You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Solutions Term 2 Chapter 4 Cell Biology
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Cell Biology Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
Basis unit of life.
(a) Cell
(b) Protoplasm
(c) Cellulose
(d) Nucleus
Answer:
(a) Cell
Question 2.
the outer most layer of an animal cell. Who am I?
(a)Cell wall
(b) Nucleus
(c)Cell membrane
(d) Nuclear membrane
Answer:
(c) Cell membrane
Question 3.
Which part of the cell is called the brain of the cell?
(a) Lysosome
(c) Mitochondria
(b) Ribosome
(d) Nucleus.
Answer:
d) Nucleus
Question 4.
________ helps in cell division.
(a) Endoplasmic reticulum
(b) Golgi complex
(c) Centriole
(d) Nucleus
Answer:
(c) Centriole
![]()
Question 5.
Suitable term for the various components of cell is _________
(a) Tissue
(b) Nucleus
(c) Cell
(d) Cell organelle
Answer:
(d) Cell organelle
Fill in the blanks:
- The jelly like substance present in the cell is called _______.
- I convert the Sun’s energy into food for the plant. Who am I?_________.
- Mature Red blood cell do not contain a ________.
- Unicellular organisms can only be seen under a ________.
- Cytoplasm plus nucleoplasm is equal to ________.
Answer:
- cytoplasm
- chloroplast
- Nucleus
- Microscope
- Protoplasma
III. True or False – If False give the correction answer
Question 1.
Animal cells have a cell wall.
Answer:
False, Plant cells have a cell wall.
Question 2.
Salmonella is a unicellular bacteria.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Cell membrane is fully permeable.
Answer:
False, Cell membrane is selectively permeable.
Question 4.
Only plant cells have chloroplasts.
Answer:
True.
![]()
Question 5.
Human stomach is an organ.
Answer:
True.
Question 6.
Ribosomes are small organelles with a membrane.
Answer:
False. Ribosomes are small organelles without a membrane.
IV. Match the following:
Question 1.
- Transporting channel – Nucleus
- Suicidal bag – Endoplasmic reticulum
- Control room – Lysosome
- Power house – Chloroplast
- Food producer – Mitochondria
Answer:
- Transporting channel – Endoplasmic reticulum
- Suicidal bag – Lysosome
- Control room – Nucleus
- Power house – Mitochondria
- Food producer – Chloroplast
V. Analogy:
Question 1.
Bacteria : microorganism :: mango tree :________
Answer:
Macroorganism.
Question 2.
Adipose : tissue :: eye :_________
Answer:
Organ
Question 3.
Cell wall: plant cell:: centriole :_________
Answer:
Animal cell.
Question 4.
Chloroplast: photosynthesis :: mitochondria :________
Answer:
Respiration.
VI. Choose Use connect alternative from the following :
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Tissue is a group of dissimilar cells.
Reason (R) : Muscle is made up of Muscle cell.
(a) Both A and R are true
(b) Both A and R are false
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A) :Majority of cells cannot be seen directly with naked eye because.
Reason (R) :Cells are microscopic.
(a) Both A and R are true
(b) Both A and R are false
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true
VII. Very short answer:
Question 1.
What are the functions of cell wall in plant cell?
Answer:
Protection, maintains shape of cell and acts as protective framework.
Question 2.
Which organelle uses energy from sunlight to make starch?
Answer:
Chloroplast uses energy from sunlight to make starch.
Question 3.
What are the main things in a nucleus?
Answer:
Nuclear envelope, Nucleolus, chromatin body.
![]()
Question 4.
What does cell membrane do?
Answer:
It acts as boundary of cell and protects it.
Question 5.
Why lysosomes are known as scavengers of the cell?
Answer:
The lysosomes are the main digestive compartments of a cell and digest damaged cell parts. Hence they are called scavengers of the cell.
Question 6.
Teacher said “A virus is not an organism” Do you agree with this statement or
not? Explain Why?
Answer:
True I agree with the statement. A virus acts as a living organism within the body of a host and behaves like a non-living thing outside. It lacks cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm and organelles. Hence it is not a organism.
VII. Give short answer :
Question 1.
Why the cell is very important for us?
Answer:
- Cell is the basic structural and functions unit of life.
- It is the building unit of living organism.
- A group of cells form a tissue which forms the organ and organ systems.
- This helps a living organism to do its functions. Hence cell is very important for us.
Distinguish between the following pairs
- Smooth ER and Rough ER
- Cell wall and cell membrane
- Chloroplast and mitochondria
Answer:
Smooth ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)
- It is smooth due to absence of Ribosomes.
- It helps in transport of steroids and lipids.
Rough ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)
- It is’rough due to presence of Ribosomes.
- It helps in protein synthesis
Cell wall
- It is seen only in plant cells.
- It is made of cellulose.
Cell membrane
- It is seen in plant and animal cells.
- It is made of proteins and lipids.
Chloroplast
- It is a organelle seen only in plant cells (green plants)
- It helps in synthesis and storage of starch.
Mitochondria
- It is a organelle seen in plant and animal cells.
- It is the centre of respiration in a cell and produces energy.
Question 3.
Write correct sequence from cell to organism?
Answer:
Cell —> Tissue —> Organ —> Organ system —> Organism.
Question 4.
Write a short note on nucleus.
Answer:
- Nucleus is seen in the cytoplasm of plant and Animal cells.
- It is surrounded by nuclear envelope.
- It has one or two nucleoli and chromatin body.
- The chromatin body stores genetic information.
Functions of Nucleus:
- It controls all the processes and chemical reactions that take place inside the cell.
- Inheritance of character from one generation to another.
Question 5.
Classify the following terms into cells, tissues, organs and write in the tabular column given below:
Neuron, Lungs, Xylem, brain, adipose, Leaf, RBC, WBC, hand, muscle, heart, ovum, squamous, phloem, cartilage.
Answer:
| Cell | Tissue | Organ |
| Neuron | Xylem | Lungs |
| RBC | Adipose | Brain |
| WBC | Muscle | Leaf |
| Ovum | Squamous | Hand |
| Phloem | Heart | |
| Cartilage |
Question 6.
On the lines given below, write about what you have learned from the activities done in this lesson.
Let me tell you about some of the important things I’ve learned about cells. First, I’ll start with… .
First, I’ll start with___________________________.
Answer:
- Cell is the basic unit of an organisms.
- Based on number of cells organisms can be classified as unicellular and multicellular organisms.
- The cells form tissues, Tissues form organs, Organ system help an organism to function.
- The cell wall is seen only in plant cells.
- Cell membrane is seen only in plant cells.
- Cell membrane is seen in all cells.
- The organelles of the cell like chloroplast, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi bodies etc help to perform cell functions.
- Nucleus is the controlling centre of a cell.
![]()
IX. Given long answer:
Question 1.
Write about any three organelles in detail.
Answer:
The three organelles are as follows
Chloroplasts:
- They are green organelles seen in plant cells only.
- They can prepare food using sun is energy and photosynthesize since they contain the pigment chlorophyll.
- They absorb the radiant energy of the sun and convert it to chemical energy to be used by plants and animals.
Golgi Complex:
- They are cell organelles which consist of membrane bound sacs stacked on top of one another and have associated secretory vesicles.
- Golgi complex helps in production of secretory substances, packaging and secretion.
Mitochondria:
- It is a oral double membrane bounded organelle.
- Aerobic respiration occurs in mitochondria and energy is released. Hence mitochondria is called as power house of the cell
- The energy produced is used for metabolic activities of the cell.
Question 2.
In a situation, how to explain, while your friend ask what is this, never seen before ?
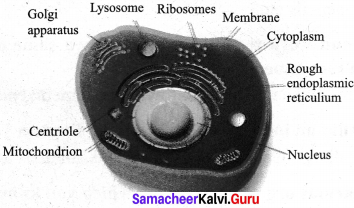
Answer:
- This is a animal cell.
- It is the basic unit of an animal body.
- Animal cell is covered by a cell membrane and lacks cell wall.
- It has organelles like mitochondia, Golgi apparatus, Ribosomes, etc..
- It differs from plant cells since it lacks chloroplast.
- It has centrioles which are not seen in plant cells.
- Nucleus is the controlling centre of the cell.
![]()
Question 3.
Compare the plant cell and the animal cell and complete the illustration given below
Answer:
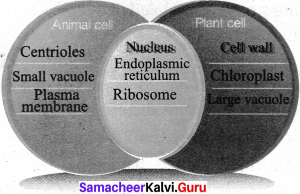
X. Higher ordear Thinking question :
Virus is called Acellular. Why?
Answer:
- Virus is made up of a outer protein coat and a nucleic acid.
- It lacks cell wall, cell membrane, organelles and cytoplasm.
- Therefore a virus is described as a cellular.
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Cell Biology Intext Activities
Activity – 1
Question 1.
Do you remember the lesson studied in previous class, how will you find whether an object is living or non – living? Write it down. An object is living or non-living?
Answer:
Living things: Living things use energy. They move or change shape.
Eg: Humans, insects, plants, animals etc.
Non-living things:
Do not move by themselves, grow or reproduce.
Eg: Rocks, car, pencils etc.
Question 2.
Form a team and work together to write down some of the functions of life, which you can remember.
Answer:
Reproduction, response to stimuli, Growth, movement, excretion
Question 3.
Do you think that an individual cell is living? Explain your answer.
Answer:
Cells are living things. Cells are found in plants, animals and Bactria.
Question 4.
Write about various organelles of a cell which you know.
Answer:
Vacuole, lysosome, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi appartus, mitochondria, chloroplast.
Activity – 2
Find out major organs that are part of the circulatory system of a human body and list out their functions.
Answer:
Organs
- Heart (Cardiovascular)
- Lungs (Pulmonary)
- Blood vessels – Arteries
- Blood vessels – Veins
Functions
- Pumps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood on different sides.
- In oxygen from incoming air enters the blood and carbon-di-oxide, a waste gas from the metabolism, leaves the blood.
- Carry blood away from the heart.
- Carry blood back to the heart.
![]()
Activity – 3
Study the pictures given and write the differences between cells that you observe in the given table
Answer:
Activity – 4
Summarise what you have learnt Now you’ve studied the internal structure of a cell. Let us summerise what we have learnt so far Complete this table by filling the main function of each of the cell structures.
Cell Structure
- Cell membrane
- Cell wall
- Cytoplasm
- Mitochondria
- Vacuole
- Chloroplast
- Endoplasmic reticulum
Function(s)
- Boundary of an animal cell.
- Supporter and protector.
- Giving a ceil its shape.
- Energy releaser.
- Support the organelle.
- Food producers.
- Synthesis protein lipids, steroids and transport them
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Cell Biology Additional Question :
Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
________ is the largest organelle
(a) Chloroplast
(b) Mitochondria
(c) Nucleus
(d) Golgi apparatus
Answer:
(c) Nucleus
Question 2.
The ______cells are spindle shaped.
(a) muscle
(b) nervous
(c) RBC
(d) epithelial
Answer:
(a) muscle
Question 3.
The________ plays a role in change of colour and taste of fruits.
(a) nucleus
(b) Golgi bodies
(c) lysosome
(d) chloroplast
Answer:
(b) Golgi bodies
Question 4.
________lacks a nucleus.
(a) Nerve cell
(b) Muscle cell
(c) RBC
(d) Brain cell
Answer:
(c) RBC
![]()
Question 5.
Starch is stored in _______
(a) chloroplast
(b) leucoplast
(c) chromoplast
(d) Golgi apparatus
Answer:
(b) leucoplast
II. Fill in the blanks.
- Plastids containing coloured pigments are called ________
- cells have the ability to multiply and develop into different types of cells.
- ________are seen only in animal cells.
- An organelle seen in bacteria and cell of higher organisms is ______
- Cell wall is made up of ________
Answer:
- Chromoplasts
- stem
- centrioles
- Ribosome
- cellulose
III. True or false – if false, give the correct statement.
Question 1.
Leucoplast store steroids.
Answer:
False, Leucoplasts store starch.
Question 2.
Bacteria is a animal cell.
Answer:
False, Bacteria is a plant cell.
Question 3.
Amoeba contains chloroplants.
Answer:
False, Amoeba does not contain chloroplasts.
Question 4.
Mitochondria can help to photosynthesize.
Answer:
False, Mitochondria can help to produce energy
![]()
Question 5.
The cytoplasm consists of 90% water.
Answer:
True
Question 6.
The body of a nerve cell is branched.
Answer:
True.
IV. Match the following:
Question 1.
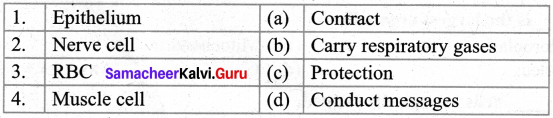
Answer:
(c)
(d)
(b)
(a)
V. Analogy:
Question 1.
Golgi: secretion :: Endoplasmic reticulum: _________
Answer:
Transport.
Question 2.
Plant tissue : Xylem :: Animal tissue : _________
Answer:
Epithelium.
Question 3.
Plant organ : stem :: Animal organ : _________
Answer:
Stomach.
VI. Assertion and Reason.
Mark the correct choice as
(a) Both A and R are true.
(b) Both A and R are false
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Stem cells can form different types of cells.
Reason (R) : They are found in plants and animals.
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false
Question 2.
Assertion (A): The cell wall has pores.
Reason (R) : Each cell is connected to its neighbouring cell.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true
VII. Very short Answers:
Question 1.
Define a tissue.
Answer:
Tissue is a group of cells organized for a specific function.
Question 2.
What is Plasmodesmata?
Answer:
Each plant cell is interconnected with its neighboring cells through openings called Plasmodesmata.
![]()
Question 3.
What is ATP?
Answer:
ATP stands for Adenosineri Phosphate and is the energy currency of a cell.
Question 4.
What is unique about embryonic stem cells?
Answer:
They can develop into any type of cell in the body. Such as blood cell, nerve cell etc.
Question 5.
Name the types of plastids.
Answer:
Chloroplasts, chromoplasts and leucoplasts.
Question 6.
Name a cell which lacks a nucleus.
Answer:
Red blood cell.
VII. Short Answer.
Question 1.
Why are lysosomes called as ‘suicidal bags of the cell’?
Answer:
Lysosoms can lyse (destroy) a cell by producing enzymes. Hence they are known as suicidal bags of the cell.
Question 2.
What is endoplasmic reticulum?
Answer:
It is an inter membranous network made up of flat or tubular sacs within the cytoplasm. Endoplasmic reticulum is of two types. They are rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum
![]()
Question 3.
List the functions of Nucleus.
Answer:
- It controls all the processes and chemical reactions that take place inside the cell.
- Inheritance of character from one generation to another.
Question 4.
Why is mitochandia known as power house of the cell?
Answer:
Aerobic respiratory reactions take place within the mitochondrion to release energy. So it is known as “The Power House’” of the cell.
Question 5.
What is a vacuole?
Question:
It is a membrane bound bag like structure filled within organic and organic molecules along with water and found in plant cells to support the organelles. Animal cell has very small vacuoles.
VIII. Long Answer
Question 1.
List the functions of cell wall.
Answer:
- Cell wall provides a frame work for support and stability.
- It allows the plant to remain rigid and upright.
- It helps to maintain the shape of the plant cell.
- It has openings called plasmodesmata through which neighboring cells are interconnected.
- It acts as a protective covering for the cell.
Question 2.
Draw a plant cell and label the parts.
Answer:
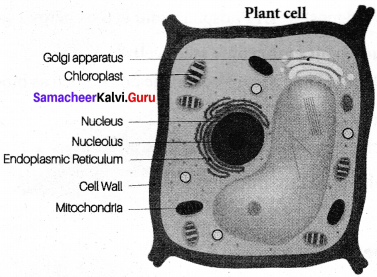
Question 3.
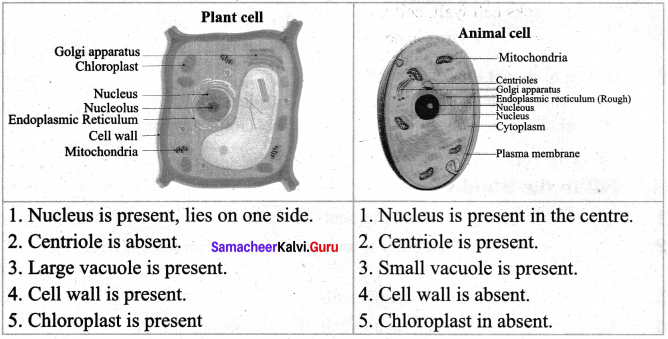
List the differences between Plant cell and Animal cell.
Answer:
Plant cell
- It has cell wall.
- It has plastids such as chloroplasts, chromoplasts etc.
- Centrioles are not seen.
- It has a large vacuole.
- It is larger in size.
Animal Cell
- Cell wall is absent.
- Plastids are absent.
- It has centrioles which help in cell division.
- Vacuoles are small or absent.
- It is smaller in size.
![]()
IX. Hots:
Question 1.
Bacterial cells can prepare food. Do you agree?
Answer:
Yes, some bacterial cells have chlorophyll pigments and can prepare food.
Question 2.
Stem cells are used by doctors to treat diseases. Do you agree with this statement?
Answer:
Yes. Stem cells can divide and form any other cell type and hence can be used to cure several diseases like spinal cord injury.