Students can Download Commerce Chapter 26 Companies Act 2013 Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Solutions Chapter 26 Companies Act 2013
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Companies Act 2013 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The Company will have to issue the notice of situation of Registered Office to the Registrar of Companies with in _____ days from the date of incorporation.
(a) 14 days
(b) 21 days
(c) 30 Days
(d) 60 Days
Answer:
(c) 30 Days
Question 2.
How does a person who envisages the idea to form a company called?
(a) Director
(b) Company Secretary
(c) Registrar
(d) Promoter
Answer:
(d) Promoter
![]()
Question 3.
For which type of capital a company pays the prescribed fees at the time of registration?
(a) Subscribed Capital
(b) Authorised Capital
(c) Paid-up Capital
(d) Issued Capital
Answer:
(b) Authorised Capital
Question 4.
Which of the following types of shares are issued by a company to raise capital from the existing shareholders?
(a) Equity Shares
(b) Right Shares
(c) Preference Shares
(d) Bonus Shares
Answer:
(b) Right Shares
Question 5.
Specify the type of resolution to be passed to choose the location of Registered Office of the company within the town or village or city.
(a) Ordinary
(b) Special
(c) Either Ordinary or Special
(d) Board
Answer:
(d) Board
Question 6.
Who can issue stock?
(a) Public
(b) Private
(c) One Person
(d) Small
Answer:
(a) Public
Question 7.
Specify the document which comes under the Negotiable Instrument Act.
(a) Share Certificate
(b) Share
(c) Share Warrant
(d) Stock
Answer:
(c) Share Warrant
Question 8.
The shares which are offered to the existing shareholder at free of cost is known as _____
(a) Bonus Share
(b) Equity Share
(c) Right Share
(d) Preference Share
Answer:
(a) Bonus Share
Question 9.
The shares which are offered first to the existing shareholder at reduced price is known as _____
(a) Bonus Share
(b) Equity Share
(c) Right Share
(d) Preference Share
Answer:
(c) Right Share
Question 10.
The Companies Act 2013 Prohibits the issue of shares at _____ to the public.
(a) Premium
(b) Par
(c) Discount
(d) Both at par and Premium
Answer:
(c) Discount
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Who is called as Promoters?
Answer:
Promotion stage begins when the idea to form a company comes in the mind of a person. The person who envisage the idea is called a ‘promoter’.
![]()
Question 2.
What is Share?
Answer:
The term Share is viewed by a layman as a fraction or portion of total capital of the company which have equal denomination.
Question 3.
What do you mean by Equity Share?
Answer:
The share of a company which do not have any preferential rights with regard to dividend and repayment of share capital at the time of liquidation of a company, is called as equity share or ordinary share.
Question 4.
What do you understand by Preference Share?
Answer:
The term ‘preference shares’ means that part of the share capital the holders of which have a preferential right over payment of dividend (fixed amount or rate) and repayment of share capital in the event of winding up of the company.
Question 5.
What is Sweat Equity Shares?
Answer:
Sweat Equity Shares means issue of shares to employees or directors at a lower price for cash or other than Cash.
Question 6.
What is Bonus Shares?
Answer:
Bonus share means to utilize the company’s reserves and surpluses. Issue of shares to existing shareholders without taking any consideration is known as Bonus Shares.
Question 7.
What is Right Shares?
Answer:
The right shares are primarily issued to the existing equity shareholders through a letter of an issue, on pro rata basis.
Question 8.
What is Private placement?
Answer:
Private placement means offer of securities or invitation to subscribe to securities to a select group of persons through private placement offer letter.
Question 9.
Define Share Warrant.
Answer:
A share warrant is a negotiable instrument, issued by the public limited company only against fully paid up shares. It is also termed as a document of title because the holder of the share warrant is entitled to the number of shares mentioned in it.
![]()
Question 10.
What is Debentures?
Answer:
When a company needs funds for extension and development purpose without increasing its share capital, it can borrow from the general public by issuing certificates for a fixed period of time and at a fixed rate of interest. Such a loan certificate is called a debenture.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between shares and stocks.
Answer:
| Basis for Difference | Shares | Stocks |
| 1. Meaning | The term ‘share’ means a fraction or unit of the total capital of the company which have equal denomination. | Stock is created from fully paid shares by passing resolution in the general meeting. The Articles of Association of the company must permit this conversion. |
| 2. Denomination | All the shares are of equal denomination. | The denomination of stocks may. differ. |
| 3. Paid up value | Shares can be partly or fully paid up. | Stock can only be fully paid up. |
Question 2.
What do you understand by Issue of Securities at Premium?
Answer:
When shares are issued at a price above the face or nominal value, they are said to be issued at a premium. For example, a share having the face value of Rs. 10 is issued at Rs. 12. Here, Rs.2 is the premium. The amount of share premium has to be transferred to an account called the ‘ Securities Premium Account’
Question 3.
What is issue of shares at discount? What conditions should be fulfilled?
Answer:
When the shares are issued at a price below the face value they are said to be issued at a discount. For example, a share having the face value of Rs 10 is issued at Rs 8. The companies act 2013, prohibits the issue of shares at discount (Section 53), except sweat Equity share.
Question 4.
State condition stipulated for capital subscription at the time of promotion.
Answer:
For capital subscription, steps to be taken are listed below:
- The fulfilling formalities to raise necessary capital.
- Adhering to SEBI guidelines in this regard.
- Observing guidelines for Disclosure and investor protection issued by SEBI.
- Issuing prospectus.
- Appointing official banker of the company for receiving application from the investors.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain different kinds of preference shares.
Answer:
There are eight types of preference shares:
- Cumulative Preference shares: As the word indicates, all dividends are carried forward until specified.
- Non-cumulative Preference shares: These are opposite of cumulative.
- Redeemable Preference shares: Such preference shares can be claimed after a fixed period or after giving due notice. ,
- Non-Redeemable Preference shares: Such shares cannot be redeemed during the lifetime of the company.
- Convertible Preference shares: The shares can be converted into equity shares after a time period. .
- Non-convertible Preference shares: Non-convertible preference shares cannot be, at any time, converted into equity shares.
- Participating Preference shares.
- Non-Participating Preference shares.
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write the difference between Debentures and Shares.
Answer:
Debentures:
- Debentures mean a loan.
- Debenture holder gets fixed rate of Interest.
- Debentures generally have a charge on the assets of the company.
- Debentures can be issued at a discount.
- Debenture holders do not have any voting right.
- Interest on debentures is payable even if there are no profits.
- Interest paid on debenture is a business expense.
Shares:
- Shares are part of the capital of a company.
- Shareholders gets dividends with a varying rate.
- Shares do not carry any such charge.
- Shares cannot be issued at a discount.
- Shareholders enjoy voting right.
- Dividend is payable only if there is profit.
- Dividend is not a business expense.
Question 2.
Brief different stages in Formation of a Company.
Answer:
Section 3 (1) of the Act states that a company may be formed for any lawful purpose by-
(a) seven or more persons, where the company to be formed is to be a public company;
(b) two or more persons, where the company to be formed is to be a private company;
(c) one person, where the company to be formed is to be One Person Company.
The process of formation of company consists of different stages:
1. Promotion: Promotion stage begins when the idea to form a company comes in the mind of a person.
2. Registration: The second stage in the formation of the company is incorporation or – registration. In this stage, the promoter has to fix name of the company, prepare the necessary documents (Memorandum and Articles of Association), fix the registered office, and name of the directors. After this, certificate of incorporation is issued.
3. Capital Subscription: A public limited company having its share capital has to pass through two stages. One of them is capital subscription. The steps for this is:
- Formalities for raising capital
- Issuing prospectus
- Appointing official banker
- Pass resolution to make allotment
4. Commencement of Business: As per section 11 of the Act, a company having share capital should file with the Registrar, declaration stating that
- Every subscriber has paid the value of shares.
- Paid up capital is not less than Rs.5 lakhs for a public limited company and Rs.1 lakh in case of a private limited company.
- It has filed the Registrar, regarding the verification of registered office. After fulfilling these details, the Registrar will issue certificate of commencement of business.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the various kinds of Debentures?
Answer:
Debenture is a document issued by the company for acknowledging the loan from the public. Debentures are classified into different categories on the basis of:
- Convertibility of the Instrument
- Security of the Instrument
- Redemption ability; and
- Registration of Instrument.
1. On the basis of convertibility:
(a) Non-Convertible Debentures: These instruments cannot be converted into equity shares.
(b) Partly Convertible Debentures: Apart of these instruments are converted into equity shares.
(c) Fully Convertible Debentures: These are fully convertible into equity shares.
(d) Optionally Convertible Debentures: The investor can have the option to either convert the debentures at a price decided by the issuer or agreed upon at the time of issue.
2. On the basis of Security:
(a) Secured Debentures: These instruments are secured by a charge on the fixed assets of the issuer company.
(b) Unsecured Debentures: These instruments are unsecured against the assets.
3. On the basis of Redeemability:
(a) Redeemable Debentures: It refers to the debentures which will be redeemed in future.
(b) Irredeemable Debentures: It is a debenture, in which no specific time is specified by the companies to pay back the money.
4. On the basis of Registration:
(a) Registered Debentures: These are issued in the name of a particular person, who is registered by the company.
(b) Bearer Debentures: These are issued to the bearer and are negotiable instruments, and are transferred by mere delivery.
![]()
Question 4.
What formalities need to be fulfilled for companies having share capital to commence business?
Answer:
A public limited company having its share capital has to pass through two more stages. One of them is capital subscription, steps to be taken at this stage are listed below:
- The fulfilling formalities to raise necessary capital.
- Following the SEBI guidelines in this regard.
- Issuing prospectus.
- Appointing official banker of the company for receiving application from the investors.
- Passing resolution for making allotment by director.
- Despatch allotment letters to allottees.
- Filing allotment return with the Registrar.
- Issuing share certificates in exchange for their allotment letter.
- Ensuring collection of minimum subscription.
Question 5.
Write the difference between Share Certificate and Share Warrant.
Answer:
Share Certificate:
- A share certificate is an instrument in writing for the legal proof of the ownership.
- Every company must issue share certificate to its shareholders.
- Normally, the holder of the share certificate is to be the member of the company.
- The share certificate is issued by the company within three months of the allotment of shares.
- No need to authorized in the Articles of Association to issue share certificate.
Share Warrant:
- A share warrant is a negotiable instrument, issued against fully paid up shares.
- There is no compulsion of the issue of share warrants by the company.
- Generally, the holder of the share warrant is not the member of the company.
- Shares warrant can be issued only when the shares are fully paid up.
- The issue of a share warrant must be authorized in the Articles of Association of the company.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Companies Act 2013 Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below:
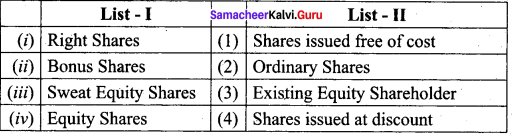
Codes:
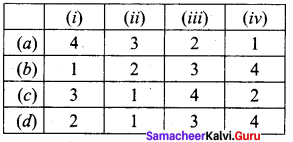
Answer:
(c) 3,1,4,2
![]()
Question 2.
The first two stages of formation of a company are
(i) Issue of prospectus
(ii) Promotion
(iii) Issue of share certificate
(iv) Registration
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer:
(b) (ii) and (iv)