
(c) division
Answer.
(b) link
4. extremely
(a) majorly
(b) initially
(c) slowly
Answer
(a) majorly
5. commonly
(a) individually
(b) usually
(c) urgently
Answer:
(b) usually
6. haul
(a) pull force
(b) push force
(c) twist force
Answer:
(a) pull force
7. slash
(a) join
(b) cut
(c) merge
Answer:
(b) cut
8. emerge
(a) disperse
(b) submerge
(c) come out
Answer:
(c) come out
9. camouflage
(a) seek
(b) colour
(c) hide
Answer:
(c) hide
10. scent
(a) stink
(b) perfume
(c) heat
Answer
(b) perfume
11. aspect
(a) characteristic
(b) respect
(c) perfect
Answer
(a) characteristic
12. prey
(a) winner
(b) victim
(c) survivor
Answer:
(b) victim
13. tiny
(a) large
(b) huge
(c) small
Answer:.
(c) small
14. estimate
(a) calculate
(b) exact
(c) appropriate
Answer:
(a) calculate
15. adult
(a) young
(b) pre-mature
(c) matured
Answer:
(c) matured
16. survive
(a) die
(b) exist
(c) kill
Answer:
(b) exist
17. fascinating
(a) interesting
(b) surprising
(c) enjoying
Answer:
(a) interesting
18. mystery
(a) interesting
(b) story
(c) puzzle
Answer
(c) puzzle
19. wonderful
(a) amazing
(b) ordinary
(c) casual
Answer:
(a) amazing
20. accidentally
(a) wantedly
(b) deliberately
(c) unintentionally
Answer:
(c) unintentionally
21. construction
(a) destruction
(b) creation
(c) confusion
Answer:
(b) creation
![]()
II. Select the Suitable Antonyms.
1. entire
(a) absolute
(b) integral
(c) partial
Answer:
(c) partial
2. largest
(a) biggest
(b) smallest
(c) tallest
Answer:
(b) smallest
3. commonly
(a) rarely
(b) frequently
(c) regularly
Answer:
(a) rarely
4. after
(a) later
(b) next
(c) before
Answer:
(c) before
5. life
(a) soul
(b) death
(c) spirit
Answer:
(b) depth
6. tiny
(a) big
(b) small
(c) little
Answer:
(a) big
7. predators
(a) hunters
(b) killers
(c) rescuers
Answer:
(c) rescuers
8. cavity
(a) crater
(b) bulge
(c) dent
Answer:
(b) bulge
9. camouflage
(a) expose
(b) mask
(c) cover
Answer:
(a) expose
10. scent
(a) aroma
(b) fragrance
(c) stink
Answer:
(c) stink
11. emerge
(a) arise
(b) submerge
(c) appear
Answer:
(b) submerge
12. haul
(a) push
(b) lift
(c) pull
Answer:
(a) push
13. natural
(a) normal
(b) common
(c) artificial
Answer:
(c) artificial
14. accidentally
(a) unintentionally
(b) deliberately
(c) unwittingly
Answer:
(b) deliberately
15. sadly
(a) happily
(b) gloomily
(c) cheerlessly
Answer:
(a) happily
16. interested
(a) keen
(b) concerned
(c) uninterested
Answer:
(c) uninterested
17. conservation
(a) preservation
(b) depletion
(c) control
Answer:
(b) depletion
18. famous
(a) infamous
(b) acclaimed
(c) eminent
Answer:
(a) infamous
19. estimate
(a) guess
(b) appraise
(c) exact
Answer:
(c) exact
20. own
(a) possess
(b) rent
(c) dominate
Answer:
(b) rent
21. adult
(a) juvenile
(b) grown-up
(c) mature
Answer:
(a) juvenile
![]()
III. State True or False.
- Turtles and tortoises are the same. [False]
- The Leatherback is the largest sea turtle. [True]
- Jackals, dogs, and pigs will not eat the eggs of Olive Ridley. [False]
- Crabs and birds will eat the tiny hatchlings. [True]
- Human activities have put the turtles in grave danger. [True]
IV. Fill in the Blanks Using the Homophones.
- The eggs are left to incubate under the warmth of the _______ (sun/son).
- Most of us have _______ (scene/seen) a tortoise in a zoo or a reptile park.
- This is _______ (quiet/quite) a problem for female Olive Ridleys for moving on land.
- Human activities during the _______ (lost/last) few decades have put sea turtles in grave danger.
- The Olive Ridley weighs up to 35 kg when fully _______ (grown/groan).
Answers:
- sun
- seen
- quite
- last
- grown
![]()
V. Choose the Correct Answers (mcq).
Question 1.
The hatchlings open the eggshell using their _______
(a) egg-tooth
(b) flippers
(c) body
Answer:
(a) egg-tooth
Question 2.
It is estimated by scientists that only one in every _______ hatchlings become an adult
(a) 5000
(b) 1000
(c) 500
Answer:
(b) 1000
Question 3.
Female hatchlings that have become adults _______
(a) find a new beach to lay their eggs
(b) return to the same beach to lay their eggs
(c) lay their eggs in the ocean
Answer:
(b) return to the same beach to lay their eggs
Question 4.
Sea Turtles are _______ species
(a) endangered
(b) out of danger
(c) extinct
Answer:
(a) endangered
Question 5.
The only way to solve the problems faced by Sea Turtles is _______
(a) to not allow the sea turtles to come ashore
(b) to systematically tackle the problems and removing threats
(c) to dig the eggs laid onshore and put them back into the sea.
Answer:
(b) to systematically tackle the problems and removing threats
![]()
VI. Very short Answer Questions.
Question 1.
Where do the reptiles spend, almost their entire life?
Answer:
Ammamma asked the children to sit upstairs in the middle room and gave. The Reptiles spend almost their entire life in the sea.
Question 2.
How many species of marine or sea turtles are there?
Answer:
There are seven species of marine or sea turtles in the world.
Question 3.
Name the five sea-turtles found in India’s coastal waters.
Answer:
The Oliver Ridley, the Hawksbill, the Green sea turtle, the Loggerhead, and the Leatherback.
Question 4.
Where do they go to lay eggs?
Answer:
They must come ashore to lay their eggs.
Question 5.
How much does an Olive Ridley weigh?
Answer:
It weighs up to 35kg when fully grown.
![]()
VII. Short Answer Questions.
Question 1.
How do the local people jackals and domestic dogs identify the turtle’s eggs?
Answer:
Jackals, domestic dogs and pigs dig up and eat the eggs by following the scent left by the turtle. Even the local people follow the tracks of the turtle to its nest and collect the eggs for eating.
Question 2.
What happens to the eggs, that escape front the people and predators?
Answer:
The eggs that escape from the people and predators hatch 45 – 60 days later. The hatchlings slash open the leathery eggshell with the help of a tiny egg – tooth.
Question 3.
How do the hatchlings read) the shore?
Answer:
When most of the eggs have hatched, the hatchlings push themselves upwards through the sand and emerge on the surface of the beach. From there, they make a hurried dash to the sea.
Question 4.
Where does nesting take place?
Answer:
Mass nesting takes place on the shore. Odisha is one of the only three places in the world, where a phenomenon known as mass nesting or Arribada takes place. Thousands of female turtles come ashore simultaneously to lay their eggs on particular beaches.
Question 5.
How can we ensure that the sea turtles will continue to exist in die year to come?
Answer:
Only by systematically tackling the problems faced by the sea turtles and removing the threats subjected to them, can we ensure that sea turtles will continue to exist in the years to come.
![]()
VIII. Paragraph Questions.
Question 1.
What problems are faced by the female turtles, when they come ashore to lay their eggs?
Answer:
Between the months of January and March, female Olive Ridleys come ashore at night to lay their eggs. This is quite a problem for them, as a turtle’s front flippers enable it to swim gracefully and effortlessly, but are not very useful for moving on land. The turtle has to haul itself laboriously onto the beach. Then it chooses a spot well away from the high tide line. There, it scoops out a nest cavity, 45 cms deep, into which it lays about 100 eggs. Then it fills the cavity and hides the nest with the sand. Finally, it returns to the sea, leaving the eggs to incubate under the warmth of the sun.
Question 2.
Describe one of the many mysteries of these fascinating reptiles
Answer:
After many years of swimming in the open ocean, the female hatchlings that have become adults return to the same beach, they were bom. They come there to lay their own eggs. How they manage to find the place after so many years in the sea is one of the many mysteries of these fascinating reptiles. It is also a wonder that they have survived natural dangers for millions of years.
Question 3.
What are the problems that affect the survival of turtles?
Answer:
People hunt the sea turtles for their meat. They collect their eggs. Sometimes the turtles are trapped in the nets of motorboats. Pollution and the dumping of plastics into the ocean affect their survival. Construction activities on nestling beaches also hurt their survival.
![]()
Picto Grammar
Subjects and Predicate
Identify the subject and the predicate in the following sentences.
Question 1.
The sun was shining brightly.
Answer:
The sun (subject) / was shining brightly (predicate).
Question 2.
The dogs were barking loudly.
Answer:
The dogs (subject) / were barking loudly (predicate).
Question 3.
The pretty girl was wearing a blue frock.
Answer:
The pretty girl (subject) / was wearing a blue frock (predicate).
Question 4.
My younger brother serves in the army.
Answer:
My younger brother (subject) / serves in the army (predicate).
Question 5.
The man and his wife were working in their garden.
Answer:
The man and his wife (subject) / were working in their garden (predicate).
Question 6.
My mother and my aunt are trained, classical dancers.
Answer:
My mother and my aunt (subject) / are trained classical dancers (predicate).
Question 7.
You don’t have to wait for me.
Answer:
You (subject) / don’t have to wait for me (predicate).
Question 8.
We will no longer tolerate this.
Answer:
We (subject) / will no longer tolerate this (predicate).
Question 9.
The little tree was covered with needles instead of leaves.
Answer:
The little tree (subject) / was covered with needles instead of leaves (predicate).
Question 10.
A rich merchant was passing by the shoemaker’s window.
Answer:
A rich merchant (subject) /was passing by the shoemaker’s window (predicate).
![]()
For each sentence given below, underline the subject once and the predicate twice.
Example: John went to the movies with his friends.
Answer:
John went to the movies with his friends.
1. The horse appeared at the starting line.
Answer:
The horse appeared at the starting line.
2. The student arrived late to class because he woke up late.
Answer:
The student arrived late to class because he woke up late.
3. John looked out of the window to check the sky.
Answer:
John looked out of the window to check the sky.
4. The audience grew very restless waiting for the play to start.
Answer:
The audience grew very restless waiting for the play to start.
5. The air in the classroom smelled fresh.
Answer:
The air in the classroom smelled fresh.
6. I felt exhausted from the anticipation.
Answer:
I felt exhausted from the anticipation.
7. The owners grew flowers all around their house.
Answer:
The owners grew flowers all around their house.
![]()
Underline the simple subjects In the following sentences.
1. I want a new car.
Answer:
I want a new car.
2. James is nice.
Answer:
James is nice.
3. The sun is moving.
Answer:
The sun is moving.
4. Max wrote the letter.
Answer:
Max wrote the letter.
5. The letter was written by Max.
Answer:
The letter was written by Max.
The simple predicate is the main verb in the sentence.
Example: Mary plays the piano.
Answer:
Plays the piano.
In this example, the verb phrase “plays the piano” is the predicate.
Example: Josephine is having a nice day.
In this example, the verb phrase “is having a nice day” is the predicate.
Underline the simple predicates in the following sentences.
1. I run with my dog.
Answer:
I run with my dog.
2. We made a cake.
Answer:
We made a cake.
3. The cake was made by us.
Answer:
The cake was made by us.
4. Jessica and Rebecca are playing the piano and singing.
Answer:
Jessica and Rebecca are playing the piano and singing.
5. We will be running in the race this Sunday.
Answer:
We will be running in the race this Sunday.
![]()
Underline the simple subjects and draw a box around the simple predicates In the following sentences.
Example: Elise is going to sing at the concert tomorrow
1. The dentist charges $6200 for an office visit.
Answer:
The dentist charges $6200 for an offce visit.
2. The baby weighed 7.2 pounds at birth.
Answer:
The baby weighed 7.2 pounds at birth.
3. We need to make a new plan.
Answer:
We need to make a new plan.
4. I want to go to the concert, but I don’t have enough money.
Answer:
I want to go to the concert, but I don’t have enough money
5. My friend and I are going to the movies tonight.
Answer:
My friend and I are going to the movies tonight.
![]()
Now try to write three complete sentences of your own.
Try to underline the simple subjects and circle the simple predicates.

Choose a subject from the box to complete each sentence.
A big spider, A buzzing bee, My notebook, A gray dolphin, My mother, My closet, The houseplant, The eye doctor, The space alien
- _________ looked for nectar in the flower.
- _________ has lots of clothes in it.
- _________ checked my vision.
- _________ needs soil, water, and sunlight.
- _________ landed the UFO.
- _________ jumped in the sea.
- _________ was upset because I broke her favorite vase.
- _________ is filled with stories that I wrote.
- _________ spun a web in the doorway.
Answers:
- A buzzing bee
- My closet
- The eye doctor
- The houseplant
- The space alien
- A gray dolphin
- My mother
- My notebook
- A big spider
![]()
Choose a predicate from the box to complete each sentence.
watered her flowers, barked all night long, drove me to school, blew in the wind, ate crickets, cut the boy’s hair, fixed the sink, slept in her crib, flew the airplane.
- The gardener _________
- The pilot _________
- The little puppy _________
- The barber _________
- James’ baby sister _________
- The flag _________
- The lizard _________
- The plumber _________
- The bus driver _________
Answers:
- watered her flowers
- flew the airplane
- barked all night long
- cut the boy’s hair
- slept in her crib
- blew in the wind
- ate crickets
- fixed the sink
- drove me to school
![]()
Creative Writing
I. Make sentence of your own
1. Beach
2. Breeze
3. Swimming
Answer:
1. We like to play on the sandy beach.
2. The trees swayed in the breeze.
3. I like swimming.
II. Picture Composition:
Question 1.
Describe the picture in about fifty words and give a suitable title. Make use of the words/phrases given below.
children
playing park
boy
hand in hand
colourful
flowers wheel
girls
performed

Answer:
Theme park
There are children playing in a theme park. Two girls are playing by the swing each hand in hand. A boy is playing with a colourful boy. Some children are playing on the giant wheel. A circus show is also being performed there. The park is full of trees and flowers.
Question 2.
Describe the picture in about fifty words and give a suitable title. Make use of the words/phrases given below.
activities
classroom
student
building
discussing
Everyone
useful
answers
skit

Answer:
Drawing Class
These children are doing various activities with enthusiasm outside their classroom. A student is drawing and two other students are playing with the building blocks. Three children are enacting a skit. There are four children sitting and discussing their activity. Everyone is busy doing something useful answers.
![]()
Question 3.
Describe the picture in about fifty words and give a suitable title. Make use of the words/phrases given below.
monkey
picture
entrance
snakes
people
animals
welcome
bears
lions

Answer:
Zoo
This is a zoo. There are plenty of animals seen in the picture. I can see monkeys, elephants, lions, rabbits, giraffes, snakes, bears, tigers, and birds. They are all at the entrance of the zoo. I can see some animals on top of the board ‘zoo’. It seems that they are all ready to welcome the people, who visit the zoo.
Question 4.
Describe the picture in about fifty words and give a suitable title. Make use of the words/phrases given below.
bird
nest
hungry
mother
food
sitting
near
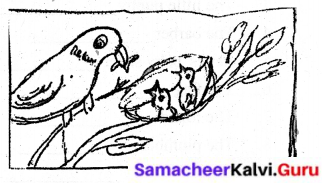
Answer:
Nest
I see a bird and two nestlings in the picture. The nestlings are seemed to be hungry. The mother bird has fetched some food. It is sitting near the nestlings. The nestlings eagerly open their beaks for the food.
![]()
Sea Turtles Summary
Section I
This lesson is about Sea Turtles which are different from Tortoise that we see in a zoo or a reptile park. There are seven species of sea turtles -out of which five are seen in India – the Olive Ridley, the Hawksbill, the Green Sea Turtle, the Loggerhead, and the Leatherback. The turtles are huge and weigh between 35 kg and 700 kg. The largest sea turtle is the Leatherback which is 2.2m long and 700 kg in weight. Sea turtles come to the shore to lay their eggs. Except for Olive Ridleys, other species have become rare in India. Mass Nesting or Arribada is a phenomenon that occurs in Odisha and other two places in the world where Olive Ridleys come ashore alone to lay their eggs.
Section II
Between January and March, female Olive Ridleys come ashore and haul (pull with force) using their front flippers onto the beach. They choose a spot away from the high tide and dig 45 cm into which they lay their eggs. They lay about 100 eggs at one time. After covering the nest with sand it returns to the sea. The eggs are left to incubate under the sun. People collect these eggs for eating. Jackals, domestic dogs, and pigs eat the eggs. After escaping from the predators, the hatchlings (little ones) come out of the eggshell with the help of an egg-tooth. After they come out they make a dash into the sea.
Section III
Weighing less than 20 grams, many of these hatchlings fall prey to crabs or birds before they reach the sea. It is estimated that one in a thousand hatchlings become an adult. After swimming for years in the sea, the adult female returns to the same beach where they were born which is an unsolved mystery. Human activities have endangered the survival of sea turtles. Problems like pollution, the dumping of plastics into the ocean, and the construction activities on nesting beaches endanger their survival. We have to tackle these problems to save the sea turtles.