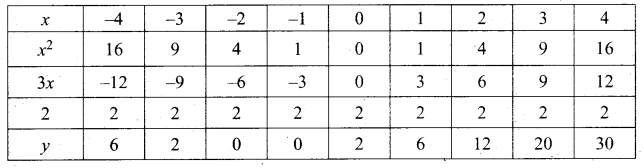
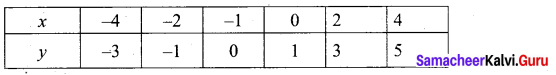
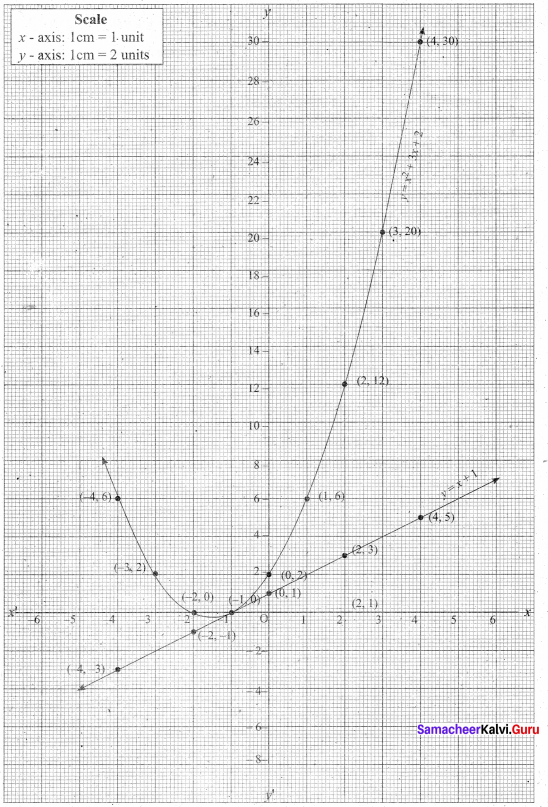
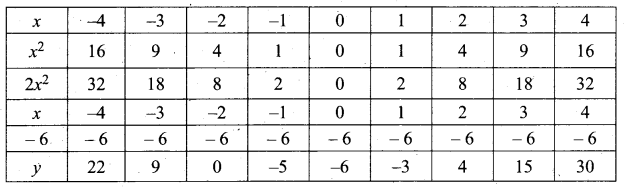
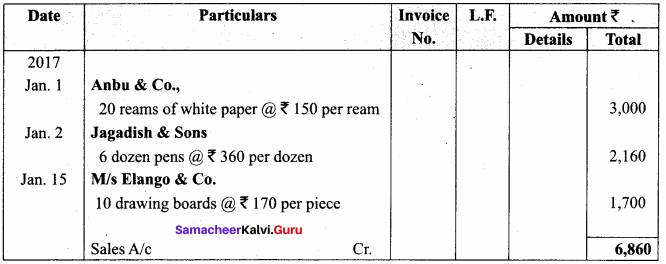
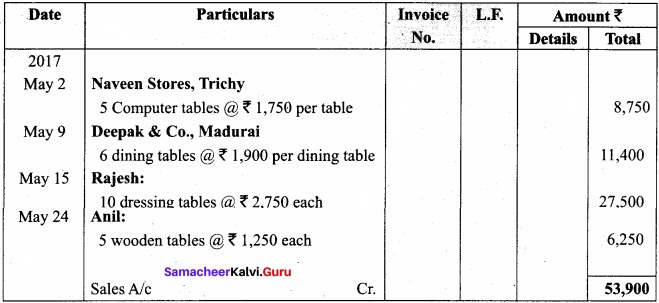
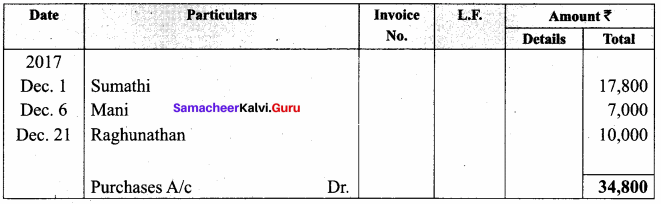
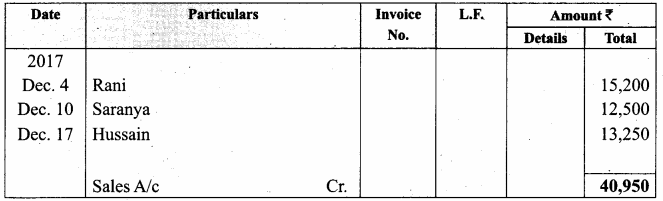
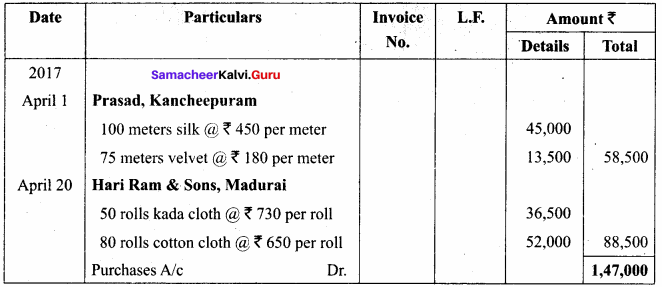
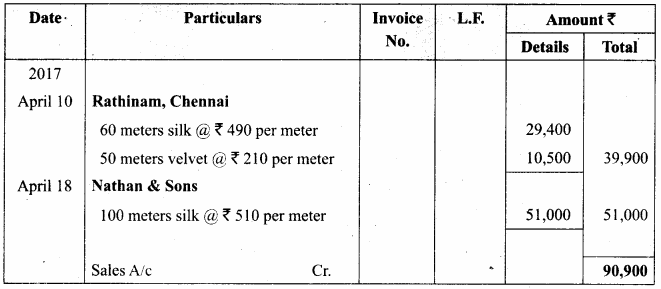
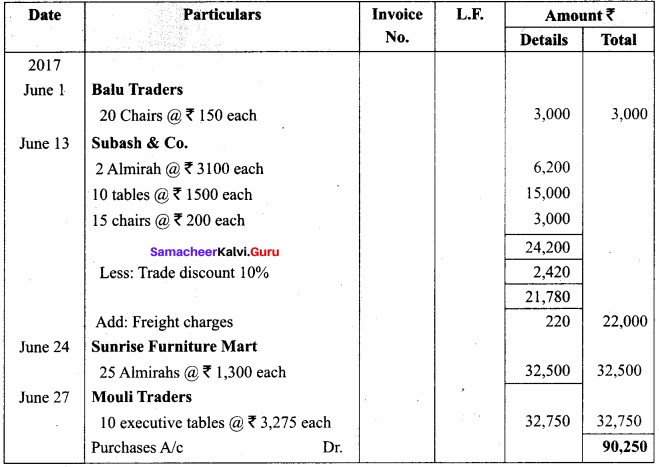
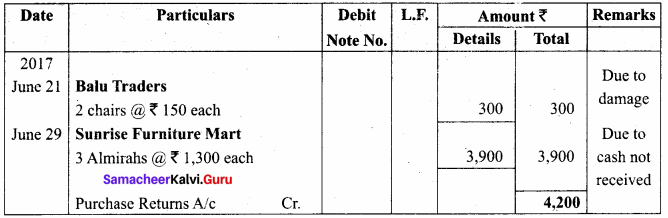
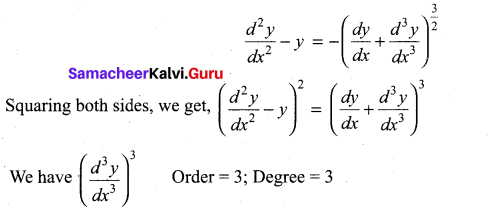
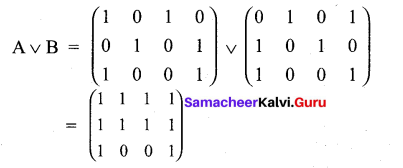
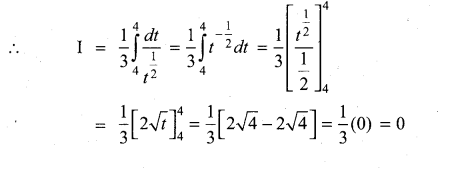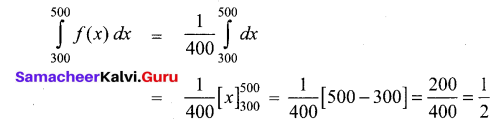Students can Download Computer Applications Chapter 1 Multimedia and Desktop Publishing Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Solutions Chapter 1 Multimedia and Desktop Publishing
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Multimedia and Desktop Publishing Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – I
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
………………………… refers to any type of application that involves more than one type of media such as text, graphics video animation and sound
(a) an executable file
(b) desktop publishing
(c) multimedia
(d) hypertext
Answer:
(c) multimedia

Question 2.
One of the disadvantages of the multimedia is its …………………………….
(a) cost
(b) adaptability
(c) usability
(d) relativity
Answer:
(a) cost
Question 3.
Expand JPEG
(a) joint photo experts gross
(b) joint photographic experts group
(c) joint processor experts group
(d) joint photographic expression group
Answer:
(b) joint photographic experts group

Question 4.
You need hardware, software and …………………….. to make multimedia.
(a) network
(b) compact disk drive
(c) good idea
(d) programming knowledge
Answer:
(b) compact disk drive
Question 5.
Match the following by choosing the right one.
(i) Text – 1.TGA
(ii) Image – 2. MIDI
(iii) Sound – 3. MPEG
(iv) Video – 4. RTF
(a) (i)-1, (ii)-2, (iii)-3, (iv)-4
(b) (i)-2, (ii)-3, (iii)-4, (iv)-1
(c) (i)-4, (ii)-1, (iii)-2, (iv)-3
(d) (i)-3, (ii)-4, (iii)-1, (iv)-2
Answer:
(c) (i)-4, (ii)-1, (iii)-2, (iv)-3

Question 6.
Find the odd one on the following which is not an image format
(a) TIFF
(b) BMP
(c) RTF
(d) JPEG
Answer:
(c) RTF

Question 7.
………………………….. is the process displaying still images they give continuous movement
(a) Text formats
(b) Sound
(c) MP3
(d) Animation
Answer:
(d) Animation
Question 8.
The live telecasting of real time program through Internet is known as ……………………………..
(a) web casting
(b) web hosting
(c) data manipulation
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) web casting

Question 9.
GIF use ………………………. color look up table
(a) 8 bit
(b) 8 KB
(c) 8 MB
(d) 8 GB
Answer:
(a) 8 bit
Question 10.
RTF file format was introduced by ……………………………
(a) TCS
(b) Microsoft
(c) Apple
(d) IBM
Answer:
(b) Microsoft
PART – II
II. Short Answers
Question 1.
Define Multimedia and their features?
Answer:
The word multimedia consists of two words “multi” and “media” which means that multiple forms of media are combined to gather and provide services like storage, communication, presentation and Input/output interactions of text, video, image, graphics and audio.
Features of Multimedia:
- The information they handle is represented digitally.
- Multimedia Systems are integrated, computer controlled and usually interactive.

Question 2.
List out Multimedia Components?
Answer:
Multimedia has five major components like text, images, sound, video and animation.
Question 3.
Classify the TEXT component in multimedia?
Answer:
Text is classified as static text and hypertext. Static text, the text or the words will remain static as a heading or in a line, or in a paragraph. A hypertext is a system which consists of nodes, the text and the links between the nodes, which defines the paths the user need to follow for the text access in non-sequential ways.

Question 4.
Classify the IMAGE component in multimedia?
Answer:
Images acts as an vital component in multimedia. These images are generated by the Image components are classified in two ways, as bitmap or raster images and as vector images. Raster or Bitmap Images:
The common and comprehensive form of storing images in a computer is raster or bitmap image.
Vector Images:
Drawing elements or objects such as lines, rectangles, circles and so on to create an images are based on Vector images.

Question 5.
Define Animation and their features?
Answer:
Animation is the process displaying still images so quickly so that they give the impression of continuous movement.
Features:
- In animation the screen object is a vector image in animation.
- The least frame rate of at least 16 frames per second gives the impression of smoothness and for natural looking it should be at least 25 frames per second.
Question 6.
List out image file formats?
Answer:
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format), BMP (Bitmap), DIB (Device Independent Bitmap), GIF (Graphics Interchange Format), JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group), TGA (Tagra), PNG (Portable Network Graphics).

Question 7.
List out audio file formats?
Answer:
WAV (Waveform Audio File Format), MP3 (MPEG Layer-3 Format), OGG, AIFF (Audio Interchange File Format), WMA (Windows Media Audio), RA (Real Audio Format).
Question 8.
List out video file formats?
Answer:
AVI (Audio/Video Interleave) and MPEG (Moving Picture Experts Group).

Question 9.
Define Multimedia Production?
Answer:
Production:
In the multimedia application, after the pre-production activities, the production phase starts. This phase includes the activities like background music selection, sound recording and so on. Text is incorporated using OCR software, Pictures shot by digital camera, Video clips are shot, edited and compressed. A pilot project is ready by this time.
Question 10.
List out Multimedia Production team members?
Answer:
Production Manager, Content Specialist, Script Writer, Text Editor, Multimedia Architect, Computer Graphic Artist, Audio and Video Specialist, Computer Programmer, Web Master.
PART – III
III. Explain in Brief Answer
Question 1.
Briefly explain about Multimedia Components?
Answer:
Multimedia has five major components like text, images, sound, video and animation.
Text:
Text is the basic components of multimedia and most common ways of communicating information to other person.
Image:
Images acts as an vital component in multimedia. These images are generated by the computer in two ways, as bitmap or raster images and as vector images.
Sound:
Sound is a meaningful speech in any language and is the most serious element in multimedia, providing the pleasure of music, special effects and so on.
Video:
Video is defined as the display of recorded event, scene.
Animation:
Animation is the process of displaying still images so quickly so that they give the impression of continuous movement.

Question 2.
Describe the features and techniques of animation?
Answer:
Animation is the process displaying still images so quickly so that they give the impression of continuous movement. In animation the screen object is a vector image in animation. Using numerical transformations the movement of that image along its paths is calculated for their defining coordinates.
The least frame rate of at least 16 frames per second gives the impression of smoothness and for natural looking it should be at least 25 frames per second. Animations may be in two or three dimensional. The two dimensional animation, bring an image alive, that occur on the flat X and Y axis of the screen, while in three dimensional animation it occurs along the three axis X, Y and Z. Animation tools are very powerful and effective. The two basic types of animations are Path animation and Frame animation.

Question 3.
Write roles and responsibilities of Production team members?
Answer:
Production Manager:
In a multimedia production, the role of production manager is to define, and coordinate, the production of the multimedia project in time and with full quality.
Content Specialist:
Content specialist is responsible for performing all research activities concerned with the proposed application’s content.
Script Writer:
The script writer visualizes the concepts in three dimensional environments.
Text Editor:
The content of a multimedia production always must flow logically and the text should always be structured and correct grammatically.
Multimedia Architect:
The multimedia architect integrates all the multimedia building blocks like graphics, text, audio, music, video, photos and animation by using an authoring software.
Computer Graphic Artist:
The role of Computer Graphic Artist is to deal with the graphic elements of the programs like backgrounds, bullets, buttons, pictures editing, 3-D objects, animation, and logos etc.
Audio and Video Specialist:
They are responsible for recording, editing sound effects and digitizing.
Computer Programmer:
The computer programmer writes the lines of code or scripts in the appropriate language.
Web Master:
The responsibility of the web master is to create and maintain an Internet web page.

Question 4.
Describe the various file formats in multimedia?
Answer:
Text Formats: RTF, Plain text, Image Formats:TIFF (Tagged Image File Format), BMP (Bitmap), DIB (Device Independent Bitmap), GIF (Graphics Interchange Format), JPEG (Jbint Photographic Experts Group), TGA (Tagra), PNG (Portable Network Graphics), Digital Audio File Formats: WAV (Waveform Audio File Format), MP3 (MPEG Layer-3 Format), OGG, AIFF (Audio Interchange File Format), WMA (Windows Media Audio), RA (Real Audio Format), Digital Video File Formats: AVI (Audio/Video Interleave), MPEG (Moving Picture Experts Group).
Question 5.
Explain animation industry and their scope?
Answer:
1. The Indian Animation Industry encompasses traditional 2D animations, 3D animation <& visual effects for films.
2. An animation Studio is a company producing animated media. Many of these studios help with the fulfillment of animation works for big brand names and have carried out outsourced projects including Nemo.
3. The first Indian animated TV series was Ghayab Aya in the year 1986. The first Indian animated film was The Banyan Deer in 1957.
PART – IV
IV. Explain in detail
Question 1.
Explain in detail Process of Multimedia ?
Steps in Multimedia Production
Answer:
Adequate time and efficient planning is required for multimedia production, which assures that the project will be proceed smoothly and certainly ensures that the information reaches the target audience. Following are the phases for development of complex multimedia projects. Multimedia and Desktop Publishing.
Conceptual Analysis and Planning:
The process of multimedia making begins with a conceptual ignition point. Conceptual analysis identifies a appropriate theme, budget and content availability on that selected theme. Additional criteria like copyright issues also are considered in this phase.
Project design:
Once the theme is finalized objectives, goals, and activities are drawn for the multimedia project. General statements are termed as goals. The specific statements in the project is known as the objectives. Activities are series of actions performed to implement an objective. These activities contribute to the Project design phase.
Pre-production:
Based on the planning and design, it is necessary to develop the project.
The following are the steps involved in pre-production:
Budgeting:
Budgeting for each phases like consultants, hardware, software, travel, communication and publishing is estimated for all the multimedia projects.
Multimedia Production Team:
The production team for a high-end multimedia project requires a team efforts. The team comprises of members playing various roles and responsibilities like Script writer, Production manager, Editor, Graphics Architect, Multimedia Architect and Web Master.
Hardware/Software Selection:
All multimedia Application requires appropriate tools to develop and playback the application. Hardware includes the selection of fastest CPU, RAM and huge monitors, sufficient disc for storing the records. Selection of the suitable software and file formats depends on the funds available for the project being developed.
Defining the Content:
Content is the “stuff’ provided by content specialist to the multimedia architect with which the application is developed, who prepares the narration, bullets, charts and tables etc.
Preparing the structure:
A detailed structure must have information about all the steps ‘along with the time line of the future action. This structure defines the activities, responsible person for each activity and the start/end time for each activity.
Production:
In the multimedia application, after the pre-production activities, the production phase starts. This phase includes the activities like background music selection, sound recording and so on. Text is incorporated using OCR software, Pictures shot by digital camera, Video clips are shot, edited and compressed. A pilot project is ready by this time.
Testing:
The complete testing of the pilot product is done before the mass production to ensure that everything is in place, thereby avoiding the failure after launch. If it’s an web . based product its functioning is tested with different browsers like Internet Explorer, Chrome, Mozilla and Netscape Navigator. If it is a locak multimedia application on a LAN it must be deployed in the server for testing purpose. After the testing process are over, the product is incorporated with valid suggested changes.
Documentation User documentation is a mandatory feature of all multimedia projects. The documentation has all the valuable information’s starting from the system requirement till the completion of testing. Contact details, e-mail address and phone numbers are provided for technical support and sending suggestions and comments.
Delivering the Multimedia Product:
Multimedia applications are best delivered on CD/DVD or in the website . In reality various challenges are faced while delivering through internet, like bandwidth problems, huge number of plug-ins required to play audio and video and long downloading time. Finally, a multimedia application is delivered in a more effective way by the integration of two mediums CD-ROM/DVD and Internet.

Question 2.
Explain in detail Techniques of Animation?
Answer:
The various animation techniques are
(i) Traditional Animation:
Traditional animation involved animators drawing by hand for each and every frame. It is creating the drawings one by one on the frame. Eg. Snow White and the Seven Dwarf Movie
(ii) Computer animation – 2D, 3D:
- The famous mickey mouse was created using the 2D animation technique.
- The first 2D animation was called Fantasmagorie. It is a short cartoon made by Emile Cohl. It is entirely in black and white
(iii) Digital 2D animation:
- Creating animations in the 2 dimensional space with the help of digital technologies is called digital 2D animation.
- Create 100s of drawing and animate them to show same kind of movement in technically called digital 2d animations.
(iv) Digital 3D animation:
3D animation models are highly realistic. They are used to create Short Films, TV Commercials.
(v) Stop-motion animation:
Using frame by frame animation, physical static objects are moved around. Eg. Movie “The Teddy Bears”.
(vi) Mechanical Animations:
Instead of robotics, machines can be animated by using the mechanical animation techniques. It helps the animator to understand how the machine works.
(vii) Chuckimation:
Chuckimation is one of the popular animation techniques created by “Action League Now!” creators. It is the combination of stop frame animation and live shots, where characters are dropped into a particular frame.
(Viii) Clay animation (or) claymation:
Pieces of clay are moulded to create characters and based on the imagination of the animator, a story is unfolded. There are oil based and water based clays available.
(ix) Typography Animation:
Typography is nothing but font faces and letters and combination of text in motion.
Eg. Titles part of movie “The Atlantic”
(x) Sand Animation:
A lit glass table is used as a canvas and the animator creates animation by moving the sand in certain directions.
(xi) ZoetrOpe Animation:
Some still images are drawn on a drum and when turned in a circular way, we will get an illusion of movement.

Question 3.
Explore the opportunities in Animation filed movie industry?
Answer:
In India, the VFX domain, or the animation and visual effects industry has been growing stronger and stronger in recent years.
- Animation and visual effects requirement for massive international projects such as HBO’s top TV series and Marvels’ hit Infinity War and Black Panther was outsourced to Indian companies in Mumbai and Pune.
- This led to the significant increase in the number of students enrolling for a VFX course.
- As such, a student that completes a 3D animation course cap hope to build a rewarding and satisfying career in the Media and Entertainment field these days.
- The timeless classics Tom and Jerry and Mickey Mouse created a milestone but the legacy is not disappointing.
- Indian animation has risen from an amateur piece of craft like “The Banyan Deer” to the million rupees project “Chhota Bheem”
- POGO, the leading cartoon channel in India is the most successful entertainment channel for kids.
- Indian animation industry is anticipated to grow faster than the IT industry.
- The industry has grown to a multibillion net work standard.
- As a result of the growing demand in industry, the scope of animation course in tremendous.
- The number of VFX artists and animators that worked on Baahubali was around 750.
- Ex. For Top animates Movies: Spider-Man, Incredibles 2, Zootopia, Inside Out, Toy Story 3, Finding Nemo, Frozen, etc.
Question 4.
Explain in detail about production team Roles and Responsibilities?
Answer:
Multimedia Production Team:
Managing team members in a way to get maximum outcome with high degree of efficiency is mandatory in multimedia production. The fine quality high-end multimedia production application requires a specialize team comprises of the following members:
Production Manager:
In a multimedia production, the role of production manager is to define, and coordinate, the production of the multimedia project in time and with full quality. The production manager should be an expertise in the technology expert, good at proposal writing, good communication skills and budget management skills. Also must have experience in human resource management and act as an efficient team leader.
Content Specialist:
Content specialist is responsible for performing all research activities concerned with the proposed application’s content. Program content refers to projects information, graphics, data or facts presented through the multimedia production.
Script Writer:
Video and film scripts represents a linear sequence of events. The script writer visualizes the concepts in three dimensional environments and if needed uses the virtual reality integration into the program.
Text Editor:
The content of a multimedia production always must flow logically and the text should always be structured and correct grammatically. Text and narration is an integrated part of the application.
Multimedia Architect:
The multimedia architect integrates all the multimedia building blocks like graphics, text, audio, music, video, photos and animation by using an authoring software.
Computer Graphic Artist:
The role of Computer Graphic Artist is to deal with the graphic elements of the programs like backgrounds, bullets, buttons, pictures editing, 3-D objects, animation, and logos etc.
Audio and Video Specialist:
The roles of these specialists are needed for dealing with narration and digitized videos to-be added in a multimedia presentation. They are responsible for recording, editing sound effects and digitizing.
Computer Programmer:
The computer programmer writes the lines of code or scripts in the appropriate language. These scripts usually develops special functions like developing the software to give the size and shape of video windows, controlling peripherals and so on.
Web Master:
The responsibility of the web master is to create and maintain an Internet web page. They converts a multimedia presentation into a web page. Final multimedia product is ready for consultation is a joint effort of the entire team. Initially, the production manager identifies the project content, while the web master provides access to a wide range of community through web-services.

Question 5.
Explain about different file formats in multimedia files?
Answer:
File Formats for Multimedia:
The following is an outline of current file formats used for the production and delivery of multimedia data.
Text Formats:
RTF Rich Text Format:
is the primary file format introduced in 1987 by Microsoft with the specification of their published products and for cross-platform documents interchange.
Plain text:
Plain text files can be opened, read, and edited with most text editors. Commonly used are Notepad (Windows), Gedit or nano (Unix, Linux), TextEdit (Mac OS X) and so on. Other computer programs are also capable of reading and importing plain text. Plain text is the original and popular way of conveying an e-mail.
Image Formats:
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format):
This format is common in desktop publishing world (high quality output), and is supported by almost all software packages. Recent versions of TIFF allows image compression, and the format is comfortable for moving large files between computers.
BMP (Bitmap):
Initially this format is in use with Windows 3.1. It is quite large and uncompressed and hence BMP is used for the high-resolution or large images.
DIB (Device Independent Bitmap):
This format which is similar to BMP, allows the files to be displayed on a variety of devices.
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format):
GIF is a compressed image format. Most of the computer color images and backgrounds are GIF files. This file format is best suitable for graphics that uses only limited colors, and it is the most popular format used for online color photos. 13-bit Color look up table is used by the GIF format to identify its color values. This format is supported widely.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group):
JPEG was designed to attain maximum image compression. It uses loss compression technique, where a compression method is referred that loses some of the data required for the image reconstruction. It works good with photographs, naturalistic artwork, and similar material but functions less on lettering, live drawings or simple cartoons.
TGA (Tagra):
It is the first popular format for high-resolution images. TGA is supported by Most of the video-capture boards.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics):
An extensible file format for the less loss, portable and well compressed storage of raster images. PNG acts as replacement for GIF and also replaces multiple common uses of TIFF. PNG works good with online viewing applications like worldwide web. So it is fully streameable with a best display option.
Digital Audio File Formats:
1. WAV (Waveform Audio File Format):
It is the most popular audio file format in windows for storing uncompressed sound files. In order to attain the. reduced file size it can also be converted to other file formats like MP3.
2. MP3 (MPEG Layer-3 Format)
3. MPEG Layer-3 format is the most popular format for storing and downloading music. The MP3 files are roughly compressed to one-tenth the size of an equivalent WAV file.
4. OGG:
A free, open source container format that is designed for obtaining better streaming and evolving at high end quality digital multimedia. It can be compared to MP3 files in terms of quality.
5. AIFF (Audio Interchange File Format):
A standard audio file format used by Apple which is like a WAV file for the Mac.
6. WMA (Windows Media Audio):
It is a popular windows media audio format owned by Microsoft and designed with Digital Right Management (DRM) abilities for copyright protection.
7. RA (Real Audio Format):
Real Audio format is designed for streaming audio over the Internet. The digital audio resources are usually stored as a computer file in computer’s hard drive or CD/DVD. Besides the variety of audio file formats available, the most common formats are wave files (.WAV) and MPEG Layer-3 files (.MP3), WMA and RA.
Digital Video File Formats:
AVI (Audio/Video Interleave):
AVI is the video file format for Windows. Here sound and picture elements are stored in alternate interleaved chunks in the file.
MPEG (Moving Picture Experts Group):
MPEG is a standard for generating digital video and audio compression under the International Standards Organization (ISO) by the group of people. The group has developed MPEG-1, the standard on which Video CD and MP3 are based, MPEG-2, the standard that supports products as Digital Television set top boxes and DVD, MPEG-4, the standard for multimedia and mobile web. MPEG-7, the standard for search of audio and visual content. Research on MPEG-21 “Multimedia Framework” has started in 2000. Simply MPEG is the standards for digital video and audio compression.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Multimedia and Desktop Publishing Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose The Best Answer
Question 1
……………………….. applications plays vital role in presenting information to the user.
(a) Power point
(b) Multimedia
(c) Star office
(d) php
Answer:
(b) Multimedia
Question 2.
In the term multimedia, multi refers to …………………………….
(a) medium
(b) single
(c) hybrid
(d) many
Answer:
(d) many

Question 3.
What is the plural form of medium?
(a) medium
(b) mediu
(c) media
(d) median
Answer:
(c) media
Question 4.
How many major components are there in Multimedia?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(d) 5

Question 5.
Which is not a multimedia components? [Pick the odd one out].
(a) Test
(b) Image
(c) Sound
Answer:
(a) Test
Question 6.
Identify the static element from the following.
(a) Video
(b) graphics
(c) Animation
Answer:
(b) graphics

Question 7.
…………………………. is the basic components of Multimedia.
(a) Video
(b) Animation
(c) Text
Answer:
(c) Text
Question 8.
In …………………… the words are given along with the images to explain about the images.
(a) Static text
(b) Hyper text
(c) Multi text
(d) Super text
Answer:
(a) Static text
Question 9.
The readability of the text depends on the ………………………….
(a) pronunciation
(b) spacing
(c) punctuation
(d) b & c
Answer:
(d) b & c

Question 10.
In how many ways, in ages can be generated by the computer?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
Answer:
(a) 2
Question 11.
Bitmap images are otherwise called as ………………………… images.
(a) multimedia
(b) vector
(c) Raster
Answer:
(c) Raster
Question 12.
The common and comprehensive form of storing images in a computer is ……………………………
(a) raster images
(b) bitmap
(c) vector
(d) both (a) &(b)
Answer:
(d) both (a) &(b)

Question 13.
The tiny dots which forms on the screen (picture elements) are called as …………………………
(a) pitel
(b) pixel
(c) dots
(d) dpi
Answer:
(b) pixel
Question 14.
……………………… is a simple matrix of pixel that forms a raster image.
(a) Bitmap
(b) Pixel
(c) Vector
(d) Animation
Answer:
(a) Bitmap
Question 15.
In determining number of colors, ……………………. bits indicates 256 colors.
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 8
(d) 16
Answer:
(c) 8

Question 16.
………………………… is a techniques used to reduce the file size of the images.
(a) Animation
(b) Rendering
(c) Compression
(d) Morphing
Answer:
(c) Compression
Question 17.
Identify which is not a compression format?
(a) GIF
(b) TIFF
(c) JPEG
(d) MIDI
Answer:
(d) MIDI

Question 18.
What is the least frame rate for smooth appearance of images?
(a) 4
(b) 8
(c) 16
(d) 32
Answer:
(c) 16
Question 19.
How many frames per second are needed for a normal natural looking images?
(a) 10
(b) 15
(c) 20
(d) 25
Answer:
(d) 25

Question 20.
If the image appears in xy axis of the screen, then it is called as ………………………… animation.
(a) picture
(b) Image xy
(c) 2D
(d) 3D
Answer:
(c) 2D
Question 21.
If the image appears inXYZ axis of the screen then it is called as ………………………. animation.
(a) 2D
(b) 3D
(c) XYZ
Answer:
(b) 3D
Question 22.
How many types of animations are there?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
Answer:
(a) 2

Question 23.
The two types of animations are …………………………
(a) Frame, object
(b) path, object
(c) path, Frame
Answer:
(c) path, Frame
Question 24.
Which animation involves moving an object on the screen with constant background?
(a) Vector
(b) Path
(c) Frame
(d) Static
Answer:
(b) Path
Question 25.
Multiple objects are allowed to travel simultaneously in ……………………………. animations.
(a) Vector
(b) Path
(c) Frame
(d) Static
Answer:
(c) Frame

Question 26.
Which one of the following is the most serious element in multimedia and provides the pleasure of music, special effects etc?
(a) Text
(b) Image
(c) Sound
(d) Video
Answer:
(c) Sound
Question 27.
What is the unit of sound?
(a) Decibels
(b) Newton
(c) Hertz
(d) Frequency
Answer:
(a) Decibels

Question 28.
MIDI stand for ………………………………..
(a) Magic In Data Interface
(b) Musical Instrument Digital Identifier ,
(c) Magnetic Induction Drive Input
(d) Most Interactive Digital Interface
Answer:
(d) Most Interactive Digital Interface
Question 29.
………………………….. Sound is a digitized sound.
(a) Recorded
(b) Digital
(c) Frame
(d) Sampled
Answer:
(d) Sampled
Question 30.
is defined as how often the samples are taken and how many numbers are used to represent the value of each sample.
(a) Digitized sound
(b) sampling rate
(c) compression
(d) compression ratio
Answer:
(b) sampling rate

Question 31.
How many types of videos are there?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 2
Question 32.
The display of recorded event, scene etc. are called as …………………………..
(a) Video
(b) Sampling
(c) Frames
(d) Modelling
Answer:
(a) Video
Question 33.
How many categories of Analog videos’are there?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 2

Question 34.
Which video format have all the components like brightness, color and synchronization are combined into one signal?
(a) Digital video
(b) MIDI
(c) Component Analog Video
(d) Composite Analog Video
Answer:
(d) Composite Analog Video
Question 35.
Which video format produces low plarity videos?
(a) Analog video
(b) Digital video
(c) Component Analog Video
(d) Composite Analog Video
Answer:
(d) Composite Analog Video

Question 36.
Which one of the following format was used for customer analog video recording tape formats?
(a) Beta max
(b) MIDI
(c) DIB
(d) BMP
Answer:
(a) Beta max
Question 37.
How many different multimedia file formats are there?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(d) 4
Question 38.
RTF stand for …………………………..
(a) Rich Text Format
(b) Real Time Format
(c) Red Tagra Format
(d) Recording to file Format
Answer:
(a) Rich Text Format

Question 39.
The RTF was introduced in the year …………………………..
(a) 1982
(b) 1985
(c) 1987
(d) 1992
Answer:
(c) 1987
Question 40.
Match the following editors with OS?
1. Gedit/Nano – (a) windows
2. Text Edit – (b) Unix / Linux
3. Notepad – (c) Mac OS
(a) 1-(b), 2-(c), 3-(a)
(b) 1-(c), 2-(b), 3-(a)
(c) 1-(a),2-(b),3-(c)
(d) 1-(b), 2-(a), 3-(c)
Answer:
(a) 1-(b), 2-(c), 3-(a)

Question 41.
Identify which is not an editor?
(a) Notepad
(b) Gotit
(c) Nano
(d) Text Edit
Answer:
(b) Gotit
Question 42.
………………………….. is the popular way of conveying an e-mail.
(a) RTF
(b) plaintext
(c) BMP
(d) TIFF
Answer:
(b) plaintext

Question 43.
TIFF is a ………………………….. Format of file.
(a) Sound
(b) Video
(c) Text
(d) Image
Answer:
(d) Image
Question 44.
identify the statement which is correct.
(i) RTF was developed by apple.
(ii) TIFF format is common in desktop publishing world.
(iii) GIF uses lossy compression technique
(iv) JPEG works good with photographs.
(a) (i), (ii), (iii) are correct
(b) (i), (iv) are correct
(c) (i), (iii) are correct
(d) (ii), (iv) are correct
Answer:
(d) (ii), (iv) are correct

Question 45.
Which is the first popular format for high resolution images?
(a) TIFF
(b) TGA
(c) JPEG
(d) GIF
Answer:
(b) TGA
Question 46.
Identify which is not an image format.
(a) DIB
(b) BMP
(c) TGA
(d) OGG
Answer:
(d) OGG
Question 47.
TIFF Stand for …………………………
(a) Time Interchange File Format
(b) Tagged Image File Format
(c) Time In File Format
(d) Task Interrupt File Format
Answer:
(b) Tagged Image File Format

Question 48.
Which one of the following format produces high quality output in DTP world?
(a) TIFF
(b) TGA
(c) PNG
(d) JPEG
Answer:
(a) TIFF
Question 49.
BMP stands for …………………………..
(a) Bitwise Manipulation
(b) Binary Manipulations
(c) Bitmap
(d) Binary Map
Answer:
(c) Bitmap
Question 50.
Pick out the correct statement from the following.
(a) GIF are good with photographs
(b) PNG is portable, good with online viewing applications
(c) TIFF produces two quality output
(d) BMP is used for high resolution & small images
Answer:
(b) PNG is portable, good with online viewing applications

Question 51.
DIB stands for …………………………..
(a) Drive in Bus
(b) Devuce Input Bias
(c) Device Interface Format
(d) Device Independent Bitmap
Answer:
(d) Device Independent Bitmap
Question 52.
GIF stands for ……………………….
(a) Graphics Interchange Format
(b) Graphics Interchange File
(c) Graphics Interface Format
(d) Grahics Interface File
Answer:
(a) Graphics Interchange Format

Question 53.
TGA means …………………………
(a) Tagged
(b) Tagra
(c) tamil graphics
(d) Tiff graphics
Answer:
(b) Tagra
Question 54.
PNG means ………………………
(a) Power Net Gate
(b) Portable
(c) Portable Network Graphics
(d) Power Network Graphics
Answer:
(c) Portable Network Graphics
Question 55.
WAV stands for …………………………..
(a) Wave
(b) Waveform
(c) Waveform Audio Video Format
(d) Waveform Audio File Format
Answer:
(d) Waveform Audio File Format

Questionv 56.
AIFF stands for ………………………..
(a) Audio Interchange File Format
(b) Audio In File Format
(c) Audio Interference File Format
(d) Audio Interrupt File Format
Answer:
(a) Audio Interchange File Format
Question 57.
WMA means ……………………………
(a) Wave Media Animation
(b) Wave Moving Animation
(c) Windows Media Audio
(d) Waveform Media Audio
Answer:
(c) Windows Media Audio
Question 58.
RA stands for ……………………………
(a) Rich Animation
(b) Real Audio
(c) Rapid Audio
(d) Raster Audio
Answer:
(b) Real Audio

Question 59.
AVI means ……………………………
(a) Audio Video Interleave
(b) Animation Video Interface
(c) Audio Video Interchange
(d) Animation Video Intechange
Answer:
(a) Audio Video Interleave
Question 60.
The MPEG layer-3 Format is ……………………………
(a) MP3
(b) MPEG
(c) MIDI
(d) JPEG
Answer:
(a) MP3

Question 61.
Which image format is used for storing high-resolution large images?
(a) TIFF
(b) BMP
(c) DIB
(d) GIF
Answer:
(b) BMP
Question 62.
Which image format allows the files to be displayed on a variety of devices?
(a) BMP
(b) DIB
(c) DIP
(d) PNG
Answer:
(b) DIB

Question 63.
What is the table used by the GIF format to identify colors?
(a) Color
(b) Look color
(c) Color Look up
(d) Color up
Answer:
(c) Color Look up
Question 64.
………………………… is a compressed image format.
(a) GIF
(b) JPEG
(c) PNG
(d) DIB
Answer:
(a) GIF

Question 65.
What is the compression technique used by JPEG image format?
(a) Lossless
(b) Lossy
(c) Full compression
(d) Half / partial
Answer:
(b) Lossy
Question 66.
Which image format is good with photographs, naturalistic artworks?
(a) TIFF
(b) BMP
(c) GIF
(d) JPEG
Answer:
(d) JPEG

Question 67.
…………………………… is the first popular format for high resolution images.
(a) JPEG
(b) TGA
(c) GIF
(d) TIFF
Answer:
(b) TGA
Question 68.
Most of the video – capture boards supports …………………………… formats.
(a) JPEG
(b) TGA
(c) GIF
(d) TIFF
Answer:
(b) TGA

Question 69.
…………………………… format is fully streameable with a best display option.
(a) JPEG
(b) GIF
(c) PNG
(d) TIFF
Answer:
(c) PNG
Question 70.
Which format works good with online viewing applications like www?
(a) PNG
(b) TIFF
(c) OGG
(d) AIFF
Answer:
(a) PNG

Question 71.
Identify which is not an image format.
(a) PNG
(b) TIFF
(c) TGA
(d) OGG
Answer:
(d) OGG
Question 72.
Identify the wrongly matched pair from the following.
(a) OGG – (i) Audio
(b) MPEG – (ii) Video
(c) MIDI- (iii) Text
(d) TGA – (iv) image
(a) (iii)
(b) (ii)
(c) (iv)
(d) (i)
Answer:
(a) OGG – (i) Audio

Question 73.
Identify which is not an Digital Audio File Format.
(a) OGG
(b) AVI
(c) AIFF
(d) WMA
Answer:
(b) AVI
Question 74.
Which format is most popular for storing and downloading music?
(a) MP3
(b) MPEG
(c) JPEG
(d) AIFF
Answer:
(a) MP3

Question 75.
…………………………… format stores uncompressed sound files.
(a) WAV
(b) MP3
(c) OGG
(d) AIFF
Answer:
(a) WAV
Question 76.
Which files are compressed to onw-tenth the size of an equivalent WAV file?
(a) WAV
(b) OGG
(c) WMA
(d) MP3
Answer:
(d) MP3

Question 77.
AIFF was developed by …………………………
(a) Microsoft
(b) Apple
(c) IBM
(d) Flash
Answer:
(b) Apple
Question 78.
……………………….. is a free, open source container format.
(a) WAV
(b) MP3
(c) OGG
(d) WMA
Answer:
(c) OGG

Question 79.
Expand DRM.
(a) Digi Read Memory
(b) Digital Rich MP3
(c) Data Read Memory
(d) Digital Right Management
Answer:
(d) Digital Right Management
Question 80.
Which digital Audio format is designed with DRM facility?
(a) WMA
(b) TIFF
(c) OGG
(d) MP3
Answer:
(a) WMA

Question 81.
Identify the format which is not developed by Microsoft?
(a) AVI
(b) WMA
(c) AIFF
(d) RTF
Answer:
(c) AIFF
Question 82.
Who developed WMA?
(a) Apple
(b) Microsoft
(c) Macromedia
(d) IBM
Answer:
(b) Microsoft

Question 83.
…………………………… abilities are provided in WMA format for copyright protection.
(a) DMA
(b) DRA
(c) DRM
(d) DMR
Answer:
(c) DRM
Question 84.
The sound and picture elements in AVI are stored in alternate …………………………… chunks in the file.
(a) interleaved
(b) interface
(c) interrupt
(d) interchange
Answer:
(a) interleaved
Question 85.
Multimedia Framework was started in the year ……………………………
(a) 1999
(b) 2000
(c) 2001
(d) 2002
Answer:
(b) 2000

Question 86.
Find the pair wrongly matched.
(i) MPEG-2 – DVD, TV set top Boxes
(ii) MPEG-4 – Multimedia
(iii) MPEG-1 – Mobile
(iv) MPEG-7 -Video CD
(v) MPEG-21 – Multimedia Framework
(a) (iii), (iv)
(b) (ii) (iii) (iv)
(c) (iii) (iv) (v)
(d) All are correct
Answer:
(a) (iii), (iv)
Question 87.
Which MPEG format is used for multimedia and mobile web?
(a) MPEG-4
(b) MPEG-21
(c) MPEG-7
(d) MPEG-2
Answer:
(a) MPEG-4
Question 88.
………………………. is a standard format for generation digital video and audio compression under the ISO.
(a) AVI
(b) MP3
(c) JPEG
(d) MPEG
Answer:
(d) MPEG

Question 89.
Which format had research on “Multimedia Framework” in the year 2000?
(a) MPEG-4
(b) MPEG-2
(c) MPEG7
(d) MPEG-21
Answer:
(d) MPEG-21
Question 90.
How many steps are there in Multimedia production?
(a) 10
(b) 11
(c) 12
(d) 13
Answer:
(c) 12
Question 91.
The first step in Multimedia production is ……………………………
(a) project design
(b) conceptual analysis
(c) planning
(d) both b & c
Answer:
(d) both b & c

Question 92.
The general statements in project design stage are termed as ……………………………
(a) goals
(b) objectives
(c) Aim
(d) planning
Answer:
(a) goals
Question 93.
The selection of fastest CPU, RAM and huge monitors, sufficient disc for storing comes under
(a) content definition
(b) RAM capacity
(c) structure preparing
(d) Hardware / Software selection
Answer:
(d) Hardware / Software selection
Question 94.
Find the correct statement from the following
(i) Start / end time of each activity are defined in preparing the structure stage.
(ii) A pilot project will be ready in the production stage.
(iii) Suggestions and comments are given in the documentation phase.
(a) (i) is correct
(b) (i) (ii) are correct
(c) (i) (iii) are correct
(d) All are correct
Answer:
(d) All are correct

Question 95.
What are the factors to be considered while delivering the multimedia applications through internet.
(a) Bandwidth
(b) Plugins
(c) Downloading time
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 96.
Which software is used to incorporate the text in the production stage?
(a) Light pen
(b) Scanner
(c) OCR
(d) OMR
Answer:
(c) OCR
Question 97.
Identify which is not a browser?
(a) Internet Explorer
(b) Trash
(c) Mozilla Firefox
(d) Google Chrome
Answer:
(b) Trash

Question 98.
Arrange the options given below in the proper order.
(i) Budgeting
(ii) project design
(iii) Documentation
(iv) Hardware / software selection
(v) Testing
(a) (ii) (i) (iv) (v) (iii)
(b) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v)
(c) (v) (iv) (iii) (ii) (i)
(d) (i) (iii) (v) (iv) (ii)
Answer:
(a) (ii) (i) (iv) (v) (iii)
Question 99.
Copyright issues are considered in the …………………………… phase.
(a) conceptual analysis and planning
(b) project design
(c) pre-production
(d) Budgeting
Answer:
(a) conceptual analysis and planning

Question 100.
How many members are there in multimedia production team?
(a) 8
(b) 9
(c) 10
(d) 12
Answer:
(b) 9
Question 101.
The production manager should not be an expertise in ……………………………
(a) technology
(b) proposal writing
(c) communication
(d) Text Narration
Answer:
(d) Text Narration
Question 102.
Identify the wrong statement.
(a) The text should always be structured
(b) The text should be grammatically correct
(c) The text must flow logically
(d) All the above statements are correct
Answer:
(d) All the above statements are correct

Question 103.
The multimedia presentation is converted into a web page by
(a) computer programmer
(b) web master
(c) graphic artist
(d) multimedia architect
Answer:
(b) web master
Question 104.
…………………………… represents a linear sequence of events.
(a) video
(b) film scripts
(c) Text
(d) a & b
Answer:
(d) a & b
Question 105.
Who plays a vital role in dealing with backgrounds, bullets, buttons, pictures editing, 3D objects, animations, logos of the programs.
(a) Multimedia Architect
(b) Web Master
(c) Computer Graphic Artist
(d) Video Specialist
Answer:
(c) Computer Graphic Artist

Question 106.
Identify the person who is not a member of Multimedia Production team.
(a) Content specialist
(b) Program debugger
(c) Script writer
(d) Text Editor
Answer:
(b) Program debugger
Question 107.
How many million consumers uses Internet, radio and video services every month?
(a) 55
(b) 45
(c) 65
(d) 75
Answer:
(a) 55

Question 108.
…………………………… is a multimedia based teaching and learning system at GMU in Germany to provide decentralized learning environment to the students.
(a) MODULO
(b) MODULES
(c) MODE
(d) MODEL
Answer:
(a) MODULO
Question 109.
…………………………… is an Education satellite launched in India to provide virtual classrooms.
(a) EDSAT
(b) EDUSAT
(c) E-SAT
(d) E SATELLITE
Answer:
(b) EDUSAT
Question 110.
……………………………. conferencing is a system that performs face to face interactions for the users.
(a) Multimedia
(b) Video
(c) Audio
(d) Both a and b
Answer:
(d) Both a and b

Question 111.
…………………………… is a free standing furnished equipped multimedia computer that allow users to retrieve information via a touch screen.
(a) Kiosk
(b) Helpdesk
(c) Customer care
(d) ATM
Answer:
(a) Kiosk
Question 112.
Banks uses Kiosks in the form of
(a) Cash
(b) Finance
(c) Credit Cards
(d) ATM
Answer:
(d) ATM
II. Short Answers
Question 1.
What are the advantages of vector images?
Answer:
Relatively small amount of data is required to represent the image and thereby only less memory is needed to store.

Question 2.
Define compression?
Answer:
Compression is a technique used to reduce the file size of images that is useful for storing large number of images and speeding transmission for networked applications.
Question 3.
Mention some compression formats?
Answer:
- GIF – Graphics Interface Format
- TIFF – Tagged Image File Format
- JPEG – Joint Photographic Experts Group
Question 4.
Define frame Animation?
Answer:
In frame animations, multiple objects are allowed to travel simultaneously and the background or the objects also changes.

Question 5.
Define sampling rate?
Answer:
Sampling rate is defined as how often the samples are taken and how many numbers are used to represent the value of each sample (bit depth, resolution and sample size).
Question 6.
Write note on MIDI?
Answer:
Musical Instrument Digital Identifier (MIDI) is a standard communication tool developed for computers and electronic instruments. This tool is flexible and easy for composing the projects in multimedia. Tools for synthesizing the sound and software for sequencing are necessary for MIDI.

Question 7.
Classify video?
Answer:
The video can be categorized into two types as:
Analog video and Digital video
Question 8.
Classify Analog video?
Answer:
Analog Video’s are classified as
- composite Analog video
- component Analog video
Question 9.
Write note on RTF text format?
Answer:
Rich Text Format is the primary file format introduced in 1987 by Microsoft with the specification of their published products and for cross-platform documents interchange.

Question 10.
Mention some text editors?
Answer:
Notepad (Windows), Gedit or nano (Unix, Linux), TextEdit (Mac OS X)
Question 11.
Compare BMP and DIB?
Answer:
DIB is similar to BMP. It allows the files to be displayed on a variety of devices.
Question 12.
Write note on Tagra?
Answer:
It is the first popular format for high-resolution images. TGA is supported by Most of the video-capture boards.

Question 13.
Write note on MP3 format?
Answer:
MPEG Layer-3 format is the most popular format for storing and downloading music. The MP3 files are roughly compressed to one-tenth the size of an equivalent WAV file.
Question 14.
Write note on WMA?
Answer:
It is a popular windows media audio format owned by Microsoft and designed with Digital Right Management (DRM) abilities for copyright protection.

Question 15.
Write note on RA Format?
Answer:
Real Audio format is designed for streaming audio over the Internet. The digital audio resources are usually stored as a computer file in computer’s hard drive or CD/DVD.
Question 16.
What are the factors to be considered while delivering the multimedia product?
Answer:
- Bandwidth issues.
- Huge Number of Plugins required to play audio and video.
- Long downloading time.
Question 17.
Name the various fields where multimedia plays a vital role?
Answer:
Education, Entertainment, Business Systems, Medical Services, Public Places and Multimedia Conferencing.

Question 18.
What is Kiosk?
Answer:
Kiosk is a free-standing furnished equipped multimedia computer that allow users to retrieve information via a touch screen. It is^ commonly used in airports and other public locations to provide directions and few mandatory information’s.
III. Explain in Brief
Question 1.
Define path animation?
Answer:
Path animation involves moving an object on a screen that has a constant background e.g. a cartoon character may move across the screen regardless of any change in the background or the character.

Question 2.
Define composite Analog video? Mention same characteristics of composite Analog video?
Answer:
Composite Analog Video has all the video components like brightness, color, and synchronization combined into one signal. Due to the combining of the video components, the quality of the composite video resulted in color blending, low clarity and high generational loss.
Question 3.
Write note on TIFF?
Answer:
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) is common in desktop publishing world (high quality output), and is supported by almost all software packages. Recent versions of TIFF allows image compression, and the format is comfortable for moving large files between computers.

Question 4.
Differentiate GIF and JPEG?
Ans
GIF:
- It is lossless format
- It is limited to 8 bit palette
- Size of GIF is more
- Good for animation works
JPEG:
- It uses lossy format
- It allows multiple colors
- It is lesser
- Good for photographs

Question 5.
Explain PNG format?
Answer:
An extensible file format for the less loss, portable and well compressed storage of raster images. PNG acts as replacement for GIF and also replaces multiple common uses of TIFF. PNG works good with online viewing applications like world wide web. so it is fully streameable with a best display option.
Question 6.
Write note on MPEG?
Answer:
MPEG is a standard for generating digital video and audio compression under the International Standards Organization (ISO) by the group of people. The group has developed MPEG-1, the standard on which Video CD and MP3 are based, MPEG-2, the standard that supports products as Digital Television set top boxes and DVD, MPEG-4, the standard for multimedia and mobile web. MPEG-7, the standard for search of audio and visual content. Research on , MPEG-21 “Multimedia Framework” has started in 2000. Simply MPEG is the standards for digital video and audio compression.

Question 7.
List out the steps in Multimedia Production?
Answer:
Conceptual Analysis and Planning, Project design, Pre-production, Budgeting, Multimedia Production Team, Hardware/Software Selection, Defining the Content, Preparing the structure, Production, Testing, Documentation and Delivering the Multimedia Product.
Question 8.
What is meant by digital library?
Answer:
Information’s are available in digital formats It include digital books, scanned images, graphics and digitized audio-visual clips etc. digital library projects were based on textual data, images, audio and video recordings were also integrated under the collection of digital library.
IV. Answer in Detail
Question 1.
Explain various components of Multimedia?
Answer:
Multimedia has five major components like text, images, sound, video and animation. They are explained in detail below:
1. Text:
is the basic components of multimedia and most common ways of communicating information to other person. Static text, the text or the words will remain static as a heading or in a line, or in a paragraph. A hypertext is a system which consists of nodes, the text and the links between the nodes, which defines the paths the user need to follow for the text access in non-sequential ways.
2. Images:
acts as an vital component in multimedia. These images are generated by the computer in two ways, as bitmap or raster images and as vector images. Raster or Bitmap Images: The common and comprehensive form of storing images in a computer is raster or bitmap image.
3. Vector images:
Drawing elements or objects such as lines, rectangles, circles and so on to create an images are based on Vector images.
Animation is the process displaying still images so quickly so that they give the impression of continuous movement. Path animation involves moving an object on a screen that has a constant background e g. a cartoon character may move across the screen regardless of any change in the background or the character.
4. Frame animation:
In frame animations, multiple objects are allowed to travel simultaneously and the background or the objects also changes.
5. Sound:
is a meaningful speech in any language and is the most serious element in multimedia, providing the pleasure of music, special effects and so on.
6. Video:
is defined as the display of recorded event, scene etc. The powerful way to convey information in multimedia applications are embedding of video. The video can be categorized in two types as Analog video and Digital video.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()




![]()
![]()