Students can Download Social Science Economics Chapter 1 Production Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Economics Solutions Term 1 Chapter 1 Production
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Production Textual Evaluation
I.Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Production refers to
(a) destruction of utility
(b) creation of utilities
(c) exchange value
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) creation of utilities
Question 2.
Utilities are in the nature of
(a) form utility
(b) time utility
(c) place utility
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
![]()
Question 3.
is carried out by extractive industries.
(a) Secondary production
(b) Primary production
(c) Tertiary production
(d) Service production
Answer :
(b) primary production
Question 4.
Primary factors are
(a) land, capital
(b) capital, labour
(c) land, labour
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) land, labour
Question 5.
The entrepreneur is also called
(a) exchanger
(b) Agent
(c) organizer
(d) communicator
Answer:
(c) organizer
II. Fill in the Blanks
- ________ means want satisfying power of a product.
- Derived factors are ________ and ________
- ________ is a fixed in supply.
- ________ is the human input into the production process.
- ________ is the man made physical goods used to produce other goods and services.
Answer:
- Utility
- Capital, Organization
- Land
- Labour
- Capital
III. Match the following
| A | B | |
| Primary production | (i) | Adamsmith |
| Time utility | (ii) | Fishing, mining |
| Wealth of nation | (iii) | Entrepreneur |
| Human capital | (iv) | Stored for future |
| Innovator | (v) | Education, health |
Answer:
- ii
- iv
- i
- v
- ii
IV.Give short answer:
Question 1.
What is production?
Answer:
Production is a process of combining various material inputs and immaterial inputs in order to make something for consumption (the output).
Question 2.
What is the utility?
Answer:
Utility means to want the satisfying power of a product.
![]()
Question 3.
Name the types of utility.
Answer:
- Form utility
- Time utility and
- Place utility
Question 4.
Name the types of production.
Answer:
There are three types of production
- Primary production
- Secondary Production
- Tertiary or Service Production
Question 5.
What are the factors of production?
Answer:
Factors of production are Land, Labour, Captial, Organization.
![]()
Question 6.
Define Labour.
Answer:
Labour is the human input into the production process.
Question 7.
Define Division of labour.
Answer:
Division of Labour means the dividing process of production into distinct and several component processes and assigning each component in the hands of labour or a set of labouress. who are specialists in particular process.
Question 8.
Write the forms of capital.
Answer:
The forms of capital are
- Physical capital
- Money capital and
- Human capital.
![]()
Question 9.
Who is the changing agent of society?
Answer:
The entrepreneur is also called ‘Organizer’. In, modem times, an entrepreneur is called ‘the changing agent of the society’.
Question 10.
Write the three characteristics of an entrepreneur.
Answer:
- Identifying profitable investible opportunities
- Deciding the location of the production unit
- Making innovations
V. Give a brief answer.
Question 1.
Explain the types of production.
Answer:
There are three types of production
- Primary production
- Secondary Production
- Tertiary or Service Production
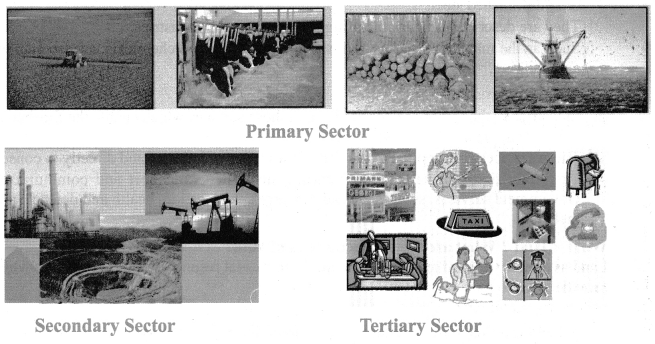
1. Primary Production:
- Primary production is carried out by ‘extractive’ industries like agriculture, forestry, fishing, mining and oil extraction.
- These industries are engaged in such activities as extracting the gifts of nature from the earth’s surface, from beneath the earth’s surface and from the oceans.
2. Secondary Production:
- This includes production in the manufacturing industry, turning out semi-finished and finished goods from raw materials and intermediate goods, conversion of flour into bread or iron ore into finished steel.
- They are described as manufacturing and construction industries.
- Such as the manufacture of cars, furnishing, clothing, and chemicals, as also engineering and building.
3. Tertiary Production
- Industries in the tertiary sector produce all those services which enable the finished goods to be put in the hands of consumers.
- These services are supplied to the firms in all types of industry and directly to consumers.
- Ex. cover distributive traders, banking, insurance, transport, and communications. Government services, such as law, administration, education, health and defense, are also included.
Question 2.
What is the land? What are the characteristics of land?
Answer:
Land as a factor of production refers to all those natural resources or gifts of nature which are provided free to man.
Characteristics of Land:
- Land is a Free Gift of Nature
- Land is fixed in supply
- Land is imperishable
- Land is a Primary Factor of Production
- Land is Immovable
- Land has some Original Indestructible Powers
- Land Differs in Fertility
Question 3.
Explain the merits and demerits of the division of labour.
Answer:
Merits of the division of labour
- It improves the efficiency of labour when labour repeats doing the same tasks.
- Facilitates the use of machinery in production, resulting in inventions.
- Time and Materials are put to the best and most efficient use.
Demerits of the division of labour
- Repetition of the same task makes labour to feel that the work is monotonous and stale. It kills the humanity in him.
- Narrow specialization reduces the possibility of labour to find alternative avenues of employment. This results in increased unemployment.
- Reduce the growth of handicrafts and the worker loses the satisfaction of having made a commodity in full.
![]()
Question 4.
Describe the characteristics of capital.
Answer:
Characteristics of Capital
- Capital is a passive factor of production
- Capital is man-made
- Capital is not an indispensable factor of production
- Capital has the highest mobility
- Capital is productive
- Capital lasts over time
- Capital involves a present sacrifice to get future-benefits
Question 5.
What are the functions of an entrepreneur?
Answer:
The functions are
- Decision making
- Management control
- Division of income
- Risk-Taking
- Uncertainty-Bearing
![]()
VI. Activity and Project
Question 1.
Students are asked to prepare a chart containing dummy images of primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors images.
Answer:
Question 2.
Students are asked to visit some local farmers and to discuss the land and its characteristics. Collect some photographs of land and make an album.
Answer:
- We visited a local farm which is built within an existing coconut grove. This thatched-roofed structure is made from materials mostly from the farm.
- The land is then made suitable for cultivation using organic farming methods.
- They grow vegetables and fruits which will produce a good yield in that soil.
- The first test the soil and make sure that it is suitable for growing vegetables and fruits.

VII. Life skills:
Question 1.
Students to know about the characteristics of entrepreneurs, Set up your classroom like an industry. Some students are asked to act like businessmen, Do the industries activities. Teacher and students together discuss the entrepreneur and their importance to the development of society.
Answer:
Role of businessman:
Ensures the smooth operation of his business. He coordinates with people to procure the factors of production namely land, labour, and capital. He has to look into the access of raw materials needed, skilled labour transport, and the prospects to market the products.
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Production Additional Question
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Indian Economy is a ______ Economy.
(a) Private
(b) Public
(c) Mixed
(d) Socialist
Answer:
(c) Mixed
Question 2.
Most of the Gross Domestic Product of our country is contributed to by the ______ sector.
(a) Tertiary
(b) Primary
(c) Secondary
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) Tertiary
Question 3.
_______ is known as ‘Father of Economics.
(a) Alfred Marshall
(b) Adam Smith
(c) Karl Mark
(d) Amartya Sen
Answer:
(b) Adam Smith
![]()
Question 4.
_______ cannot be stored.
(a) Land
(b) Capital
(c) Organisation
(d) Labour
Answer:
(d) Labour
II. Fill in the blanks:
- _____ can be both customers of the producers and suppliers to the producers.
- Entrepreneurship is otherwise called ______
- ______ is more perishable than other factors of production.
- The Theory of Moral Sentiments’ was written by ______
Answer:
- Consumers
- Organization
- Labour
- Adam Smith
III. Match the following:
| Primary sector | i | Defence |
| Secondary sector | ii | Cotton Industry |
| Tertiary sector | iii | Food Production |
Answer:
- ii
- iii
- i
IV. Answer the following in one or two sentences:
Question 1.
What is a mixed economy?
Answer:
An Economy in which Private and Public sectors co-exist is a mixed economy.
Eg. India.
Question 2.
Name the components of Human activity.
Answer:
Production and consumption.
Question 3.
What are the primary factors of production?
Answer:
Land and Labour
![]()
Question 4.
What are the derived factors of production?
Answer:
Capital and Organisation.
Question 5.
What is capital?
Answer:
Capital is man-made physical goods used to produce other goods and services. In short, Capital means money.
VI. Answer the following in Detail:
Question 1.
Explain the types of utility.
Answer:
Types of Utility
- Form utility: If the physical form of a commodity is changed, its utility may increase. Eg. Cotton increases, if it is converted into clothes.
- Place utility: If a commodity is transported from one place to another, its utility may increase. Eg. If rice transported from Tamilnadu to Kerala, its utility will be more.
- Time utility: If the commodity is stored for future usage, its utility may increase. Eg. Agricultural commodities like Paddy, Wheat, etc. are stored for the regular uses of consumers throughout the year.
Question 2.
Mention the characteristics of Labour.
Answer:
- Labour is more perishable than other factors of production.
- Labour cannot be stored.
- Labour is an active factor of production.
- Labour is not homogeneous.
- Labour cannot be separated from the labourer.
- Labour is mobile.
- Individual labour has only limited bargaining power.
- He cannot fight with his employer for a rise in wages or improvement in work-place conditions.
![]()
Question 3.
Mention the characteristics of an entrepreneur.
Answer:
- An entrepreneur is a person who combines the different factors of production (land, labour, and capital), in the right proportion
- Initiates the process of production and bears the risk involved in it.
- He is not only responsible for producing the socially desirable output but also to increase social welfare.
- Identifying profitable investible opportunities
- Deciding the location of the production unit
- Making innovations
- Deciding the reward payment
- Taking risks and facing uncertainties