You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 1 Chapter 3 Matter Around Us
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Matter Around Us Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the appropriate answer.
Question 1.
_____ is not made of matter.
(a) gold ring
(b) iron nail
(c) light ray
(d) oil drop
Answer:
(c) light ray
Question 2.
200 ml of water is poured into a bowl of 400 ml capacity. The volume of water now will be
(a) 400 ml
(b) 600 ml
(c) 200 ml
(d) 800 ml
Answer:
(c) 200 ml
Question 3.
Seeds from water-melon can be removed by _____ method.
(a) hand-picking
(b) filtration
(c) magnetic separation
(d) decantation
Answer:
(a) hand-picking
Question 4.
Lighter impurities like dust when mixed with rice or pulses can be removed by
(a) filtration
(b) sedimentation
(c) decantation
(d) winnowing
Answer:
(d) winnowing
Question 5.
_____ is essential to perform winnowing activity.
(a) Rain
(b) Soil
(c) Water
(d) Air
Answer:
(d) Air
Question 6.
The filtration method is effective in separating a mixture
(a) Solid-solid
(b) Solid-liquid
(c) liquid-liquid
(d) liquid-gas
Answer:
(b) Solid-Liquid
Question 7.
From the following, _____ is not a mixture.
(a) coffee with milk
(b) lemon juice
(c) water
(d) ice cream embedded with nuts
Answer:
(c) water
![]()
II. True or False. If False, give the correct statement.
Question 1.
Air is not compressible.
Answer:
False. Air is highly compressible.
Question 2.
Liquids have no fixed volume but have a fixed shape.
Answer:
False. Liquids have fixed volume but have no fixed shape.
Question 3.
Particles in solids are free to move.
Answer:
False. Particles of solid can not move freely (or) Particles of liquid are free to move.
Question 4.
When pulses are washed with water before cooking, the water is separated from them by the process of filtration.
Answer:
False. When pulses are washed with water before cooking the water is separated from them by the process of decantation.
Question 5.
Strainer is a kind of sieve which is used to separate a liquid from a solid.
Answer:
True.
Question 6.
Grain and husk can be separated by winnowing.
Answer:
True.
Question 7.
Air is a pure substance.
Answer:
False. Air is a mixture of gases.
Question 8.
Butter from curds is separated by sedimentation.
Answer:
False. Butter from curd is separated by Churning.
![]()
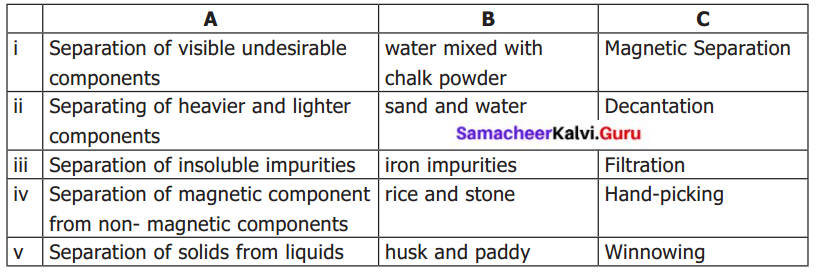
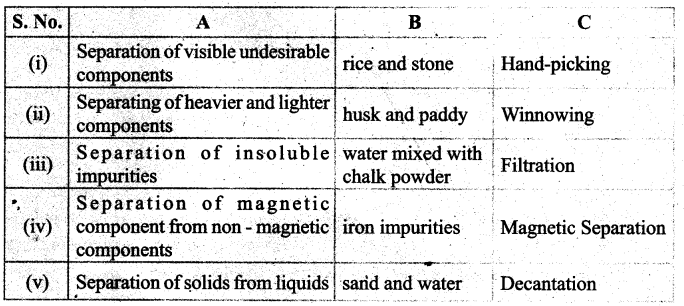
III. Match the following.
(a)
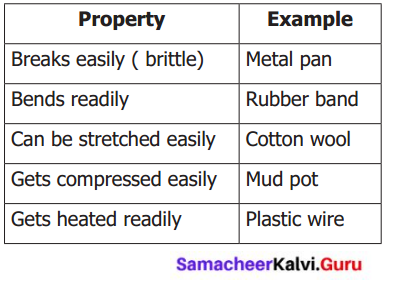
Answer:
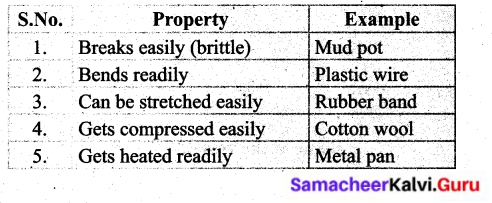
(b)
Answer:
IV. Fill In the blanks.
- Matter is made up of ______
- In solids, the space between the particles is less than in ______
- Grains can be separated from their stalks by ______
- Chilies are removed from ‘upma’ by the ______ method.
- The method employed to separate clay particles from water is ______
- Among the following items: safety pins, pencil and rubber band, ______ will get attracted to a magnet.
- Water obtained from tube wells is usually ______ water.
Answers:
- atoms
- liquids and gases
- Threshing
- handpicking
- Filtration
- Safety pins
- Impure
![]()
V. Complete the given analogy.
- Solid: rigidit :: gas: ______
- Large Inter-particle space: gas:: ______ :solid
- Solid: definite shape :: ______ : shape of the vessel.
- Husk-grains: winnowing:: Sawdust-Chalk piece : ______
- Murukku from hot oil: ______ : coffee powder residue from decoction: ______
- Iron – sulphur mixture : ______ :: Mustard seeds from Urad-dhal: rolling
Answers:
- Flexibility.
- Little inter-particle space.
- Liquid.
- Filtration
- Filtration
- Magnetic separation.
![]()
VI. Give a very short answer.
Question 1.
Define the term matter?
Answer:
Matter is defined as anything which occupies space and has mass.
Question 2.
How can husk or fine dust particles be separated from rice before cooking?
- The husk or fine dust particles can be separated from rice by washing the rice with water before cooking.
- The lighter impurities float while heavier rice grains sink to the bottom. (It is sedimentation).
- Then the water with the impurities is carefully poured away by decantation, leaving clean rice at the bottom.
Question 3.
Why do we separate mixtures?
Answer:
We separate mixtures:
- to remove impurities or harmful components (eg: stones from rice),
- to separate useful component from other components (eg: petrol from petroleum)
- to obtain a substance in highly pure form (eg: gold from gold mines).
Question 4.
Give an example for mixture and justify your answer with reason.
Answer:
Milk is an example for the mixture.
It contains water, fat, protein etc. Since two or more compounds are mixed in a physical combination, milk is a mixture.
Question 5.
Define sedimentation?
Answer:
The settling down of a heavier component of a mixture, when allowed to remain undisturbed for some time, is called sedimentation.
Question 6.
Give the main difference between a pure substance and an impure substance.
Answer:
Pure substance:
- It is made up of only one kind of particles
- Unadulterated
Impure substance:
- It is made up of two or more toxic particles
- Adulterated
![]()
VII. Give a short answer :
Question 1.
A rubber ball changes its shape on pressing. Can it be called a solid?
Answer:
Yes, It has a definite shape and volume. Its particles cannot move freely. It confirms the solid properties.
Question 2.
Why do gases not have fixed shape?
Answer:
- Gases possess more intermolecular space and less forces of attraction.
- They can move freely at any direction.
- They have the property of filling the entire part of a container by taking the shape of the container.
So, gases do not have fixed shape.
Question 3.
What method will you employ to separate cheese (Paneer) from milk? Explain.
Answer:
Filtration:
- Heat the milk
- Add lime Juice or vinegar after few minutes
- Cheese will float on the liquid
- Use strainer to separate the cheese (paneer) from milk.
Question 4.
Look at the picture given below and explain the method of separation illustrated.

Answer:
The method is called as Sieving. It is used to separate solid particles of different sizes. Ex. bran from flour.
Question 5.
How can you separate a mixture of a large number of tiny bits of paper mixed with pulses/dal?
Answer:
Bits of paper are separated from pulses/dal by winnowing. Bits of paper have less weight and get easily blown away by the wind. The pulses/dal are heavier particles and will fall down closer.
Question 6.
What is meant by food adulteration?
Answer:
Food adulteration is the process in which the quality of food is lowered either by the addition of inferior quality material or by extraction of valuable ingredients.
Question 7.
Mr. Raghu returns home on a hot summer day and wants to have buttermilk. Mrs. Raghu has only curds. What can she do to get buttermilk? Explain
Answer:
Method to prepare buttermilk from curd:
- Using a hand chumer, the curd has to be blended well.
- Two cups of chilled water are to be added after churning the curd.
- The water is to be mixed well so there are no lumps.
- Ingredients, such as chaat masala shall be added before serving the buttermilk.
![]()
VIII. Question based on Higher Order Thinking Skills.
Question 1.
Distinguish between properties of Solid, liquid, gas. Draw a suitable diagram.
Answer:
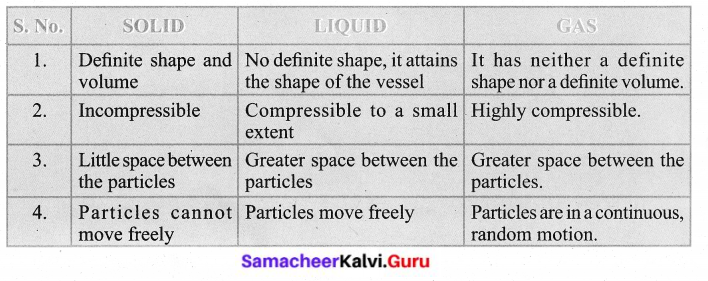
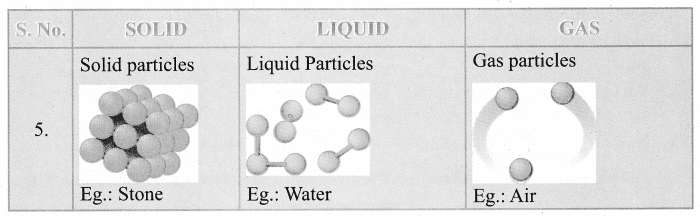
Question 2.
Using a suitable apparatus from your laboratory separate the mixture of chalk powder, mustard oil, water, and coins. Draw a flow chart to show the separation process.
Answer:
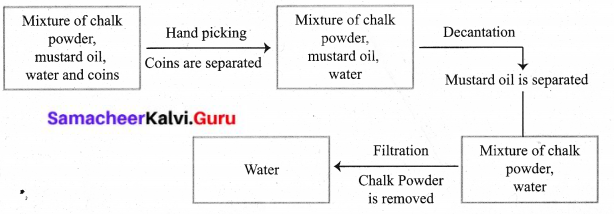
![]()
Question 1.
Malar’s mother was preparing to cook dinner. She accidentally mixed ground nuts with urad-dhal. Suggest a suitable method to separate the two substances so that Malar can have ground nuts to eat.
Answer:
- Separation of groundnuts and Urad-dhal.
- Wire mesh as a strainer sieve is used to separate ground nuts and Urad-dhal. Because both are solids of different sizes.
Question 2.
In a glass containing some water, tamarind juice and sugar is added and stirred well. Is this a mixture can you tell why? Will this solution be sweet? or sour? or both sweet and sour?
Answer:
Yes. It is a mixture. It has more than one kind of particle, i.e. Tamarind, Water, and Sugar are mixed together. This solution will be sweet and sour.
Question 3.
Justify your answer.
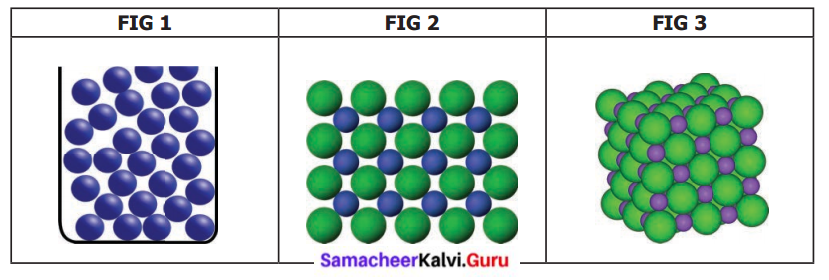
The arrangement of particles in three different phases of matter is shown above.
(a) Which state is represented by fig. 1?
(b) In which will be the interparticle attraction maximum?
(c) Which one of them cannot be contained in an open vessel?
(d) Which one can take the shape of its container?
Answer:
(a) Liquid state, is represented by Fig 1.
(b) In Fig. 3 the interparticle attraction will be maximum because it is in a solid-state.
(c) Fig. 2 cannot be contained in an open vessel, as it is in the gaseous state.
(d) Fig. 1 can take the shape of its container, as it is in the liquid state.
![]()
IX. Life Skills-Debate
Question 1.
Debate on “Food adulteration and detection”.
Answer:
Food is a basic requirement for life. It should be pure, nutritious, and free from any type of adulteration.
Adulteration :
Sometimes, things that we buy in the market are mixed with harmful and unwanted substances. Food can also get adulterated due to carelessness or lack of proper handling. It will not possible to check for adulteration on visual examination. Following tests will help even a layman or non-technical person to detect adulterants in some of the products.
Detection:
Milk: Adulterants used can be water, starch, urea, sucrose, detergents, neutralizer, formalin etc. These adulterants are used to increase the thickness, viscosity, and shelf life of milk.
Test: Put a drop of milk on a polished vertical surface. The drop of pure milk either stops or flows slowly leaving a white trail behind it. Whereas milk adulterated with water will flow immediately without leaving a mark. We can also use Lactometer for measuring the specific density of milk.
Sugar: Adulterant: Chalk
Test: Dissolve sugar in a glass of water, chalk will settle down at the bottom
Ice Cream: Adulterant: washing Powder
Test: Put some lemon juice on ice-cream, bubbles come out in the presence of washing powder
Test: Take one teaspoonful of melted ghee or butter with an equal quantity of cone. Hydrochloric acid in a test tube and add to it a pinch of cane sugar. Shake well for one minute and let it stand for five minutes. The appearance of crimson colour in the lower layer shows the presence of vanaspati.
We must be careful about the common adulterants in our food. We might be eating a dangerous dye, sawdust, industrial starch, or other contaminated foods which are a major source of diseases. And thus, we invite diseases rather than good health. Food adulteration is basically lowering the quality of food. So, we must be aware of such adulteration.
![]()
XI. Sequence Type
Question 1.
Write the sequence of steps you would use for making tea.
Use the words : mixture, dissolve, filtrate and residue.
Answer:
- Take Tea powder and Milk
- Heat the milk, then add tea powder.
- Add sugar to taste and, Stir well.
- The sugar will be dissolved in the mixture.
- Filter the mixture. Tea (filtrate) flows down through filter paper.
- Tea leaves settle as residue on the filter paper.
![]()
XII. Topic enrichment – Project.
Question 1.
Make a fruit or vegetable salad. Give reasons why you think it is a mixture.
Answer:
Fruit Salad:
Discard the skin of a banana, papaya, orange, apple, pineapple, guava, and make small slices. Add pomegranate and grapes. Then mix with cream milk and honey. Now the fruit salad is ready. As this Fruit Salad is a physical combination of two or more substances, it is a mixture.
Vegetable Salad:
It is prepared with the primary ingredients of tomato, cucumber, onion, carrot, mint, lemon juice, and dried chili peppers. As this Vegetable Salad is a physical combination of two or more substances, it is a mixture.
Question 2.
Connect with sports
Air is not a pure substance. It helps us in many ways from breathing to playing. Balloon sports are very popular sport. The basis of how the balloon works are that hot air is lighter than cool air. which makes the balloon rise up Find out more about Hot Air balloons.

Answer:
The hot air balloon consists of three parts: an envelope- which contains heated air, a basket, and a burner system which creates an open flame by burning a mix of liquid propane and air.
The basic principle behind hot air balloons is the use of hot air to create buoyancy, which generates lift.
Hot air weighs less than the same volume of cold air, because it is less dense. It means that hot air will rise up and float when there is cold air around it.
Nowadays, most hot air balloons are made of nylon. The melting point of this material is approximately 230° C. The temperature inside a hot air balloon is usually kept below 120° C.
Hot air balloon festivals are held annually in many places throughout the year, allowing hot air balloon operators to gather- as well as for the general public to participate in various activities.
Hot air balloon flights are not possible in the rain. This is because the heat inside of the balloon can bring rain to boiling temperatures on top of the balloon, thereby destroying hot air balloon fabric.
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Matter Around Us Intext Activities
Activity 1
Take a few crystals of sugar. Observe them carefully with the help of a magnifying lens.
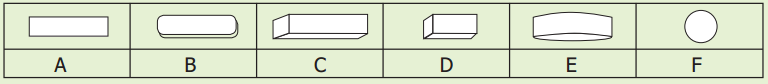
Which of the shapes given above resembles a sugar crystal?
A B C D E F
Answer:
D
Now place a few sugar crystals in a teaspoon full of water. What happens to the sugar crystals?
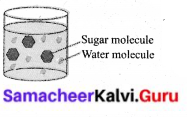
A sugar crystal is also made up of molecules. When sugar dissolves in water, the sugar crystals break down and the molecules of sugar get distributed in water. This makes water sweet to taste. The sugar molecules are extremely small, that is why we are not able to see them. Small amount of matter has nfany millions of molecules in it. (1 million =10 lakhs).
Activity 2
Sit together in groups of three. Look at objects given below. Are they familiar to you? Are they same or different? On what basis did you group them? Is there only one way of doing it or more ways? Discuss with your group members and note it down.

Answer:
There are various objects. There are many ways to group them. For example,
Pencil & books – Used for Studying
Bucket and comb – Made of Plastic
Table and ladle – Made of Wood
Glass of water and spectacles – Light can pass through
Apple and iron box – Light cannot pass through
Cow and bird – Living things
Feathers and paper cup – Will float in water
Apple or piece of stone – Will sink in water
Scrub brush and broom – Rough
Try to fill in the following table.
Answer:
Things that float:
- Feathers
- Plastic Comb
- Paper cups
Things that sink:
- Glass
- Piece of stone
- Apple
![]()
Activity 3
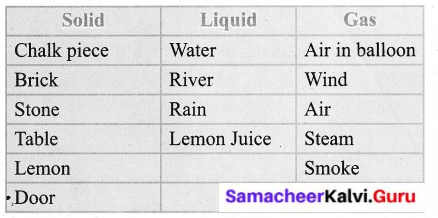
Work in a group of two. Malar was asked to group some items based on their physical states. This was the table she made. Do you agree with her? Correct the table if you do not agree and submit it to your teacher.
Answer:
Activity 4
Question 1.
Lift an uninflated cycle tube. Inflate it and lift it again. Is there a change in the weight? Can we see that air has mass?
Answer:
The weight of the inflated cycle tube is more than the weight of the uninflated cycle tube. So we can say that air is also matter though we cannot see, it occupies and also has mass.
Test Yourself
- Name an object which is brittle and transparent ______
- Name an object which can be stretched ______
- Name two objects which can be bent ______
Answer:
- Glass
- Rubber band
- Feather, Paper cup
![]()
Activity 5
Let us take two sachets of juice. In both the sachets, it is written 100ml. Let us empty two sachets and pour the juice into the following glasses.
Question 1.
Does its shape also change? Yes / No

Answer:
Yes.
Question 2.
Does its volume change? when it is poured into a big glass or a small one? Yes / No.
Answer:
No.
Question 3.
How will you find out whether the volume has changed or not?
Answer:
With the help of a graduated beaker, we can find out whether the volume has changed or not.
A liquid needs a container and takes the shape of a container because the particles slide past one another and keep moving. The amount of juice is the same in both glasses. The volume of a liquid remains the same whether it is kept in a large container or a small one but its shape changes.
Try it yourself.
Identify the mixture the table given below. Write “yes” for mixture and no if it is not a mixture. You may also write “I do not know” and later discuss with your teacher.
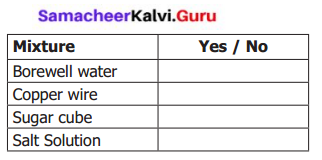
Answer:

![]()
Activity 6
Think and find out, is it a good idea to separate the bran from flour?
Answer:
No. It is not a good idea to separate bran from flour. Because, Bran is rich in dietary fiber, and essential fatty acids. It contains significant quantities of starch, protein, vitamins. It is also a source of phytic acid. In foreign countries, it is used as a nutrient and production of oils.
Activity 7
Group Activity – Students are divided into 4 groups
Each group should suggest a method to separate mixtures and also give reasons why they used a particular method and what property of the components forms the basis for separation. Examples should be drawn from day-to-day life. After the group presents its method to the rest of the class, the whole class will discuss and analyse if the suggested method will work and then make a note of it in the form given below:
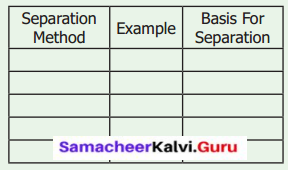
Answer:
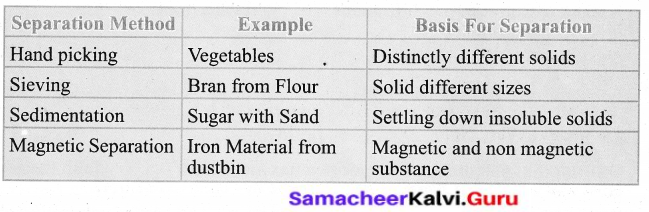
![]()
Activity 8
Collect and share information on common adulterants and their detection in foodstuff in the class. Watch the youtube video: 10 simple tricks to find adulterated food, https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=_XLi WunnudY
Answer:
(i) Argemone seed in the mustard seed.
Argemone seed is crushed with a hammer its cotyledon is white in colour.
Mustard seed is crushed with a hammer its cotyledon is yellow in colour.
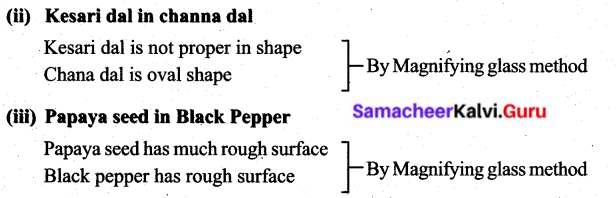
(iv) Tea Powder
Adultered tea powder – add water: The water is changed in red colour
Original tea powder – add water: The watercolor will be yellow
(v) Chill Powder
Adultered Chilli povder – add water: The colour of the water is changed to red colour
Good quality chilli powder – add water: The colour of the water will be yellow.
(vi) Adulterated Turmeric powder is added with HCl. The mixture is red in colour then add water. No change.
Original Turmeric power is added with HCl. The mixture is red in colour then add water. The red colour is changed into colourless.
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Matter Around Us Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
All the matter made of ______
(a) Particles
(b) Atoms
(c) Elements
(d) Mixture
Answer:
(b) Atoms
Question 2.
Intermolecular forces of attractions are maximum in
(a) liquids
(b) plasma particles
(c) solids
(d) gases
Answer:
(c) solids
Question 3.
A drop of water contains about ______ water particles.
(a) 1021
(b) 1012
(c) 1022
(d) 1020
Answer:
(a) 1021
Question 4.
The method of separating substances based on size, color, and shape is called
(a) Hand-picking
(b) Winnowing
(c) Threshing
(d) sieving.
Answer:
(a) Hand-picking
Question 5.
has definite shape and volume.
(a) Solid
(b) Liquid
(c) Gas
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Solid
Question 6.
The space between _______ particles is the greatest one.
(a) solid
(b) liquid
(c) gas
(d) cold
Answer:
(c) gas
Question 7.
For removing grains from stalks, the _______ method is used.
(a) Winnowing
(b) Sieving
(c) Churning
(d) Threshing
Answer:
(d) Threshing
Question 8.
Very tiny insoluble solid separated from a liquid is _______
(a) Winnowing
(b) Churning
(c) Sieving
(d) Filtration
Answer:
(b) Churning
Question 9.
_______ is a smallest particle.
(a) Molecule
(b) Element
(c) Atom
(d) Substance
Answer:
(c) Atom
Question 10.
We mix rice, dal, salt, chilies, pepper, ghee, and other ingredients to make Pongal. So Pongal is also a _____
(a) Mixture
(b) Compound
(c) Element
(d) Matter
Answer:
(a) Mixture
![]()
II. State whether the following statements are True or False. If false give the correct statement.
Question 1.
Gas like the state of Matter that exists at extremely cold temperatures used in the field of cryogenics.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
The particles in the matter are extremely small and can be seen even with a powerful microscope.
Answer:
False. The particles in the matter are extremely small and cannot be seen even with a powerful microscope.
Question 3.
The Cow and Birds are nonliving things.
Answer:
False. The Cow and Birds are living things.
Question 4.
The feather and paper cup can float on the water.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
The force of attraction between liquid particles is more than solid particles.
Answer:
False. The force of attraction between liquid particles is less than solid particles.
Question 6.
Gases have neither a definite shape nor a definite volume.
Answer:
True.
Question 7.
Water particles have no space between them.
Answer:
False. Water particles have space between them.
Question 8.
Liquid is affected by gravity less than anything.
Answer:
False. Liquid is effected by gravity more than anything.
![]()
III. Fill in the blanks.
- Stars including Sun are covered in _______
- Tiny particles present in all matter are called as _______
- A _______ substance is made up of only one kind of particle.
- The purity of gold is expressed in terms of _______
- _______ is used to separate gravel from the sand at a construction site.
- _______ process is done after sedimentation.
- RO is a process for removing impurities from _______ to make it potable.
- Turmeric powder is adulterated with a _______ chemical.
- In most houses people use a commercial water filter to remove impurities and also kill the harmful germ in water using _______
- The principle used in washing machines to squeeze out dirt from a cloth is called _______
- _______ is not affected by gravity.
- An example of a substance to be obtained in highly pure form is _______
Answers:
- Plasma
- atoms and molecules
- pure
- Carat
- Wire mesh
- Decantation
- Water
- bright yellow
- UV-rays
- centrifugation
- Gas
- Gold from gold mines
![]()
IV. Complete the Analogy.
- Bucket: Plastic :: Table : _______
- Water : Liquid :: Apple : _______
- Made up of one kind of particles : Pure substance :: Chemical combination of two or more element: _______
- Mixture containing iron: Magnetic separation:: Muddy water: _______
- Removal of Harmful germs : UV rays :: Removal of Impurities from water : _______
Answers:
- Wood
- Solid
- Compound
- Filtration
- RO process
V. Short Answers.
Question 1.
Mention any two characteristics of the particles of matter.
Answer:
- Particles of matter have a lot of space in between them.
- Particles of matter attract each other.
Question 2.
How the matter is grouped on the basis of physical states?
Answer:
Matter can be grouped into three states:
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gas.
Question 3.
What is meant by compound?
Answer:
Compound is the substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements.
Question 4.
Define the term ‘Diffusion’.
Answer:
Diffusion is the tendency of particles to spread out in order to occupy the available space.
Question 5.
What is Decantation?
Answer:
After sedimentation, the supernatant liquid is slowly poured out from the container without disturbing the sediment.
Question 6.
How the substance of gaseous particles change to a liquid state?
Answer:
When pressure on a gas is increased, its molecules come closer together, and its temperature is reduced, which removes enough energy to make it change from the gaseous to the liquid state.
Question 7.
Give any two characters of a pure substance.
Answer:
- A pure substance is made up of only one kind of particle.
- It may be elements or compounds.
Question 8.
Air is a mixture. Justify.
Answer:
Air contains Oxygen, Nitrogen, Carbon dioxide, Water vapour, Noble gases, etc. So it is a Mixture.
Question 9.
Give the characters a mixture.
Answer:
- Mixture is an impure substance and contains more than one kind of particle.
- In the mixture, the components are mixed in any proportion.
Question 10.
What is meant by separation?
Answer:
The process by which the components of the mixture are isolated and removed from each other to get a pure substance is called separation.
Question 11.
What are the steps involved in the separation of sand, salt, and water?
Answer:
Sedimentation, decantation, filtration, evaporation, and condensation.
Question 12.
Give any two examples of adulterated food.
Answer:
- Used tea leaves are used as adulterants in tea.
- Small stones are mixed with rice.
![]()
VI. Long Answer.
Question 1.
Classify the following based on their physical states.
Stone, Air, Kerosene, LPG, Book, Eraser, Smoke, Coconut oil, Petrol, Cool drinks.
Answer:
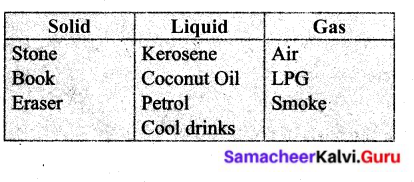
Question 2.
Fill up the column B with the correct term, given in the options below: (Sedimentation, Churning, Sieving, Threshing, Filtration)
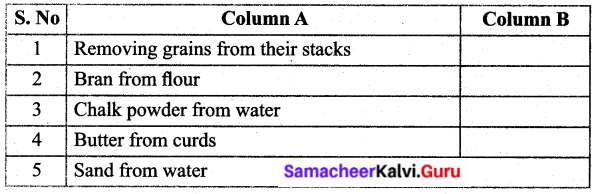
Answer:
- Threshing
- Sieving
- Filtration
- Churning
- Sedimentation
Question 3.
What is Decantation? Explain with Diagram.
Answer:
The water with the impurities is carefully poured away leaving clean rice at the bottom. This is called a decantation.
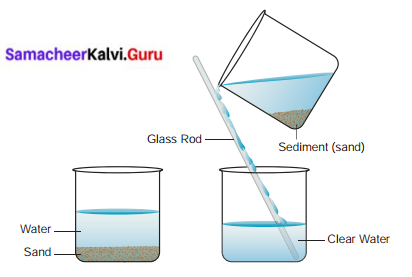
- This process is done after sedimentation.
- The supernatant liquid is slowly poured out from the container without disturbing the sediment.
- The part that has settled down is called sediment.
- The water that is obtained after decantation is called the decanoate.
- The process of removal of water above the sediment is called decantation.
- But even after decantation, the water is not completely free from fine soil particles.
- By the process of filtration, we can remove soil particles.