You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 2 Motion
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Motion Textbook Exercises
I. Choose the correct answer.
This is free online Displacement calculator. enter Initial and final value then click on calculate and result will be instant displayed
Question 1.
The area under velocity-time graph represents the
(a) velocity of the moving object
(b) displacement covered by the moving object
(c) speed of the moving object
(d) acceleration of the moving object
Answer:
(d) acceleration of the moving object
Question 2.
Which one of the following is most likely not a case of uniform circular motion?
(a) Motion of the Earth around the Sun
(b) Motion of a toy train on a circular track
(c) Motion of a racing car on a circular track
(d) Motion of hour’s hand on the dial of the clock
Answer:
(a) Motion of the Earth around the Sun
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the following graph represents uniform motion of a moving particle?
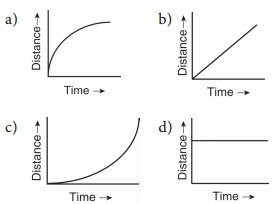
Answer:
(b) 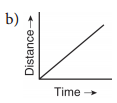
Question 4.
The centrifugal force is
(a) a real force
(b) the force of reaction of centripetal force
(c) virtual force
(d) directed towards the centre of the circular path
Answer:
(c) virtual force
The Velocity Calculator is a free tool to predict how much work a team will complete during upcoming iterations.
II. Fill in the blanks.
- Speed is a ____________ quantity whereas velocity is a _____________ quantity.
- The slope of the distance-time graph at any point gives ____________
- Negative acceleration is called ____________
- Area under velocity-time graph shows ___________
Answer:
- scalar, vector
- speed
- retardation (or) deceleration
- displacement
This displacement calculator finds the displacement (distance traveled) by an object using its initial and final velocities as well as the time traveled.
III. True or False.
- The motion of a city bus in a heavy traffic road is an example of uniform motion.
- Acceleration can get a negative value also.
- Distance covered by a particle never becomes zero but displacement becomes zero.
- The velocity-time graph of a particle falling freely under gravity would be a straight line parallel to the x axis.
- If the velocity-time graph of a particle is a straight line inclined to X-axis then its displacement – time graph will be a straight line.
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
IV. Assertion and Reason Type Question.
Mark the correct choice as:
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If the assertion is true but the reason is false.
(d) If the assertion is false but the reason is true.
![]()
Question 1.
Assertion: The accelerated motion of an object may be due to change in magnitude of velocity or direction or both of them.
Reason: Acceleration can be produced only by change in magnitude of the velocity. It does not depend the direction.
Answer:
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
Question 2.
Assertion: The Speedometer of a car or a motor-cycle measures its average speed.
Reason: Average velocity is equal to total displacement divided by the total time taken.
Answer:
(d) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Question 3.
Assertion: Displacement of a body may be zero when distance travelled by it is not zero.
Reason: The displacement is the shortest distance between initial and final position.
Answer:
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
V. Match the following.
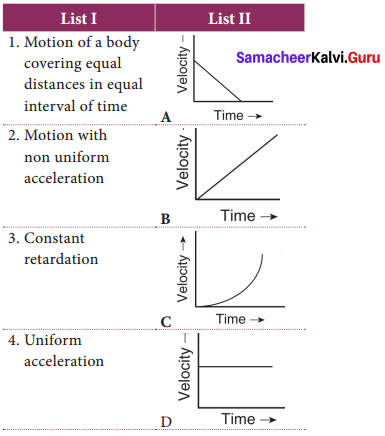
Answer:
1. (D)
2. (C)
3. (A)
4. (B)
VI. Answer briefly.
Question 1.
Define velocity.
Answer:
- Velocity is the rate of change of displacement. It is the displacement with unit time. It is a vector quantity. The SI unit of velocity is ms-1
- Thus, Velocity = Displacement/time taken.
Question 2.
Distinguish distance and displacement.
Answer:
|
S.No. |
Distance |
Displacement |
| 1. | The actual length of the path traveled by a moving body irrespective of the direction | The change in position of a moving body in a particular direction |
| 2. | Scalar quantity | Vector quantity |
Question 3.
What do you mean by uniform motion?
Answer:
An object is said to be in uniform motion if it covers equal distances in equal intervals of time howsoever big or small these time intervals may be.
![]()
Question 4.
Compare Speed and Velocity.
Answer:
| S.No. | Speed |
Velocity |
| 1. | The rate of change of distance | The rate of change of displacement |
| 2. | Scalar quantity | Vector quantity |
| 3. | Speed = \(\frac{\text { Distance travelled }}{\text { time taken }}\) | Velocity = \(\frac{\text { Displacement }}{\text { time taken }}\) |
Question 5.
What do you understand about negative acceleration?
Answer:
If velocity decreases with time the value of acceleration is negative.
Note: Negative acceleration is called retardation or deceleration.
Question 6.
Is the uniform circular motion accelerated? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
When an object is moving with a constant speed along a circular path, the velocity changes due to the change in direction. Hence it is an accelerated motion.
Question 7.
What is meant by uniform circular motion? Give two examples of uniform circular motion.
Answer:
When an object moves with constant speed along a circular path, the motion is called uniform circular motion.
Ex. (i) Revolution of Earth around the Sun
(ii) Revolution of Moon around the Earth.
VII. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
Derive equations of motion by graphical method.
Answer:
An object is in motion with initial velocity u attains a final velocity v in time t due to acceleration a, with displacement S.
Let us try to derive these equations by graphical method. Equations of motion from velocity – time graph:
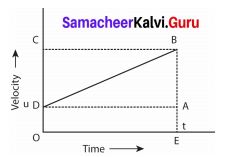
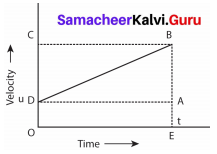
Graph shows the change in velocity with time for an uniformly accelerated object. The object starts from the point D in the graph with velocity u. Its velocity keeps increasing and after time t it reaches the point B on the graph.
The initial velocity of the object = u = OD = EA
The final velocity of the object = v = OC = EB
Time = t = OE = DA
Also from the graph we know that, AB = DC
For First equation of motion
By definition, acceleration = change in velocity / time
= (final velocity – initial velocity)/time
= (OC – OD) / OE = DC / OE
a = DC/t
DC = AB = at
From the graph EB = EA + AB
v = u + at ….(1)
This is first equation of motion.
For Second equation of motion
From the graph the distance covered by the object during time t is given by the area of quadrangle DOEB
s = area of the quadrangle DOEB
s = area of the rectangle DOEA + area of the triangle DAB
= (AE × OE) + (1/2 × AB × DA)
s = ut + 1/2at2 ….(2)
This is second equation of motion.
For Third equation of motion
From the graph the distance covered by the object during time t is given by the area of the quadrangle DOEB. Here DOEB is a trapezium. Then
s = area of trapezium DOEB
= 1/2 × sum of length of parallel side × distance between parallel sides
= 1/2 × (OD + BE) × OE
s = 1/2 × (u + v) × t
Since a = (v – u) / t or t = (v – u)/a
Therefore = 1/2 × (v + u) × (v – u)/a .
2as = v2 = u2 + 2as
v2 = u2 + 2as ………(3)
This is third equation of motion.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain different types of motion.
Answer:
Different types of motion:
- Linear motion: The motion of an object along a straight line is known as linear motion.
Ex: Car moving on a straight road. - Circular motion: The motion of an object in a circular path is known as circular motion.
Ex: Earth revolving around the sun. - Oscillatory motion: Repetitive to and fro motion of an object at regular interval of time is called oscillatory motion. Ex: Motion of pendulum of a clock.
- Random motion: The disordered or irregular motion of a body is called random motion.
Ex: Movement of fish underwater.
VIII. Exercise problems.
Question 1.
A ball is gently dropped from a height of 20m. If its velocity increases uniformly at the rate of 10 ms– 2. With what velocity will it strike the ground? After what time will it strike the ground?
Given: height = 20 m
acceleration = 10 ms– 2
Formula: For free falling body,
- v = gt
- s = 1/2 gt2
Solution:
time taken to strike the ground
s = 1/2 gt2
20m = 1/2 × 10 ms – 2 × t2
t2 = \(\frac{40 m}{10 m s^{-2}}\) = 4s 2
∴ t = 2s - Velocity of the ball when it strikes ground v = gt
v = 10ms– 2 × 2s
v = 20ms– 1
Question 2.
An athlete completes one round of a circular track of diameter 200 m in 40 s. What will be the distance covered and the displacement at the end of 2 m and 20 s?
Given: Diameter of circular track = 200m
time to complete = 40s
Formula: Circumference of circular track = d. π m
speed = distance/time
Solution:
Circumference of the track = d.π
= 200 × 3.14 = 628m
speed = \(\frac{628 m}{40 s}\) = 15.7 ms– 1
Distance covered in 2 min 20 s = speed × time
In the given time athlete covers 31/2 rounds = 2198m
The final position of athlete is as shown in figure (A – initial position, B – final position)
∴ Displacement = Distance × time
= 200 m
![]()
Question 3.
A racing car has a uniform acceleration of 4 ms– 2. What distance it covers in 10 s after the start?
Given: acceleration = 4ms– 2.
time = 10s and initial velocity = 0
Formula: s = ut + 1/2 at2
Solution:
distance covered s = 0 × t + 1/2 × 4 ms– 2 × (10 s)2.
s = 1/2 × 4 ms– 2 × 100 s2
= 1/2 × 400m
= 200m
Solved Examples.
Question 1.
An object travels 16 m in 4 s and then another 16 m in 2 s. What is the average speed of the object?
Solution:
Total distance travelled by the object =16m + 16m = 32m
Total time taken = 4s + 2s = 6s
Average speed = \(\frac{\text { Total distance travelled }}{\text { total time taken }}\) = \(\frac{32}{6}\) = 5.33 ms– 1
Therefore, the average speed of the object is 5.33 ms– 1.
Question 2.
A sound is heard 5 s later than the lightning is seen in the sky on a rainy day. Find the distance of location of lightning? Given the speed of sound = 346 ms– 1
Solution:
Speed = \(\frac{\text { Distance }}{\text { time }}\)
Distance = speed x time = 346 x5 = 1730 m
Thus, the distance of location of lightning = 1730 m
Question 3.
The brakes applied to a car produce an acceleration of 6 ms– 2 in the opposite direction to the motion. If the car takes 2 s to stop after the application of brakes, calculate the distance traveled during this time.
Solution:
We have been given a = – 6 ms– 2, t = 2s and v = 0
From the equation of motion,
v = u + at
0 = u + (- 6 × 2) .
0 = u – 12 ∴ u = 12 ms– 1
s = ut + 1/2 at2
= (12 × 2) + 1/2 (- 6 × 2 × 2) .
= 24 – 12 = 12m
Thus, the car will move 12 m before it stops after the application of brakes.
Question 4.
A 900 kg car moving at 10 ms– 1 takes a turn around a circle with a radius of 25 m.
Determine the acceleration and the net force acting upon the car.
Solution:
When the car turns around circle, it experiences centripetal acceleration a = \(\frac{v^{2}}{r}\)
a = \(\frac{(10)^{2}}{25}=\frac{100}{25}\) ∴ a = 4ms– 2
Net force acting upon the car,
F = ma = 900 × 4 = 3600N
ACTIVITY
Question 1.
Look around you. You can see many things: a row of houses, large trees, small plants, flying birds, running cars and many more. List the objects which remain fixed at their position and the objects which keep on changing their position.
Answer:
- The objects which remain fixed at their position, and do not change their position are a row of houses, large trees and small plants.
- The objects which keep on changing their position are flying birds, running cars and buses.
![]()
Question 2.
Tabulate the distance covered by a bus in a heavy traffic road in equal intervals of time and do the same for a train which is not in an accelerated motion. From your table what do you understand?
Answer:
The bus covers unequal distance in equal intervals of time but the train covers equal distances in equal intervals of time.
(The students can do this activity by themselves)
Question 3.
Observe the motion of a car as shown in the figure and answer the following questions:
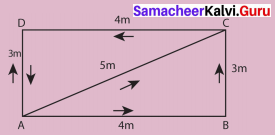
Compare the distance covered by the car through the path ABC and AC. What do you observe? Which path gives the shortest distance to reach D from A? Is it the path ABCD or the path ACD or the path AD?
Answer:
- AB + BC
ABC = 4m + 3m=7m
AC = 5 m - AB + BC + CD
ABCD = 4m + 3m + 4m = 11m
ACD = AC + CD = 5m + 4m = 9m
AD = 3 m
The shortest distance to reach D from A will be AD, that is 3 m.
Question 4.
Take a large stone and a small eraser. Stand on the top of a table and drop them simultaneously from the same height?
What do you observe? Now, take a small eraser and a sheet of paper. Drop them simultaneously from the same height?
What do you observe? This time, take two sheets of paper having same mass and crumple one of the sheets into a ball. Now, drop the sheet and the ball from the same height. What do you observe?
Answer:
Both the stone and the eraser have reached the surface of the Earth almost at the same time in the absence of air medium (vacuum). But in air medium, due to friction, air offers resistance to the motion of free falling objects. The eraser reaches the first, the sheet of paper reaches later. The air resistance exerted on the sheet of paper is much higher than that of the eraser. The paper crumpled into a ball reaches ground first and plain sheet of paper reaches later, although they have equal mass. The air resistance offer to the plain sheet of paper is much higher than that offered to the paper ball. This is because the magnitude of air resistance depends on the area of objects exposed to air.
![]()
Question 5.
Take a piece of thread and tie a small piece of stone at one of its ends. Rotate the stone to describe a circular path with constant speed by holding the thread at the other end. Now, release the thread and let the stone go. Can you tell the direction in which the stone moves after it is released?
Answer:
The stone moves along the straight line tangential to the circular path. This is because once the stone releases, it continues to move along the direction it has been moving at that instant.
Question 6.
Take a piece of rope and tie a small stone at one end. Hold the other end of the rope and rotate it such that the stone follows a circular path.
Do you experience any pull or push in your hand?
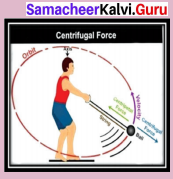
In this activity, a pulling force that acts away from the centre is experienced. This is called as centrifugal force.
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Motion Additional Questions:
I. Choose the best answer.
Question 1.
The area under velocity time graph represents ………….
(a) Velocity of the moving object
(b) Displacement covered by the moving object
(c) Speed of the moving object
Answer:
(b) Displacement covered by the moving object
Question 2.
Unit of acceleration is ………………
(a) ms– 1
(b) ms– 2
(c) ms
(d) ms2
Answer:
(b) ms– 2
Question 3.
When a body starts from rest, the acceleration of the body after 2 second in ………………. of its displacement.
(a) Half
(b) Twice
(c) Four times
(d) One fourth
Answer:
(a) Half
II. Short Answer Questions.
Question 1.
A bus travels, a distance of 20 km from Chennai central to airport in 45 minutes. What is the average speed?
Given: Distance = 20 km = 20,000 m
Time = 45 min = 2700 s
Formula: Average speed = \(\frac{\text { Total Distance }}{\text { Total Time taken }}\)
Solution:
Average speed = \(\frac{20 \mathrm{km}}{45 \mathrm{min}}=\frac{20,000 \mathrm{m}}{2700 \mathrm{s}}\)
= \(\frac{200 m}{27 s}\) = 7.4 ms – 1
Question 2.
Why did the actual speed differ from average, speed?
Answer:
Actual speed gives instantaneous speed of a body at any instant but average speed is the total distance covered by total time taken.
Question 3.
Mention the uses of velocity-time graph.
Answer:
- Area covered under velocity – time graph gives us the displacement
- Slope of the velocity – time graph gives us the acceleration.
![]()
Question 4.
The speed of a particle is constant. Will it have acceleration? Justify with an example.
Answer:
- When a particle is moving with a constant speed along a straight line, it has no acceleration.
- When a particle is moving with a constant speed along a circular path, the velocity changes due to the change in direction. Hence it has a acceleration.
Ex. Revolution of Earth around the Sun.
Question 5.
Distinguish distance and displacement of a moving object.
Answer:
|
S.No. |
Distance |
Displacement |
| 1. | The actual length of the path traveled by a moving body irrespective of the direction | The change in position of a moving body in a particular direction |
| 2. | Scalar quantity | Vector quantity |
III. Answer the following Question briefly.
Question 1.
Derive the three equations of motion by graphical method.
An object is in motion with initial velocity u attains a final velocity v in time t due to acceleration a, with displacement s.
Let us try to derive these equations by graphical method. Equations of motion from velocity-time graph:
Graph shows the change in velocity with time for an uniformly accelerated object. The object starts from the point D in the graph with velocity u. Its velocity keeps increasing and after time t it reaches the point B on the graph.
The initial velocity of the object = u = OD = EA
The final velocity of the object = v = OC = EB
Time = t = OE = DA
Also from the graph we know that, AB = DC
For First equation of motion
By definition, acceleration = change in velocity / time
= (final velocity – initial velocity)/time
= (OC – OD) / OE = DC / OE
a = DC/t
DC = AB = at
From the graph EB = EA + AB
v = u + at …….(1)
This is first equation of motion.
For Second equation of motion
From the graph the distance covered by the object during time t is given by the area of quadrangle DOEB
s = area of the quad-rectangle DOEB
s = area of the rectangle DOEA + area of the triangle DAB
= (AE × OE) + (1/2 × AB × DA)
s = ut + 1/2at2 ….(2)
This is second equation of motion.
For Third equation of motion
From the graph the distance covered by the object during time t is given by the area of the quadrangle DOEB. Here DOEB is a trapezium. Then
s = area of trapezium DOEB
= 1/2 × sum of length of parallel side × distance between parallel sides
= 1/2 × (OD + BE) × OE
s = 1/2 × (u + v) × t
since a = (v – u) / t or t = (v – u)/a
Therefore s = 1/2 × (v + u) × (v – u)/a
2as = v2 – u2
v2 = u2 + 2 as ………..(3)
This is third equation of motion.
I. Choose the best answer.
Question 1.
In a 100 m race, the winner takes 10s to reach the finishing point. The average speed of the winner is ……….. ms– 1.
Answer:
(b) 10
II. Choose correct statement.
Question 1.
(a) Action and reaction forces act on same object
(b) Action and reaction forces act on different objects
Both (a) and (b) are possible
Neither (a) nor (b) is correct
Answer:
(a) is wrong
(b) is correct.
III. Short Answer Questions.
Question 1.
A motorcycle travelling at 20 ms– 1 has an acceleration of 4 ms– 2. What does it explains about the velocity of the motorcycle?
Answer:
It explains that the motorcycle travels with uniform velocity.
Question 2.
Complete the following sentences.
(a) The acceleration of the body that moves with a uniform velocity will be …………….. .
Answer:
constant
(b) A train travels from A to station B with a velocity of 100 km/h and returns from station B to station A with a velocity of 80 km/h. Its average velocity during the whole journey in ……………. and its average speed is ……………… .
Answer:
zero, 90 km/h
![]()
Question 3.
Distinguish speed and velocity.
Answer:
| S.No. | Speed |
Velocity |
| 1. | The rate of change of distance | The rate of change of displacement |
| 2. | Scalar quantity | Vector quantity |
| 3. | Speed = \(\frac{\text { Distance travelled }}{\text { time taken }}\) | Velocity = \(\frac{\text { Displacement }}{\text { time taken }}\) |
Question 4.
What is meant by negative acceleration?
Answer:
If v < u, i.e. if final velocity is less than initial velocity, the velocity decreases with time and the value of acceleration is negative. It is called negative acceleration. It is also called as retardation (or) deceleration.
IV. Answer the following Question.
Question 1.
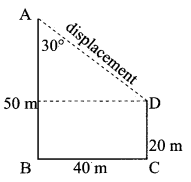
A boy moves along the path ABCD. What is the total distance covered by the boy? What is his net displacement?
(a) Total distance covered by a boy = 110 m
(b) Net displacement = \(\sqrt{30^{2}+40^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{2500}\)
= 50 m