You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Economics Solutions Chapter 3 Money and Credit
Money and Credit Textual Exercise
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
1. Certain metals like ….. (gold/iron) were used as a medium of exchange in ancient times.
2. The Head Quarters of the RBI is at ….. (Chennai / Mumbai).
3. International trade is carried on in terms of …… (US Dollars / Pounds).
4. The currency of Japan is ……. (Yen/Yuan)
Answers:
1. gold
2. Mumbai
3. US Dollars
4. Yen
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. …… system can be considered as the first form of trade.
2. Money supply is divided into ……
3. The first printing press of the RBI was started at ………
4. …… act as a regulator of the circulation of money.
5. The thesis about money by B.R. Ambedkar is ……..
Answers:
1. Barter
2. four
3. Nasik, Maharashtra
4. The Reserve Bank of India
5. The Problem of the Rupee
III. Match the following:
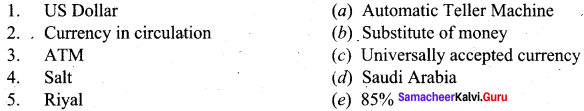
Answers:
1. (c)
2. (e)
3. (a)
4. (b)
5. (d)
![]()
IV. Give short answers.
Question 1.
Why was money invented?
Answer:
- At-home planning the expenses is based on the monthly incomes, pending expenditure, savings, payment of interest etc.
- The budgets of a country or state are also framed on the basis of money.
- The government, as well as, private institutions and industries calculate their financial status through money.
- A common item with a standard value for the effective exchange of goods was needed. Therefore money was invented.
Question 2.
What is ancient money?
Answer:
- Measuring the quantity and value of the goods exchanged were found very difficult. To solve these issues they fixed a common item with a standard value for the effective exchange of goods.
- Gold, silver, and copper were called ancient money.
Question 3.
What were the items used as barter during the olden days?
Answer:
Leather, beads, shells, tobacco, salt, com, cattle, and even slaves were exchanged as barter, say economists.
![]()
Question 4.
What is spice route? Why was it called so?
Answer:
- Pepper, spices, pearls, gems, rubies and muslin clothes were exported from the eastern sea of Tamil Nadu.
- Pepper and spices took a major share of the exports. Hence this route was called the spice route.
Question 5.
What is natural money?
Answer:
- The metals such as silver and gold gained importance gradually all over the world.
- So, these metals were used as a standard value in the exchange of goods.
- This was called natural money.
Question 6.
Why were coins of the low value printed in large quantities?
Answer:
- Mines had a limited reserve of the metals.
- An alternative was found and coins were made using metals with lesser value.
- These were used to buy and sell goods of lesser value.
- It was used as the money of the poor people.
Hence the coins of low value were printed in large quantities.
![]()
Question 7.
What is meant by foreign exchange?
Answer:
- Currency is the medium of exchange in a country.
- The Indian currency is called the Indian Rupee.
- In a country, the foreign currency is called foreign exchange.
- The purchasing capacity of all currencies in the world are compared using the US dollar as the standard currency.
- This value differs from country to country.
- Most of the international trade transactions are carried out in the US dollar.
V. Answer in Detail.
Question 1.
Explain how money is transacted in the digital world.
Answer:
Money has become an inseparable part of everyone’s life today. It has changed its form in the economic front. Money transactions are done through many ways in the electronic world. One has to visit the bank and fill in a challan or produce a cheque to withdraw money from his account.
Now this practice is gradually vanishing. Instead, one can easily withdraw the necessary amount from an Automated Teller Machine (ATM), with the help of an ATM debit card. One can easily withdraw the money needed at any time at ATMs located everywhere. A person can deposit money in their account without visiting the branch.
Similarly, credit cards are also available, through which things are bought on credit and the amount can be paid later.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain in detail the role of RBI in the country.
Answer:
- A government has the responsibility to regulate the money supply and oversee the monetary policy.
- Hoarding of money must be avoided at all costs in a country’s economy.
- Only then money can be saved in banks.
- All the major and important banks were nationalised (1969) in India.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regulates the circulation of currency in India.
- The Reserve Bank of India started its operations on 1st April 1935.
- It was permanently moved to Mumbai from the year 1937.
- RBI was nationalised in 1949. 85% of the printed currency is let for circulation.
- According to the statistics available as in August 2018, currency worth 19 lakh crore is in circulation.
Question 3.
Write in detail about the various functions of money.
Answer:
When money replaced the barter system, a lot of practical issues were solved. Money acts a medium of exchange, a unit of measurement, a store of value, and a standard of deferred payments. It plays an important role in transactions.
The medium of Exchange: Money should be accepted liberally in exchange for goods and services in a country.
Unit of Account: Money should be the common, standard unit of calculating a country’s total consumer goods, products, services etc. For example, if a book costs ₹ 50, it means that the price of the book is equal to 50 units of money. Money is used to measure and record financial transactions in a country.
A Store of Value: Money is used as a store of purchasing power. It can be used to finance future payments.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the divisions of the money supply?
Answer:
The money supply is divided into four;
M1 = Currency held with the public + cash Reserves in commercial and Co-operative banks + cash reserves in the RBI.
M2 = M1 + Money saved in Post office and bank savings accounts
M3 = M1 + Time Deposits in Commercial and co-operative banks
M4 = M3 + Post office savings Money
VI. Write the correct statement.
A.
1. The barter system flourished wherever civilizations thrived.
2. This was the initial form of trade.
(i) 1 is correct; 2 is wrong
(ii) Both 1 and 2 are correct
(iii) Both 1 and 2 are wrong
(iv) 1 is wrong; 2 is correct
Answer:
(ii) Both 1 and 2 are correct
B.
1. Most of the international trade transactions are carried out in US dollars.
2. No other country except the US carries out trade in the world.
(i) Both the statements are correct.
(ii) Both the statements are wrong.
(iii) 1 is correct; 2 is wrong
(iv) 1 is wrong; 2 is correct
Answer:
(iii) 1 is correct; 2 is wrong
VII. Project and activity.
Question 1.
Visit a local museum and collect information about the coins displayed there.
Answer:
You can do this activity under the guidance of your teacher.
![]()
Question 2.
Imagine you are going abroad for a Post Graduation course in architecture. Write a letter to the Branch Manager regarding an education loan.
Answer:
18.04.2019
Chennai
From
Deepa
18, Meenakshi Nagar
Nerkundram
To
The Branch Manager
HDFC Bank
T. Nagar
Chennai-600 017
Respected Sir,
Sub: Request for Educational Loan
I am Deepa, a student of Architecture living in Chennai. I have completed my degree course with 85% marks. I have got an opportunity to pursue a Post Graduation course in Architecture at King’s College, London. As I belong to an economically weaker section, I need your help in funding my studies. I am applying for an educational loan at your esteemed bank. I herewith enclose the copies of my mark sheet and admission letter. Could you please consider my request for the loan? I shall be obliged for the same.
Thank you,
Yours sincerely,
Deepa
Enclosures:
1. B.Arch. mark sheet
2. Admission Letter for Post Graduation in Architecture
| To The Branch Manager HDFC Bank T. Nagar, Chennai – 600 017 |
VIII. Life skills – Student Activity.
Question 1.
Observe a 20 rupee note. What is written on it?
Answer:
• RESERVE BANK OF INDIA
• GUARANTEED BY THE CENTRAL GOVERNMENT
• I PROMISE TO PAY THE BEARER THE SUM OF TWENTY RUPEES
Students can write other words written in different languages:
• …………………………………………….
• …………………………………………….
Question 2.
Prepare a family budget for a month.
Answer:
- The class will be divided into 4 groups.
- They will be asked to prepare a family budget with the help of parents.
- The report will be presented in the class by each group.
Money and Credit Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
1. ………….. (Ancient men/Modern men) hunted and gathered food.
2. …………. (Goods/Metals) be termed as the first form of money.
3. ……… (The later Cholas/The early Cholas) allowed the traders to have their own army.
4. All the major and important banks were nationalised in ……. (1969/1970) in India.
5. The currency of England is …………. (Pound/Dollar).
6. The currency of Saudi Arabia is ………. (Ringgit/Riyal).
Answers:
1. Ancient men
2. Metals
3. The later Cholas
4. 1969
5. Pound
6. Riyal
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks.
- The …….. system was the initial form of international trade.
- …… plays a predominant and inseparable role in all our lives.
- The first form of money is ……….
- ……… issued a coin of silver weighing 178 grams which were termed as the Rupiya.
- A government has the responsibility to regulate the money supply and oversee the ……… policy.
- ………. attempts to meet the educational aspirations of the society.
- There is no security required for the loan amount upto ₹ ………. lakhs.
- The …… regulates the circulation of currency in India.
- The Indian currency is called the ………
- Till 1947, the currency notes with the image of …….. were in circulation.
Answers:
- Barter
- Money
- Metals
- Sher Shah Suri
- Monetary
- Educational loan
- 4 lakhs
- Reserve Bank of India
- Indian Rupee INR
- King George VI
III. Match the following.

Answers:
1. (f)
2. (g)
3. (a)
4. (b)
5. (d)
6. (c)
7. (e)
IV. Give short answers.
Question 1.
Give a short account of the life of ancient men.
Answer:
Ancient man hunted and gathered food. He lived in caves and forests. In later stages, he invented weapons for hunting and gathering food. Later, he invented fire and learned to practice agriculture. He used mud to build houses and settle down in a place, and also to make earthenware.
![]()
Question 2.
How does money play a predominant and inseparable role in all our lives?
Answer:
The Government, as well as, private institutions and industries calculate their financial status through money. Thus, money plays a predominant and inseparable role in all our lives.
Question 3.
How were the later cholas treated the traders?
Answer:
The later Cholas allowed the traders to have their own army. Historical evidences state that during this period, small traders and producers gave credit to the Tamil traders to support their export needs.
Question 4.
Where were the barter system flourished?
Answer:
The barter system flourished wherever civilizations thrived. This system was active not only within a civilization, but also among civilizations. This was the initial form of international trade.
Question 5.
What is currency?
Answer:
Currency is the medium of exchange in a country. The Indian currency is called the Indian Rupee (INR). In a country the foreign currency is called foreign exchange.
Purchasing capacity of all currencies in the world are compared using the US dollar as the standard currency. This value differs from country to country.
![]()
Question 6.
What do the Government do with the savings in the banks?
Answer:
A major portion of the savings in banks are used for the development of industries, economic growth and various development schemes for the welfare of the poor.
Question 7.
What is Credit?
Answer:
Farmers avail credit during monsoons for buying seeds, agricultural input and other expenses. Traders and small entrepreneurs need credit for their needs. Even large industries receive credit to take up their new projects.
![]()
Question 8.
Give an account of Self Help Groups.
Answer:
People who live in a particular place or those who are involved in a certain work join together as a group and start saving. These are called as Self Help Groups. The nationalised banks provide help to these groups through micro-credit. Credit given though Self Help Groups for street vendors, fishermen, especially women and the poor really make a difference in their life.
V. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
How is currency printed in India?
Answer:
In 1925, the British government established a government press at Nasik in Maharashtra. Currencies were printed three years later. In 1974, a press was started in Dewas, Madhya Pradesh. (Security Printing and Minting Corporation of India Ltd.) In the 1990s. two more presses were started in Mysuru, Karnataka and Salboni in West Bengal to print bank notes. The Reserve Bank of India has the authority to decide the value of currency to be printed and how the amount should reach its destination safely. Around ten thousand workers are employed here. Countries like Sri Lanka, Bhutan, Iraq and Africa have drawn contracts for printing their currencies and sent to the respective countries.
Though the RBI has the power to print up to ten thousand rupee notes, at present a maximum of upto rupees two thousand is printed.
![]()
Question 2.
Write in detail the Foreign Exchange rate equivalent to US Dollars.
Answer:
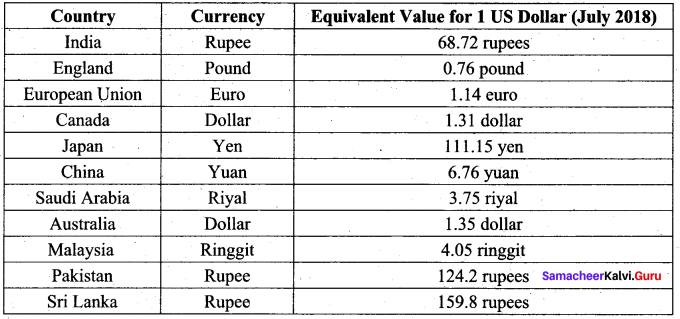
VI. Write the correct statement.
A.
1. Money is recognized as a standard record for the payment of a thing or service.
2. Using this currency, people can purchase things, pay taxes and repay debts.
(i) Both 1 and 2 are correct
(ii) Both 1 and 2 are wrong
(iii) 1 is correct; 2 is wrong
(iv) 1 is wrong; 2 is correct
Answer:
(i) Both 1 and 2 are correct
B.
1. Paper money was introduced because metal supply was limited.
2. All the major and important banks were nationalised in 1964, in India.
(i) Both 1 and 2 are correct
(ii) Both 1 and 2 are wrong
(iii) 1 is correct; 2 is wrong (iv) 1 is wrong; 2 is correct
Answer:
(iii) 1 is correct; 2 is wrong
HOTS
Question 1.
How important is foreign exchange to one’s country?
Answer:
- During any Crisis Foreign exchange reserves come to the rescue of any country. It absorbs the distress related to such crisis.
- It increases the confidence in the monetary and exchange rate policies of the government.
- Foreign exchange reserves are the foreign currencies held by the Country’s Central Bank. They are also called Foreign currency reserves (or) Foreign reserves. They manage their currencies.
Thus foreign exchange is important to any country.