Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Accountancy Model Question Paper 5 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Accountancy Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 11th Accountancy Model Question Paper 5 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III, and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer. - Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered in the above three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 90
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [20 × 1 = 20]
Question 1.
Who is considered to be the internal user of the financial information?
(a) Creditor
(b) Employee
(c) Customer
(d) Government
Answer:
(b) Employee
![]()
Question 2.
GAAPs are:
(a) Generally Accepted Accounting Policies
(b) Generally Accepted Accounting Principles
(c) Generally Accepted Accounting Provisions
(d) None of these .
Answer:
(c) Generally Accepted Accounting Provisions
Question 3.
The rule of stock valuation ‘cost price or realisable value’ whichever is lower is based on the accounting principle of:
(a) Materiality
(b) Money measurement
(c) Conservation
(d) Accrual
Answer:
(c) Conservation
Question 4.
In India, Accounting Standards are issued by …………………..
(a) Reserve Bank of India
(&) The Cost and Management Accountants of India
(c) Supreme Court of India
(d) The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
Answer:
(d) The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
Question 5.
Accounting equation is formed based on the accounting principle of ………………..
(a) Dual aspect
(b) Consistency
(c) Going Concern
(d) Accrual
Answer:
(a) Dual aspect
![]()
Question 6.
Real account deals with …………………
(a) Individual persons
(b) Expenses and losses
(c) Assets
(d) Incomes and gains
Answer:
(c) Assets
Question 7.
If the total of the debit side of an account exceeds the total of its credit side, it means:
(a) Credit balance
(b) Debit balance
(c) NIL balance
(d) Debit and credit balance
Answer:
(b) Debit balance
Question 8.
The amount brought into the business by the proprietor should be credited to ……………..
(a) Cash account
(b) Drawings account
(c) Capital account
(d) Suspense account
Answer:
(c) Capital account
Question 9.
While preparing the trial balance, the accountant finds that the total of the credit column is short by ₹ 200. This difference will be…………
(a) Debited to suspense account
(b) Credited to suspense account
(c) Adjusted to any of the debit balance
(d) Adjusted to any of the credit balance
Answer:
(b) Credited to suspense account
![]()
Question 10.
Purchase returns book is used to record …………….
(a) returns of goods to the supplier for which cash is not received immediately
(b) returns of assets to the supplier for which cash is not received immediately
(c) returns of assets to the supplier for which cash is received immediately
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) returns of goods to the supplier for which cash is not received immediately
Question 11.
A cash book with discount, cash and bank column is called …………….
(a) Simple cash book
(b) Double column cash book
(c) Three column cash book
(d) Petty cash book
Answer:
(c) Three column cash book
Question 12.
In Triple column cash book, the balance of bank overdraft brought forward will appear in ……………….
(a) Cash column debit side
(b) Cash column credit side
(c) Bank column debit side
(d) Bank column credit side
Answer:
(d) Bank column credit side
Question 13.
A bank statement is a copy of ……………..
(a) Cash column of the cash book
(b) Bank column of the cash book
(c) A customer’s account in the bank’s book
(d) Cheques issued by the business
Answer:
(c) A customer’s account in the bank’s book
Question 14.
A bank reconciliation statement is prepared to know the causes for the difference between:
(a) The balance as per the cash column of the cash book and bank column of the cash book
(b) The balance as per the cash column of the cash book and bank statement
(c) The balance as per the bank column of the cash book and the bank statement
(d) The balance as per petty cash book and the cash book
Answer:
(c) The balance as per the bank column of the cash book and the bank statement
Question 15.
Wages paid for installation of machinery wrongly debited to wages account is an error of ……………..
(a) Partial omission
(b) Principle
(c) Complete omission
(d) Duplication
Answer:
(b) Principle
![]()
Question 16.
Depreciation provided on machinery is debited to ……………..
(a) Depreciation account
(b) Machinery account
(c) Trading account
(d) Provision for depreciation account
Answer:
(a) Depreciation account
Question 17.
Amount received from IDBI as a medium term loan for augmenting working capital:
(a) Capital expenditures
(b) Revenue expenditures
(c) Revenue receipts
(d) Capital receipts
Answer:
(d) Capital receipts
Question 18.
Carriage inwards will be shown ………….
(a) In the trading account
(b) In the profit and loss account
(c) On the liabilities side
(d) On the assets side
Answer:
(a) In the trading account
Question 19.
Accrued interest on investment will be shown
(a) On the credit side of profit and loss account
(b) On the assets side of balance sheet
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
![]()
Question 20.
An example of output device is ………………..
(a) Mouse
(b) Printer
(c) Scanner
(d) Keyboard
Answer:
(b) Printer
Part – II
Answer any seven questions in which question No. 21 is compulsory: [7 × 2 = 14]
Question 21.
What is hardware?
Answer:
The physical components of a computer constitute its hardware. Hardware consists of input devices and output devices that make a complete computer system.
Question 22.
What is outstanding expense?
Answer:
Expenses which have been incurred in the accounting period but not paid till the end of the accounting period are called outstanding expenses.
Question 23.
Write a short note on revenue receipts.
Answer:
Receipts which are obtained in the normal course of business are called revenue receipts. It is recurring in nature. The amount received is generally small.
![]()
Question 24.
Mention any two methods of depreciation.
Answer:
- Straight line method
- Written down value method.
Question 25.
Give rectifying journals for the following:
1. Goods sold to Anand for Answer: 1,000 on credit was not entered in the sales book.
2. An amount of Answer: 400 paid for repairs to the machinery stands wrongly posted to machinery account.
Answer:
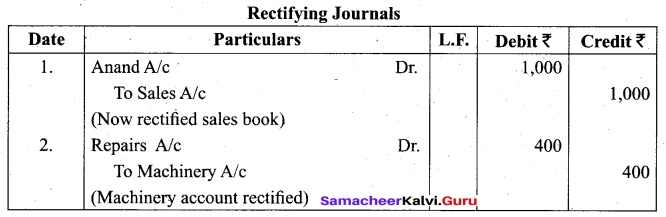
Question 26.
What is “Full Disclosure Principle” of accounting?
Answer:
Accounts must disclose Ml and fair information. It implies that the accounts must be prepared honestly and all material information should be disclosed in the accounting statement.
Question 27.
Classify the following into personal, real and nominal accounts.
1. Capital 2. Building 3. Outstanding wages 4. Salaries.
Answer:
1. Capital – Personal account.
2. Building – Real account.
3. Outstanding wages – Representation personal account.
4. Salaries – Nominal account.
Question 28.
Mention any two utilities of ledger.
Answer:
- Quick information about a particular account.
- Control over business transactions.
Question 29.
What is a ‘Debit note’?
Answer:
A ‘debit note’ is a document, bill or statement sent to the person to whom goods are returned. This statement informs that the supplier’s account is debited to the extent of the value of goods returned.
![]()
Question 30.
What is “Imprest Money”?
Answer:
The amount given to the petty cashier in advance is known as “Imprest Money”. The word
imprest means payment in advance.
Part – III
Answer any seven questions in which question No. 31 ¡s compulsory: [7 × 3 = 21]
Question 31.
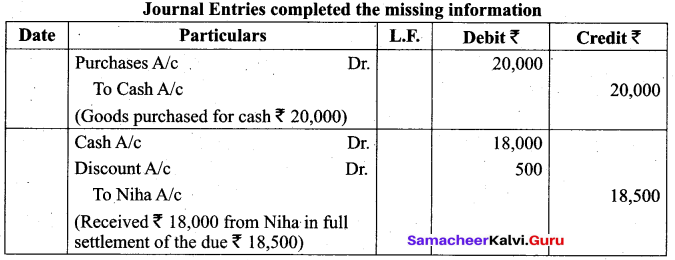
Fill in the missing information in the following journal entries:
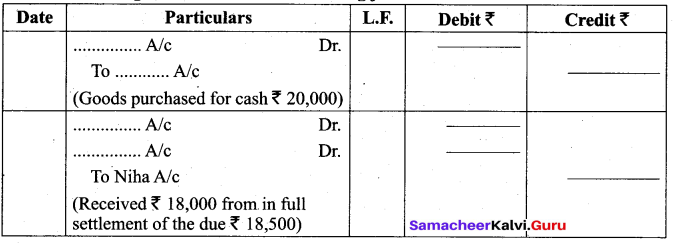
Answer:
Question 32.
Give journal entries and post them to cash account.

Answer:

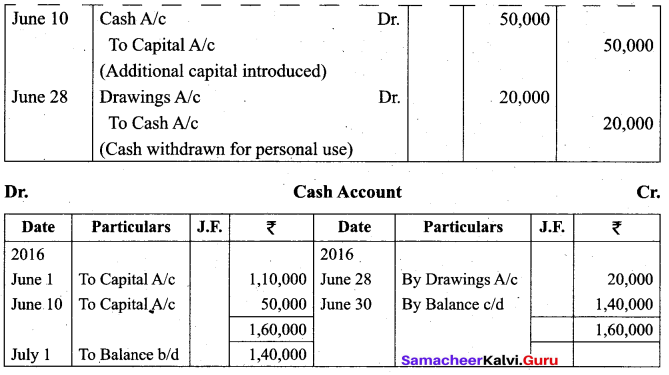
![]()
Question 33.
Prepare a trial balance with the following information:
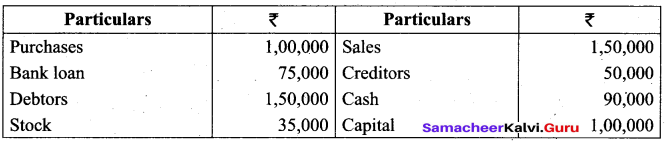
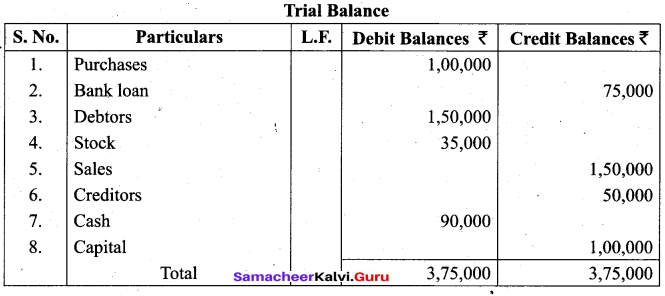
Answer:
Question 34.
From the following transactions of Ram Home Appliances for July, 2017 prepare purchases book.
| Date | Particular |
| 2017 July 5 | Purchased on credit from Kannan & Co., 50 iron boxes @ ₹ 500 each 10 grinders @ ₹ 3,000 each |
| July 6 | Purchased for cash from Siva & Brothers 25 fans @ ₹ 1,250 each |
| July 10 | Purchased from Balan & Co., on credit 20 grinders @ ₹ 2,500 each 10 mixies @ ₹ 3,000 each Trade discount 10% Delivery charges ₹ 1,000 |
| July 20 | Purchased on credit, one copier machine from Kumar for ₹ 35,000 |
Answer:
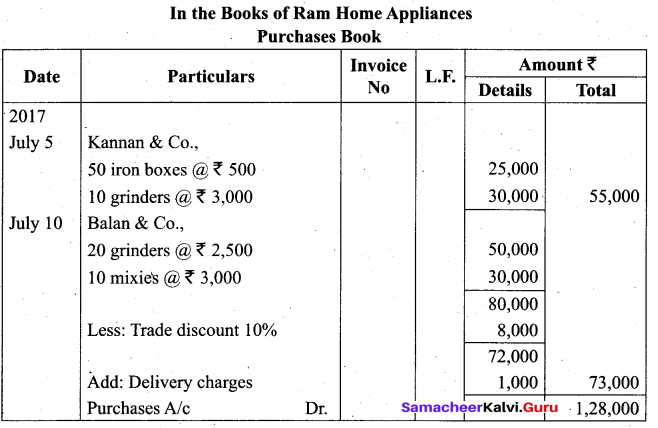
![]()
Question 35.
From the following particulars of Simon traders, prepare a bank reconciliation statement as on 31st March, 2018.
(a) Debit balance as per bank statement ₹ 2,500.
(b) Cheques deposited amounting to ₹ 10,000, not yet credited by bank.
(c) Payment through net banking for ₹ 2,000, omitted in the cash book.
Answer:

Question 36.
Rectify the following errors before the preparation of trial balance:
(a) Returns outward book was undercast by ₹ 2,000.
(b) Returns inward book total was taken as ₹ 15,000 instead of ₹ 14,000.
(c) The total of the purchases account was carried forward ₹ 100 less.
Answer:
(a) Returns outward account should be credited with ₹ 2,000.
(b) Returns inward account should be credited with ₹ 1,000.
(c) Purchases account should be debited with ₹ 100.
Question 37.
From the following information, calculate the amount of depreciation and rate of depreciation under straight line method.
Purchase price of machine ₹ 2,00,000.
Expenses to be capitalized ₹ 50,000.
Estimated residual value ₹ 15,000.
Expected useful life 5 years
Answer:
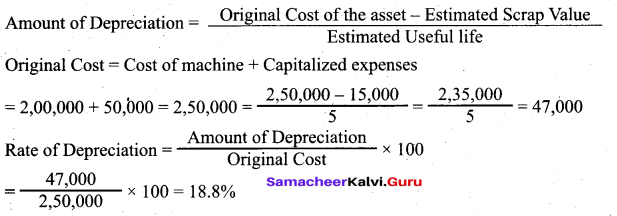
![]()
Question 38.
Find out the amount of sales from the following information.
| Particulars |
₹ |
| Opening Stock | 20,000 |
| Purchase less returns | 70,000 |
| Direct expenses | 10,000 |
| Closing Stock | 30,000 |
| Gross profit margin (on sales) | 20% |
Answer:
Cost of goods sold = Opening stock + Net purchases + Direct expenses – Closing stock ‘ ‘ =20,000 + 70,000 + 10,000 – 30,000 = 70,000
Let the sales be = 100
Less: Gross profit (20% on sales, i:e., 100) = 20
Cost of goods sold = 80
Therefore, percentage of gross profit on cost of goods sold is \(\frac{20}{80} \times 100\) = 25%
Gross profit = 25% on ₹ 70,000 i.e., \(\frac{25}{1000} \times 100\) x 70,000 = ₹ 17,500
Sales = Cost of goods sold + Gross profit
= 70,000+ 17,500 = 87,500 Sales = 87,500
Question 39.
Ascertain net profit or net loss from the following.
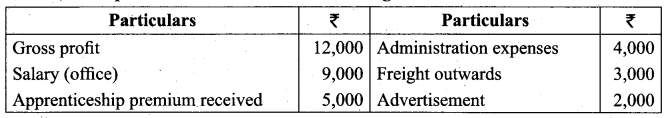
Answer:
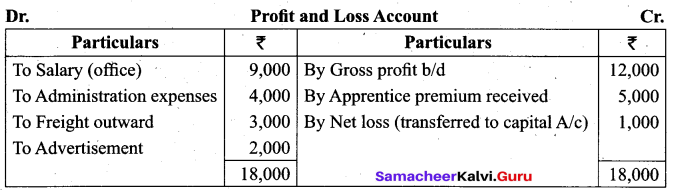 `
`
Question 40.
Enter the following transactions in a single column cash book of Ramalingam for the month of July, 2017.
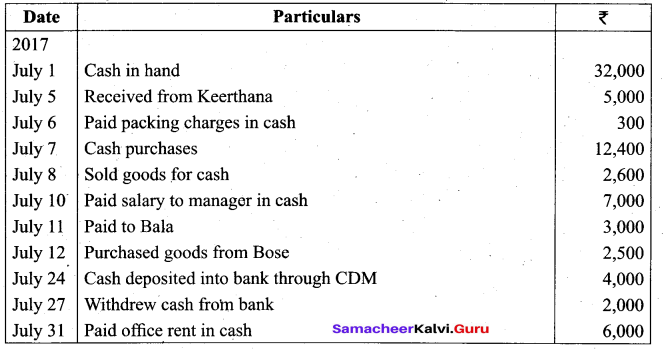
Answer:
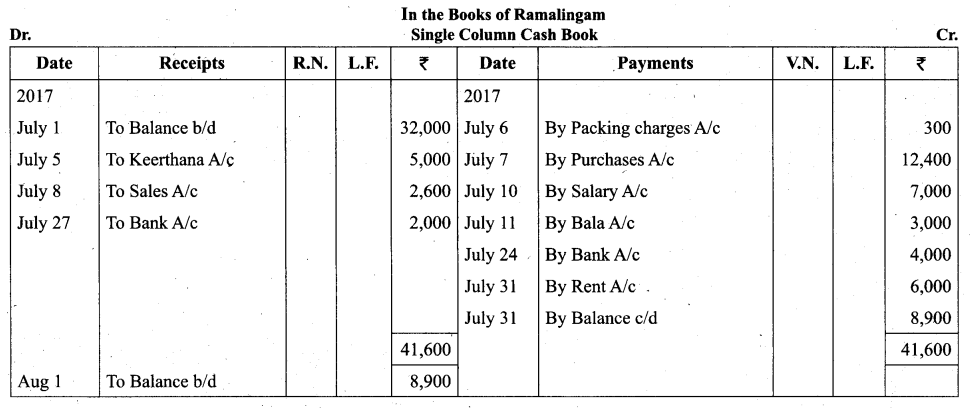
![]()
Part – IV
Answer all the questions: [7 × 5 = 35]
Question 41.
(a) A trader received his bank statement on 31st December, 2017 which showed an overdraft balance ₹ 12,000. On the same day, his cash book showed a debit balance of ₹ 2,000. Analyse the following transactions. Choose the possible causes and prepare a bank reconciliation statement to show the causes of differences.
a. Cheque deposited for ₹ 2,000 on 21st December, 2017. Bank credited the same on 26th December, 2017.
b. Cheque issued for payment on 26th December, 2017 amounting to ₹ 2,500, not yet presented until 31st December, 2017.
c. Bank charges amounting to?₹ 200 not yet entered in the cash book.
d. Online payment for ₹ 1,500 entered twice in the cash book.
e. Cheque deposited amounting ₹ 1,000, but omitted in the cash book. The same cheque was dishonoured by bank, but not yet entered in cash book.
f. Cheque deposited, not yet entered by bank amounting ₹ 17,800.
Answer:
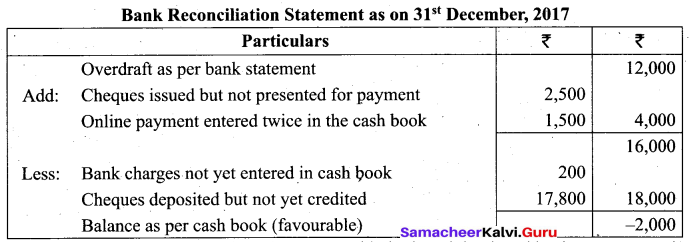
Note: Transactions (a) and (e) have been entered in both cash book and bank statement so it will not be entered.
[OR]
(b) From the following trial balance of Sharan, prepare Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ending 31st December, 2017 and Balance sheet as on that date. The Closing stock on 31st December, 2017 was valued at ₹ 2,50,000.
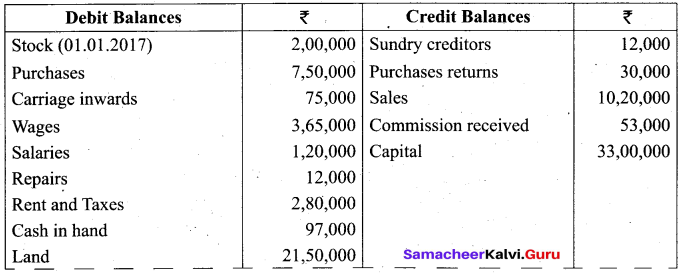
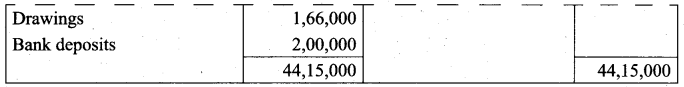
Answer:
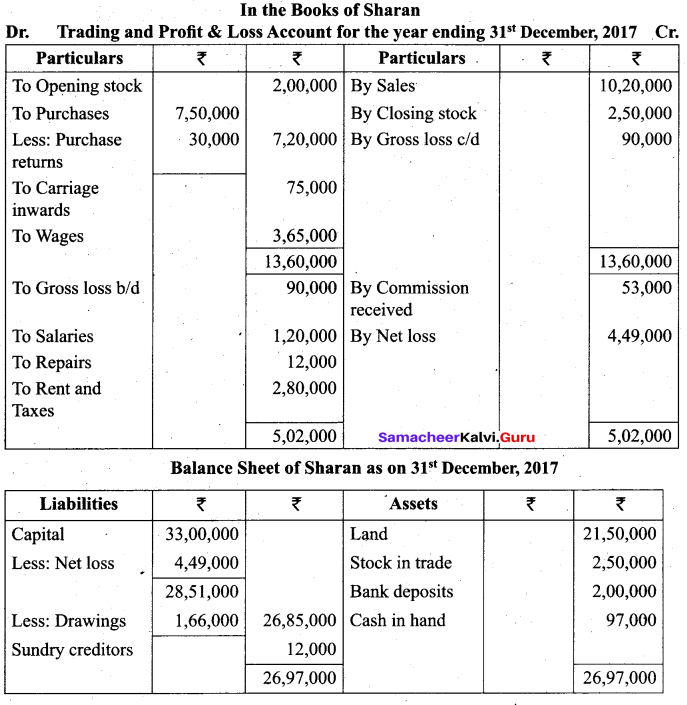
![]()
Question 42.
(a) The following errors were located after the preparation of trial balance. The difference in trial balance has been taken to suspense account. Rectify them.
a. The total of purchases book was carried forward ₹ 70 less.
b. The total of sales book was carried forward ₹ 340 more.
c. The total of purchases book was carried forward ₹ 150 more.
d. The total of sales book was carried forward ₹ 200 less.
e. The total of purchases returns book was carried ₹ 350 less.
Answer:
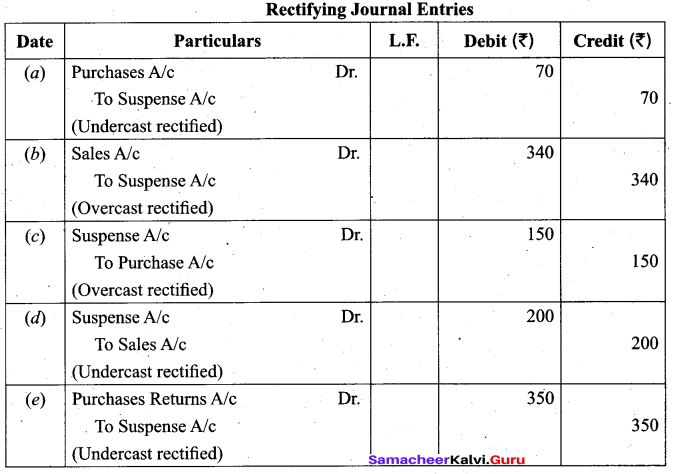
[OR]
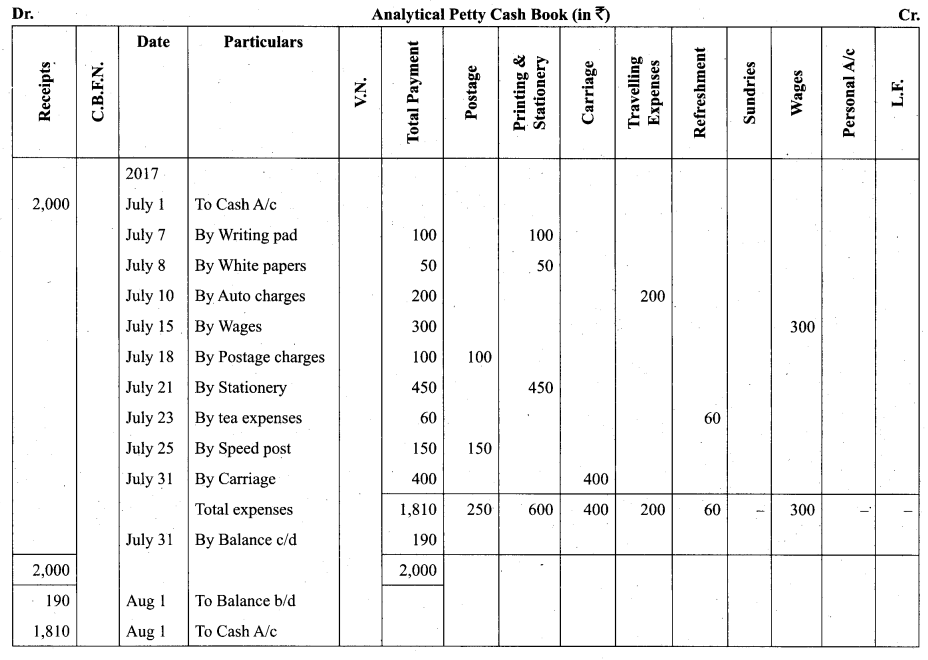
(b) Prepare analytical Petty cash book from the following particulars under imprest system:
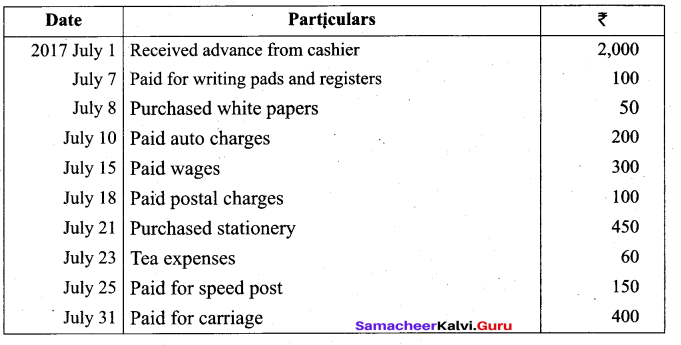
Answer:
Question 43.
(a) Calculate the amount of depreciation and rate of depreciation from the following by using ‘straight line method’. Also give journal entries for the first two years. The books are closed on 31st December every year.
January 1, 2016 payment to vendor for purchase of machinery ₹ 1,00,000.
January 1, 2016 transport cost ₹ 1,000.
January 1, 2016 installation cost ₹ 9,000.
Estimated scrap value at the end of the life ₹ 5,000.
Estimated life 10 years.
Answer:
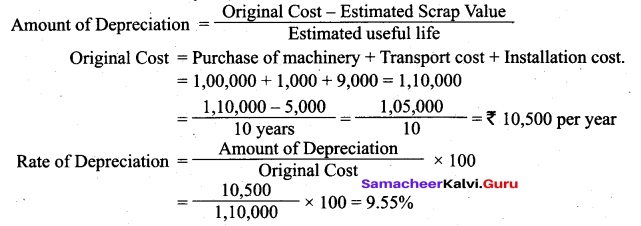
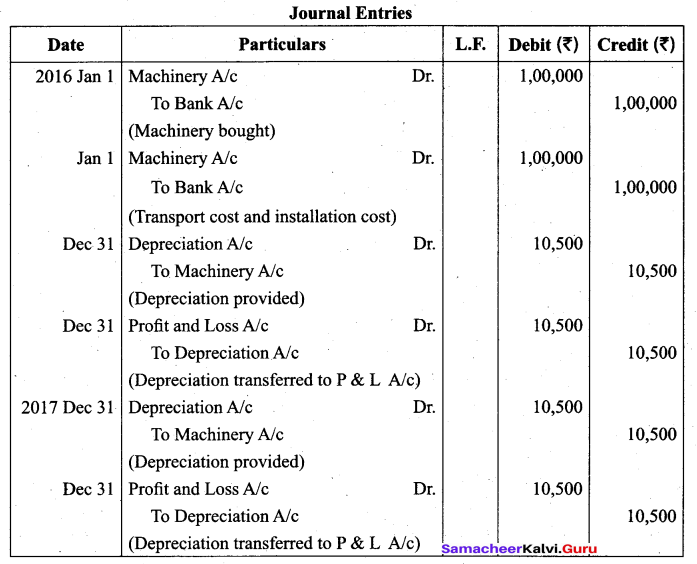
![]()
[OR]
(b) Write out a cash book with discount, cash and bank columns in the books of Mahendran.
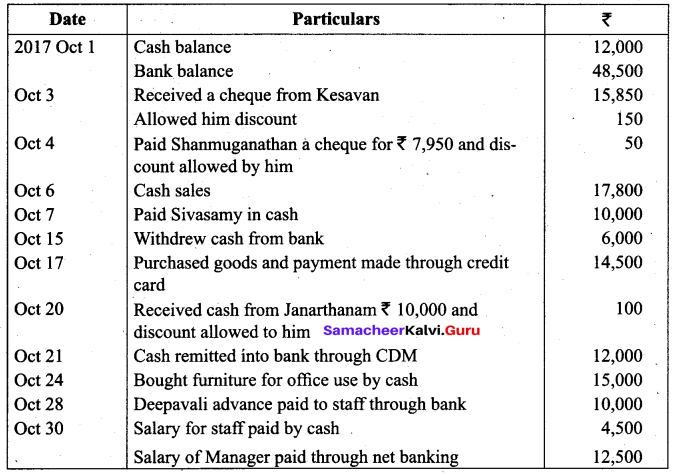
Answer:
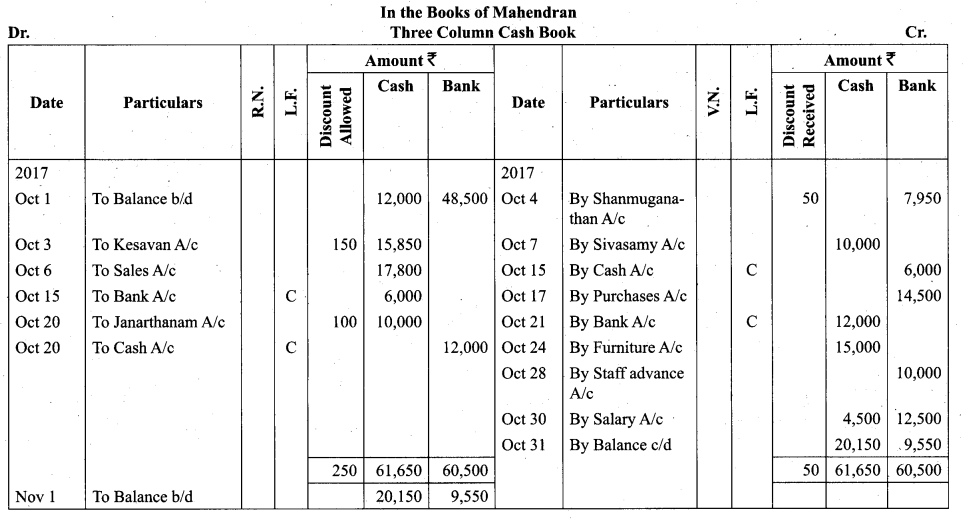
Question 44.
(a) Enter the following transactions in the proper subsidiary books of Suman who is dealing in electronic goods for the month of January, 2017.
| Date |
Particulars |
| 2017 Jan 2 | Purchased from MIs. Raj Electronics on credit
20 cell phones @ ₹ 5,500 per piece 10 colour TV’s @ ₹ 14,500 per piece |
| Jan 5 | Purchased from M/s. Ruby Electronic on credit
10 radios @ ₹ 1,650 per piece 8 tape recorders @ ₹ 2,500 per piece Trade discount on all items @ 10% |
| Jan 10 | Returned to MIs. Raj Electronics 4 cell phones damaged and cash not received. |
| Jan 20 | Purchased from MIs. Suganthi Electronics on credit
10 radios @ ₹ 3,700 per piece 2 sony colour TV’s @ ₹ 27,000 per piece Trade discount @ 5% on all items. |
Answer:
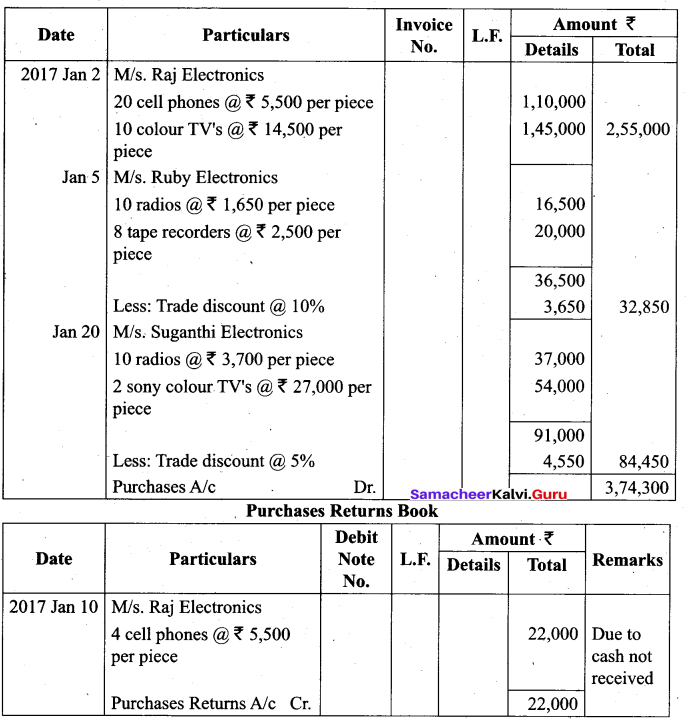
[OR]
(b) From the following balances obtained from the books of Siva, prepare Trading and Profit and Loss Account.
Tamil Nadu 11th Accountancy Model Question Paper 5 English Medium – 28
Adjustments:
a. Closing stock on 31.12.2016 was ₹ 4,500.
b. Manager is entitled to receive commission @ 5 % net profit after providing such commission.
Answer:
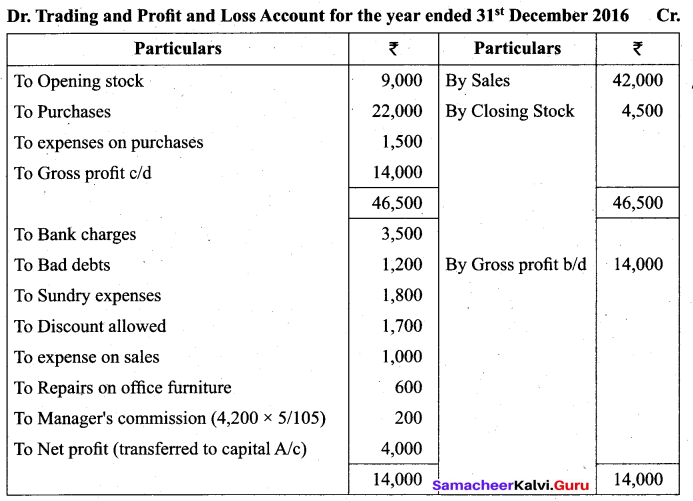
![]()
Question 45.
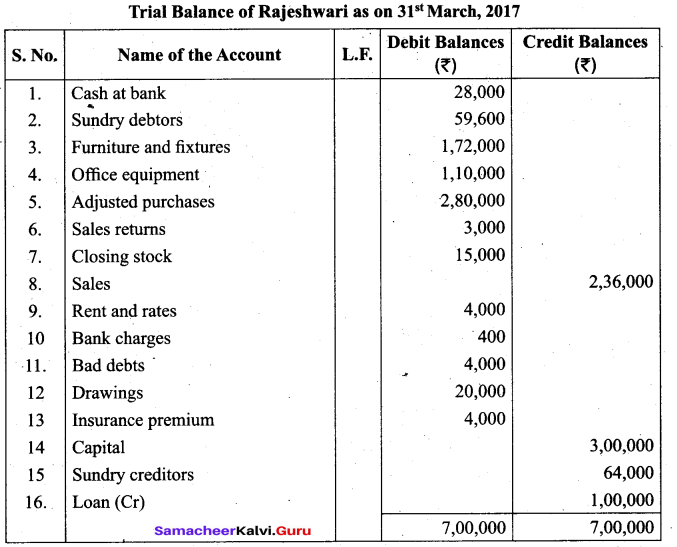
(a) From the following balances extracted from the books of Rajeshwari as on 31st March, 2017, prepare the trial balance.
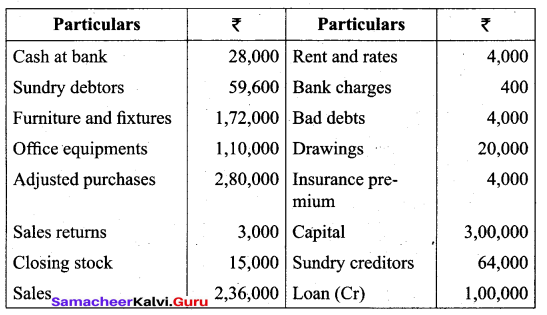
Answer:
[OR]
(b) Identify the following items into capital or revenue:
1. Audit fees paid ₹ 10,000.
2. Labour welfare expenses ₹ 5,000.
3. ? 2,000 paid for servicing the company vehicle.
4. Repair to furniture purchased second hand ₹ 3,000.
5. Rent paid for the factory ₹ 12,000.
Answer:
1. Revenue
2. Revenue
3. Revenue
4. Capital
5. Revenue
![]()
Question 46.
(a) Show the direct ledger posting for the following transactions:
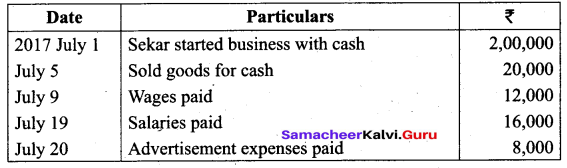
Answer:
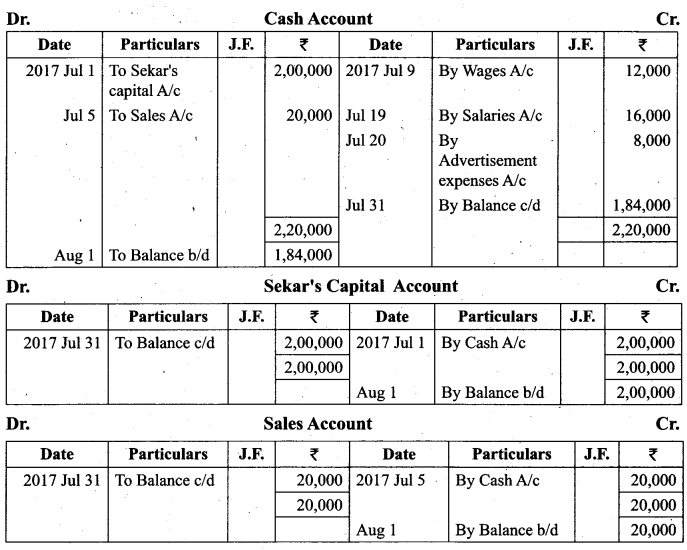
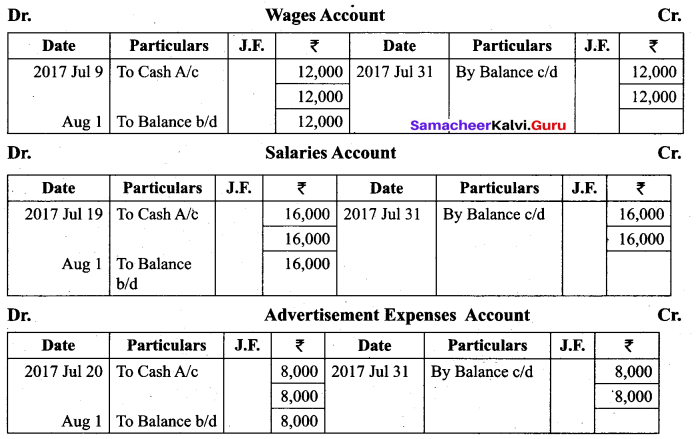
![]()
[OR]
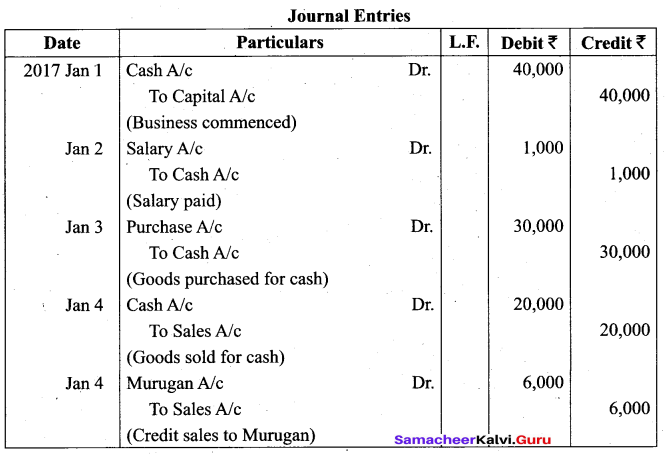
(b) Complete the missing informations:
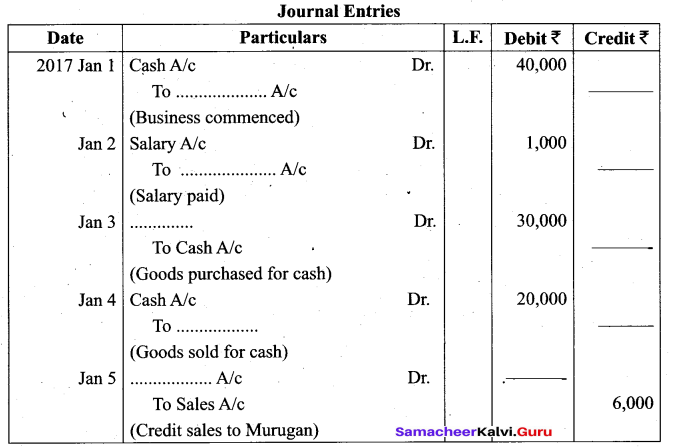
Answer:
Question 47.
(a) Complete the missing informations:
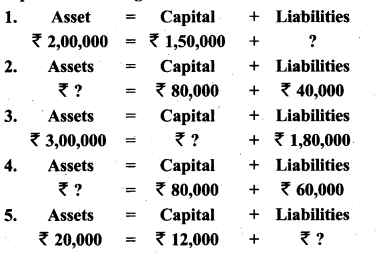
Answer:
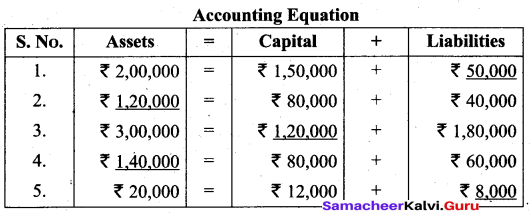
![]()
[OR]
(b) Give examples for,the followings:
1. Increase in capital and increase in asset.
2. Decrease in liability and decrease in asset.
3. Increase in one asset and decrease in another asset.
4. Decrease in one liability and increase in another liability.
5. Decrease in one asset and increase in another asset.
Answer:
1. Commenced business with cash ₹ 1,00,000.
2. Paid to creditors ₹ 10,000.
3. Bought furniture for cash ₹ 5,000.
4. Accepted a bill drawn by creditors for ₹ 20,000.
5. Sold goods for cash ₹ 10,000.