You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 3 Chapter 3 Chemistry in Everyday Life
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Chemistry in Everyday Life Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the appropriate answer :
Question 1.
Soaps were originally made from _______
(a) proteins
(b) animal fats and vegetable oils
(c) chemicals extracted from the soil
(d) foam booster
Answer.
(b) animal fats and vegetable oils
Question 2.
The saponification of a fat or oil is done using ……….. solution for hot process.
a. potassium hydroxide
b. sodium hydroxide
c. sodium chloride
d. sodium hydroxide
Answer:
b. sodium hydroxide
Question 3.
Gypsum is added to the cement for _______
(a) fast setting
(b) delayed setting
(c) hardening
(d) making paste
Answer:
(b) delayed setting
Question 4.
Phenol is ……..
a. carbolic acid
b. acetic acid
c. benzoic acid
d. hydrochloric acid
Answer:
a. carbolic acid
Question 5.
Natural adhesives are made from _______
(a) Protein
(b) fat
(c) starch
(d) vitamins
Answer:
(c) starch
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
- _______ gas causes tears in our eyes, while cutting onions.
- Water, coconut oil and ________ are necessary for soap preparation.
- _______ is called as farmer’s best friend.
- _______ fertilizer is ecoffiendly.
- _______ is an example for natural adhesive.
Answers:
- Propanethial s-oxide
- animal fat
- Earthworm
- Organic
- Starch dissolved in water
![]()
III. True or False. If False, give the correct statement :
Question 1.
Concentrated phenol is used as a disinfectant.
Answer:
False. Low concentrated phenol is used as a disinfectant.
Question 2.
Gypsum is largely used in medical industries.
Answer:
False. Gypsum is largely used in cement preparation.
Question 3.
Plaster of Paris is obtained from heating gypsum.
Answer:
True.
Question 4.
Adhesives are the substances used to separate the components.
Answer:
False. Adhesives are the substances used to join the components.
Question 5.
NPK are the primary nutrients for plants.
Answer:
True.
![]()
IV. Match the following :
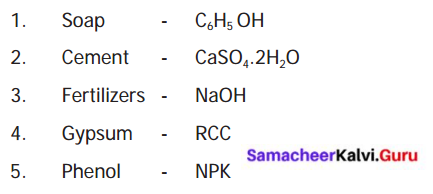
Answer:
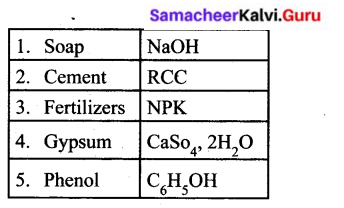
V. Arrange the following statements in correct sequence :
- Pour that solution into an empty match box, soap can be obtained after drying.
- Take necessary quantity of water in ajar.
- Then add coconut oil drop by drop and stir it well.
- Add concentrated sodium hydroxide in the jar and allow it to cool.
- Try this soap to wash your hand kerchief.
- Cover your work area with old newspaper.
Answers:
- Cover your work area with old newspaper.
- Take necessary quantity of water in a jar.
- Add concentrated sodium hydroxide in the jar and allow it to cool.
- Then add coconut oil drop by drop and stir it well.
- Pour that solution into an empty match box, soap can be obtained after drying.
- Try this soap to wash your hand kerchief.
![]()
VI. Analogy :
Question 1.
Urea : Inorganic fertilizer;
Vermi compost: _______
Answer:
Organic fertilizer.
Question 2.
_______ : Natural adhesives ;
Cello tape : Artifical adhesives.
Answer:
Starch dissolved in water.
![]()
VII. Give Very Short Answer:
Question 1.
What are the three main constituents of soap?
Answer:
- Water (H2O)
- Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
- Coconut Oil (Vegetable Oils / Animal Fats)
Question 2.
What are the two different types of molecules found in the soap?
Answer:
- Loving water molecules.
- Hating water molecules.
Question 3.
Give an example of inorganic fertilizer.
Answer:
- Urea
- Super Phosphate
- Ammonium Sulphate
- Potassium Nitrate
Question 4.
Mention any three physical properties of phenol?
Answer:
- Weak acid
- High volatile
- White crystalline powder.
Question 5.
Explain the uses of plaster of Paris.
Answer:
- In making blackboard chalks.
- In surgery for setting fractured bones.
- For making casts for statues and toys, etc.
- In the construction industry.
Question 6.
What are the ingredients of the cement?
Answer:
- Limestone
- Clay
- Gypsum
Question 7.
Why gypsum is used in cement production?
Answer:
Gypsum is added to control the “setting of cement”. So, Gypsum is added to the cement at the final grinding process.
![]()
VIII. Give Short Answer:
Question 1.
Why earthworm is called a farmer’s friend?
Answer:
Earthworms take organic wastes as food and produce compost castings. So earthworms are known as Farmers’ Friends because of the multitude of services they provide to improve soil health and consequently plant health.
Question 2.
Explain the process of manufacturing cement.
Answer:
The cement is manufactured by crushing naturally occurring minerals such as lime clay and gypsum through a milling process.
Question 3.
What are the uses of Gypsum?
Answer:
Uses of Gypsum:
- It is used as fertilizers.
- It is used in the process of making cement.
- It is used in the process of making Plaster of Paris.
![]()
IX. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
How are detergents manufactured?
Answer:
Materials required:
- 35ml of H2O.
- 10ml of NaOH
- 60 ml of Coconut Oil
Process:
- Cover your work area with an old newspaper.
- Take 35 ml of H2O in a jar.
- Add 10 ml of Con. NaOH and allow it to cool.
- Then add 60 ml of Coconut Oil drop by drop and stir it well.
- Pour that solution into an empty matchbox, Soap can be obtained after getting dried.
![]()
X. Questions based on Higher Order Thinking Skills
Question 1.
Ravi is a farmer; he rears many cattle on his farm. His field has many biowastes. Advise Ravi on how to change this biowaste to compost by using vermicomposting techniques. Explain the benefits of vermi castings.
Answer:
- A cement tub is to be constructed to a height of 2’A feet and a breadth of 3 feet.
- Put the Bio-wastes in the cement tub with 5 cm height.
- Add a few earthworms with the Bio-waste.
- Then add sawdust, or coir waste and husk on the top of Bio-wastes.
- Then add sand to form a layer of 3 cm.
- Then add garden waste on the layer of sand.
- Then spray with water.
- All layers must be moistened with water.
- After 10 to 15 days, we get vermicompost manure.
Benefits:
- It is rich in all essential nutrients.
- It improves soil structure, texture, and prevents soil corrosion.
- It contains valuable hormones like auxons, gibberellin, etc.
- It neutralizes the soil protection.
![]()
XI. Project :
- Take 100 ml of hot water in a glass jar.
- Add 50 grams of maida powder to the hot water and stir it well.
- A paste-like substance is formed. Add a small quantity of copper sulphate for long use.
- Now you test this paste by binding your damaged book.
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students themselves
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Chemistry in Everyday Life Intext Activities
Activity 1
Question 1.
Discuss with your group and list out a few chemicals which we use in our home and school.
_______________________
_______________________
Answer:
We are using the following Chemicals in our home and school:-
Detergents, Air fresheners, Disinfectant, Glass cleaning chemicals, Detergents, Shampoo, Lubricants, Metal polishers, Restroom cleaning chemicals, Naphthalene, Bathing soap, Hit.
![]()
Activity 2
Preparation of Soap
Materials Required: 35 ml of water, 10 g of Lye (Sodium hydroxide), 60 ml of coconut oil.
Process: Cover your work area with an old newspaper. Take 35 ml of water in a jar. Add 10 grams of concentrated sodium hydroxide and allow it to cool.
Then add 60 ml of coconut oil drop by drop and stir it well. Pour that solution into an empty matchbox, soap can be obtained after getting dried.
Try this soap to wash your handkerchief.
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students themselves
Activity 3
Collect various kinds, of soap wrapper. Complete the following table based on the information provided in the wrapper.
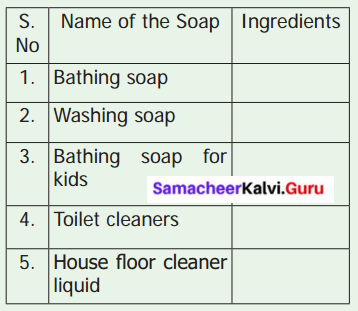
Inference: The nature of the soaps varies according to its constituents.
Answer:

![]()
Activity 4
Make a visit to the agriculture field in your area. List out the various crops and types of fertilizers used there.
| S.No | Name of the Crop | Name of the Fertilizer |
| 1. | ||
| 2. | ||
| 3. |
Answer:
| S.No | Name of the Crop | Name of the Fertilizer |
| 1. | Rice and wheat | Urea, Potassium Nitrate |
| 2. | Tomato | Super Phosphate |
| 3. | Potato and Mango | Potassium Nitrate |
![]()
Activity 5
Take three empty tumblers of the same size and name them A, B, and C. Add two teaspoonful of cement to each container. Then pour one teaspoonful of water in container A and two spoonfuls of water in B and three spoonfuls of water in C.
After an hour, observe which container of the cement set fast? Touch the containers and see if they are warm or cool. From this experiment, we understand that water and cement should be mixed in a certain ratio for a fast setting.
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students themselves
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Chemistry in Everyday Life Additional Questions
I. Choose the appropriate answer:
Question 1.
_______ change results in the change of the substance.
(a) Physical
(b) Chemical
(c) Biological
(d) Zoological
Answer:
(b) Chemical
Question 2.
The percentage composition of Nitrogen in Ureas is ………..
(a) 23%
(b) 13%
(c) 21%
(d) 46%
Answer:
(d) 46%
Question 3.
_______ is the important material in construction industry.
(a) Soap
(b) Adhesives
(c) Cement
(d) Fertilizers
Question 4.
Who invented cement?
(a) Edison
(b) Joseph Aspdin
(c) Robert Hooke
(d) Robert Brown
Answer:
(b) Joseph Aspdin
Question 5.
_______ concrete is a composite material by mixing iron mesh with cement.
(a) Mortar
(b) m-sand
(c) Reinforced cement
(d) Gypsum
Answer:
(c) Reinforced cement
Question 6.
The molecular formula of ‘Plaster of Paris’ is
(a) CaSO4. ½ H2O
(b) CaSO4. H2O
(c) CaSO4. 2H2O
(d) CaSO4. 3H2O
Answer:
(a) CaSO4. ½ H2O
Question 7.
The chemical name of gypsum is
(a) Magnesium sulphate hydrate
(b) Calcium sulphate hemihydrate
(c) Carbolic acid
(d) Calcium sulphate dihydrate
Answer:
(d) Calcium sulphate dihydrate
Question 8.
is used in making blackboard chalks.
(a) Plaster of Paris
(b) Gypsum
(c) Epsom
(d) Phenol
Answer:
(a) Plaster of Paris
Question 9.
_________ is used as surgical antiseptic.
(a) Epsom
(b) Phenol
(c) Gypsum
(d) None of these
![]()
II. Fill up the blanks:
- Burning of paper is the best example of _______ change.
- _______ is the branch of science which deals with the study of particles around us.
- Salt is a combination of the chemicals _______ and _______.
- We could prepare soft idly as a result of a chemical change named _______ takes place in the idly batter.
- We are using _______ to remove strong stains on the clothes.
- _______ help plant grows and restore soil fertility.
- _______ is the organic tertillzer.
- _______ invented Portland cement.
- _______ is medicine for skin problems.
- Calcium sulphate hemihydrate is called as _______
- _______ is used in mouthwash in low concentrations.
- The adhesive used in puncture shop is _______
Answers:
- Chemical
- Chemistry
- Sodium, Chlorine
- fermentation
- Wash powder
- Organic fertilizers
- Compost
- Joseph Aspdin
- Epsom
- Plaster of Paris
- Piano
- Artificial adhesive
![]()
III. True or False. If False, give the correct statement:
Question 1.
Water boiling into water vapour is an example of chemical change.
Answer:
False. Water boiling into water vapour is an example of Physical change.
Question 2.
Chemists identify gypsum as a natural indicator.
Answer:
False. Chemists identify turmeric powder as a natural indicator.
Question 3.
The water we drink is a combination of hydrogen and oxygen.
Answer:
True.
Question 4.
When we soak onion in water, then the irritation is increased.
Answer:
False. When we soak onion in water then the irritation is reduced.
Question 5.
Mortar is a paste of cement and sand mixed with water.
Answer:
True.
Question 6.
Fertilizers containing only plant or animal-based materials or those synthesized by microorganisms are called inorganic fertilizers.
Answer:
False. Fertilizers containing only plant or animal-based materials or those synthesized by microorganisms are called organic fertilizers,
Question 7.
‘Portland’ cement resembled the high-quality building stones found in Portland, England.
Answer:
True.
Question 8.
Reinforced Cement Concrete is a mixture of cement, sand, and gravel.
Answer:
False. Concrete is a mixture of cement, sand, and gravel.
Question 9.
Gypsum is used in the process of making cement.
Answer:
True
Question 10.
Gypsum is used in improving plant growth in agriculture.
Answer:
False. Epsom is used in improving plant growth in agriculture.
![]()
IV. Match the following :
| 1. | Sodium Chloride | – | (a) | CaSO41/2H2O |
| 2. | Calcium sulphate dihydrate | – | (b) | C2H5Oh |
| 3. | Magnesium sulphate hydrate | – | (c) | CaSO4.2H2O |
| 4. | Calcium sulphate hemihydrate | – | (d) | NaCl |
| 5. | Phenol | – | (e) | MgSO4.H2O |
Answer:
- – d
- – c
- – e
- – a
- – b.
![]()
V. Analogy:
Question 1.
H2O : Water :: NaCl: ________
Answer:
Sodium Chloride.
Question 2.
Used to join components : Adhesives :: Clean the body _______
Answer:
Soaps.
Question 3.
Organic fertilizer : Compost:: Inorganic fertilizer _______
Answer:
Superphosphate.
Question 4.
Used as fertilizer : Gypsum :: Helps nerves function properly : _______
Answer:
Epsom.
Question 5.
Making casts for statues : Plaster of Paris :: Used as mouthwash : _______
Answer:
phenol.
![]()
VI. Give Short Answer :
Question 1.
Define physical change.
Answer:
In physical change only the shape, size (or) volume changes; the state of the matter may also change.
Question 2.
What is the use of an indicator?
Answer:
The use of an indicator is to identify whether the material is an acid (or) base medium.
Question 3.
How to prepare soft idly?
Answer:
We could prepare soft idly as a result of a chemical change named fermentation that takes place in the idly batter. During fermentation, the idly batter undergoes a chemical change by bacteria.
Question 4.
If we soak onion in water the irritation is reduced. Why?
Answer:
It is due to the presence of a chemical, propanethial s-oxide in onion. This is easily volatile. When we cut onion, some of the cells are damaged and the chemical comes out. It becomes vapour and reaches our eyes result in irritation and tears in the eyes. If we soak onion in water, the chemical is diluted and it cannot reach our eyes. So the irritation is reduced.
Question 5.
Write some materials prepared by chemical changes.
Answer:
Soaps, fertilizers, cement, gypsum, Epsom, plaster of Paris, phenol are the materials.
![]()
Question 6.
Define Principal nutrients.
Answer:
Nitrogen (N), Phosphorous (P), and Potassium (K) are the three important nutrients among the various nutrients needed for plant growth. These three are called Principal Nutrients.
Question 7.
Differentiate between organic and inorganic fertilizer.
Answer:
Organic fertilizers:
- A plant (or) animal-based materials synthesized by micro-organisms
- Prepared easily.
- Economical
- Example: Vermicompost, Compost
Inorganic fertilizers:
- Natural elements by making them undergo chemical changes.
- Prepared complicated
- Not economical
- Example: Urea, Superphosphate, Ammonium Phosphate.
Question 8.
Why the cement is called Portland cement?
Answer:
It was named Portland cement because it resembled the high-quality building stones found in Portland, England.
Question 9.
What are the uses of cement?
Answer:
- It is used to construct houses.
- It is used to construct dams, bridges.
Question 10.
What is the use of Epsom Salt?
Answer:
- In medicine, it eases the stress and relaxes the body.
- In agriculture, it improves plant growth.
- It is used as medicine for skin problems.
- Helps muscles and nerves function properly.
Question 11.
Define Adhesives.
Answer:
A paste-like material that is used to join two components together is called adhesive.
![]()
VII. Answer in detail :
Question 1.
How soaps clean clothes?
Answer:
- We are using wash powder to remove strong stains on the clothes.
- The detergent molecules have two sides, one side “water-loving”, other “water-hating”.
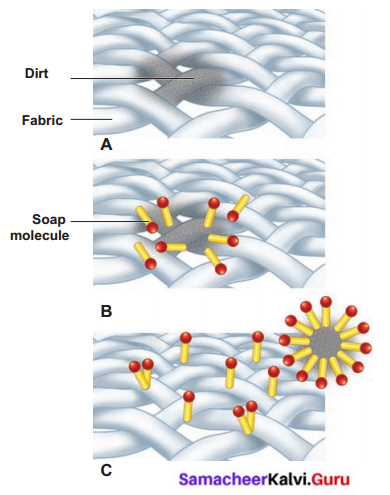
- Water hating goes and joins with dirt and oil in the cloth while the water-loving joins with the water molecules.
- When you agitate the cloth the dirt is surrounded by many molecules and is taken away from the cloth.
- The cloth becomes clean, and the dirt surrounded by the detergent molecules floats in the water making it dirty.