You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Geography Solutions Term 1 Chapter 2 Weather and Climate
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Weather and Climate Textbook Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Earth’s atmosphere contains about …………… percentage of nitrogen and oxygen.
(a) 78% and 21%
(b) 22% and 1%
(c) 21% and 0.97%
(d) 10% and 20%
Answer:
(a) 78% and 21%
Question 2.
…………… is generally defined as the average conditions of the weather of a place or a region.
(a) Earth
(b) Atmosphere
(c) Climate
(d) sun
Answer:
(c) climate
Question 3.
The earth receives energy from …………….
(a) Current
(b) Electro magnetic radiation
(c) Waves
(d) Heat
Answer:
(b) Electro magnetic radiation
![]()
Question 4.
Which one the following represents places with equal amount of rainfall
(a) Isotherm
(b) Isohel
(c) Isobar
(d) Isohyets
Answer:
(d) Isohyets
Question 5.
………….. is used to measure the humidity.
(a) Anemometer
(b) Barometer
(c) Hygrometer
(d) Thermometer
Answer:
(c) hygrometer
II. Fill in the Blanks
- ……………… refers to the condition of atmosphere for a short period of time.
- The scientific study of weather is called ………………
- The highest temperature ever recorded on the earth is …………….
- ……………. is a ratio between the actual amount of water vapour and the maximum amount of water vapour the air can hold.
- …………….. and ……………. are measured by anemometer and wind vane respectively.
- ………………. are imaginary lines which connect the same temperatures of different places.
Answer:
- Weather
- Meterology
- 56.7°C
- Relative humidity
- Wind speed, Wind direction
- Isotherms
III. Match the following
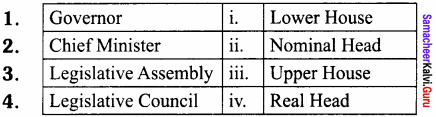
Answer:
- iv
- iii
- v
- i
- ii
IV. State whether the following statements are True or False
Question 1.
The atmosphere is a layer of gases surrounding the planet.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
The Scientific study of weather is called Climatology.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
The Scientific study of weather is called meterology.
![]()
Question 3.
Isohel refers equal sunshine.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Humidity is calculated by Aneroid Barometer.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
Air pressure is calculated by an Aneroid Barometer.
V. Answer in brief
Question 1.
Define‘weather’.
Answer:
Weather is the day-to-day condition of the atmosphere at any place as regards sunshine, air pressure, humidity precipitation, and other elements.
Question 2.
What is insolation?
Answer:
Insolation is the solar radiation that reaches the earth’s surface. The earth and its atmosphere get heated from the sun through insolation.
![]()
Question 3.
What is meant by atmospheric pressure?
Answer:
The weight of air above a given area on the earth’s surface is called atmospheric pressure or air pressure.
Question 4.
Write a short note on “Planetary winds”
Answer:
- Planetary Winds are the ones which blow almost in the same direction throughout the year. So, they are called Permanent or planetary winds.
- Trade winds, Westerlies, and polar easterlies are the types of prevailing winds.
Question 5.
What are “Isolines”?
Answer:
- The distribution of weather elements is shown by means of Isolines on maps.
- Isolines are those which join the place of equal values.
VI. Distinguish the following
Question 1.
Weather and climate.
Answer:
Weather:
- Weather is the day to day condition of the atmosphere at any place
- Refers to short periods like a day, a week, a month, etc.,
- Sunshine, temperature, cloud cover, wind, fog condition, air pressure, humidity precipitation are some weather elements.
Climate:
- Average condition of the weather of a place or a region.
- Determined by measuring weather elements for a long period of time usually for 35 years
- Latitude, Altitude, the direction of winds, distance from the sun, Ocean currents are some of the factors determining climate.
Question 2.
Absolute and relative humidity.
Answer:
Absolute humidity:
- Mass or weight of water vapour present per unit volume of air.
- Expressed usually in grams per cubic metre of air.
Relative humidity:
- The ratio between the actual amount of water vapour present in the air and the maximum amount of water vapour it can hold at a given temperature.
- Expressed as a percentage.
![]()
Question 3.
Permanent and seasonal winds.
Answer:
Permanent winds:
- The ones which blow almost in the same direction throughout the year.
- Also called Planetary winds. Example Trade wings, Weather winds
Seasonal winds:
- Winds change their direction according to the season in a year. Blow from sea to land in summer and land to sea in winter.
- Also called Monsoon winds. Example Northeast monsoon winds, Southwest monsoon winds
VII. Give reasons.
Question 1.
The Weather and climate in different regions vary.
Answer:
The weather and climate in different regions vary because of temperature, precipitation, pressure, humidity and wind.
Question 2.
Temperature decreases with an increase in altitude.
Answer:
Temperature varies both horizontally and vertically. The temperature always decreases with increasing height is known as the Lapse rate which is 6.5 degrees Celsius per 1000 meters in the troposphere.
![]()
Question 3.
Mountain climbers carry oxygen cylinders while ascending peaks.
Answer:
Mountain Climbers carry oxygen cylinders while ascending peak because, at very high altitudes, pressure and available oxygen get so low that people can become sick and even die.
VIII. Answer in a paragraph.
Question 1.
How is temperature measured?
Answer:
- The temperature of a unit volume of air at a given time is measured in scales like Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin.
- Meteorologist measures the temperature by the Thermometer, Stevenson screen and minimum and maximum Thermometer.
- The energy received by the earth through insolation is lost by outgoing radiation.
- The atmosphere is mainly heated by outgoing radiation from 2 to 4 pm.
- So the maximum temperature is recorded between 2 and 4 pm regularly and the minimum temperature is recorded around 4 am before sunrise.
Question 2.
Write about the wind and its types.
Answer:
The wind systems are broadly categorized into three as follows:
- Planetary winds
- Seasonal winds
- Local winds.
Planetary winds:
- Planetary winds are one which blows almost in the same direction throughout the year.
- So, they are called permanent or planetary winds. Trade winds, Westerlies, and polar easterlies are the types of prevailing winds.
Seasonal winds:
- Seasonal winds are those which change their direction according to the season in a year.
- They are called monsoon winds. These winds blow from sea to land during summer and land to sea during winter.
Local winds:
- Local winds are the winds that blow over a small area only during a particular time of a day or a short period of a year.
- Land and Sea breezes are examples of these winds.
![]()
Question 3.
List out the weather elements and associated measuring instruments.
Answer:
Temperature, rainfall, pressure, humidity, and wind are the major elements of weather and climate.
1. Temperature:
Measured in scales like Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin. Meteorologists measure the temperature by the Thermometer. Stevenson screen and minimum and maximum thermometer.
2. Rain:
Is a major component of the water cycle and is the source of most of the fresh water on the earth. Rainfall is measured by a rain gauge.
3. Air Pressure:
Meteorologist uses barometer/aneroid barometer to measure air pressure. Barograms are used for recording continuous variation in atmospheric pressure.
4. Humidity:
A hygrometer is used to measure the humidity, (which comprises wet and dry bulb plate side by side in the Stevenson screen)
V. Wind
1. Meteorologist measures wind direction using wind vane or weather cock. Wind speed is measured by an anemometer. Wind need rose is a diagram used to depict the direction and periods (No. of days) of prevailing winds on the map.
2. Meteorograph or triple register is an instrument which records wind speed and direction, sunshine, and precipitation. It also provides graphic representation.
IX. Give any three suggestions to reduce global warming.
- …………………………..
- ………………………….
- ………………………….
Answer:
- Switching over to renewable energy sources.
- Reduce water wastage
- Shrinking carbon profile.
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Geography Weather and Climate Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The ……………. receive slanting sun’s rays.
(a) Polar regions
(b) Equator
(c) Torrid zone
(d) the Indian Ocean
Answer:
(a) Polar regions
Question 2.
The degree of heat present in the air is termed as ……………..
(a) Pressure
(b) Humidity
(c) Temperature
(d) Rainfall
Answer:
(c) temperature
Question 3.
Which of the following represents places of equal sunshine ……………..
(a) Isotherm
(b) Isohel
(c) Isobar
(d) Isohyet
Answer:
(b) Isohel
![]()
Question 4.
The distribution of temperature is shown by means of ……………..
(a) Isocryme
(b) Isohel
(c) Isobar
(d) Isotherm
Answer:
(d) Isotherm
Question 5.
Based on the heat received from the sun, the earth is divided into ………………. zones.
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 2
(d) 5
Answer:
(a) 3
Question 6.
The standard air pressure at sea level is ………………
(a) 1014.25 mb
(b) 1016.25 mb
(c) 1013.25 mb
(d) 1020.25 mb
Answer:
(c) 1013.25 mb
Question 7.
The scale is a scale for measuring wind speeds.
(a) Richter
(b) Vernier
(c) Ratio
(d) Beaufort
Answer:
(d) Beaufort
Question 8.
…………….. has a large area where the average wind speed is low.
(a) France
(b) India
(c) Brazil
(d) Australia
Answer:
(c) Brazil
II. Fill in the blanks
- The word climate is derived from the word …………… which means inclination.
- The lowest temperature ever recorded on the earth was at …………… station in Antarctica.
- There is a close relationship between …………… and rainfall distribution.
- Generally, rainfall is high in …………… region.
- Rainfall is high in the equatorial region and …………… gradually towards poles.
- A low-pressure system is also called …………… and ……………
- High pressure is called …………….
- …………… is used to show the distribution of air pressure.
- The highest air pressure at sea level was recorded at …………… Russia.
- The small variations in pressure that exist largely determine the …………… and …………… patterns of the earth.
- The level of humidity …………… towards poles form equator.
- ……………. air holds more water vapour.
Answer:
- Klimo
- Soviet Vostok
- Temperature
- Equatorial
- Decreases
- Depression, cyclones
- Anticyclones
- Iso bar
- Agata
- wind, storm
- Decreases
- Warm
III. Match the following

Answer:
- iii
- i
- iv
- ii
IV. State whether the following statements are True or False
Question 1.
The climate does not often change like the weather.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Soil does not affect the distribution of temperature.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
Soil affects the distribution of temperature.
Question 3.
The lowest temperature ever recorded on the earth is – 89.2°C.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question 4.
Humans are sensitive even to a small variations in pressure.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
Humans are not sensitive even to a small variations in pressure.
V. Answer in brief
Question 1.
State the composition of gases in the atmosphere.
Answer:
Earth’s atmosphere contains about 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 0.97% argon, 0.03% carbon dioxide, and 0.04% trace amounts of other gases and water vapour.
Question 2.
Define temperature.
answer:
Temperature is one of the key elements of weather and climate. The degree of heat present in the air is termed as temperature.
Question 3.
What does temperature influence?
Answer:
The temperature influences the level of humidity, the process of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
Question 4.
Name the three mechanisms through which the earth received heat from solar radiation.
Answer:
Radiation, Conduction, and Convection.
Question 5.
Define Low pressure.
Answer:
A low-pressure area is an area in the atmosphere where the pressure is lower than its surrounding areas. In this situation, the wind from the surroundings blows towards the center of low pressure.
![]()
Question 6.
Define High pressure.
Answer:
High pressure is an area of the atmosphere where the barometric pressure is higher than its surrounding areas. In this case, the wind from the center of high pressure blows towards the surrounding low-pressure areas.
Question 7.
What does low pressure and high pressure lead to?
Answer:
Low pressure leads to cloudiness, wind, and precipitation. High pressure leads to fair and calm weather.
Question 8.
Define Humidity.
Answer:
Humidity refers to the degree of water vapour present in the atmosphere in gaseous form at a particular time and place.
Question 9.
Mention the effects of relative humidity.
Answer:
Relative humidity affects human health and comfortness. Very high and very low humidity are injurious to health. It also affects the stability of different objects, buildings, and electrical applications.
Question 10.
How do the passengers in aircraft remain comfortable while flying?
Answer:
Aircraft take time to get used to the altitude as the quick move from high pressure to low pressure can cause decompression sickness. Aircraft create artificial pressure in the cabin which makes the passengers remain comfortable while flying.
![]()
Question 11.
Mention a few least windy places on earth.
Answer:
Gabon, Congo, and DR Congo in Africa, Sumatra, Indonesia, and Malaysia are the least windy places on earth.
Question 12.
Write a note on Al – Balakhi.
Answer:
Al – Balakhi, an Arab Geographer collected climatic data from the Arab travellers and prepared the First climatic Atlas of the world
VI. Distinguish the following
Question 1.
Seasonal and Local winds.
Answer:
Seasonal winds:
- Winds change their direction according to the season in a year. Also called monsoon winds.
- Example North East and Southwest monsoon winds.
Local winds:
- Winds blow over a small area only during a particular time of a day or a short period of a year.
- Example Land and Sea breezes.
VII. Give Reason for the following
Question 1.
The polar regions are extremely cold in winters.
Answer:
The earth is spherical in shape. So, the sun’s rays fall unevenly on the earth’s surface. The Polar regions receive slanting sun’s rays. Hence there is little or no sunlight, thus there are extreme cold winters.
Question 2.
Temperature varies with time due to changes.
Answer:
Temperature varies with time due to changes in the level of radiation which reaches the earth’s surface. This is due to the motions of the earth (The rotation and revolution) and the inclination of the earth’s axis.
![]()
Question 3.
Our ears pop in Airplanes.
Answer:
As you go up in an airplane, the atmospheric pressure becomes lower than the pressure of the air inside your ears. Your ears pop because they are trying to equalize or match the pressure.
VIII. Answer in a Paragraph
Question 1.
Explain the Heat Zones of the earth.
Answer:
Heat zones of the earth:
The fact that the earth is spherical in shape results in different parts of the earth getting heated differently. Based on the heat received from the sun, Earth is divided into three heat zones. They are
1. Torrid Zone:
It is a region between the tropic of cancer and the tropic of Capricorn. This region receives the direct rays of the sun and gets the maximum heat from the sun. This zone is known as the torrid or the tropical zone
2. Temperate zone:
This zone lies between the Tropic of cancer and the Arctic circle in the Northern Hemisphere and between the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic circle in the Southern Hemisphere. This zone gets the slanting rays of the sun and the angle of the sun’s rays goes on decreasing towards the poles. Thus this zone experiences moderate temperature.
3. Frigid Zone:
The frigid zone lies between the Arctic circle and the North Pole and between the Antarctic Circle and the South Pole. This region is also known as the Polar region. Since it receives extremely low temperatures throughout the year, these regions are covered with snow.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the ways in which humidity is expressed.
Answer:
1. Specific humidity is a ratio of the water vapor content of the mixture to the total air content on a mass basis. It is expressed in grams of vapour per kilogram of air.
2. Absolute Humidity is the mass or weight of water vapour present per unit volume of air. It is expressed usually in grams per cubic meter of air.
3. Relative humidity is a ratio between the actual amount of water vapour present in the air and the maximum amount of water vapour it can hold at a given temperature. It is expressed as a percentage.