You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 1 Chapter 2 Force and Motion
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Force and Motion Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
Unit of speed is
(a) m
(b) s
(c) kg
(d) m/s
Answer:
(d) m/s
Question 2.
Oscillatory motion among the following is
a. Rotation of the earth about its axis
b. Revolution of the moon about the earth
c. To and fro movement of a vibrating string
d. All of these.
Answer:
c. To and fro movement of a vibrating string
Question 3.
The correct relation among the following is
(a) Speed = distance × time
(b) speed = distance / time
(c) Speed = time / distance
(d) speed = 1/ (distance × time)
Answer:
(b) speed = distance / time
Question 4.
Gita rides with her father’s bike to her uncle’s house which is 40 km away from her home. She takes 40 minutes to reach there.
Statement 1 : She travels with a speed of 1 km/minute
Statement 2: She travels with a speed of 1 km/hour
a. Statement 1 alone is correct.
b. Statement 2 alone is correct
c. Both statement 1 and 2 are correct.
d. Neither statement 1 nor statement 2 is correct.
Answer:
a. Statement 1 alone is correct.
![]()
II. Find whether the following statements are true or false. – if false give the correct answer.
Question 1.
To and fro motion is called oscillatory motion.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
Vibratory motion and rotatory motion are periodic motions.
Answer:
False.
Vibratory motion and oscillatory motion are periodic motions.
Question 3.
Vehicles moving with varying speeds are said to be in uniform motion.
Answer:
False.
Vehicles moving with varying speeds are said to be in non-uniform motion.
(OR)
Vehicles moving with uniform speeds are said to be in uniform motion.
Question 4.
Robots will replace humans in the future.
Answer:
False. Robots will not replace humans in the future.
![]()
III. Fill in the blanks.
- A bike moving on a straight road is an example of _______ motion.
- Gravitational force is a _______ force.
- The motion of a potter’s wheel is an example of _______ motion.
- When an object covers equal distances in equal interval of time, it is said to be in _______ motion.
Answers:
- Linear
- Non-Contact Force
- rotatory
- uniform
IV. Match the following

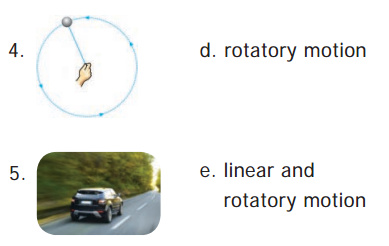
Answers:
- c
- d
- b
- a
- e
![]()
V. Analogy
Question 1.
kicking a ball: contact force :: falling of leaf: ________?
Answer:
Noncontact force.
Question 2.
Distance : metre :: speed : _______ ?
Answer:
metre/second.
Question 3.
circulatory motion :: a spinning top :: oscillatory motion : _______ ?
Answer:
Swinging of a pendulum.
![]()
VI. Given below Is the distance-traveled by an elephant across a forest with uniform speed. Complete the data of the table given below with the idea of uniform speed.
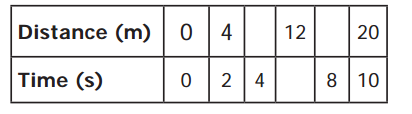
Answer:
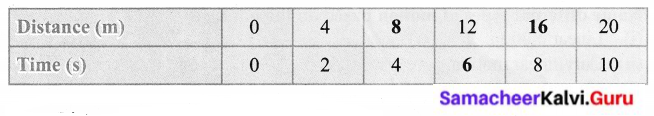
(i) Distance/Time = \(\frac { 4 }{ 2 } \) × 4 = \(\frac { 16 }{ 22 } \) = 8
(ii) Distance / Time = \(\frac { 4 }{ 2 } \) × 8 = \(\frac { 32 }{ 2 } \) = 16
(iii) Time/Distance = \(\frac{1 \emptyset}{2 \emptyset}\) × 12 = \(\frac { 12 }{ 2 } \) = 6
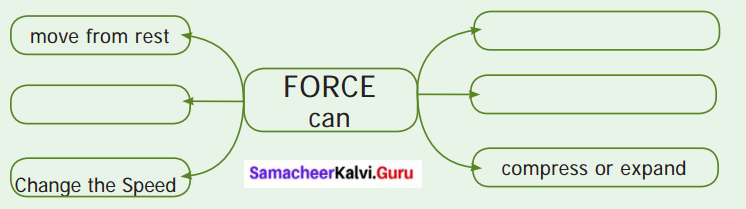
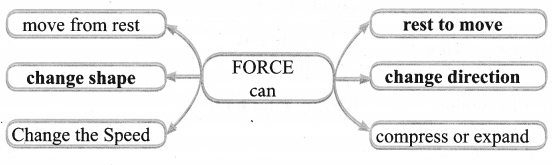
VII. Complete the web chart.
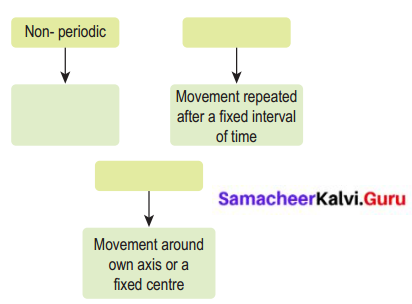
Answer:
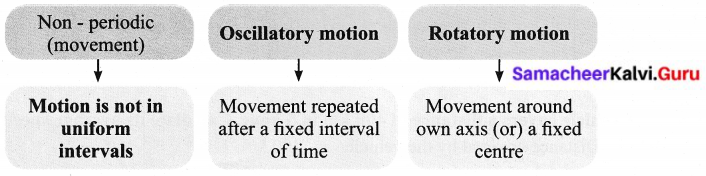
VIII. Give one word for the following statements.
Question 1.
The force acts on an object without physical contact with it.
Answer:
non-contact forces.
Question 2.
A change in the position of an object with time.
Answer:
Motion.
Question 3.
The motion repeats itself after a fixed interval of time.
Answer:
Oscillatory motion.
Question 4.
The motion of an object travels equal distances in equal intervals of time.
Answer:
Uniform motion.
Question 5.
A machine capable of carrying out a complex series of actions automatically.
Answer:
Artificial intelligence.
![]()
IX. Answer the following in a sentence or two.
Question 1.
Define force.
Answer:
Force is a push or pull by an animate or inanimate agency.
Question 2.
Name different types of motion based on the path.
Answer:
- Linear motion;
- Curvilinear;
- Circular motion;
- Rotatory motion;
- Oscillatory motion
- Irregular motion.
Question 3.
If you are sitting in a moving car, will you be at rest or motion with respect to your friend sitting next to you?
Answer:
I will be at rest with respect to my friend sitting with me in a moving car.
Question 4.
The rotation of the earth is a periodic motion. Justify
Answer:
Rotation of the earth is a periodic motion because it takes an equal interval of time for all rotations.
Question 5.
Differentiate between rotational and curvilinear motion.
Answer:
Rotational motion:
The movement of a body about its own axis
Ex: Rotating tape
Curvilinear motion:
Movement of a body along a curved path
Ex. Throwing a ball.
![]()
X. Calculate
Question 1.
A vehicle covers a distance of 400 km in 5 hours. Calculate its average speed.
Answer:
Distance covered by the vehicle = 400 km
Time taken = 5 hour

XI. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
What is motion? Classify different types of motion with examples.
Answer:
Motion is a change in the position of an object with respect to time.
Types of motion based on the path:
- Linear motion: moving in a straight line, like a person walking on a straight path.
- Curvilinear motion: moving ahead by changing direction like a throwing ball.
- Circular motion: moving in a circular path. Ex. Swirling store tied to the rope.
- Rotatory motion: The movement of a body about its own axis. Ex. Revolution of the earth around the sun.
- Oscillatory motion: Coming back to the same position after a fixed time interval. Ex pendulum.
- Zigzag (irregular): like the motion of a bee or people walking in a crowded street.
Motion-based on duration:
Periodic motion: motion repeated in equal intervals of time. Ex. Revolution of the moon around the earth.
Nonperiodic motion: motion is not repeated in equal interval Ex. Sabing swing.
Motion-based on speed :
Uniform motion: The object covers the uniform distance in uniform intervals.
Non- uniform motion: if an object covers different distances at different intervals of times. Ex. The motion of a vehicle.
![]()
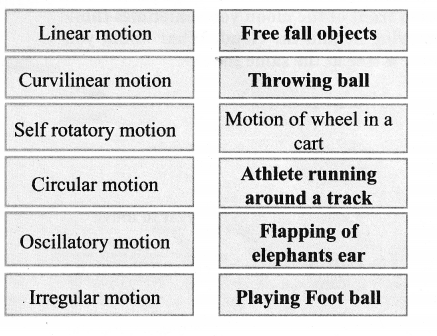
XII. Fill with examples.
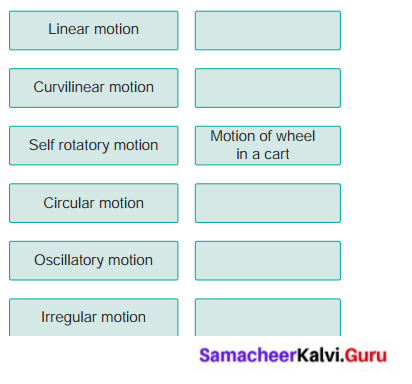
Answer:
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Force and Motion Intext Activities
Activity – 1
Can you identify whether it is push or pull that results in motion in the following cases?
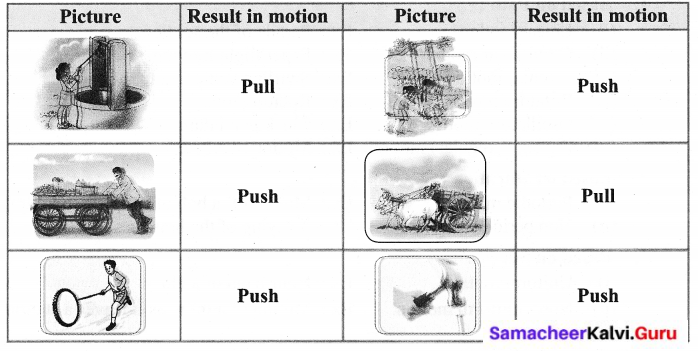
Event 2:
The girl on the swing is moving with respect to the seat of the swing.
She is at rest with respect to the garden.
Event 3:
Nisha is going to her grandmother’s house by bicycle The girl on the bicycle is moving with respect to the road.
She is at rest with respect to the bicycle.
Activity – 2
Moon or Cloud?
Observe the moon on a windy night with a fair bit of cloud cover in the sky. As a cloud passes in front of the moon you sometimes think it is the moon which is moving behind the cloud. What would you think if you were to observe a tree at the same time?
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students themselves
Activity – 3
Fill in the empty spaces.
Answer:
Can you give example for contact and non-contact forces?
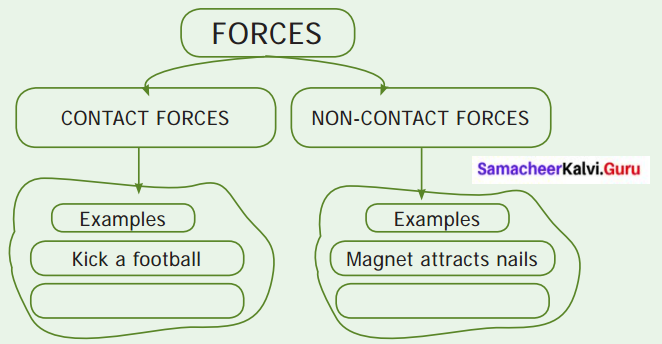
Answer:
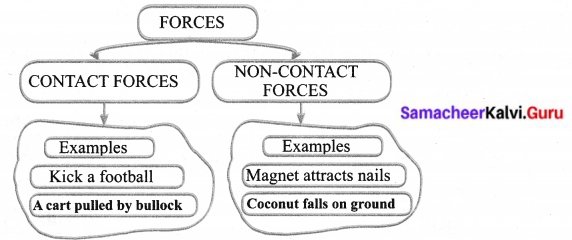
Activity – 4
Play with a pencil
Please do what Shanthi did…
- Shanthi took a pencil and sharpened it with a sharpener.
- Then she drew a circle using the pencil and a compass.
- Later she took her ruler (scale) and drew a straight line in another paper.
- Then she kept the pencil between her finger and moved it back and forth.
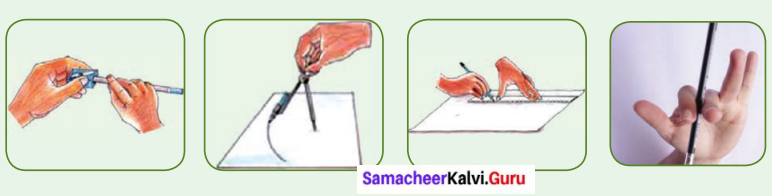
Now, look at the motion of the pencil in all these four cases. How was it?
- In the first case, the pencil rotated in its axis.
- In the second case, it went in a circle.
- In the third case, the pencil travelled in a straight line.
- The fourth case, the pencil tip moved back and forth, that is it oscillated like a swing.
![]()
Activity – 5
Activity – 6
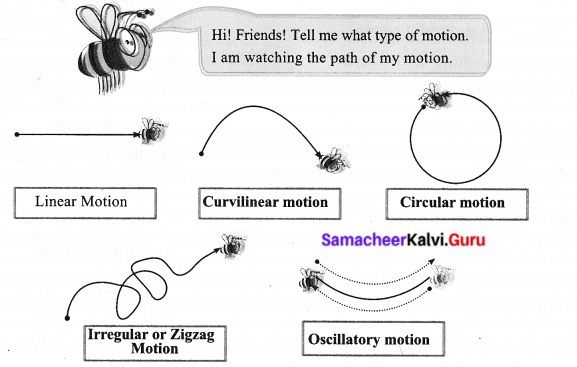
Classify the following according to the path it takes.
Linear, Curvilinear, Circular, Rotatory, Oscillatory, Zigzag (irregular)
- A sprinter running a 100 m race – Linear Motion
- A coconut falling from a tree – Linear Motion
- striking a coin in a carom board game – Zigzag Motion
- Motion of flies and mosquitoes – Zigzag Motion
- Beating of heart – Oscillatory Motion
- Children playing in a swing – Oscillatory Motion
- The tip of hands of a clock – Rotatory Motion
- Flapping of elephant’s ears – Oscillatory Motion
- A stone is thrown into the air at an angle – Curvilinear Motion
- Movement of people in a bazaar – Zigzag Motion
- Athlete running around a track – Circular Motion
- Revolution of the moon around the earth – Circular Motion
- The movement of a ball kicked in a football match – Curvilinear Motion
- Motion of a spinning top – Rotatory Motion
- Revolution of the earth around the sun – Circular Motion
- Swinging of a pendulum – Oscillatory Motion
- Children skidding on a sliding board – Linear Motion
- Skidding down a playground slide – Zigzag Motion
- Wagging tail of a dog – Oscillatory Motion
- Flapping of a flag in wind – Oscillatory Motion
- A car driving around a curve – Circular Motion
- Woodcutter cutting with a saw – Linear Motion
- Motion of water wave – Oscillatory Motion
- Motion of piston inside a syringe – Linear Motion
- Bouncing ball – Oscillatory Motion
add five motions you observe to this list:
- Falling fruits from the tree – Linear Motion
- Ceiling fan running – Rotatory Motion
- Car running on the straight road – Linear Motion
- Swirling stone tied to the rope – Circular Motion
- Motion of sewing machine needle – Oscillatory Motion
![]()
Activity

Answer:
The Taxi driver travelled at the highest speed.
How do we say? Let us calculate how long they travelled in One Hour?
Distance travelled by Car in One Hour = 80 km (160 ÷ 2)
Distance travelled by the Bus in One Hour = 50 km (200 ÷ 4)
Distance travelled by Truck in One Hour = 60 km (300 ÷ 5)
Have you found out? say now.
Fastest Taxi, Slowest Bus.
![]()
Our speed…
Let us play a small game. Go to the playground with your friends. Mark 100 metre distance for a race. Conduct a friendly running race and calculate the time they took to complete the distance by stopwatch. Now fill up the following table.
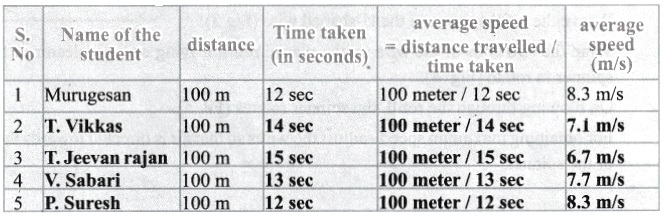
Compute the following Numerical Problems.
- If you travel 10 kilometres in 2 hours, your speed is 5 km per hour. (10 km/2 hours)
- If you travel 15 kilometres in 1/2 hour, you would travel 30 km in one hour, and your speed is 30 km per hour. (15 km × 2/1 hours)
- If you run fast at 20 kilometres per hour for 2 hours, you will cover 40 km. (20 km × 2 hours)
Activity
Multiple Motion to a Sewing Machine
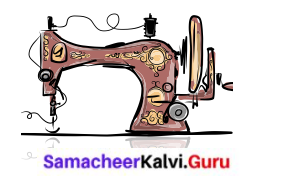
The motion of the needle
Periodic (or) Oscillatory motion
The motion of the wheel
Rotatory motion
Motion of footrest
Oscillatory motion
![]()
Activity – 7
Simple Spinner
Let us enjoy by making a simple spinner. Make it by the following instruction.
Cut a 2cm long piece from an old ball-pen refill and make a hole in its center with a divider point (Fig 1).
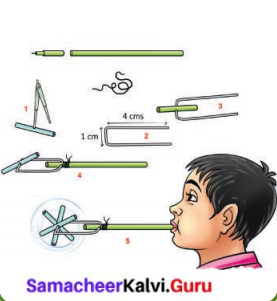
Take a thin wire of length 9cm and fold it into a U-shape (Fig 2).
Weave the refill spinner in the U-shaped wire (Fig 3).
Wrap the two ends of the wire on the plastic refill, leaving enough clearance for the spinner to rotate (Fig 4).
On blowing through the refill, the spinner rotates (Fig 5).
For obtaining maximum speed – adjust the wires so that air is directed towards the ends of the spinner.
Have you enjoyed with a simple spinner? Do you observe the motions in the toy? Can you answer the following question?
- Motion of the air in tube is _____________ motion.
- Motion of the refill stick _____________ motion.
- The toy converts _____________ motion into _____________ motion.
Answers:
- Linear
- Rotatory
- Linear, Rotatory
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Force and Motion Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
_______ is an ancient Indian astronomer.
(a) C.V. Raman
(b) Aryabhata
(c) Usain Bolt
(d) Edison
Answer:
(b) Aryabhata
Question 2.
What is the path of the housefly buzzing around the room?
(a) Periodic motion
(b) Non- Periodic motion
(c) circular motion
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Non- Periodic motion
Question 3.
Identify the Periodic motion among the following :
(a) a horse running in a race
(b) the revolution of the moon around the earth
(c) a coconut falling from a tree
(d) paper flight moving
Answer:
(b) the revolution of the moon around the earth
Question 4.
The cheetah the fastest animal among terrestrial animals run with an average speed of
(a) 100 km /hr
(b) 200 km/hr
(c) 112 km/hr
(d) 10 km /hr.
Answer:
(c) 112 km/hr
Question 5.
_______ are robots scaled down to microscopic size in order to put them into very small spaces to perform a function.
(a) Car robots
(b) Home robots
(c) Game robots
(d) Nanobots
Answer:
(d) Nanobots
Question 6.
A _______ is the fastest land animal.
(a) Horse
(b) Lion
(c) Cheetah
(d) Tiger
Answer:
(c) Cheetah
Question 7.
A cheetah can run with an average speed of _______
(a) 112 km/h
(b) 121 km/h
(c) 211 km/h
(d) 122 km/h
Answer:
(a) 112 km/h
![]()
II. Find whether the following sentences are true or false. If false Correct the statement.
Question 1.
Motion occurs when the object is pulled or pushed by an agency.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
Force executed by touching the body is called non – contact force.
Answer:
False. Force executed by touching the body is called contact force.
Question 3.
Gravity pushes the ripen coconut from the tree to the ground.
Answer:
False. Gravity pulls the ripen coconut from the tree to the ground.
Question 4.
Throwing paper aeroplane is the best example of linear motion.
Answer:
False. Throwing paper aeroplane is the best example of curvilinear motion.
Question 5.
The movement of a body about its own axis like a rotating top is linear motion.
Answer:
False. The movement of a body about its own axis like a rotating top is Rotatory
Question 6.
Motion repeated in equal intervals of time is called as periodic motion.
Answer:
True.
![]()
III. Fill in the blanks.
- _________ are push or pull by an animate or inanimate agency.
- Application of force in an object results in motion from a state of _________
- Fast oscillations are referred to as _________
- Motion repeated in equal intervals of time is called _________
- _________ are automatic machines.
- The term Robots comes from a tech word _________
- _________ is die study of robots in science.
Answers:
- Forces
- rest
- vibrations
- periodic motion
- Robots
- robota
- Robotics
![]()
IV. Complete the web chart.
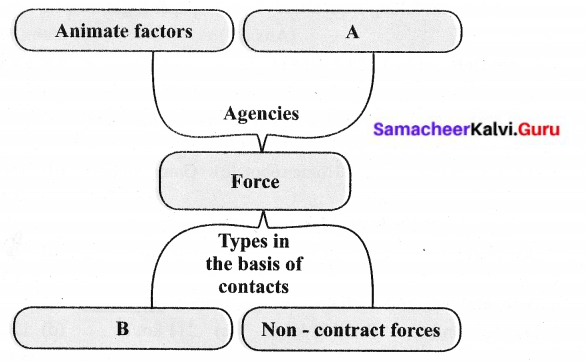
Answer:
- A – In animate factors,
- B – Contact forces.
V. Answer the following in one or two sentences.
Question 1.
What is meant by the State of Rest?
Answer:
When there is no change of position of an object with respect to time and if it remains stationary it is called rest.
Question 2.
What is a non-contact force?
Answer:
The force applied without touching the object is known as non-contact force.
Question 3.
What is the contact force?
Answer:
When the force is in contact with the object then it is known as contact force.
Question 4.
Give the properties of force.
Answer:
- Forces can change the state of a body from rest to motion or motion to rest.
- Forces can change the shape of the body.
Question 5.
A bus moves with a speed of 40 km and crosses 200 km and then how many hours has that bus taken to travel?
Answer:
Time (t) = \(\frac{distence}{AverageSpeed}\)
Time (t) = \(\frac{200 km}{400 km/h}\) = 5 hours
Question 6.
Define Average speed.
Answer:
The distance travelled by an object in unit time is called average speed.
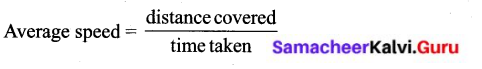
Question 7.
List out the types of motion on the basis of speed.
Answer:
There are two types:
- Uniform motion,
- Non-uniform motion.
Question 8.
Define uniform motion.
Answer:
If an object covers uniform distances in uniform intervals, then the motion of the object is called uniform motion.
Question 9.
Why robots are used in many places?
Answer:
Robots can perform mechanical and repetitive jobs faster, more accurately than human beings. It can also handle dangerous materials and explore distant planets.
Question 10.
What are the important parts of a robot?
Answer:
Electronic sensors are a robot’s eyes and ears. These are the important parts.
Question 11.
What are nanobots?
Answer:
Nanobots are robots scaled down to microscopic size in order to put them into very small places to perform a function.
Question 12.
What are the uses of future robots?
Answer:
- It could be placed in the bloodstream to perform surgical procedures.
- It could target cancer cells and destroy them without touching healthy cells nearby.
![]()
VI. Answer in Detail.
Question 1.
Classify the following motions according to the path it takes.
- A coconut falling from a tree
- Heartbeat
- A stone is thrown into the air at an angle
- Movement of people in a bazaar
- The motion of a spinning top
Answers:
- A coconut falling from a tree – Linear Motion
- Heartbeat – Oscillatory Motion
- A stone is thrown into the air at an angle – Curvilinear Motion
- Movement of people in a Bazar – Zigzag Motion
- The motion of a spinning top – Rotatory Motion
Question 2.
Classify the following motions based on duration and speed.
- Coconut falls to the ground
- A cart pulled by a bullock
- Train journey
- A bouncing ball
- Revolution of the Moon around the earth
Answers:
- Non-periodic Motion
- Non-periodic Motion
- Non-uniform Motion
- Periodic Motion
- Uniform Motion