You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 3 Chapter 2 Water
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Water Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the appropriate answer :
Question 1.
Around 97% of water available on earth is _______ water.
(a) fresh
(b) pure
(c) Salty
(d) polluted
Answer:
(c) Salty
Question 2.
Which of the following is not a part of water cycle?
a. evaporation
b. condensation
c. rain
d. distillation
Question 3.
Which of the following processes add water vapour to the atmosphere?
i. Transpiration
ii. Precipitation
iii. Condensation
iv. Evaporation
(a) ii and iii
(b) ii and iv
(c) i and iv
(d) i and ii
Answer:
(c) i and iv
Question 4.
About 30% of the freshwater is found in?
a. glaciers
b. groundwater
c. other sources of water
d. 0.3%
Answer:
b. groundwater
Question 5.
Using R.O. plant at home eliminates a lot of non-potable water. The best way to effectively use the expelled water of R.O. plant is _______
(a) make the expelled water go and seep near the bore well
(b) use it for watering plants
(c) to drink the expelled water after boiling and cooling
(d) to use for cooking as the water is full of many nutrients
Answer:
(b) use it for watering plants
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks :
- Only _______ percent of natural water is available for human consumption.
- The process of changing water into its vapour is called _______
- _______ is built on rivers to regulate water flow and distribute water.
- Water levels in rivers increase greatly during _______
- Water cycle is also called as _______
Answer:
- 0.3
- Evaporation
- Dam
- Raining
- Hydrological cycle
![]()
III. True or False. If False, give the correct statement:
Question 1.
Water present in rivers, lakes and ponds is unfit for use by human beings.
Answer:
False. Water present in rivers, lakes and ponds is fit for use by human beings.
Question 2.
Seas are formed when the water table meets the land surface.
Answer:
False. Ponds are formed when the water table meets the land surface.
Question 3.
The evaporation of water takes place only in sunlight.
Answer:
True.
Question 4.
Condensation results in the formation of dew on the grass.
Answer:
True.
Question 5.
Seawater can be used for irrigation as such.
Answer:
False. Seawater cannot be used for irrigation as such.
![]()
IV. Match the following :
| 1. Flood | Lake |
| 2. Surface water | Evaporation |
| 3. Sunlight | Water vapour |
| 4. Cloud. | Pole |
| 5. Frozen water | Increased rainfall |
Answer:
| 1. Flood | Increased rainfall |
| 2. Surface water | Lake |
| 3, Sunlight | Evaporation |
| 4. Cloud | Water vapour |
| 5. Frozen water | Pole |
![]()
V. Arrange the following statements in the correct sequence :
- These vapours condense to form tiny droplets of water.
- The water droplets come together to form large water droplets.
- The heat of the sun causes evaporation of water from the surface of the earth, oceans, lakes, rivers, and other water bodies.
- The large water droplets become heavy and the air cannot hold them, therefore, they fall as rain.
- Water vapour is also continuously added to the atmosphere through transpiration from the surface of the leaves of trees.
- Warm air carrying clouds rises up.
- Higher up in the atmosphere, the air is cool.
- These droplets floating in the air along with the dust particles form clouds.
Answer:
- The heat of the sun causes evaporation of water from the surface of the earth, oceans, lakes, rivers, and other water bodies.
- Water vapour is also continuously added to the atmosphere through transpiration from the surface of the leaves of trees.
- Higher up in the atmosphere, the air is cool.
- These vapours condense to form tiny droplets of water.
- These droplets floating in the air along with the dust particles form clouds.
- Warm air carrying clouds rises up.
- The water droplets come together to form large water droplets.
- The large water droplets become heavy and the air cannot hold them, therefore, they fall as rain.
![]()
VI. Analogy:
Question 1.
Population explosion : Water scarcity :: Recycle : __________
Answer:
Water Management.
Question 2.
Groundwater : __________ :: Surface water : lakes
Answer:
Tube wells
VII. Give Very Short Answer:
Question 1.
Name four different sources of water.
Answer:
Different sources of water are wells, canals, tanks, ponds, rivers, water tanks, hand pipes.
Question 2.
How do people in cities and rural areas get water for various purposes?
Answer:
In the city, people get water from water tanks, hand pipes, and bore wells.
In rural areas, people get water from wells, canals, ponds, and rivers.
Question 3.
Take out a cooled bottle of water from the refrigerator and keep it on a table. After some time you notice a puddle of water around it. Why?
Answer:
- The cooled water bottle has a very cold exposed surface.
- Due to the cool surface, there is a condensation of water-vapor from the air on the surface of a water bottle. It is because of the fact that water vapour is present in the atmosphere.
- The condensed water molecules spread around the bottle.
- So a puddle of water is noticed after some time.
Question 4.
We could see clouds almost every day. Why doesn’t it rain daily?
Answer:
- The millions of tiny droplets do not collide with one another to form larger droplets.
- The air around the clouds is not cool.
Question 5.
Name the places where water is found as ice.
Answer:
Ice is present in the top of tall mountains, glaciers, and polar regions.
Question 6.
How do aquatic animals manage to live in the Arctic and Antarctic Circle?
Answer:
In Arctic and Antarctic circle, water in lakes and ponds will be frozen and a solid layer of ice is formed on the surface of water. Still aquatic animals living under the ice do not die. This is because the floating layer of ice acts as a protective coat and does not permit heat to escape from water. So as the surface water alone turns to ice, the aquatic animals manage it.
Question 7.
What are the types of rainwater harvesting?
Answer:
Two types of rainwater harvesting are
(a) Collecting water from where it falls.
Example: Collecting water from the rooftops of the houses or buildings (Roof water harvesting).
(b) Collecting flowing rainwater.
Example: Collecting rainwater by constructing ponds with bund.
![]()
VIII. Give Short Answer:
Question 1.
Differentiate between surface water and groundwater.
Answer:
Surface water:
- Water present on the surface of the earth.
- Ex: River, lake, ponds, streams, or freshwater.
Groundwater:
- Water present beneath the earth’s surface in soil.
- Ex: open wells, tube wells (or) hand pumps, Spings, etc.
Question 2.
Write a few slogans of your own on the topic “Save Water”?
Answer:
Save water slogans:
- Conserve water, conserve life.
- Save water, and it will save you.
- It takes a lot of blues to stay green.
- Don’t let life slip down the drain.
- Don’t flush our planet’s most valuable source.
Question 3.
About 71% of the earth’s surface is covered with water, then why do we face scarcity of water?
Answer:
About 71% of the earth’s surface is covered with water and even then we face scarcity of water. Reasons:
- 97% of total water is found in seas and oceans, which is salty and not fit for human consumption.
- Only 3% found in the freshwater and that too available in polar ice caps and glaciers.
- Out of 3% freshwater, only 0.3% is available to us as surface water, in lakes, rivers, and swamps.
Question 4.
Give a reason for the following statement – Sewage should not be disposed of in rivers or oceans before treatment.
Answer:
- Sewage should not be disposed of in rivers or oceans before treatment.
- If we dispose of sewage before treatment the rivers and oceans will be polluted.
- Aquatic animals and species will die due to pollution.
- We can not use the river water for our day to day life.
Question 5.
The freshwater available on earth is only 3%. We cannot increase the amount of water. In that case, how can sustain the water level?
Answer:
- Bringing awareness to the people.
- Recycling of water.
- Minimizing the use of chemical fertilizers.
- Controlling deforestation.
- Adopting drip irrigation and sprinkler irrigation in agriculture.
- Rainwater harvesting.
![]()
IX. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
What is potable water? List down its characteristics?
Answer:
- Potable water is water which is safe to drink.
- On average the human body requires 2-3 litres of water per day for proper functioning.
Characteristics of potable water :
- Cleaned of harmful contaminants.
- It is transparent.
- It is odourless and colourless.
- It is harmless or free from disease-causing bacteria.
Question 2.
Who is known as Waterman of India? Browse the net and find the details about the award, the Waterman received for water management. State the findings by drafting a report.
Answer:
- Dr. Rajendra Singh is known as the “Waterman of India”.
- He is a well-known water conservationist and environmentalist.
- His team built rainwater storage tanks, check dams, and other time-tested as well as path-breaking techniques.
- His team build over 8600 johads to collect rainwater for all seasons, has brought water back to over 1000 villages and revived five rivers in Rajasthan.
Awards:
- He won the Stockholm Water prize in 2005, an award known as “The Noble Prize for Water”.
- Ramon Magsaysay Award in 2001.
- Jamnlal Bajaj Award in 2005.
Question 3.
What is rainwater harvesting? Explain in a few sentences how it can be used in houses.
Answer:
- Direct collection and use of rainwater are called rainwater harvesting.
- The system is easy to install, operate, and maintain for all types of houses.
- An excellent and valuable source of water in emergencies.
- Reduces rainwater runoff and solve drainage problems in houses.
- Ideal solution for the inadequacy of water.
- Increase groundwater level.
![]()
X. Questions based on Higher Order Thinking Skills :
Question 1.
When there is no pond or lake in an area, will there be the formation of clouds possible in that area?
Answer:
Yes, the formation of clouds is possible in that area because plants also release water vapour by transpiration process. This water vapour will form clouds.
Question 2.
To clean the spectacles, people often breathe out on glasses to make them wet. Explain why do the glasses become wet.
Answer:
When a person breathes out on glasses, some amount of water vapour also comes out in exhaled air. This water vapour condenses on the glasses and thus the glasses become wet.
![]()
XI. Crossword :
DOWN:
1. A method of water conservation.
2. Process of getting water vapour from seawater.
6. Water stored in dams is used for generation of _____
ACROSS
3. _______ is a large body of non-potable water found in nature.
4. In summer, the body loses water as _______
5. Plants undergo _______ and contribute to the water cycle.
Answer:
Down:
1. Recycling
2. Evaporation
6. Electricity
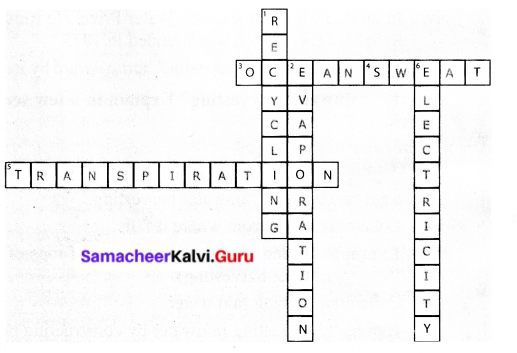
Across:
3. Ocean
4. Sweat
5. Transpiration
![]()
XI.
Question 1.
Observe the given graph carefully and answer the questions.
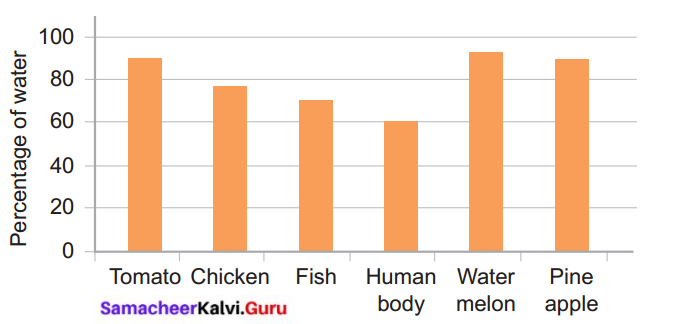
a. What percentage of water is seen in fish?
b. Name the food item that has the maximum amount of water in its content.
c. Name the food item that has a minimum amount of water in its content.
d. Human body consists of about _________ percentage of water.
e. Specify the food item that can be consumed by a person when he/she is suffering from dehydration.
Answer:
a. 70% of water is seen in fish.
b. Watermelon has the maximum amount of water in its content.
c. Fish has a minimum amount of water in its content.
d. 60%.
e. Watermelon is a food item that can be consumed by a person when he/she is suffering from dehydration.
Question 2.
Look at the map of Tamilnadu showing annual rainfall and answer the questions given below.
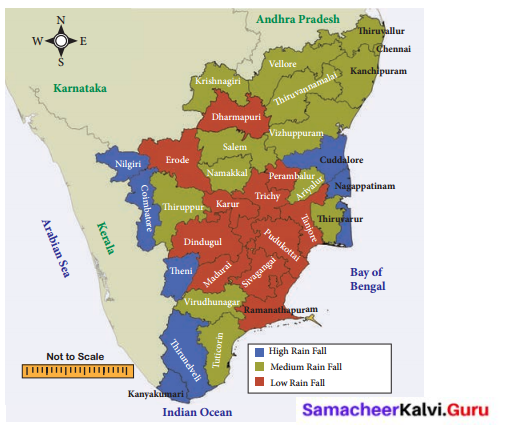
a. Identify the districts that get only low annual rainfall in Tamilnadu.
b. Identify the districts that get a medium annual rainfall in Tamilnadu.
c. State the districts that enjoy high annual rainfall in Tamilnadu.
Answer:
a. Dharmapuri, Erode, Karur, Trichy, Perambalur, Tanjore, Pudukottai, Dindugul, Madurai, Sivagangai, Ramanathapuram.
b. Thiruvallur, Chennai, Kanchipuram, Vellore, Krishnagiri, Thiruvannamalai, Salem, Namakkal, Vizhupuram, Ariyalur, Thiruvarur, Thiruppur, Virudunagar, Tuticorin.
c. Cuddalore, Nagapattinam, Nilgiri, Coimbatore, Theni, Thirunelveli, Kanyakumari.
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Water Intext Activities
Activity 1
The relative amount of water at various sources
Take a 20 litre bucket, a 500 ml mug, a 150 ml tumbler, and a 1 ml spoon. If the capacity of the bucket is 20 litre, then it represents the total amount of water present on the Earth.
Now, transfer a mug of water from the bucket and it is 500 ml and then it represents the total amount of freshwater present in the Earth. The water left in the bucket represents seas and oceans. This water is not fit for human use.

The water present in the mug represents the freshwater which is present in frozen form on snow-covered mountains, glaciers, and polar ice caps. This water is also not readily available for human use. Next, transfer 150 ml of water to the tumbler, then it represents the total amount of groundwater. Finally, take one-fourth spoonful of water while the capacity of the spoon is 1 ml, then it represents the total amount of surface water (i.e) water seen in all the rivers, lakes, and ponds of the world. It can be taken as potable water.
When such a small amount of potable water is available, then we should be more cautious in handling water. Is it not?
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students themselves
Activity 2
Conduct the activity with common salt, sand, chalk powder, charcoal powder, and copper sulphate.
Fill up the following table.
| Substance | Dissolves in water | Does not dissolve in water |
| common salt | ||
| sand | ||
| chalk powder | ||
| charcoal powder | ||
| copper sulphate |
From the above activity, we could observe that common salt and copper sulphate dissolve in water and contribute their properties like colour and other properties to water but sand, chalk powder, and charcoal powder do not dissolve in water.
Answer:
| Substance | Dissolves in water | Does not dissolve in water |
| common salt | ✓ | |
| sand | ✓ | |
| chalk powder | ✓ | |
| charcoal powder | ✓ | |
| copper sulphate | ✓ |
![]()
Activity 3
Water contains dissolved salts
Take some tap water in a china dish and heat it. Continue heating till all the water gets dried up. Stop the heating and look at the china dish. What do you observe inside the china dish?
Deposits of some solid particles on the surface of the china dish can be observed. The deposit is of salts that are dissolved in water. This shows that water has dissolved salts in it.
Note: Do not use distilled water or water from purifier or RO unit and the like for this activity.
Activity 4
Spread a piece of wet cloth in the sunlight. Observe after some time. Where has the water in the wet cloth gone?

The water evaporates into the atmosphere due to the heat of the sun.
![]()
Activity 5
Condensation of water vapour
Take a glass half-filled with water. Wipe the outer surface of the glass with a clean piece of cloth. Add some ice into the water. Wait for one or two minutes. Observe the changes that take place on the outer surface of the glass.
From where do water drops appear on the outer side of the glass?
The cold surface of the glass containing icy water cools the air around it and the water vapour of the air condenses on the surface of the glass. This process is also the result of the condensation of water vapour.
Activity 6
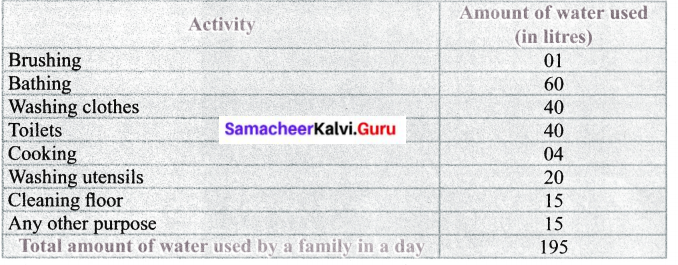
Estimation of water consumed by a family on a day
Answer:
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Water Additional Questions
I. Choose the appropriate answer:
Question 1.
_______ form of water is present in the mountain and the polar regions.
(a) Solid
(b) Liquid
(c) Gaseous
(d) All these
Answer:
(a) Solid
Question 2.
The melting point of Ice is ……….
(a) 100°C
(b) 0°C
(c) 0.100°C
(d) 10°C
Answer:
(b) 0°C
Question 3.
_______ water contains 0.05% to 1% of salts.
(a) Brackish
(b) Fresh
(c) Sea
(d) Sewage
Answer:
(b) Fresh
Question 4.
The human body requires ………. litres of water per day for proper functioning.
(a) 2 – 3 litres
(b) 3 – 4 litres
(c) 4 – 5 litres
(d) 1 – 2 litres
Answer:
(b) 3 – 4 litres
Question 5.
In plants, the loss of water in the form of vapour from the aerial parts through _______
(a) Root
(b) Shoot
(c) Stomatal Pores
(d) Fruit
Ans:
(c) Stomatal Pores
Question 6.
_______ water is obtained through open wells, tube wells or hand pumps, springs.
(a) Surface
(b) Frozen
(c) Saline
(d) Ground
Ans:
(d) Ground
Question 7.
_______ of Asia’s largest rivers flow from the Himalayas.
(a) 10
(b) 9
(c) 11
(d) 15
Answer:
(a) 10
Question 8.
Volume of liquid is measured by _______
(a) Gallon
(b) Litre
(c) Cusec
(d) Estuaries
Answer:
(c) Mangrove
Question 9.
_______ forests are found in pichavaram near Chidambaram
(a) Green
(b) Grasslands
(c) Mangrove
(d) Estuaries
Answer:
(c) Mangrove
![]()
II. Fill up the blanks:
- _______ plays a vital role in the evolution and survival of life.
- _______ is present in the air around us.
- In the distribution of a total of 0.3% of surface water, _______ has 87% surface water.
- The molecular formula of water is _______
- The oceanic volcanoes which are present inside also add _______ to the sea.
- Every year _______ is observed as the world water day.
- The water vapour gets cooled and changes into tiny water droplets that form _______ in the sky.
- A larger portion of water is _______ % of the total available fresh water in a frozen state.
- The water level in the reservoirs is measured in _______
- Adoption of _______ and irrigation in agriculture.
Answers:
- Water
- Vapour
- Lakes
- H2O
- Salt
- March 22nd
- Clouds
- 68.7
- Cubic feet per second (cusecs)
- Drip, Sprinkler
![]()
III. True or False. If False, give the correct statement:
Question 1.
Mountains help to regulate the temperature of our earth.
Answer:
False. Water helps to regulate the temperature of our earth.
Question 2.
Solid form of water is present in underground.
Answer:
False. Liquid form of water is present in underground.
Question 3.
Water while passing through layers of soil dissolves salt and minerals to a maximum extent.
Answer:
True.
Question 4.
Water freeze at 100° Celsius at normal pressure.
Answer:
False. Water freeze at 0° celsius at normal pressure.
Question 5.
When the air around the clouds is cool, these drops of a waterfall in the form of snow or rain.
Answer:
True.
Question 6.
Direct collection and use of rainwater are called rainwater harvesting.
Answer:
True.
Question 7.
Estuaries are harmful to unique plants and animal species.
Answer:
False. Estuaries are home to unique plants and animal species.
![]()
IV. Analogy:
Question 1.
Ice berg : Solid form :: Water vapour : _______
Answer:
Gaseous Form.
Question 2.
Contain more than 3% of salt: _______ :: upto 3% of salt dissolved : Brackish water.
Answer:
Seawater.
Question 3.
Water bodies meet the sea : Estuaries :: Wet lands : _______
Answer:
Swamps.
Question 4.
Napier Bridge area : _______ :: Pallikkaranai: Wet land.
Answer:
Estuaries.
![]()
V. Give Short Answer:
Question 1.
Give the uses of water.
Answer:
Cooking food, washing clothes, cleaning utensils, bathing, agricultural, etc.
Question 2.
What are the three forms of water?
Answer:
Water is available in solid, liquid, and vapour forms.
Question 3.
Which places have fresh water?
Answer:
Ponds, pools, rivers, tube wells have fresh water.
Question 4.
How is 3% of freshwater distributed?
Answer:
Polar ice caps and glaciers – 68.7%
Groundwater – 30.1%
Another source of water – 0.9%
Surface water – 0.3%
Question 5.
Define – Saline water.
Answer:
Water with a large amount of dissolved solids is not potable or suitable for drinking. Such water is called saline water.
Question 6.
How water is classified based on its salinity?
Answer:
Based on salinity, water is classified into three main categories. Such as Freshwater, Brackish water, and Seawater.
Question 7.
What are the salts dissolved in seawater?
Answer:
The salts are dissolved in seawater are sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, and calcium chloride.
Question 8.
Define Water cycle.
Answer:
The water on the earth evaporates into the atmosphere due to the heat of the sun. The water vapour in the atmosphere forms clouds. From the clouds, waterfalls on the earth in the form of rain or snow. By this natural process, water gets renewed. This is called the water cycle.
Question 9.
What is Condensation?
Answer:
Water vapour which enters into the atmosphere by evaporation moves upward with air, gets cooled, and changes into tiny water droplets that form clouds in the sky. This process is known as condensation.
Question 10.
What is transpiration?
Answer:
It is the process of loss of water from the aerial parts of a plant in vapour form. This is called transpiration.
Question 11.
What is frozen water?
Answer:
Water that is present in the frozen form as polar ice caps and glaciers are called frozen water. A large portion of water is 68.7% of the total available freshwater is in a frozen state.
Question 12.
Define – Scarcity of water.
Answer:
There is no change in the total quantity of water available on earth. It remains the same. But the water useful for plants, animals, and man is decreasing day by day. It is called Scarcity of water.
Question 13.
List the wetlands in Tamilnadu.
Answer:
- Pichavaram Mangroves near Chidambaram.
- Muthupet Mangrove wet-land.
- Pallikkaranai wet-land in Chennai.
- Chembarambakkam in Kancheepuram is a few examples of swamps in Tamilnadu.
Question 14.
What is meant by the conservation of water?
Answer:
Saving water for future generations by using water carefully and in a limited way is the conservation of water.
![]()
VI. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Draw and describe the total water on earth by a pie chart.
Answer:
If the total water on earth be 100%, let’s see what percent would be the availability of freshwater. Look at the pie chart given below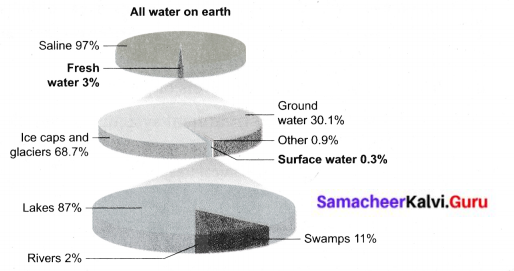
From the pie chart, it can also be noted that 97% of water is saline water. Only 3% found in the freshwater and that too in polar ice caps and glaciers. So this portion of water is not readily available for drinking.
The distribution of the total available (3%) freshwater is as follows:
Polar ice caps and glaciers – 68.7%
Groundwater – 30.1 %
Another source of water – 0.9%
Surface water – 0.3%
The distribution of total 0.3% of surface water is as follows:
Lakes – 87%
Rivers – 2%
Swamps – 11%
Thus the above pie chart explains that we have a very small amount of freshwater available for human usage and so maintaining the water table and the conservation of water is very essential.
Question 2.
What are the methods of water conservation? Explain?
Answer:
1. Water management:
- Bringing awareness to the people.
- Recycling water by separating pollutants.
- Minimize the use of fertilizers.
- Controlling deforestation.
- Adopt drip and sprinkler irrigation in agriculture.
2. Rainwater harvesting:
- Collecting water from where it falls:
- Collecting water from the rooftops.
- Collecting flowing rainwater
- Collecting rainwater by constructing dams.
Question 3.
Give the importance of water.
Answer:
The importance of water:
- Our body uses water in all its cells, organs, and tissues to help regulate its temperature and maintain other bodily functions.
- On average, the human body requires 2-3 litres of water per day for proper functioning.
- Water helps in the digestion of food and the removal of toxins from the body.
- Water is used in domestic activities like cooking, bathing, washing clothes, washing utensils, keeping houses and common places clean, watering plants, etc.
- It is also essential for the healthy growth of farm crops and farm stock and is used in the manufacture of many products.
- Industry depends on the water at all levels of production.
Question 4.
Describe water distribution and treatment system through the flow chart.
Answer:

Question 5.
What are the reasons for the scarcity of water?
Answer:
The main reasons for the scarcity of water are:
- Population explosion.
- Uneven distribution of rainfall.
- The decline of the ground water table.
- Pollution of water.
- Careless use of water.