Students can Download Chemistry Chapter 12 Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 12 Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Chapter 12 Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids Text Book Evaluation
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids Multiple Choice Questions
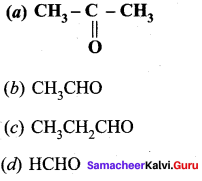
Question 1.
The correct structure of the product ‘A’ formed in the reaction
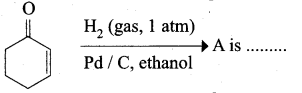
Answer:
Question 2.
The formation of cyanohydrin from acetone is an example of …………..
(a) nucleophilic substitution
(b) electrophilic substitution
(c) electrophilic addition
(d) Nucleophilic addition
Answer:
(d) Nucleophilic addition
Question 3.
Reaction of acetone with one of the following reagents involves nucleophilic addition followed by elimination of water. The reagent is ………….
(a) Grignard reagent
(b) Sn / HCl
(c) hydrazine in presence of slightly acidic solution
(d) hydrocyanic acid
Answer:
(c) hydrazine in presence of slightly acidic solution
Question 4.
In the following reaction,
Product ‘X’ will not give
(a) Tollen’s test
(b) Victor meyer test
(c) Iodoform test
(d) Fehiing solution test
Answer:
(b) Victor meyer test
Hint:
(x) reduces tollens reagent and Fehiing solution and it also answers iodoform test.
Question 5.
In the following reaction,
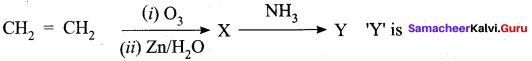
(a) Formaldehyde
(b) diacetoneammonia
(c) hexamethylene tetra amine
(d) oxime
Answer:
(c) hexamethylene tetra amine
Hint:
X – HCHO
Y – (CH2)6 N4
Question 6.
Predict the product Z in the following series of reactions
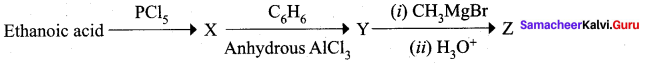
i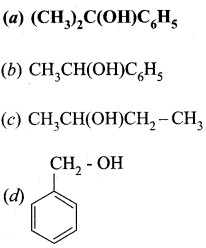
Answer:
![]()
Hint:
Question 7.
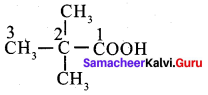
Assertion: 2, 2 – dimethyl propanoic acid does not give HVZ reaction.
Reason: 2 – 2, dimethyl propanoic acid does, not have – a hydrogen atom
(a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) if both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) assertion is true but reason is false
(d) both assertion and reason are false
Answer:
(a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Hint:
Question 8.
Which of the following represents the correct order of acidity in the given compounds
(a) FCH2COOH > CH3COOH > BrCH2COOH > CICH2COOH
(b) FCH2COOH > CICH2COOH > BrCH2COOH > CH3COOH
(c) CH3COOH > CICH2COOH > FCH2COOH > Br – CH2COOH
(d) ClCH2COOH > CH3COOH > BrCH2COOH > ICH2COOH
Hint.
– I effect increases the acidity. If electronegativity is high, – I effect is also high.
Question 9.
Benzoic acid
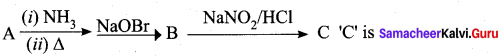
(a) anilinium chloride
(b) O – nitro aniline
(c) benzene diazonium chloride
(d) m – nitro benzoic acid
Answer:
(c) benzene diazonium chloride
Hint:
Question 10.
Ethanoic acid
![]()
2 – bromoethanoic acid. This reaction is called ……………
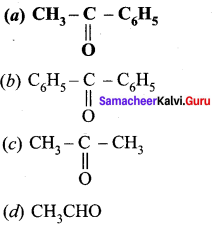
(a) Finkeistein reaction
(b) Haloform reaction
(c) Hell – Volhard – Zelinsky reaction
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) Hell – Volhard – Zelinsky reaction
Question 11.
![]()
(a) acetyl chloride
(b) chlro acetic acid
(c) α – chiorocyano ethanoic acid
(d) none of these
Hint:
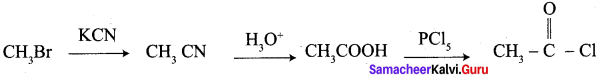
Question 12.
Which one of the following reduces tollens reagent ………
(a) formic acid
(b) acetic acid
(c) benzophenone
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) formic acid
Hint:

Question 13.
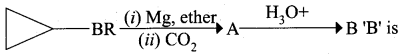
Answer:
Hint:
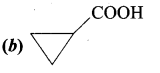
Question 14.
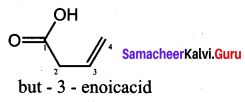
The TUPAC name of
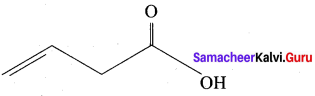 ……………………
……………………
(a) but – 3 – enoicacid
(b) but 1 – ene – 4 – oicacid
(c) but 2 – ene – 1 – oic acid
(d) but – 3 – ene – 1 – oicacid
Answer:
(a) but – 3 – enoicacid
Hint:
Question 15.
Identify the product formed in the reaction
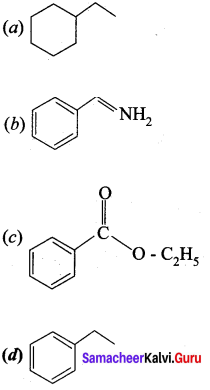
Answer:
Hint:
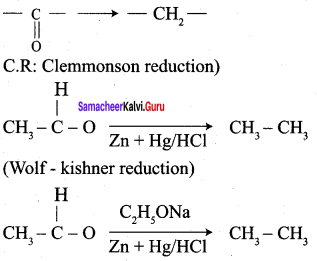
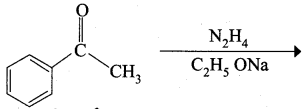
![]() Group is reduced to CH2 – (Wolff – Kishner reduction)
Group is reduced to CH2 – (Wolff – Kishner reduction)
Question 16.
In which case chiral carbon is not generated by reaction with HCN
Answer:
Hint:
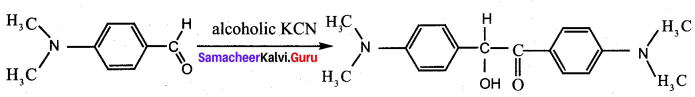
Question 17.
Assertion: p – N, N – dimethyl aminobenzaldehyde undergoes benzoin condensation
Reason: The aldehydic (- CHO) group is meta directing
(a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) if both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) assertion is true but reason is false
(d) both assertion and reason are false
Answer:
(b) if both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Hint:
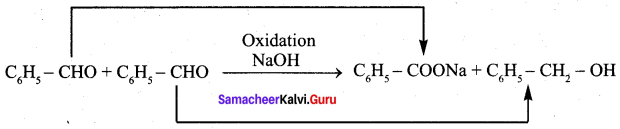
Question 18.
Which one of the following reaction is an example of disproportionation reaction …………….
(a) Aldol condensation
(b) cannizaro reaction
(c) Benzoin condensation
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) cannizaro reaction
Hint:
Question 19.
Which one of the following undergoes reaction with 50% sodium hydroxide solution to give the corresponding alcohol and acid …………
(a) Phenylmethanal
(b) ethanal
(c) ethanol
(d) methanol
Answer:
(a) Phenylmethanal
Question 20.
The reagent used to distinguish between acetaldehyde and benzaldehyde is ………..
(a) Tollens reagent
(b) Fehling’s solution
(c) 2, 4 – dinitrophenyl hydrazine
(d) semicarbazide
Answer:
(b) Fehling’s solution
![]()
Question 21.
Phenyl methanal is reacted with concentrated NaOH to give two products X and Y. X reacts with metallic sodium to liberate hydrogen X and Y are ………….
(a) sodiumbenzoate and phenol
(b) Sodium benzoate and phenyl methanol
(c) phenyl methanol and sodium benzoate
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) phenyl methanol and sodium benzoate
Hint:
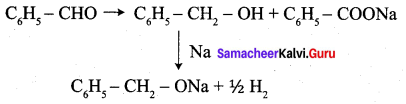
Question 22.
In which of the following reactions new carbon – carbon bond is not formed?
(a) Aldol condensation
(b) Friedel craft reaction
(c) Kolbe’s reaction
(d) Wolf kishner reduction
Answer:
(d) Wolf kishner reduction
Question 23.
An alkene “A” on reaction with O3 and Zn – H2O gives propanone and ethanol in equimolar ratio. Addition of HCl to alkene “A” gives “B” as the major product. The structure of product “B” is ……………
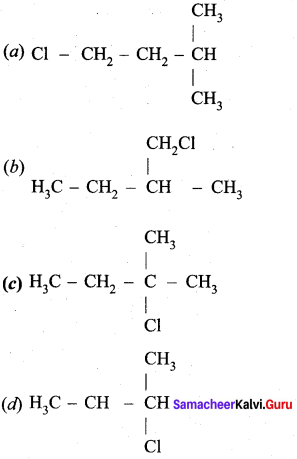
Answer:
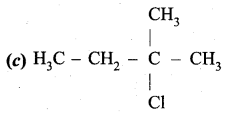
Hint:
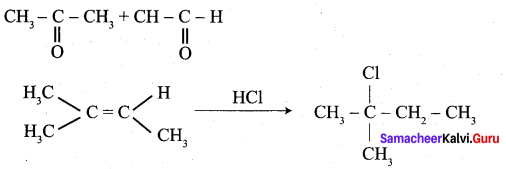
Question 24.
Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular mass. It is due to their ………………
(a) more extensive association of carboxylic acid via van der Waals force of attraction
(b) formation of carboxylate ion
(c) formation of intramolecular H – bonding
(d) formation of intermolecular H – bonding
Answer:
(d) formation of intermolecular H – bonding
Question 25.
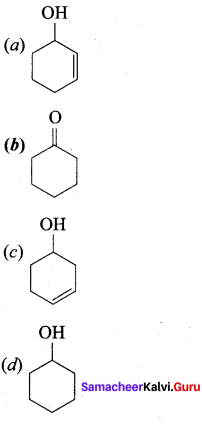
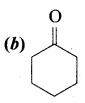
Of the following, which is the product formed when cyclohexanone undergoes aldol condensation followed by heating?
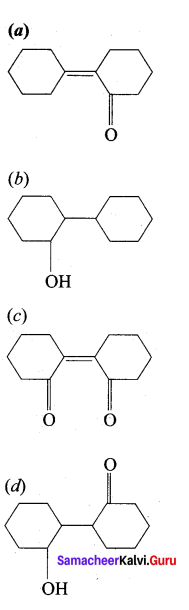
Answer:
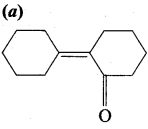
Hint:
II. Answer the following questions.
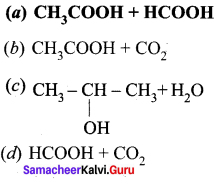
Question 1.
How is propanoic acid is prepared to start from
- an alcohol
- an alkyl halide
- an alkene
Preparation of propanoic acid from,
Answer:
1. Alcohol:
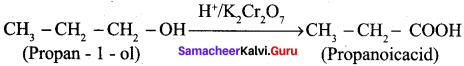
2. Alkylhalide:
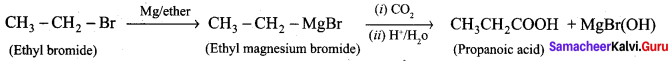
3. Alkene:

Question 2.
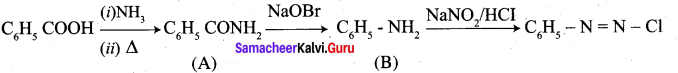
A Compound (A) with molecular formula C2H3N on acid hydrolysis gives(B) which reacts with thionyichioride to give compound(C). Benzene reacts with compound (C) in presence of anhydrous AlCl3 to give compound (C). Compound (C) on reduction with gives (D). Identify (A), (B), (C) and D. Write the equations.
Answer:
1. Compound (A) with molecular formula C2H3N is methyl cyanide. (CH3CN)
2. Methyl cyanide (A) on hydrolysis gives acetic acid (B)
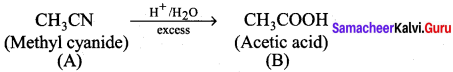
3. Acetic acid (B) with thionyl chloride to give acetyl chloride (C)

4. Benzene reacts with acetyl chloride (C) in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 to give acetophenone (D)

5. Acetyl chloride (C) on reduced in the presence of Pd / H2 and Barium sulphate, to gives acetaldehyde (E).
Question 3.
Identify X and Y
![]()
Answer:
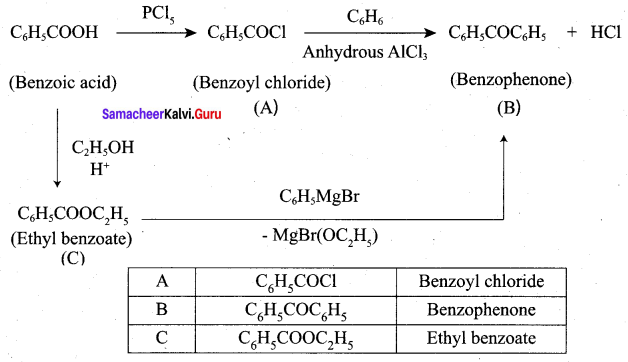
Question 4.
Identify A, B and C
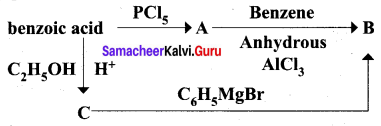
Answer:
Question 5.
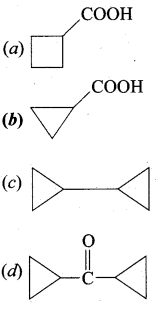
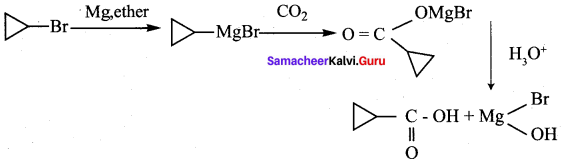
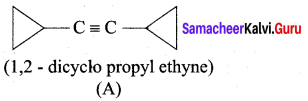
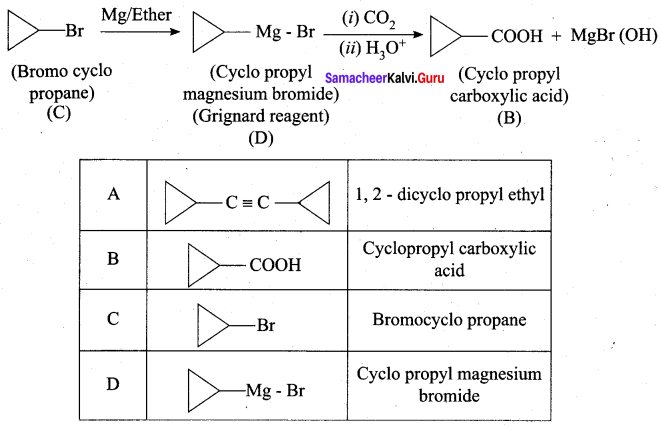
A hydrocarbon A(molecular formula C8H10) on ozonolysis gives B(C4H6O2 ) only. Compound C( C3H5Br) on treatment with magnesium in dry ether gives (D) which on treatment with CO2 followed by acidification gives (B). Identify A, B, C and D.
Answer:
1. Molecular formula C8H10 is 1, 2 – di-cyclopropyl ethyne.
2. 1, 2 – dicyclo propyl ethyne (A) on ozonolysis to give cyclo propyl carboxylic acid (B)
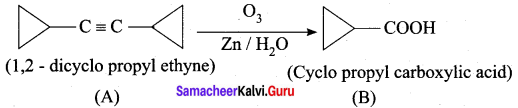
3. Compound C3H5Br is Bromo cyclopropane (C), which on reacts with Mg in dry ether gives Grignard reagent (D) which on treatment with CO2 followed by acidification gives cyclopropyl carboxylic acid (B).
Question 6.
Identify A, B, C and D
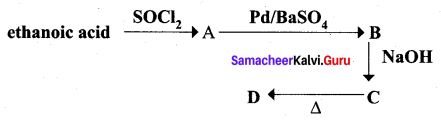
Answer:
Question 7.
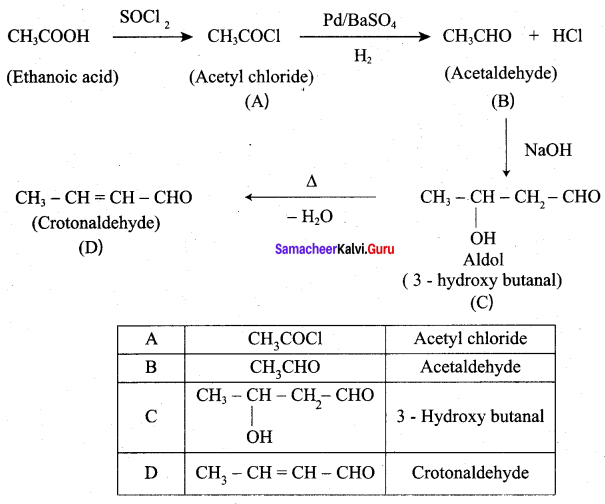
An alkene (A) on ozonolysis gives propanone and aldehyde (E). When (B) is oxidised (C) is obtained. (C) is treated with Br2 JP gives (D) which on hydrolysis gives (E). When propanone is treated with HCN followed by hydrolysis gives (F). Identify A, B, C, D and E and F.
Answer:
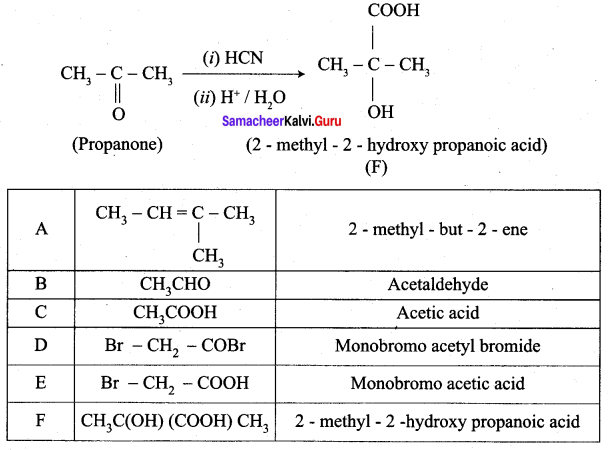
1. 2 – methyl – but – 2 – ene (A) on ozonolysis gives propanone and acetaldehyde (B)
2. Acetaldehyde (B) is oxidised to give acetic acid (C), which on further treated with Br2 / P give monobromo acetyl bromide (D) which on hydrolysis gives monobromo acetic acid (E).
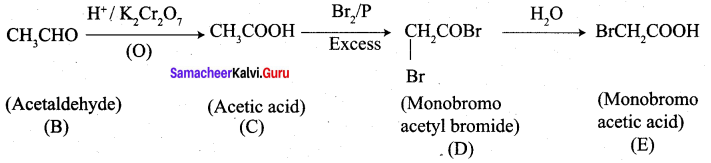
3. Propanone is treated with HCN followed by hydrolysis to gives 2 – methyl – 2 – hydorxy propanoic acid (F)
Question 8
How will you convert benzaldehyde into the following compounds?
- benzophenone
- benzoic acid
- 2 – hydroxyphenylaceticacid.
Answer:
1. conversion of benzaldehyde into benzophenone.
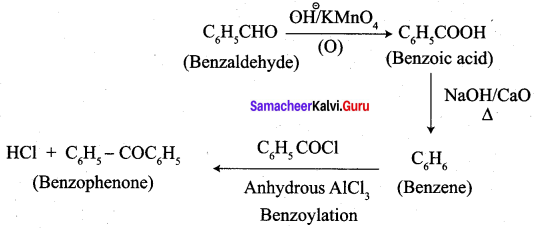
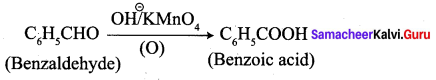
2. conversion of benzaldehyde into benzoic acid.
3. conversion of benzaldehyde into 2 – hydroxy phenyl acetic acid.
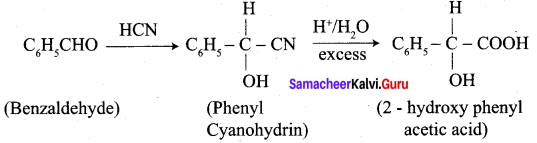
Question 9.
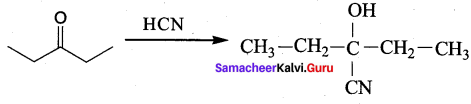
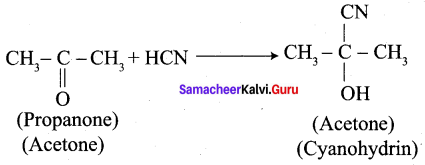
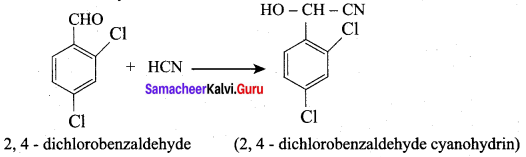
What is the action of HCN on
- propanone
- 2, 4 – dichlorobenzaldehyde.
Answer:
1. Propanone reacts with HCN.
2. 2, 4 – dichlorobenzaldehyde reacts with HCN.
Question 10.
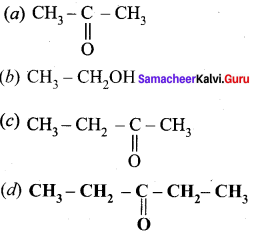
A carbonyl compound A having molecular formula C5H10O forms crystalline precipitate with sodium bisuiphate and gives positive iodoform test. A does not reduce Fehling solution. Identify A.
Answer:
1. 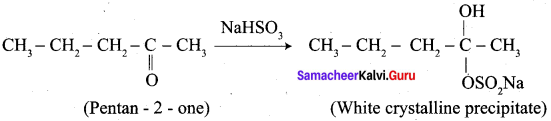
2. Pentan – 2 – one gives positive iodoform test, but it does not reduce Fehling’s solution.
3. Hence carbonyl compound A having molecular formula C5H10O is pentan – 2 – one.
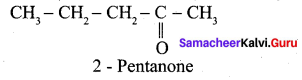
Question 11.
Write the structure of the major product of the aldol condensation of benzaldehyde with acetone.
Answer:
Step 1:
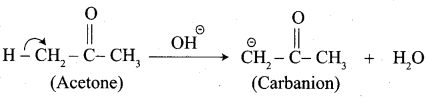
Step 2:
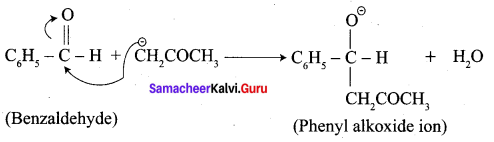
Step 3:
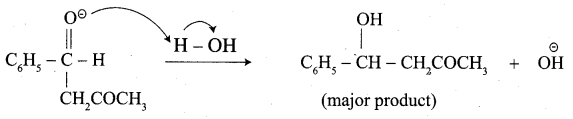
Step 4:
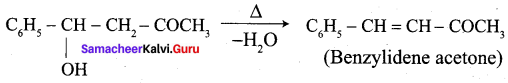
Question 12.
How are the following conversions effected
- propanal into butanone
- Hex – 3 – yne into hexan – 3 – one.
- phenylmethanal into benzoic acid
- phenylmethanal into benzoin
Answer:
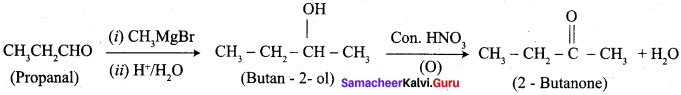
1. propanal into butanone
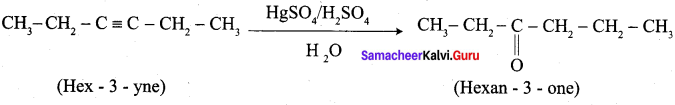
2. Hex – 3 – yne into hexan – 3 – one
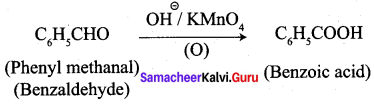
3. phenylmethanal into benzoic acid
4. phenyl methanal into benzoin
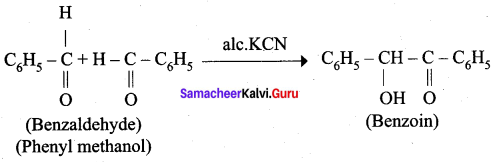
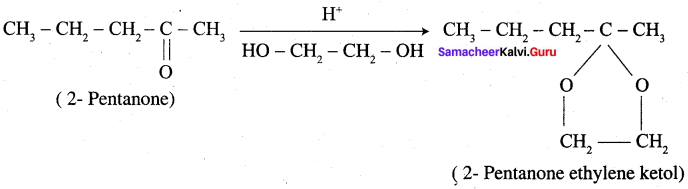
Question 13.
Complete the following reaction.
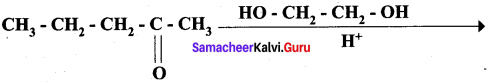
Answer:
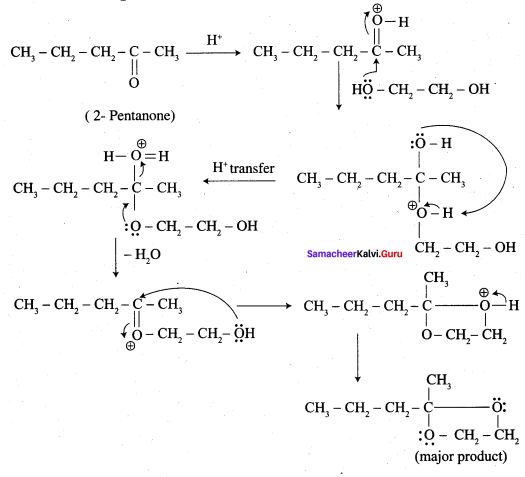
Overall reaction:
Question 14.
Identify A, B and C
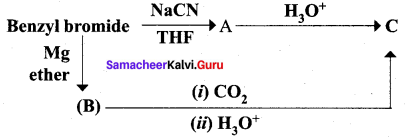
Answer:
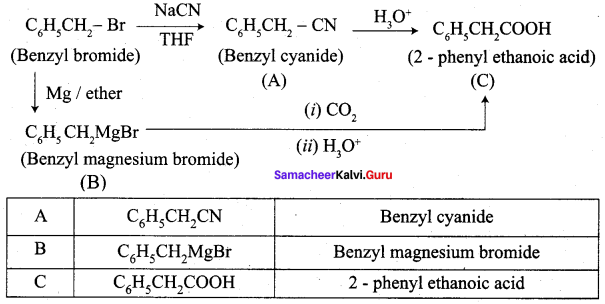
Question 15.
When ketones are undergo oxidation, the C – C bond Is cleaved. When a strong oxidising agent is used to oxidise 2, 5 – dimethyl hexan – 3 – one mention the products with their names.
Answer:
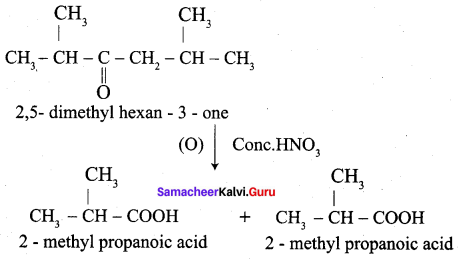
Question 16.
How will you convert following conversion?
- Acetic acid into acetic anhydride
- Methyl acetate into ethyl acetate
- Methyl acetate into acetamide
- Acetyl chloride into acetophenone
- Sodium acetate into ethane
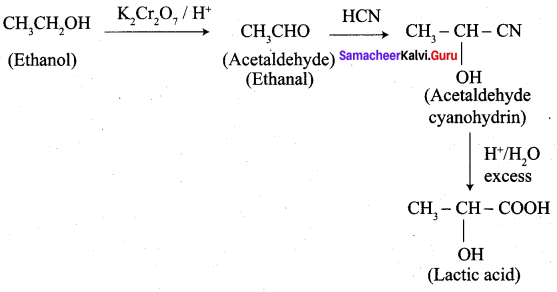
- Ethanal into lactic acid
- Toluene into benzoic acid
- Benzaldehyde into malachite green
- Benzaldehyde into Cinnamic acid
- Ethyne into acetaldehyde
Answer:
1. Conversion of Acetic acid into acetic anhydride
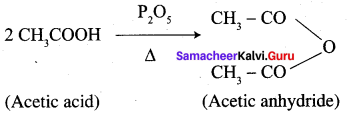
2. Conversion of Methyl cyanate into acetamide.

3. Conversion of Methyl cyanate into acetamide.
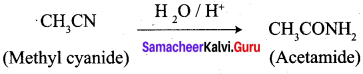
4. Conversion of Acetyl chloride into acetophenone.

5. Conversion of Sodium acetate into ethane.
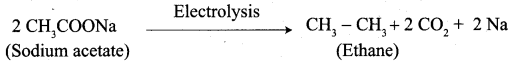
6. Conversion of Ethanal into lactic acid.
7. Conversion of Toluene into benzoic acid.
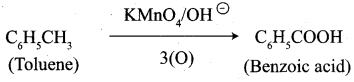
8. Conversion of Benzaldehyde into malachite green.
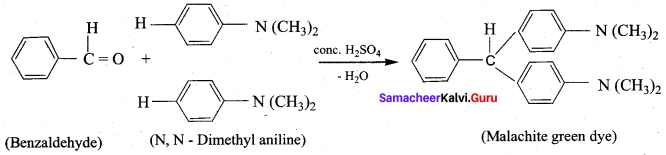
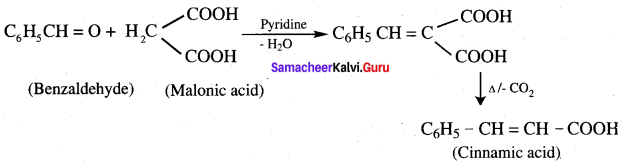
9. Conversion of benzaldehyde into cinnamic acid.
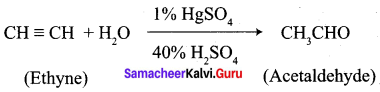
10. Conversion of Ethyne into acetaldehyde.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids Evaluate yoursel
Question 1.
Write the IUPAC name for the following compound.
Answer:
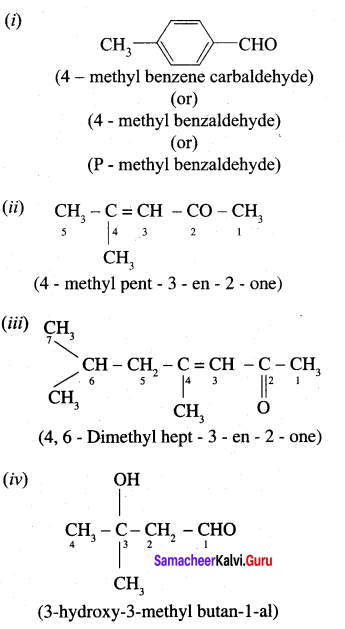
Question 2.
Write all possible structural isomers and position isomers for the ketone represented by the molecular formula C5H10O.
Answer:
Molecular formula C5H10O exhibits following possible ketone structural isomers and position isomers.
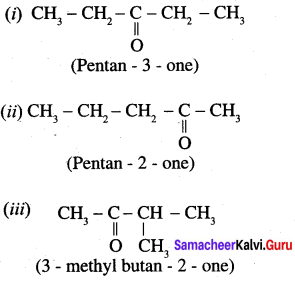
Question 3.
What happens when the following alkenes are subjected to reductive ozonolysis.
- propene
- 1 – Butene
- Isobutylene
Answer:
1. propene
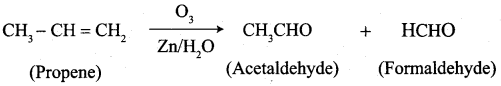
2. 1 – Butene
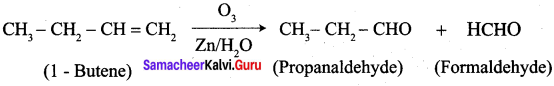
3. Isobutylene
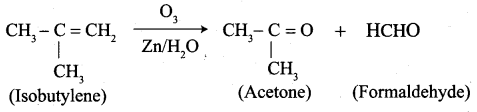
Question 4.
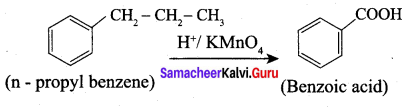
What happens when n-propyl benzene is oxidised using H+ / KMnO4?
Answer:
When n – propyl benzene is oxidised with H+ / KMnO4 to gives benzoic acid.
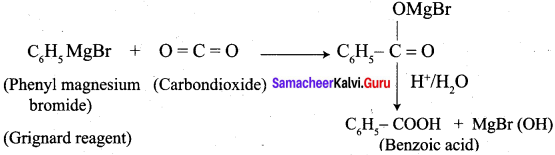
Question 5.
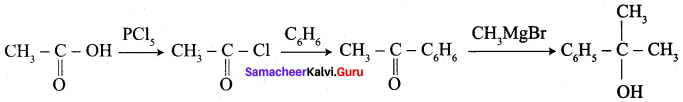
How will you prepare benzoic acid using Crignard reagent.
Answer:
Preparation of benzoic acid using Grignard reagent:
Question 6.
Why acid anhydride are preferred to acyl chloride for carrying out acylation reactions?
Answer:
- Since acyl chlorides are more reactive, their reactions are very fast and difficult to control.
- Acid anhydrides are less reactive than acyl chlroides and their reactions can be easily controlled.
- Hence acid anhydrides are preferred to acyl chlorides for carrying out acylation reactions.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids Additional Questions
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids 1 Mark Questions and Answers
I. Choose the best answer.
Question 1.
Which one of the following aldehyde is derived from vitamin B, function as a co – enzyme?
(a) Pyridoxal
(b) Formaldehyde
(c) Ethanal
(d) Propanal
Answer:
(a) Pyridoxal
Question 2.
Which one of the following is used in the manufacture of Bakelite?
(a) Methanal
(b) Ethanal
(c) Phenyl methanal
(d) Butanal
Answer:
(a) Methanal
![]()
Question 3.
Which is used as a drug to reduce fever?
(a) Diethyl ether
(b) Acetone
(c) Acetophenone
(d) Paracetamol
Answer:
(d) Paracetamol
Question 4.
The IUPAC name of Acrolein is
(a) Prop – 2 – enal
(b) Propanal
(c) Ethenal
(d) 1 – butanal
Answer:
(a) Prop – 2 – enal
Question 5.
The IUPAC name of crotanaldehyde CH3 – CH = CH – CHO is …………….
(a) Prop – 2 – enal
(b) But – 2 – enal
(c) Ethenal
(d) Phenyl methanal
Answer:
(b) But – 2 – enal
Question 6.
The IUPAC name of is
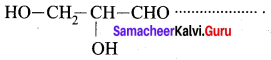 …………………..
…………………..
(a) Glyceraldehyde
(b) Acrolein
(c) 2, 3 – dihydroxy propanal
(d) Butanal
Answer:
(c) 2, 3 – dihydroxy propanal
Question 7.
Which one of the following is called Mesityl oxide?
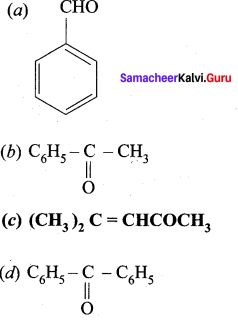
Answer:
![]()
Question 8.
Which one of the following is called 3 – oxopentanal?
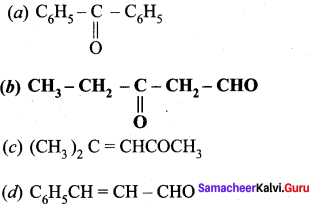
Answer:
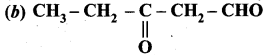
Question 9.
Which one of the following is names as 3 – methyl cyclopentanone?
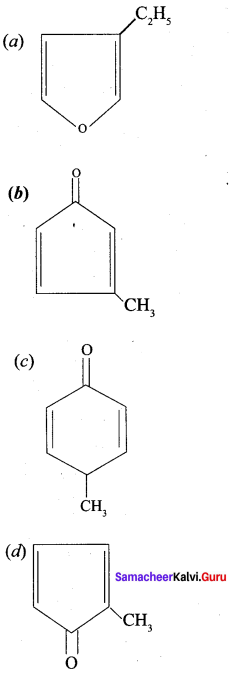
Answer:
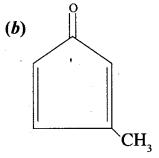
Question 10.
Which one of the following is the hybridised state of C atoms in carbonyl carbon?
(a) sp
(b) sp3d
(c) sp3
(d) sp2
Answer:
(d) sp2
Question 11.
Which of the following reagent is used to get aldehyde from alcohol by oxidation method?
(a) Na2Cr2O7
(b) KMnO4
(c) PCC
(d) LiAlH4
Answer:
(c) PCC
Question 12.
The product formed when but – 2 – ene is on ozonolysis is ………….
(a) Propanone
(b) Methanal
(ç) Ethanal
(d) Butanal
Answer:
(ç) Ethanal
Question 13.
Which one of the following should be ozonolysed to get a mixture of ethanal and propanone?
(a) Propene
(b) But – 2 – ene
(c) Ethylene
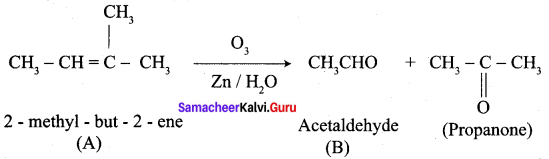
(d) 2 – methyl – but – 2 – ene
Answer:
(d) 2 – methyl – but – 2 – ene
![]()
Question 14.
The products formed when propene is ozonolysed are …………….
(a) HCHO + CH3CHO
(b) CH3CHO
(c) HCOOH + CH3COOH
(d) CH3COCH3
Answer:
(a) HCHO + CH3CHO
Question 15.
Identify the products formed when But- 1-ene undergoes reductive ozonolysis?
(a) HCHO + CH3CHO
(b) HCHO + CH3CH2CHO
(c) CH3COCH3 + CH3CHO
(d) HCHO + CH3COCH3
Answer:
(b) HCHO + CH3CH2CHO
Question 16.
Which one of the following should be subjected to reductive ozonolysis to get only formal dehyde?
(a) CH ≡ CH
(b) CH3 – CH = CH2
(c) CH2 = CH2
(d) CH3 – CH3
Answer:
(c) CH2 = CH2
Question 17.
What are the products formed when Isobutylene is subjected to ozonolysis?
(a) HCHO + CH3CHO
(b) CH3COCH3 + HCHO
(c) CH3CHO + CH3COCH
(d) CH3COCH3 + CH3CH2CHO
Answer:
(b) CH3COCH3 + HCHO
Question 18.
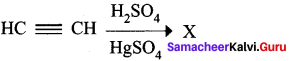
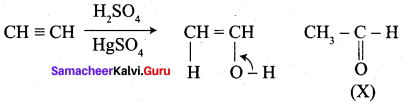
Which one of the following is formed when acetylene is hydrolysed in the presence of HgSO4 and H2SO4?
(a) Ethanal
(b) Ethylene
(c) Ethane
(d) Ethanol
Answer:
(d) Ethanol
Question 19.
Hydrolysis of prop – 1 – yne in the presence of HgSO4 and H2SO4 gives ……………
Answer:
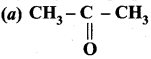
Question 20.
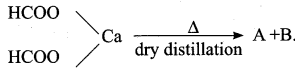
Answer:
(a) CaCO3 + H2
(b) CO2 + H2O + Ca
(c) HCHO + CaCO3
(d) CO + H2O + Ca(OH)2
Answer:
(c) HCHO + CaCO3
Question 21.
Calciwn acetate on dry distillation gives …………
(a) Acetic acid
(b) Propanone
(c) Ethanol
(d) Propanal
Answer:
(b) Propanone
Question 22.
Which of the following calcium salts are required to get ethanal by dry distillation process?
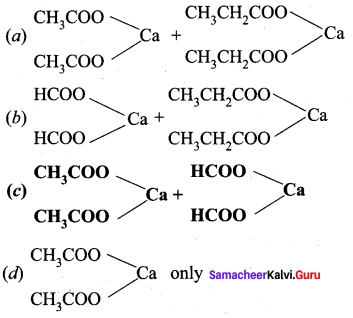
Answer:
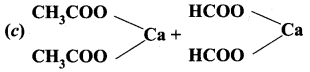
Question 23.
The conversion of acetyl chloride to acetaldehyde by the action of Pd/BaSO4 is called ………………..
(a) Perkin’s reaction
(b) Stephens reaction
(c) Clemmenoon reduction
(d) Rosenmund reduction
Answer:
(d) Rosenmund reduction
Question 24.
Which of the following cannot be prepared by Rosenmund reduction method?
(a) Acetaldehyde
(b) Formaldehyde
(c) Ketone
(d) Both b & c
Answer:
(d) Both b & c
![]()
Question 25.
In Rosenmunds reduction, the action of BaSO4 is …………….
(a) Promoter
(b) Catalyst poison
(c) Positive catalyst
(d) Negative catalyst
Answer:
(b) Catalyst poison
Question 26.
Which one of the following is an intermediate product in Stephen’s reaction?
(a) Amines
(b) Amides
(c) Imines
(d) Amino acid
Answer:
(c) Imines
Question 27.
Which one of the following is used as selective reducing agent in the conversion of cyanide to aldehyde?
(a) Raney Ni
(b) LiAlH4
(c) SnCl2 / HCl
(d) DIBAL – H
Answer:
(d) DIBAL – H
Question 28.
Identify the product formed when benzaldehyde reacts with chromyl chloride?
(a) Benzoic acid
(b) Benzaldehyde
(c) Phenyl methanol
(d) Phenol
Answer:
(b) Benzaldehyde
Question 29.
The conversion reaction of Benzene to Benzaldehyde is known as ……………..
(a) Rosenmund reduction
(b) Stephen reduction
(c) Gattermann koch reaction
(d) Friedel – crafts reaction
Answer:
(c) Gattermann koch reaction
![]()
Question 30.
Which one of the following is used to convert acetyl chloride to acetone?
(a) CdCl2
(b) CrO2CI2
(c) Cu2CI2
(d) NaCl
Answer:
(a) CdCl2
Question 31.
Which one of the following is the best method to prepare alkyl aryl ketone and diaryl ketones?
(a) Stephen reaction
(b) Knoevengal reaction
(c) Ciemmenson reduction
(d) Friedel crafts reaction
Answer:
(d) Friedel crafts reaction
Question 32.
The product formed when Benzoyl chloride reacts with benzene is ………….
(a) Benzyl benzoate
(b) Benzophenone
(c) Benzyl chloride
(d) Benzyl alcohol
Answer:
(b) Benzophenone
Question 33.
Which one of the following is used as catalyst in Friedel Crafts reaction?
(a) Anhydrous ZnCl2
(b) Anhydrous CuCl2
(c) Anhydrous AlCl3
(d) Androus CaCl2
Answer:
(c) Anhydrous AlCl3
Question 34.
During nucleophilic addition reaction, the hybridisation of carbon changes from
(a) sp2 to sp3
(b) sp3 to sp2
(c) sp to sp3
(d) dsp2 to sp3
Answer:
(a) sp2 to sp3
Question 35.
Which one of the following is formed as a product when ethanal is treated with 2 equivalent of methanol?
(a) 1, 1 – dimethoxy methane
(b) 1 ,2 – dimethoxy ethane
(c) 1, 1 – dimethoxy ethane
(d) 1, 1 – diethoxy ethane
Answer:
(c) 1, 1 – dimethoxy ethane
Question 36.
Which aldehyde does not give aldimine with etheral ammonia solution?
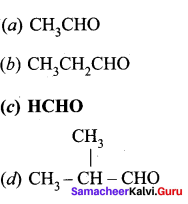
Answer:
![]()
Question 37.
Identify the product formed when acetaldehyde reacts with ammonia?
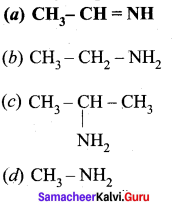
Answer:
![]()
Question 38.
Which one of the following is formed when methanal reacts with ammonia?
(a) Tetramethylene hexamine
(b) Hexamethylene tetramine
(c) Formaldehyde ammonia
(d) Aldimine
Answer:
(b) Hexamethylene tetramine
![]()
Question 39.
Which one of the following is used as, an urinary antiseptic?
(a) Urotropine
(b) Urea formaldehyde
(c) Formalin
(d) Aldimm
Answer:
(a) Urotropine
Question 40.
Which one of the reactions gives an explosive RDX?
(a) Nitration of phenol
(b) Nitration of glycol
(c) Nitration of urotropine
(d) Nitration of glycerol
Answer:
(c) Nitration of urotropine
Question 41.
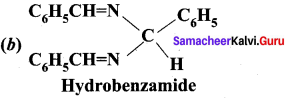
Which one of the following is called hydrobenzamide?
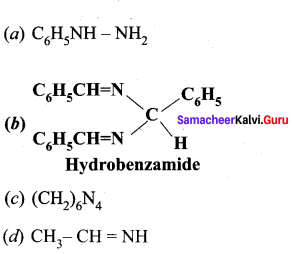
Answer:
Question 42.
Which one of the following is formed when benzaldehyde reacts with ammonia?
(a) Benzalamine
(b) Benzylamine
(c) Hydrobenzarnide
(d) Benzarnide
Answer:
(c) Hydrobenzarnide
Question 43.
Which rule governes the oxidation of unsymmetrical ketone?
(a) Markovnikoff’s rule
(b) Popoff s rule
(c) Antimarkovnikoff s rule
(d) Hund’s rule
Answer:
(b) Popoff s rule
Question 44.
What are the products formed when 2-butanonc is oxidised by conc – HNO3?
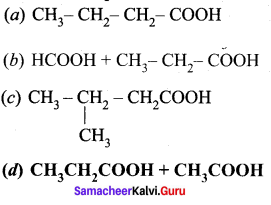
Answer:
![]()
Question 45.
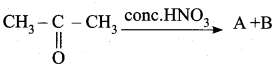
In this reaction A and B are …………
Answer:
![]()
Question 46.
Name the product formed Acetaldehyde reacts with Zinc amalgam and conc.HCl?
(a) Propane
(b) Ethane
(c) Ethene
(d) Ethanal
Answer:
(b) Ethane
Question 47.
The reagent used in the Conversion of ![]() group into – CH2 – group is …………..
group into – CH2 – group is …………..
(a) Zn + Hg / HCl
(b) NH2 – NH2 + C2H5ONa
(c) mg / Hg / H2O
(d) either (a) or (b)
Answer:
(d) either (a) or (b)
Question 48.
The product formed when Acetone is subjected to Clemmenson reduction is ……………..
(a) Acetic acid
(b) Propanoic acid
(c) Propane
(d) Propanal
Answer:
(c) Propane
![]()
Question 49.
Which one of the following is formed when acetone is treated with magnesium amalgam and water?
(a) Pinacol
(b) Acetyl acetone
(c) Aceto acetic ester
(d) 1 ,2 – dimethyl butane 1, 2 – diol
Answer:
(a) Pinacol
Question 50.
Which one of the following does not undergo halo form reaction?
Answer:
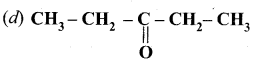
Question 51.
Which one of the following undergoes halo form reaction?
(a) HCHO
(b) C6H5CHO
(c) CH3CHO
(d) CH3 – CH2 – CH2OH
Answer:
(c) CH3CHO
Question 52.
Which one of the following is formed when acetaldehyde is warmed with dilute NaOH?
(a) But – 2 – enal
(b) Butan – 1 – al
(c) 3 – hydroxy butanal
(d) 2 – hydroxybutanoic acid
Answer:
(c) 3 – hydroxy butanal
Question 53.
The IUPAC naine of Acetaldol is ……………
(a) 3 – hydroxy butanal
(b) Aldol
(c) 2 – hydroxy butanal
(d) Butanal
Answer:
(a) 3 – hydroxy butanal
Question 54.
Which one of the following is formed when benzaldehyde reacts with acetaldehyde?
(a) Cinnamic acid
(b) Cinnamaldehyde
(c) Benzylidene acetone
(d) 3 – hydroxy propanal
Answer:
(b) Cinnamaldehyde
Question 55.
The crossed aldol condensation product of the reaction between Formaldehyde and Acetaldehyde is ………………
(a) 3 – hydroxy propanol
(b) 3 – hydroxy propanal
(c) 2 – hydroxy butanal
(d) 3 – hydroxy butanal
Answer:
(b) 3 – hydroxy propanal
![]()
Question 56.
The reaction of benzaldehyde with 50% NaOH is called …………..
(a) Benzoin condensation
(b) Claisen – schmidt reaction
(c) Perkin’s reaction
(d) Cannizaro reaction
Answer:
(d) Cannizaro reaction
Question 57.
The reaction of phenyl methanal and ethanal in the presence of dilute NaOH is known as ……………..
(a) Cannizaro reaction
(b) Aldol condensation
(c) Claisen – schmidt condensation
(d) Perkin’s reaction
Answer:
(c) Claisen – schmidt condensation
Question 58.
What is the second step in Cannizaro reaction mechanism?
(a) Attack of OH– on carbonyl carbon
(b) Acid base reaction
(c) Protonation of carbonyl oxygen
(d) Hydride ion transfer
Answer:
(d) Hydride ion transfer
Question 59.
The first step take place in Cannizaro reaction mechanism is ……………..
(a) Aftack of OH– on carbonyl carbon
(b) Protonation of carbonyl oxygen
(c) Acid base reaction
(d) Hydride ion transfer
Answer:
(a) Aftack of OH– on carbonyl carbon
Question 60.
Which one of the following is formed when benzaldehyde reacts with alcoholic KOH?
(a) Benzyl alcohol
(b) Potassium henzoate
(c) Benzoin
(d) Benzoic acid
Answer:
(c) Benzoin
Question 61.
What is the name of the reaction of alcoholic KOH with Benzaldehyde’?
(a) Cannizaro reaction
(c) Benzoin condensation
(b) Perkin’s reaction
(d) Aldol condensation
Answer:
(c) Benzoin condensation
![]()
Question 62.
Which one of the following is formed when benzaldehyde reacts with acetic anhydride?
(a) Cinnamaldehyde + Acetaldehyde
(b) Cinnamic acid + Acetic acid
(c) Benzyl alcohol + Benzoic acid
(d) Benzal aniline + Acetic acid
Answer:
(b) Cinnamic acid + Acetic acid
Question 63.
What is the name of the reaction between Benzaldehyde and acetic anhydride?
(a) Peridn’s reaction
(b) Knoerenagal reaction
(c) Cannizaro reaction
(d) Kolbe’s reaction
Answer:
(a) Peridn’s reaction
Question 64.
What are the reagents required to prepare Benzal aniline (or) Schiff’s base?
(a) Benzyl amine + Ammonia
(b) Benzal amine + Ammonia
(c) Benzaldehyde + Aniline
(d) Phenol + Aniline
Answer:
(c) Benzaldehyde + Aniline
Question 65.
Which one of the following is the formula of Schiff’ s base’?
(a) C6H5 – NH NH2
(b) C6H5 CH = N – C6H5
(b) Perkin’s reaction
(d) Aldol condensation
Answer:
(b) C6H5 CH = N – C6H5
Question 66.
Which one of the following is used as a catalyst in Knoevenagal reaction?
(a) Pyrimidine
(b) Pyridine
(c) PCC
(d) CdCl2
Answer:
(b) Pyridine
Question 67.
Which one is formed when Benzaldehyde reacts with Malonic acid in the presence of Pyridine?
(a) Cinnamaldehyde
(b) Benzoin
(c) Hydrobenzamide
(d) Cinnamic acid
Answer:
(d) Cinnamic acid
Question 68.
Name the product formed when Benzaldehyde reacts with N,N – dimethyl aniline in the presence of conc.H2SO4?
(a) Cinnamic acid
(b) Skiffs base
(c) Malachite green dye
(d) p – hydroxy azodye
Answer:
(c) Malachite green dye
Question 69.
Identify the product formed when benzaldehyde reacts with chlorine in the presence of conc.FeCl3?
(a) m – chlorobenzaldehyde
(b) O – chlorobenzaldehyde
(c) p – chiorobenzaldehyde
(d) Benzoyl chloride
Answer:
(a) m – chlorobenzaldehyde
Question 70.
Identify the product formed when benzaldehyde reacts with chlorine in the absence of catalyst?
(a) p – chiorobenzaldehyde
(b) O – chiorobenzaldehyde
(c) Benzoyl chloride
(d) m – chlorobenzaldehyde
Answer:
(c) Benzoyl chloride
![]()
Question 71.
Which one of the following is used to test ketones?
(a) lodoform test
(b) Tollen’s reagent test
(c) Fehling’s solution test
(d) Benedict’s solution test
Answer:
(a) lodoform test
Question 72.
Which one of the following is not used to identify aldehydes?
(a) Benedict’s solution test
(b) Fehling’s solution test
(c) Dye test
(d) Tollen’s reagent test
Answer:
(c) Dye test
Question 73.
What is the colour change take place when Fehling’s solution is added to an aldehyde?
(a) Red to blue
(b) Blue to red
(c) Red to green
(d) Green to blue
Answer:
(b) Blue to red
Question 74.
Which one of the following is used for preserving biological specimens?
(a) Urotropine
(b) Formalin
(c) Schiff’s base
(d) Benzoin
Answer:
(b) Formalin
Question 75.
Which one of the following is formed when phenol is heated with formalin?
(a) Bakelite
(b) PVC
(c) Polyurethane
(d) Polyester
Answer:
(a) Bakelite
![]()
Question 76.
RDX is otherwise named as …………….
(a) Cyclonite
(b) Cyclohexane
(c) 1, 4 – dione
(d) Cyclohexanol
Answer:
(a) Cyclonite
Question 77.
Which one of the following is used as a hypnotic?
(a) Acetaldehyde
(b) Formalin
(c) Paraldehyde
(d) Formaldehyde
Answer:
(c) Paraldehyde
Question 78.
Which one of the following is used in silvering of mirrors?
(a) Paraldehyde
(b) Benzaldehyde
(c) Acetone
(d) Acetaldehyde
Answer:
(d) Acetaldehyde
Question 79.
Which one of the following is used in the manufacture of smokeless powder (cordite)?
(a) Acetone
(b) Acetaldehyde
(c) Acetic acid
(d) Formaldehyde
Answer:
(a) Acetone
Question 80.
Which one of the following is used as nail polish remover?
(a) CH3CHO
(b) HCHO
(c) CH3COCH3
(d) C6H5COCH3
Answer:
(c) CH3COCH3
Question 81.
Which is used in the manufacture of thermosoftening plastic perspex?
(a) Acetaldehyde
(b) Formaldehyde
(c) Acetone
(d) Acetophenone
Answer:
(c) Acetone
Question 82.
Which of the following is called hyphone?
Answer:
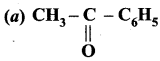
Question 83.
Which of the following is used in the preparation of benzhydrol drop?
(a) Benzaldehyde
(b) Benzophenone
(c) Acetophenone
(d) Benzoin
Answer:
(b) Benzophenone
Question 84.
Consider the following statements.
(i) Terminal olefins gives Formaldehyde as one of the product
(ii) Oxidation of alcohols using pcc yield carboxylic acids
(iii) Catalytic dehydrogenation of alcohols give either aldehyde or ketone.
Which of the above statement is/are not correct?
(a) (ii) only
(b) (i) & (iii)
(c) (ii) & (iii)
(d) (ii) only
Answer:
(a) (ii) only
![]()
Question 86.
Consider the following statements:
(i) Formaldehyde is a gas at room temperature and acetaldehyde is a volatile liquid.
(ii) The oxidation of symmetrical ketones is governed by Popoti’s rule.
(iii) Aliphatic aldehyde react with primary amines in the presence of base gives Schiff’s base.
Which of the above statement is/are not correct?
(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) only
(c) (ii) & (iii)
(d) (i) & (ii)
Answer:
(c) (ii) & (iii)
Question 87.
The JUPAC name of is
(a) Benzene carboxylic acid
(b) Benzoic acid
(c) 2 – phenyl ethanoic acid
(d) 2 – phenyl acetic acid
Answer:
(c) 2 – phenyl ethanoic acid
Question 88.
The formula of malonic acid is …………
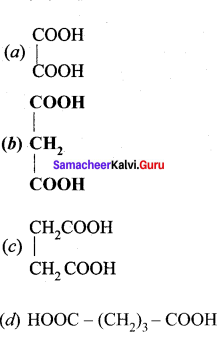
Answer:
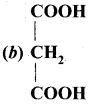
Question 89.
The IUPAC name of HOOC – (CH2)4 – COOH is ………………
(a) Adipic acid
(b) Butane dioic acid
(c) Hexane diolc acid
(d) Glutaric acid
Answer:
(c) Hexane diolc acid
Question 90.
Which one of the following is the formula of Succinic acid?
(a) HOOC – CH2 – COOH
(b) HOOC – (CH2)2 – COOH
(c) HOOC – (CH2)4 – COOH
(d) HOOC – (CH)3 – COOH
Answer:
(b) HOOC – (CH2)2 – COOH
Question 91.
Consider the following statements.
(i) In – COOH group, the centre carbon atom and both the oxygen atoms are in sp3 hybridisation.
(ii) RCOOH can be represented as a resonance hybrid of two canonical structures.
(iii) Carboxylic carbon is less electrophilic than carbonyl carbon because of the reasonan structure.
Which of the above statement is/are correct?
(a) (iii) only
(b) (ii) only
(c) (i) only
(d) (i) & (ii)
Answer:
(b) (ii) only
Question 92.
Which one of the following reacts with methyl magnesium iodide followed by acid hydrolysis yield acetic acid?
(a) Solid CO2
(b) HCHO
(c) CH3CHO
(d) CH3CN
Answer:
(a) Solid CO2
![]()
Question 93.
Which one of the following acid cannot be prepared from grignaid reagent by the action of dry ice?
(a) CH3COOH
(b) C6H5COOH
(c) CH3 – CH2COOH
(d) HCOOH
Answer:
(d) HCOOH
Question 94.
Which one of the following is formed as a product when Benzoic anhydride is hydrolysed?
(a) Benzoin
(b) Benzoic acid
(c) Benzyl alcohol
(d) Benzaldehyde
Answer:
(b) Benzoic acid
Question 95.
Consider the following statements.
(i) Carboxylic acids have higher boiling point than aldehyde and ketone due to the association of carboxylic acid.
(ii) Vinegar is 60 to 80% solution of acetic acid in water
(iii) Higher carboxylic acids are insoluble in water due to increased hydrophobic interaction of hydrocarbon part.
Which of the above statement is/are not correct’?
(a) (iii) only
(b) (ii) only
(c) (i) only
(d) (i) & (iii)
Answer:
(b) (ii) only
![]()
Question 96.
Which one of the following is formed when ethanoic acid is treated with HI and Red phosphorous?
(a) Ethane
(b) Ethene
(c) Ethyne
(d) Methane
Answer:
(a) Ethane
Question 97.
What will be the product formed when sodium acetate is treated with sodalime?
(a) C2H6
(b) CH4
(c) CH3COOH
(d) (CH3CO)2O
Answer:
(b) CH4
Question 98.
The reaction of electrolysis of sodium acetate to form ethane is known as ………………..
(a) Kolbe’s electrolytic decarboxylation
(b) Perkin’s reaction
(c) Clemmenson reaction
(d) Cannizaro reaction
Answer:
(a) Kolbe’s electrolytic decarboxylation
Question 99.
Sodium formate solution on electrolysis gives at anode.
(a) Methane + CO2
(b) Ethane + CO2
(c) H2 + CO2
(d) Formic acid
Answer:
(c) H2 + CO2
Question 100.
Which one of the following is formed when acetic acid is heated with phosphorous pentoxide?
(a) CH3COCH3
(b) CH3CONH2
(c) CH4
(d) (CH3CO)2O
Answer:
(d) (CH3CO)2O
Question 101.
The reaction of acetic acid with Cl2 and red phosphorous is named as ………………
(a) Kolbe’s reaction
(b) Reimer – Tiemann reaction
(c) HeII – volhard – zelinsky reaction
(d) Knoevenagal reaction
Answer:
(c) HeII – volhard – zelinsky reaction
Question 102.
Which one of the following does not undergo friedel crafts reaction?
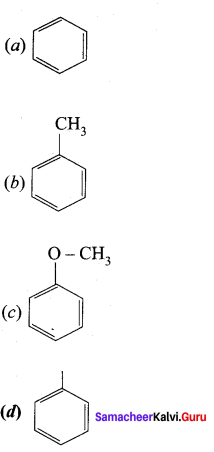
Answer:
Question 103.
Which one of the following can act as a reducing agent?
(a) C6H5COOH
(b) HCOOH
(c) CH3COOH
(d) CH3 – CH2COOH
Answer:
(b) HCOOH
Question 104.
Consider the following statements.
(i) Carboxylic acids turn red litmus blue.
(ii) Carboxylic acids give brisk efferrescence with NaHCO3
(iii) Carboxylic acid is warmed with alcohol and conc. H2SO4 gives fruity odour ester.
Which of the above statement is/are not correct?
(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) only
(c) (iii) only
(d) (i) & (iii)
Answer:
(a) (i) only
Question 105.
Which is one the correct order of strength of carboxylic acid?
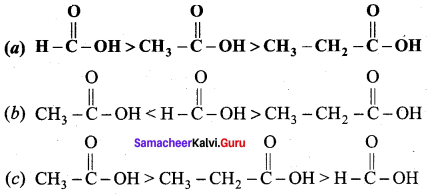
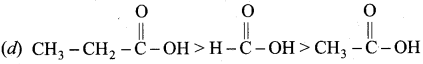
Answer:
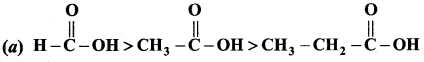
Question 106.
The correct increasing order acid strength of carboxylic acid is …………
(a) F – CH2 – COOH > I – CH2 – COOH > CI – CH2 – COOH > Br – CH2 – COOH
(b) Br – CH2 – COOH > F – CH2COOH > I – CH2COOH > Cl – CH2 – COOH
(c) F – CH2 – COOH > CI – CH2COOH > Br – CH2COOH > I – CH2COOH
(d) Br – CH2 – COOH > CI – CH2 – COOH > I – CH2COOH > F – CH2COOH
Answer:
(c) F – CH2 – COOH > CI – CH2COOH > Br – CH2COOH > I – CH2COOH
Question 107.
The increasing order of acid strength is ………….
(a) CH3COOH > CI2CHCOOH > CCI3CCOOH > ClCH2COOH
(b) CI3CCOOH > CI2CH COOH > CICH2COOH > CH3COOH
(c) CH2COOH < CI2CH COOH < CCl3CCOOH < ClCH2COOH
(a) Cl2CH – COOH < CCI3COOH < ClCH2COOH < CH3COOH
Answer:
(b) CI3CCOOH > CI2CH COOH > CICH2COOH > CH3COOH
Question 108.
The relative acidities of various organic compounds are ……………
(a) RCOOH > ArOH > H2O > ROH > RC ≡ CH
(b)RCCH > ArOH > ROH > H2O > RCOOH
(c) ROH > R ≡ CH > ArOH > RCOOH > H2O
(d) H2O > ROH > RCOOH > ArOH > RC ≡ CH
Answer:
(a) RCOOH > ArOH > H2O > ROH > RC ≡ CH
Question 109.
The correct order of the basicity of the leaving group is …………..
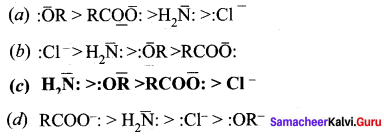
Answer:
![]()
Question 110.
The conversion of Ethyl acetate to propyl acetate by the action of propyl alcohol is named as
(a) Esterification
(b) Transesterfication
(c) Acid hydrolysis of ester
(d) Alkaline hydrolysis of ester
Answer:
(b) Transesterfication
Question 111.
Ethyl acetate undergoes self condensation in the presence of strong base to give ………………..
(a) Ethyl aceto acetate + Ethanol
(b) Ethyl aceto acetate + Acetic acid
(c) Ethyl aceto propionate + propanol
(d) Ethyl ethanoate + Ethanoic acid
Answer:
(a) Ethyl aceto acetate + Ethanol
![]()
Question 112.
Methyl cyanide on acid hydrolysis gives
(a) Acetyl chloride
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Acetamide
(d) Acetic anhydride
Answer:
(c) Acetamide
Question 113.
Which one of the following is the product formed when acetamide is treated with P2O5?
(a) Acetonitrile
(b) Methylamine
(c) Ethyl cyanide
(d) Methanamine
Answer:
(a) Acetonitrile
Question 114.
Identify the product formed when acetamide reacts with LiAIH4?
(a) Methyl amine
(b) Aceto nitrite
(c) Ethyl amine
(d) Ethylcyanide
Answer:
(c) Ethyl amine
Question 115.
Which one of the following is used as a medicine in the treatment of gout?
(a) CH3COOH
(b) C6H5COOH
(c) CH3CONH2
(d) HCOOH
Answer:
(d) HCOOH
Question 116.
Which one of the following is used as a coagulating agent for rubber latex?
(a) Ethanoyl chloride
(b) Butanoic acid
(c) Methanoic acid
(d) Benzoic acid
Answer:
(c) Methanoic acid
Question 117.
Which one of the following is used as food preservative?
(a) Sodium formate
(b) Sodium acetate
(c) Sodium benzoate
(d) Acetamide
Answer:
(c) Sodium benzoate
![]()
Question 118.
Which one of the following is used in detection and estimation of – OH and – NH2 group in organic compounds?
(a) Acetic anhydride
(b) Acetyl chloride
(c) Acetamide
(d) Ethyl acetate
Answer:
(b) Acetyl chloride
Question 119.
Which one of the following is used in the preparation of medicine like aspirin and phenacetin?
(a) Acetyl chloride
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Acetamide
(d) Acetic anhydride
Answer:
(d) Acetic anhydride
Question 120.
Which one of the following is used in the preparation of Artificial fruit essences?
(a) Ethanoic acid
(b) Acetamide
(c) Ethyl acetate
(d) Acetic anhydride
Answer:
(c) Ethyl acetate
Question 121.
Acetone and acetaldehyde are differentiated by ………….
(a) NaOH + I2
(b) Ag(NH3)2+ (Tollens’s reagent)
(c) I2
(d) NaOH + NH3
Answer:
(b) Ag(NH3)2+ (Tollens’s reagent)
Question 122.
The most suitable reagent for the conversion of is R – CH2OH → RCHO …………..
(a) KMnO4
(b) K2Cr2O7
(c) CrO3
(d) Pcc
Answer:
(d) Pcc
Question 123.
Which of the following will not give iodoform test?
(a) Isopropyl alcohol
(b) Ethanol
(c) Eth anal
(d) Benzyl alcohol
Answer:
(d) Benzyl alcohol
![]()
Question 124.
Products of the following reaction …….
![]()
(a) CH3CHO + CH3CH = CHO
(b) CH3COOH + CH3CH2CHO
(c) CH3COOH + HOOCCH2CH3
(d) CH3COOH + CO2
Answer:
(b) CH3COOH + CH3CH2CHO
Question 125.
Identify the reagents X and Y are ………………
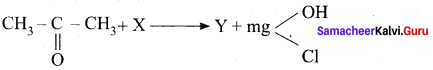
(a) X = MgCl2 Y = CH3CH = CH2
(b) X = CH3 MgCI Y = C6H5COCH3
(c) X = CH3 MgCI Y = (CH3)3C – OH
(d) X = C6H5 MgCI Y = (CH3)3C – OH
Answer:
(c) X = CH3 MgCI Y = (CH3)3C – OH
Question 126.
Reduction of > C = O to – CH2 can be carried out with ……………
(a) Ni
(b) Na/C2H5OH
(c) NH2 – NH2 + C2HONa
(d) LiAIH4
Answer:
(c) NH2 – NH2 + C2HONa
Question 127.
Which of the following is incorrect?
(a) FeCl3 is used in the detection of phenols
(b) Fehlings solution is used in the detection of aldehyde
(c) Tollen’s reagent is used in the detection of unsaturation
(d) NaHSO3 is used in the detection of carbonyl compounds
Answer:
(c) Tollen’s reagent is used in the detection of unsaturation
![]()
Question 128.
Which of the following products is formed when Benzaldehyde is treated with CH3MgBr and the addition product so obtained is subjected to acid hydrolysis?
(a) Secondary alcohol
(b) Primary alcohol
(c) Phenol
(d) Tertiary alcohol
Answer:
(a) Secondary alcohol
Question 129.
The reagent used to distinguish formaldehyde and acetaldehyde is …………..
(a) Tollen’s reagent
(b) Fehling’s solution
(c) Schiff’s reagent
(d) Caustic soda solution
Answer:
(d) Caustic soda solution
Question 130.
Which of the followìng will not give halo form test?
(a) Ethanal
(b) Ethanol
(c) Propan – 2 – one
(d) Pentan – 3 – one
Answer:
(d) Pentan – 3 – one
![]()
Question 131.
Which of the following does not turn schiff’s reagent to pink?
(a) Formaldehyde
(b) Benzaldehyde
(c) Acetone
(d) Acetaldehyde
Answer:
(c) Acetone
Question 132.
Which will not give acetamide on reaction with ammonia?
(a) Acetic acid
(b) Acetyl chloride
(c) Acetic anhydride
(d) methyl formate
Answer:
(d) methyl formate
Question 133.
The addition of HCN to carbonyl compounds is an example of ………….. reaction.
(a) N ucleophilic substitution
(b) Electrophil ic addition
(c) Nucleophilic addition
(d) Electrophilic substitution
Answer:
(c) Nucleophilic addition
Question 134.
Cinnamic acid is formed when C6H5CHO condenses with (CH3CO)2O in the presence of ……………
(a) Conc.H2SO4
(b) CH3COONa
(c) Na metal
(d) Anhydrous ZnCI2
Answer:
(b) CH3COONa
![]()
Question 135.
The molecular formula of Urotropine is …………..
(a) (CH2)6N4
(b) (CH2)4N6
(c) (CH2)2N2
(d) (CH2)6N6
Answer:
(a) (CH2)6N4
Question 136.
Bakelite is a thermosetting plastic produced by …………….
(a) HCHO + C6H5CH2OH
(b) HCHO + C6H5OH
(c) CH3CHO + C6H5OH
(d) HCHO + CH3COCH3
Answer:
(b) HCHO + C6H5OH
Question 137.
Aldehydes and ketones are reduced to hydrocarbon by the action of ………….
(a) LiAlH4
(b) H2 / Pd + BaSO4
(c) Na + Hg/HCI
(d) NH2 – NH2 / C2H5ONa
Answer:
(d) NH2 – NH2 / C2H5ONa
Question 138.
What is the name of the reaction when benzaldehyde changes into Benzyl alcohol?
(a) Friedel – crafts reaction
(b) Kolbe’s reaction
(c) Cannizaro reaction
(d) Wurtz reaction
Answer:
(c) Cannizaro reaction
Question 139.
Aldehyde turns pink with …………..
(a) Benedict solution
(b) Schiff ‘s base
(c) Fehiing solution
(d) Tollen’s reagent
Answer:
(b) Schiff ‘s base
Question 140.
Which of the following would undergo aldol condensation?
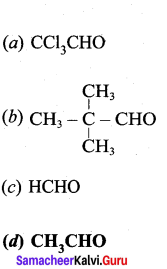
Answer:
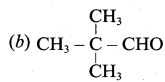
Question 141.
Which one of the following undergoes reaction with 50% NaOH solution to give the corresponding alcohol and acid?
(a) Butanal
(b) Phenyl methanal
(c) Phenol
(d) Ethanal
Answer:
(b) Phenyl methanal
![]()
Question 142.
Hexa methylene tetramine is used as ………………
(a) analgesic
(b) antipyretic
(c) Urinary antiseptic
(d) all of these
Answer:
(c) Urinary antiseptic
Question 143.
The compound which gives acetone on ozonolysis is …………
(a) CH3 – CH = CH – CH3
(b) (CH3)2C = C(CH3)2
(c) C6H5CH = CH2
(d) CH3 – CH = CH2
Answer:
(b) (CH3)2C = C(CH3)2
Question 144.
Predict the product X in the sequence of the reaction
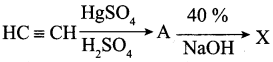
Answer:
Question 145.
From which of the following, tertiary butyl alcohol is obtained by the action of methyl magnesium iodide?
(a) HCHO
(b) CH3COCH3
(c) CH3CHO
(d) CO2
Answer:
(b) CH3COCH3
Question 146.
Tdentifý the product “C” in the sequence of the reaction.
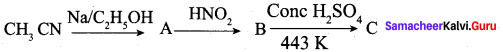
(a) CH3CH2NH2
(b) CH3CH2OH
(c) CH2 = CH2
(d) CH3CHO
Answer:
(c) CH2 = CH2
Question 147.
O3 reacts with CH2 = CH2 to form ozonide. On hydrolysis it forms …………….
Answer:
![]()
Question 148.
Ethyne on reaction with water in the presence of HgSO4 and H2SO4 gives …………….
(a) Propanone
(b) Ethanal
(c) Ethane
(d) Ethanol
Answer:
(b) Ethanal
Question 149.
Which of the aldehyde is most reactive?
(a) C6H5CHO
(b) CH3CHO
(c) HCHO
(d) CH3 – CH2 – CHO
Answer:
(c) HCHO
Question 150.
Acetaldehyde does not answer
(a) lodoform test
(b) Lucas test
(c) Benedict test
(d) Tollen’s reagent test
Answer:
(b) Lucas test
II. Fill In the blanks.
- The aldehyde Pyridoxal function as a ………….
- p – acetylated amino phenol is used to reduce ………….
- The TUPAC name of CH3 – CH = CH – CHO is ………….
- The TUPAC name of CH2 = CH – CHO is ………….
- The formula of mesityl oxide is ………….
- The name of
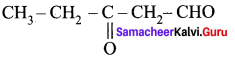 is ………….
is …………. - But – 2 – ene gives 2 moleafethanal by ………….
- …………. Olefines give formaldehyde as one of the product.
- Hydration of …………. in the presence of 40% dilute sulphuric acid and 1% HgSO4 gives Ethanal.
- Calcium formate on …………. gives methanal and CaCO3.
- Dry distillation of …………. gives propanone and CaCO3.
- Tn Rosenmund’s reduction reaction …………. is the catalyst and …………. is the catalytic poison.
- …………. selectively reduces alkyl cyanide to form imines which on hydrolysis gives aldehyde.
- Side chain oxidation of toluene in the presence of KMnO4 gives ………….
- The oxidising agent used to convert toluene to benzaldehyde is ………….
- Acetyl chloride reacts with …………. to form acetone.
- Addition of …………. finds application in. the separation and purification of carbonyl compounds.
- Aliphatic aldehyde except …………. react with an ethereal solution of ammonia to form aldimines.
- Formaldehyde reacts with ammonia to form …………. which is used to treat urinary infection.
- Nitration of Urotropine under controlled condition gives an explosive ………….
- RDX is also called …………. or ………….
- With ammonia, benzaldehyde form a complex condensation product called ………….
- The oxidation of unsymmetrical ketone is governed by ………….
- The reducing agent used in Clemmensen reduction is ………….
- The reducing agent used in woif-kishner reduction is ………….
- Symmetric diols are called ………….
- Aldehydes which do not have …………. undergo disproportionation reaction (or) cannizaro reaction.
- The reagent used in the conversion of Benzaldehyde to Benoin is ………….
- In Knoevenagal reaction …………. act as the basic catalyst.
- The formula of Benzal aniline (or) Schiffs base is ………….
- Benzaldehyde condenses with N, N – dimethyl aniline in the presence of strong acids to form ………….
- …………. is ammoniacal silver nitrate solution.
- …………. is a mixture of CuSO4 + Sodium citrate + NaOH.
- 40% aqueous solution of formaldehyde is known as …………..
- Paraldehyde is used in medicine as ………….
- Acetone is used in the manufacture of thermo softening plastic ………….
- …………. is used in perfumery and as a hypnotic under the name hyphone.
- …………. cannot be prepared by grignard reagent since the acid contains only one carbon atom.
- Most of carboxylic acid exist as …………. in its vapour state.
- …………. is 6 to 8% solution of acetic acid in water.
- …………. is used to convert acetic acid to ethane at 473 K.
- …………. reaction is generally used for the preparation of esters of higher alcohol from that of a lower alcohol.
- Formic acid is used in medicine for treatment of ………….
- The conversion of acetamide to methylamine by the action of caustic alkali and Bromine is known as ………….
- …………. is used as food preservative.
- …………. is used in the detection and estimation of – OH, – NH2, groups in organic compounds.
- …………. is used in the preparation of artificial fruit essences.
- The conversion of Benzene to Benzaldehyde by the action of carbon monoxide and HCl is known as ………….
- The product formed when formaldehyde condensed with acetone is ………….
- Benzaldehyde condenses with acetaldehyde to form ………….
Answer:
- Coenzyme
- Fever
- But – 2 – enal
- Prop – 2 – enal
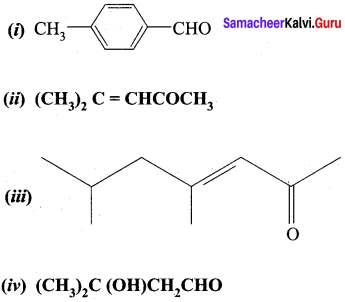
- (CH3), C = CHCOCH3
- 3-Oxo pentanal
- Ozonolysis
- Terminal
- Ethyne
- Dry distillation
- Calcium ethanoate
- Pd, BaSO4
- Diisobutvl aluminum hydride
- Benzoic acid
- CrO2Cl2 Chromyl chloride
- Dimethyl cadmium
- NaHSO3
- Formaldehyde
- Urotropinc (or) Hexamethylene tetramine
- RDX (or) Research and development explosive
- Cyclonite(or)cyclotrimethylene trinitramine
- Hydrobenzamide
- Popott’s rule
- Zn + Hg / conc.HCl
- NH2 – NH2 + C2H5ONa
- Pinacol
- a – hydrogen atom
- Alcoholic KCN
- Pyridine
- C6H5CH = N – C6H5
- Triphenyl methane dye or malachite green dye
- Tollen’s reagent
- Benedict’s solution
- Formalin
- Hypnotic
- Perspex
- Acetophenone
- Formic acid HCOOH
- Dimer
- Vinegar
- HI + Red P
- Transesterification
- Gout
- Hoff mann’s degradation
- Sodium benzoate
- Acetyl chloride
- Ethyl acetate
- Gattermann – koch reaction
- 4 – hydroxy – butane – 2 – one
- Cinnamaldehyde
III. Match the following.
Match the column I and II using the code given below the column.
Question 1.
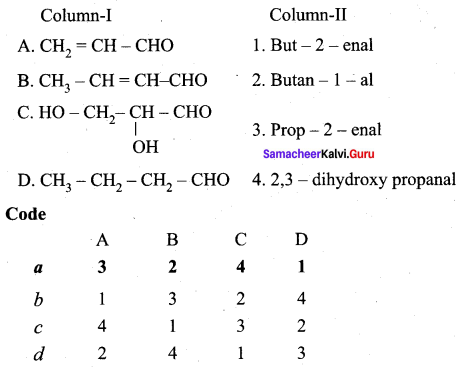
Answer:
(a) 3 2 4 1
Question 2.
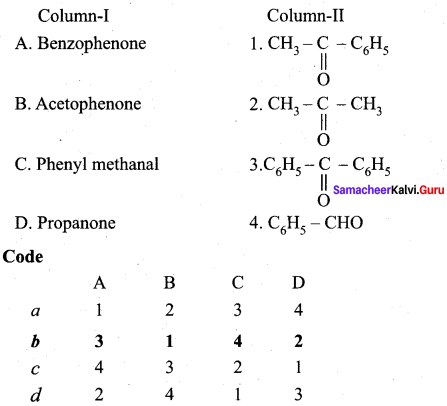
Answer:
(b) 3 1 4 2
Question 3.
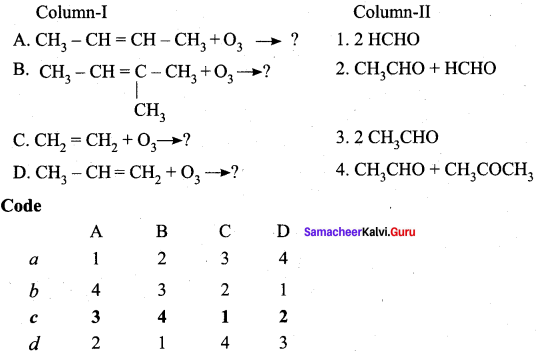
Answer:
(c) 3 4 1 2
Question 4.
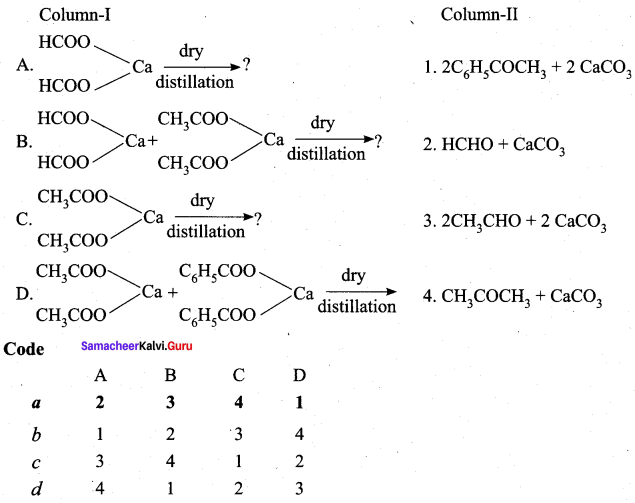
Answer:
(a) 2 3 4 1
Question 5.
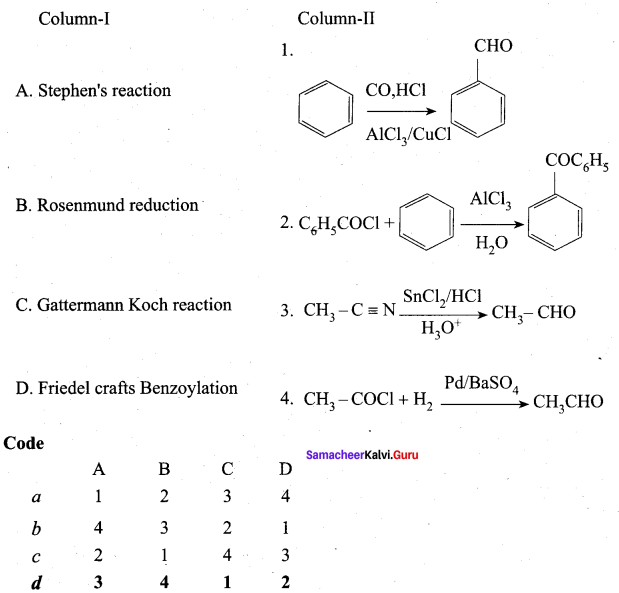
Answer:
(d) 3 4 1 2
Question 6.
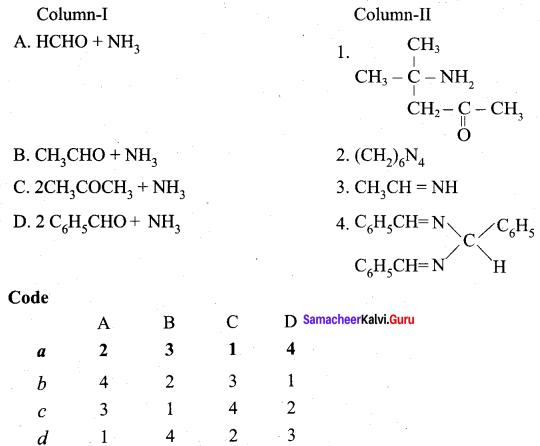
Answer:
(a) 2 3 1 4
Question 7.
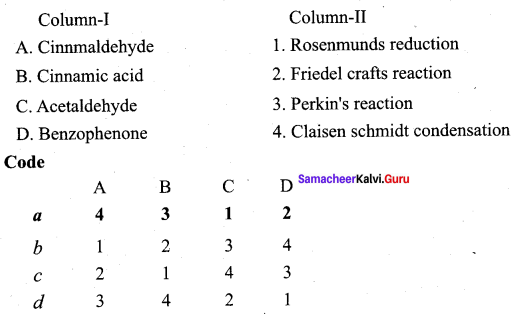
Answer:
(a) 4 3 1 2
Question 8.
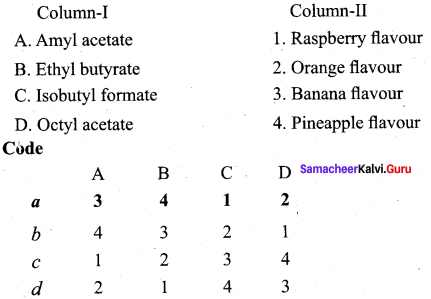
Answer:
(a) 3 4 1 2
Question 9.
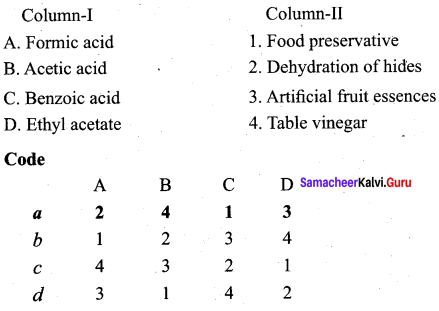
Answer:
(a) 2 4 1 3
Question 10.

Answer:
(a) 3 1 4 2
Question 11.
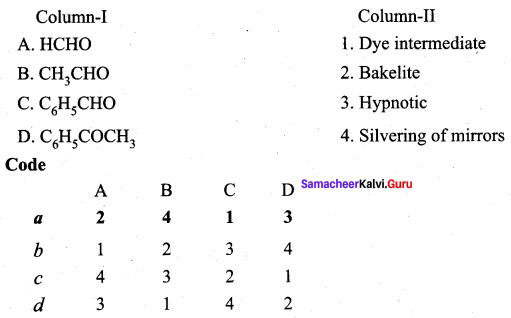
Answer:
(a) 2 4 1 3
Question 12.

Answer:
(a) 2 3 4 1
IV. Assertion and reasons.
Question 1.
Assertion(A): In Rosenmund’s reduction, BaSO4 act as catalyst pòison.
Reason (R): In Rosenmund’s reduction, BaSO4 act as catalytic poison to pd catalyst so that aldehyde cannot be further reduced ti alcohol.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 2.
Assertion(A): Aldehydes and ketones have high high boiling point as compared to hydrocarbon and ether of comparable molecular mass.
Reason (R): It is due to weak molecular association in aldehydes and ketones arising out of the dipole – dipole interactions.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are wrong
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 3.
Assertion(A): The boiling point of aldehydes and ketones are much lower those of corresponding alcohols and carboxylic acids.
Reason (R): Alcohols and carboxylic acids possess intermolecular hydrogen bonding and so have high boiling point.
(a) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct and R ¡s the correct explanation of A
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are correct and R ¡s the correct explanation of A
![]()
Question 4.
Assertion(A): Aldehydes and ketones have high dipole moment.
Reason (R): The carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen. Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon and it attracts the shared pair of electron which makes the carbonyl group as polar.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 5.
Assertion(A): Addition of sodium bisuiphite finds application in the separation and purification of carbonyl compound.
Reason (R): The bisuiphite addition compound is water soluble and the solution is treated with mineral acid to regenerate the carbonyl compounds.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) A is correct but R is wrong
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 6.
Assertion(A): Acetaldehyde does not undergo cannizaro reaction.
Reason (R): Cannizaro reaction is a characteristic of aldehyde having no α – H atom. Acetaldehyde contains 3 α – H atoms.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R. is not correct explanation of A
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 7.
Assertion(A): Acetaldehyde and acetone are readily undergo aldol condensation reaction in the presence of dilute base.
Reason (R): Aldehyde or ketone having α – hydrogen atom add together to give aldol or ketol.
(a) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
![]()
Question 8.
Assertion(A): Carboxylic acids have higher boiling point than aldehyde and ketone of comparable molecular mass.
Reason (R): This is due to more association of carboxylic acid. Molecules through intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
(a) Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 9.
Assertion(A): Lower aliphatic carboxylic acids arc miscible with water but higher carboxylic acids are insoluble in water.
Reason (R): Lower carboxylic acids are able to form hydrogen bond with water whereas higher carboxylic acids have increased hydrophobic interaction of hydrocarbon part.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation Of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation Of A.
Question 10.
Assertion(A): Carboxylic acid do not give the characteristic reaction of carbonyl group as given by aldehyde and ketone.
Reason (R): The carbonyl carbon of carboxylic acid is involved in resonance.
(a) Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A
Answer:
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 11.
Assertion(A): Benzoic acid does not undergo friedel crafts reaction.
Reason (R): This is due to the strong deactivating nature of the carboxyl group
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
![]()
Question 12.
Assertion(A): Formic acid can act as a strong reducing agent
Reason (R): Formic acid contains both aldehyde as well as an acid group.
(a) Both A and R are wrong
(b) A is correct but R is wrong
(c) A is wrong but R is correct
(d) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(d) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 13.
Assertlon(A): Trichioro acetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid.
Reason (R): Cl– is a electron withdrawing group and acidity increases with increasing number of electron withdrawing substituents on the α – carbon.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct reason of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not correct reason of A.
(c) A is correct but R is wrong
(d) A is wrong but R is correct.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct reason of A.
V. Find the odd one out and give the reasons.
Question 1.
(a) Methanal
(b) Ethanal
(c) Phenyl metbanal
(d) Prop – 2 – enal
Answer:
(c) Phenyl metbanal
It is an aromatic aldehyde where as others are aliphatic aldehydes.
![]()
Question 2.
(a) Formic acid
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Benzoic acid
(d) Propanoic acid
Answer:
(d) Propanoic acid
It can act as reducing agent where as other acids are not act as reducing agents.
Question 3.
(a) HCHO
(b) C6H5CHO
(c) CCI3CHO
(d) CH3CHO
Answer:
(d) CH3CHO
CH3CHO. It contains α – H atom and undergoes aldol condensation where as others do not have α – H atoms and they undergo cannizaro reactions.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids 2 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write the name of the following compounds.
Answer:
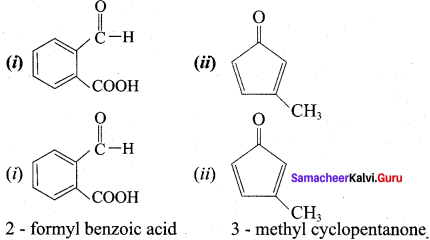
Question 2.
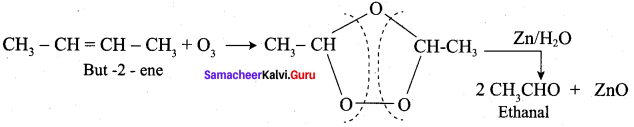
What happens But – 2 – ene is ozonised followed by hydrolysis?
Answer:
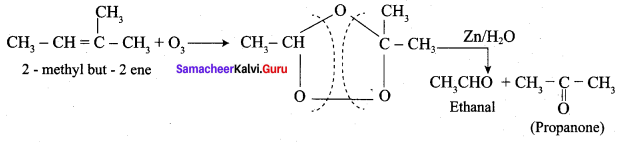
Question 3.
Explain the action of ozone with 2 – methyl but – 2 – ene followed by hydrolysis with zinc?
Answer:
Question 4.
What happens when Ethyne is hydrolysed in the presence of HgSO4 and H2SO4?
Answer:
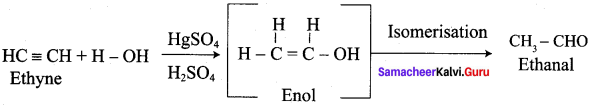
Question 5.
How would you convert prop – 1 – yne to propanone?
Answer:
Prop – 1- lyne on hydrolysis with HgSO4 and H2SO4 gives propanone as product.
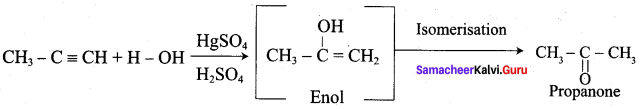
Question 6.
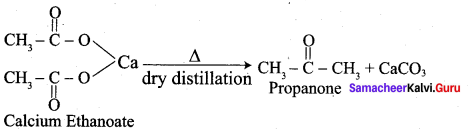
Explain about the dry distillation of Calcium ethanoate.
Calcium ethanoate on dry distillation gives propanone as product.
Answer:
Question 7.
Explain Rosenmund reduction.
Answer:
Aldehydes can be prepared by the hydrogenation of acid chloride, in the presence of palladium supported by Barium sulphate. This reaction is called Rosenmund reduction.
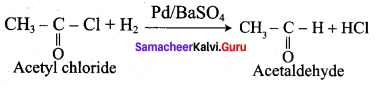
In the above reaction, BaSO4 act as a catalytic poison to palladium catalyst, so that aldehyde cannot be further reduced to alcohol.
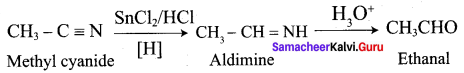
Question 8.
Explain Stephen’s reaction.
Answer:
In Stephen’s reaction, alkyl cyanide are reduced using SnCl2 / HCI, imines arc formed which on hydrolysis gives corresponding aldehyde.
Question 9.
Explain the action of Diisobutyl aluminium hydride (DIBAL – H) and H2O with hex – 4 – en nitrile.
Answer:

Question 10.
Explain about Cattermann – koch reaction.
Answer:
Benzene reacts with carbon monoxide and HCl in the presence of AlCl3 and CuCl to give Benzaldehyde. This reaction is known as Gattermann – Koch reaction.
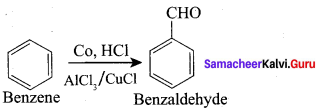
Question 11.
How would you manufacture benzaldehyde from toluene?
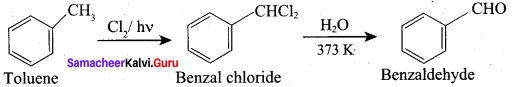
This is the commercial method for the manufacture of Benzaldehyde.
Question 12.
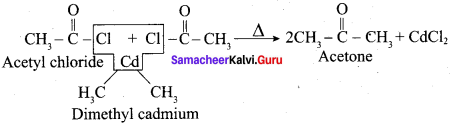
Explain the action of dialkyl cadmium with acetyl chloride?
Answer:
Question 13.
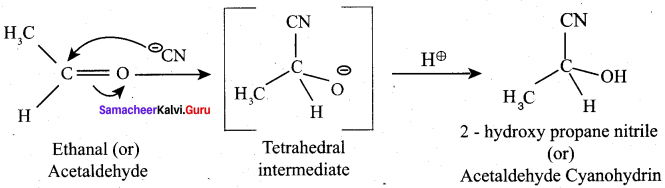
Explain the nucleophilic addition of HCN with eth anal?
Answer:
Question 14.
Which reaction finds application in the separation and purification ofcarbonyl compound? Explain.
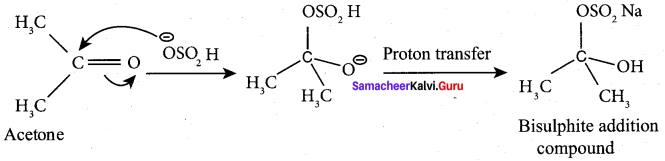
The bisuiphite compound is water soluble and the solution is treated with minerai acid to regenerate the carbonyl compound. So the above reaction is used in the separation and purification of carbonyl compound.
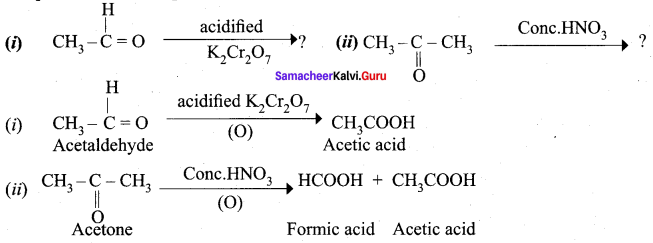
Question 15.
Complete the following reactions.
Answer:
Question 16.
What Is Clemmensen reduction ? Explain it.
Answer:
Aldehyde and ketones when heated with zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid give hydrocarbons. This reaction is known as Clemmensen reduction.
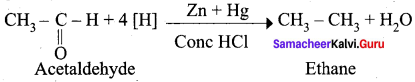
Question 17.
Complete the following reactions.
Answer:
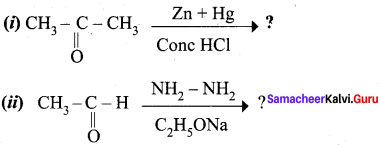
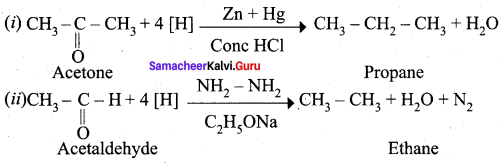
Question 18.
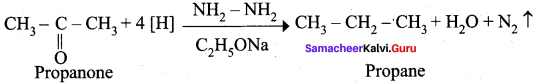
Explain Wolf Kishner reduction with suitable example.
Answer:
Wolf Kishner reduction:
Question 19.
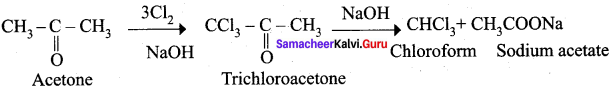
How would you obtain chloroform from acetone?
Answer:
When acetone is treated with chlorine and alkali, chloroform is formed.
Question 20.
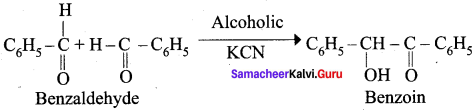
What happen when alcoholic KCN reacts with Benzaldehyde? (or) explain Benzoin condensation.
Answer:
Benzaldehyde reacts with alcoholic KCN to form Benzoin.
Question 21.
Explain about SchilT’s reagent test?
Answer:
Dilute solution of aldehyde when added to Schifl’s reagent (Rosaniline hydrochloride dissolved in water and its red colour decolourised by passing SO2) yields its red colour. This is known as Schiffs’ test for aldehyde. Ketones do not give this test. Acetone however gives a positive test but slowly.
Question 22.
What are used of Urotropine? Give its structure.
Answer:
This is the structure of Urotropme (Hexamethylene tetramine)
1. Urotropine is used as a medicine to treat urinary infection.
2. Nitration ofUrotropine under controlled condition gives an explosive RDX (Research and development explosive). It is also called cyclonite or cyclotri methylene trinitramine.
Question 23.
Mention the uses of aromatic ketone.
Answer:
- Acetophenone has been used in perfumery arid as a hypnotic under the name hyphone.
- Benzophenone is used in perfumery and in the preparation of benzhydrol drop.
Question 24.
Write the structure and IUPAC name of the following compounds?
(i) Malonic acid
(ii) Succinic acid
(iii) Glutaric acid
(iv) Adipic acid
Answer:
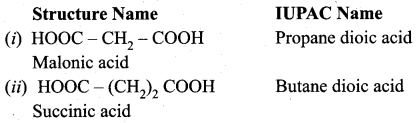
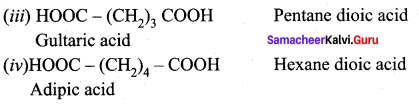
Question 25.
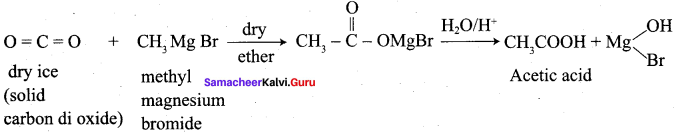
Starting from methyl magnesium iodide, how would you prepare acetic acid?
Answer:
Question 26.
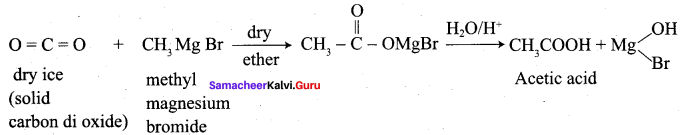
Convert phenyl magnesium bromide into Benzoic acid?
Answer:
Question 27.
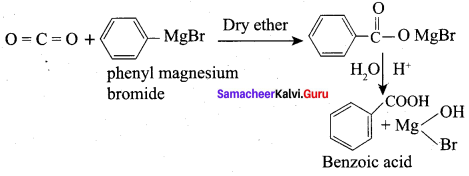
Explain the hydrolysis reaction of the following with equation?
- (CH3CO)2O
- (C6H5CO)2O
Answer:
Question 28.
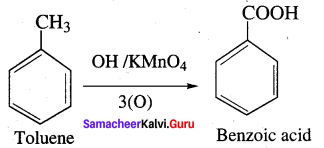
Explain the action of alkaline potassium permanganate with toluene?
Answer:
Question 29.
Lower aliphatic carboxylic acids are miscible with water but higher carboxylic acids are insoluble in water. Give reason. (or) Acetic acid is soluble in water but hexanoic acid in insoluble in water. Why?
Answer:
Aliphatic acids are miscible with water due to the formation of hydrogen bonds with water. Higher carboxylic acids are insoluble in water due to increased hydrophobic interaction of hydrocarbon part. Thats why acetic acid is soluble in water whereas hexanoic acid is insoluble in water.
![]()
Question 30.
What is Vinegar? How will you get glacial acetic acid?
Answer:
- Vinegar is 6 to 8% solution of acetic acid in water.
- Pure acetic acid is called glacial acetic acid. Because it forms ice like crystal when cooled.
When aqueous acetic acid is cooled at 289.5 K, acetic acid solidifies and forms ice like crystals, where as water remains in liquid state and removed by filtration. This process is repeated to obtain glacial acetic acid.
Question 31.
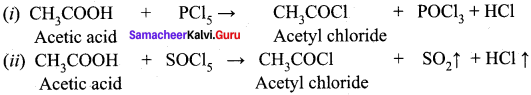
Explain the action of the following reagents with acetic acid.
(i) PCI5
(ii) SOCI2
Answer:
Question 32.
Complete the following reactions.
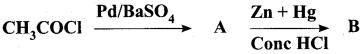
Answer:
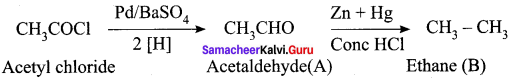
Question 33.
What happens when thionyl chloride reacts with benzoic acid?
Answer:
When Benzoic acid reacts with thionyl chloride, Benzoyl chloride is formed as product.
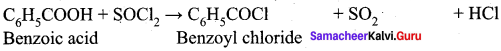
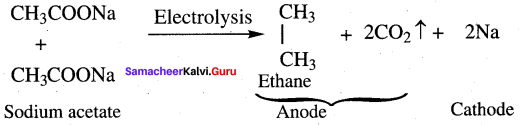
Question 34.
Explain Kolbe’s electrolytic decarboxylation.
Answer:
The aqueous solution of sodium or potassium salts of carboxylic acid on electrolysis gives alkanes at anode. This reaction is called kolbe’s electrolysis.
Question 35.
What happens when ammonia reacts with acetic acid?
Answer:
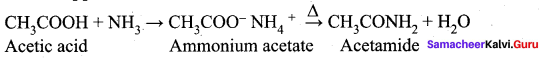
Question 36.
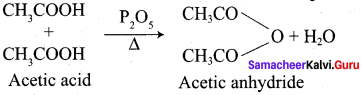
Explain the action of heat on acetic acid in the presence of phosphorous pentoxide.
Answer:
Question 37.
Explain the a – halogenation take place in acetic acid. (or) Explain IIell-Volhard-zelinsky reaction (HVZ reaction)?
Answer:
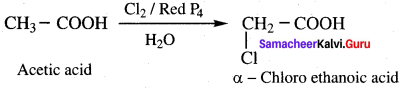
Carboxylic acids having an α – hydrogen are halogenated at the α – position on treatment with chlorine or bromine in the presence of small amount of red phosphorus to form a – halo carboxylic acids. This reaction is known as Hell – Volhard – Zelinsky reaction (HVZ reaction)
Question 38.
Acidity increases with increasing number of electron rithdrawing substituents on the α – carbon. Explain with example.
Answer:
Acidity increases with increasing number of electron withdrawing substituents on the α – carbon atom. For example,
Cl3C – COOH > Cl2CH – COOH > Cl – CH2COOH > CH3COOH
The effect of various, electron withdrawing groups on the acidity of a carboxylic acid follows the order,
– NO2 > – CN > – F > – Cl > – Br > – I > Ph
Question 39.
Trichloro acetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid. Give reason.
Answer:
Cl– is an electron withdrawing substituent. Acidity increases with the increasing number of electron withdrawing substituents on the α – carbon. So trichioro acetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid. CCI3COOH is more acidic than CH3COOH.
Question 40.
Fluoro acetic acid is more acidic than iodoacetic acid. Give reason.
Answer:
Acidity increases with increasing electro negativity of the substituents. F is more electro negative.
F – CH2 – COOH > Cl – CH2COOH > Br – CH2 – COOH > 1 – CH2 – COOH
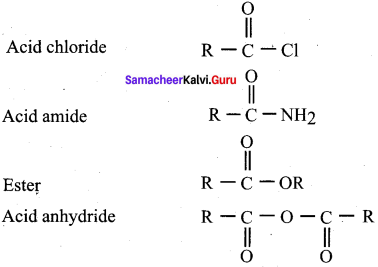
So Fluoro acetic acid is more acidic than iodoacetic acid.
Question 41.
What are carboxylic acid derivatives? Give four examples.
Answer:
1. Carboxylic acid derivatives are compounds in which carboxylic acid – OH group is replaced by the atom or the group.
2. 
Question 42.
Which is the best method to prepare acetyl chloride from acetic acid? why?
Answer:
Acetyl chloride is prepared from acetic acid by the action of thionyl chloride. This method is superior to others as the by products being gases escape leaving the acid chloride in the pure state.
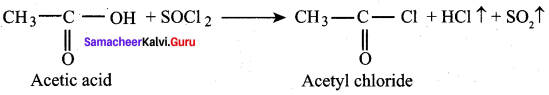
Question 43.
Acetyl chloride fumes when exposed to air. Give reason.
Answer:
Acetyl chloride emit pale fumes of hydrogen chloride when exposed to air on account of their reaction with water vapour.

Question 44.
What happens when acetyl chloride is treated with ethanol?
Answer:
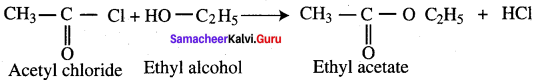
This reaction is also known as alcoholysis.
Question 45.
Explain ammonolysis reaction of acid chloride (or) what happens when ammonia reacts with acetvl chloride?
Answer:
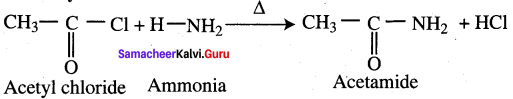
Question 46.
What happens when acetic anhydride reacts with ethyl alcohol?
Answer:
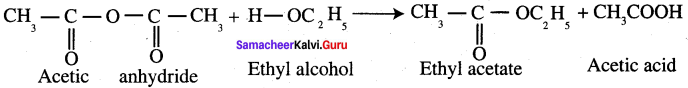
Question 47.
Explain the reaction of ammonia with acetic anhydride.
Answer:

Question 48.
Complete the following reaction.
Answer:
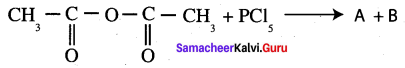

Question 49.
What is transesterification? Explain with example.
Answer:
Esters of an alcohol can react with atiother alcohol in the presence of a mineral acid to give the ester of second alcohol. The interchange of alcohol portions of the esters is termed transesterification.
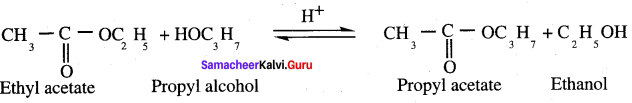
Question 50.
Explain the action of ammonia with ethyl acetate.
Answer:

Question 51.
How is ethyl acetate react with PCL5?
Answer:
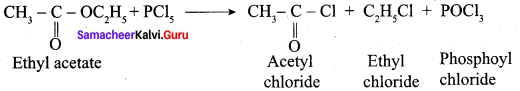
Question 52.
What happens when methyl cyanide is partially hydrolysed by cold conc. HCl?
Answer:
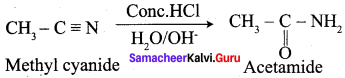
Question 53.
Explain the action of P2O5 with acetamide with equation.
Answer:
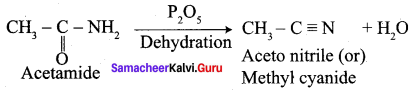
Question 54.
Describe Hoffmann degradation reaction. (or) How would you obtain methyl amine from acetamide?
Answer:
Acetamide reacts with bromine in the presence of caustic alkali to form a primary amine carrying one carbon less than the parent amide.
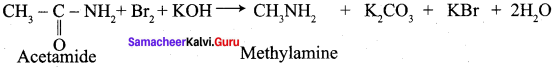
Question 55.
How would you preparate ethyl amine from acetamide?
Answer:
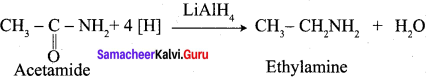
Question 56.
What are the used of acetyl chloride?
Answer:
- Acetyl chloride is used as acetylating agent in organic analysis
- it is used in the detection and estimation of – OH, – NH2 groups in organic compounds.
![]()
Question 57.
Arrange the following compounds ¡n increasing order of their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions.
- Ethanal, Propanal, Propanone, Butanone
- Benzaldehyde, p – Tolualdehyde, p – Nitrobenzaldehyde, Acetophenone
Answer:
- Butanone < Propanone < Propanal <Ethanal
- Acetophenone < p – Tolualdehyde < Benzaldehyde < p – Nitrobenzaldehyde
Question 58.
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) PhCH2CH2COOH
(ii) (CH3)2C = CHCOOH
Answer:
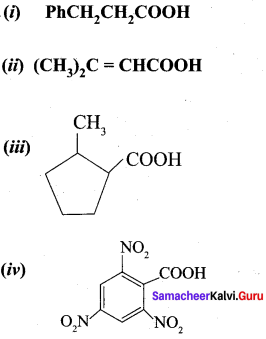
- 3 – Phenylpropanoic acid
- 3 methylbut – 2 – enoje acid
- 2 – methylcyclohexane carboxylic acid
- 2, 4, 6 – Trinitorbenzoic acid or 2, 4, 6, – Trinitrobenzene carboxylic acid
Question 59.
Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol? Why?
Answer:
In carboxylate ion -ve charge is delocalised over two oxygen atoms whereas in phenoxide ion the -ve charge is delocalised over one oxygen atom. Therefore carboxylate ion is more stable than phenoxide ion and that is why carboxylic acids are more acidic than phenols.
Question 60.
How is aminoethane obtained from ethanal (acetaldehyde)?
Answer:
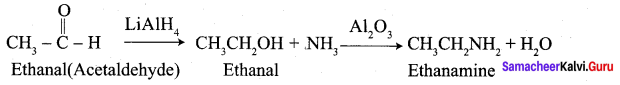
Question 61.
Why HCOOH does not give Hell – Voihard Zelinsky reaction but CH3COOH does?
Answer:
CH3COOH contains α – hydrogen atom and hence gives HVZ reaction but HCOOH does not contain an α – hydrogen atom and hence does not give HVZ reaction.
Question 62.
Write IUPAC names of the following.
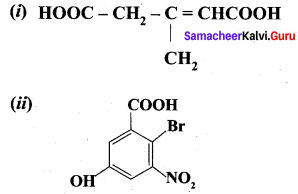
Answer:
- 3 – Methylpent – 2 – 3n 3 – 1, 5 – dioic acid
- 6 – Bromo -3 – hydroxy- 5 – nitrobenzoic acid
Question 63.
Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pair of compounds.
- Phenol and Benzoic acid
- Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
Answer:
- By adding feme chloride, phenol will give violet colour whereas benzoic acid will not react.
- Adding I2 and NaOH, Acetophenone will give yellow ppt. of iodoform whereas benzaldehyde will not react.
Question 64.
Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pair of compounds.
- Propanoyl chloride and propanoic acid
- Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
Answer:
1. On adding NaHCO3, solution to each of them, propanoyl chloride will not react whereas propanoic acid will give brisk èfferevescence due to the evolution of CO2.
2. On adding I2 and NaOH, Acetophenone will give yellow ppt, of iodoform whereas benzaldehyde will not react
Question 65.
Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pair of compounds.
- Propanal and propanone
- Benzaldehyde and Benzoic acid
Answer:
- On adding Tollen’s reagent, propanal will give silver mirror whereas propanone does not react.
- On adding NaHCO3 solution, benzaldehyde will not react whereas benzoic acid will give brisk effervescence due to the evolution of CO2.
![]()
Question 66.
Out of acetophenone and benzophenone, which one will give iodoform test? Write the reaction involved. (The compound should have CH3CO group to show the iodoform test).
Answer:
Acetophenone (C6H5COCH3) contains the group (CH3CO) attached to the carbon atom and hence give lodoform test while benzophenone does not contain this group and hence does not give iodoform test.
Question 67.
Why does methanal not give aidol condensation while ethanol forms an aldol?
Answer:
This is because only those compounds which haie α – hydrogen atoms can undergo aldol condensation reactions. Ethanol possesses α – hydrogen and therefore undergoes aldol condensation. Methanal does not have α – hydrogen atoms, hence does not undergo aldol condensation reactions.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids 3 Mark Questions and Answers.
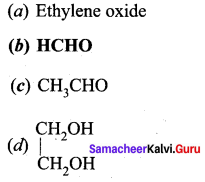
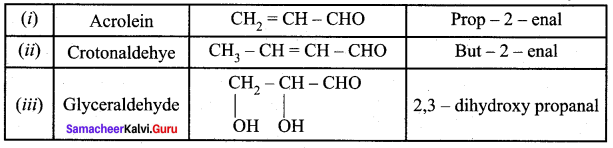
Question 1.
Draw the structure and IUPAC name of the following compounds.
(i) Acrolein
(ii) Crotonaldehyde
(iii) Glyceraldehyde
Answer:
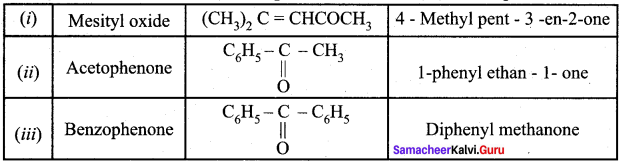
Question 2.
Draw the structure and IUPAC name of the following compounds.
(i) Mesityl oxide
(ii) Acetophenone
(iii) Benzophenone
Answer:
Question 3.
Explain about the structure of carbonyl group.
Answer:
1. The carbonyl carbon
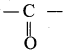
is sp2 hybridised and carbon – oxygen bond is similar to carbon carbon double bond in alkenes. The carbonyl carbon forms three o bonds using their three sp2 hybridised orbital. One of the sigma bond is formed with oxygen and the other two with hydrogen and carbon (in aldehydes) or with two carbons (in ketones). All the three ‘a’ bonded atoms arc lying on the same plane.
2. The fourth valence electron of carbon remains in its unhybridised ‘2p’ orbital which lies perpendicular to the plane and it overlaps with 2p orbital of oxygen to form a carbon – oxygen bond.
3. The oxygen atom has two non-bonding pairs of electrons, which occupy its remaining two P orbitais. Oxygen, the second most electro negative atom attracts the shaired pair of electron between the carbon and oxygen towards itself and hence the bond is polar. This polarisation contributes to the reactivity of aldehydes and ketones.
Question 4.
How are the following compounds are prepared by the dry distillation of calcium salt of carboxylic acids?
(i) Methanal
(ii) Ethanal
Answer:
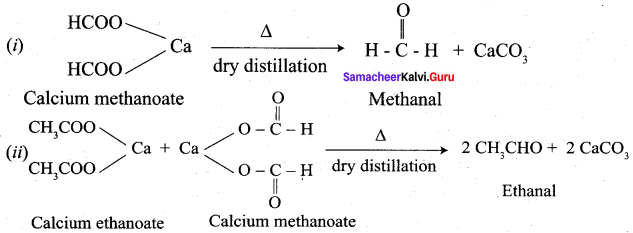
Question 5.
How will you prepare benzaldehyde from methyl benzene? (or) Explain Etard reaction.
Answer:
When chromylchloridc is used as an oxidising agent, toluene gives benzaldehyde. This reaction is called Etard reaction. Acetic anhydride and CrO3 can also be used for this reaction.
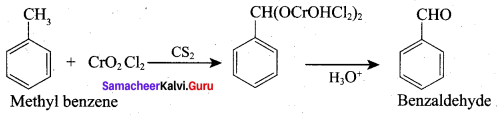
Question 6.
How would you prepare the following compounds by Friedel Crafts acylation?
(i) Acetophenone
(ii) Benzophenone
Answer:
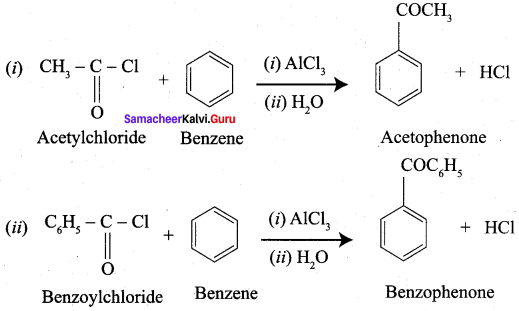
Question 7.
Aldehydes and ketones have high boiling point as compared to hydrocarbons and ethers of comparable molecular mass and less than that of alcohols. Give reason.
Answer:
Aldehydes and ketones have high boiling point as compared to hydrocarbons and ethers of comparable molecular mass. It is due to the weak molecular association in aldehyde and ketone arising out of the dipole-dipole interactions.
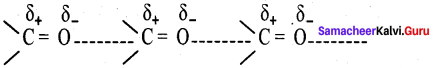
These dipole – dipole interactions are weaker than intermolecular H – bonding. The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are much lower than those of corresponding alcohols and carboxylic acids which possess inter molecular hydrogen bonding.
Question 8.
Explain the mechanism of nucleophilic addition reactions of aldehyde and ketone?
Answer:
1. Nucleophilic addition reaction is the most common reactions of aldehydes and ketones. The carbonyl carbon cames a small degree of positive charge.
2. Nucleophile such as CN– can attack the carbonyl carbon and uses its bond pair to forni a new carbon – nucleophile’ a ‘bond, at the same time two electrons from the carbon – oxygen double bond move to the most electronegative oxygen atom.
3. This results in the formation of an alkoxide ion. In this process, the hybridisation of carbon changes from sp2 to sp3
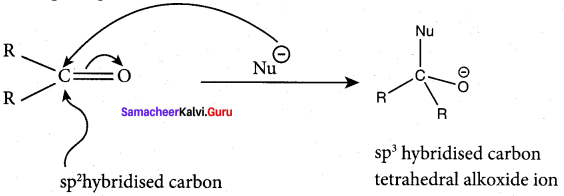
The tetrahedral intermediate can be protonated by water or an acid to form an alcohol.
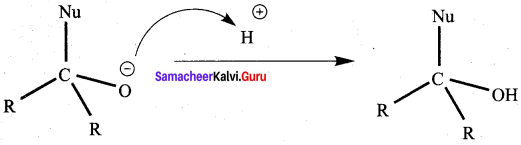
Question 9.
How acetone reacts with the following reagents?
(i) NH2OH
(ii) NH2 – NH2
(iii) C6H5NH – NH2
Answer:
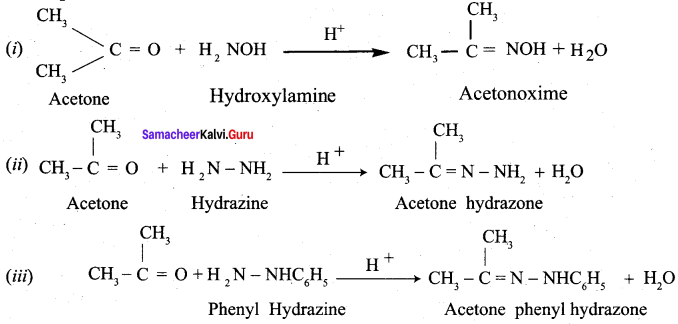
Question 10.
What is Urotropine? How is It prepared? Mention Its structure and uses.
Answer:
1. Urotropine is hexamethylene tetramine. N
2. Formaldehyde reacts with ammonia to form hexamethylene tetramine, which is called Urotropine. HC CH1 CH
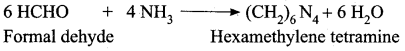
3. Urotropine is used as a medicine to treat urinary infection.
4. Nitration of Urotropine under controlled condition gives an explosive RDX (Research and development explosive). It is also called cyclonite or cyclotri methylene trinitramine.
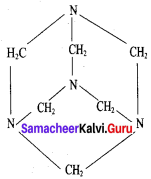
Question 11.
What is popoff ‘s rule? Explain with an example.
Answer:
The oxidation of unsymmetrical ketones is governed by Popoff’s rule. It states that during the oxidation of an unsymmetrical ketone, a (C – CO) bond is cleaved in such a way that the keto group stays with the smaller alkyl group. Example:
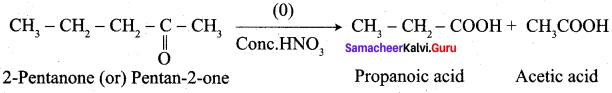
Question 12.
Explain the action of magnesium amalgam and water with acetone?
Answer:
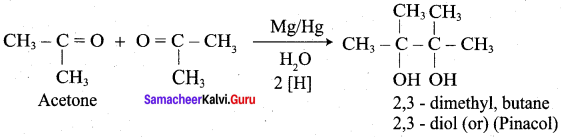
Question 13.
Describe crossed aldol condensation with two examples.
Answer:
Aldol condensation can takes place between two different aldehyde or ketones or between one aldehyde and one ketone is called crossed or mixed aldol condensation. E.g.,
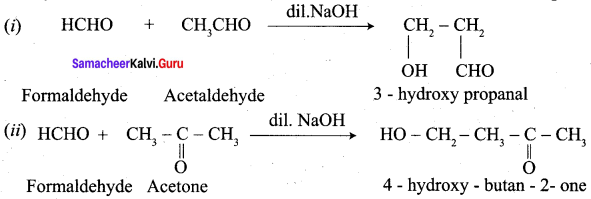
Question 14.
Explain Claisen – Schmidt condensation.
Answer:
Benzaldehye condenses with acetaldehyde or acetone in the presence of dil. alkali at room temperature to form unsaturated aldehyde (or) ketone. This type of reaction is called Claisen – Schmidt condensation.
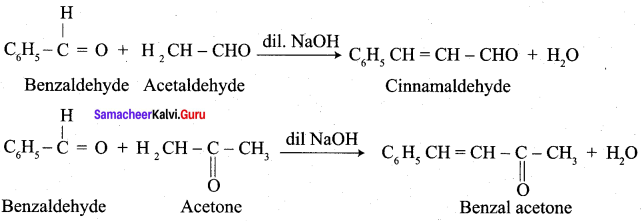
Question 15.
What is crossed cannizaro reaction? Explain It.
Answer:
When Cannizaro reaction (Auto redox reaction) takes place between two different aldehyde, the reaction is called as crossed cannizaro reaction.
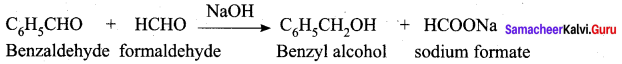
In crossed cannizaro reaction more reactive aldehyde is oxidized and less reactive aldehyde is reduced.
Question 16.
How will you prepare malachite green dye from Benzaldehyde?
Answer:
Benzaldehyde condenses with tertiary aromatic amines like N, N – dimethyl aniline in the presence of strong acids to triphenyl methane dye.
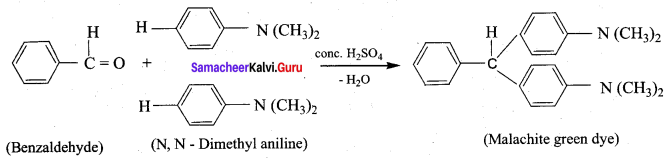
Question 17.
How Is chlorine react with Benzaldehyde?
- In the presence of catalyst
- In the absence of catalyst
Answer:
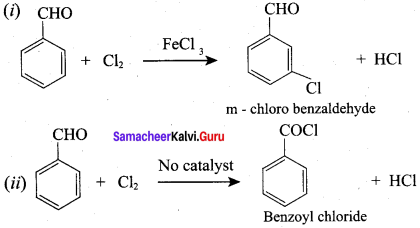
Question 18.
Explain about 3 test for aldehyde
Answer:
1. Tollen’s reagent test:
When an aldehyde is warmed with Tollens reagent(Ammonical silver nitrate), a bright silver mirror is produced due to the formation of silver metal. This reaction is also called silver mirror test for aldehydes.
![]()
2. Fehlings solution Test:
Fehlings solution is prepared by mixing equal volumes of Fehlings solution ‘A’ containing aqueous copper sulphate and Fehlings solution ‘B’ containing alkaline solution of sodium potassium tartarate (RocheLle salt) When aldehyde is warmed with Fehlings solution deep blue colour solution is changed to red precipitate of cuprous oxide.

3. Benedict’s solution Test:
Benedict’s solution is a mixture of CuSO4 + sodium citrate + NaOH. Cu2+ is reduced by aldehyde to give red precipitate of cuprous oxide.
![]()
Question 19.
Mention the uses of formaldehyde.
Answer:
- 40% aqueous solution of formaldehyde is called formalin. It is used for preserving biological specimens.
- Formalin has hardening effect, hence it is used for tanning.
- Formalin is used in the production of thermo setting plastic known as bakelite, which is obtained by heating phenol with formalin.
![]()
Question 20.
What are the uses of acetaldehyde?
Answer:
- Acetaldehyde is used for silvering of mirrors
- Paraldehyde is used in medicine as a hypnotic.
- Acetaldehyde is used in the commercial preparation of organic compounds like acetic acid, ethyl acetate etc.,
Question 21.
Write about the uses of Acetone.
Answer:
- Acetone is used as a solvent, in the manufacture of smokeless powder (cordite)
- It is used as a nail polish remover.
- It is used in the preparation of suiphonal, a hypnotic.
- It is used in the manufacture of thermosoftening plastic Perspex.
Question 22.
What are the uses of Benzaldehyde?
Answer:
- as a flavoring agent
- in perfumes
- in dye intermediates
- as starting material for the synthesis of several other organic compounds like cinnamaldehyde, cinnamic acid, benzoyl chloride etc.
Question 23.
Carboxylic acids have higher boiling pint than aldehyde, keton and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. Give reason.
Answer:
Carboxylic acids have higher boiling point due to more association of acid molecules through inter molecular hydrogen bonding.
In fact, most of the carboxylic acids exist as dimer in its vapour phase.
Question 24.
What happens when ethanoic acid reacts with the following reagents?
- LiAIH4
- Red P, Hl
Answer:
1. When ethanoic acid reacts by LiAIH4, partial reduction take place and ethanol is formed as a product.
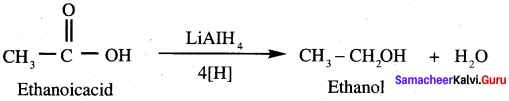
2. When ethanoic acid is treated with HI and red phosphorous, complete reduction take place and alkane is formed as a product.
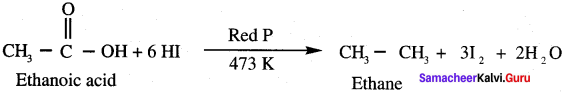
Question 25.
Explain the action of sodalime with sodium acetate. Name the type of reaction involved in ¡t.
Answer:
When sodium acetate is treated with sodalime, methane is formed.
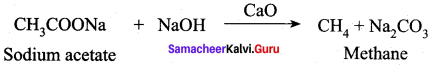
Removal of CO2 from carboxyl group take place in it and this is called decarboxylation
Question 26.
Explain about electrophilic substitution in Benzoic acid with example.
Answer:
Benzoic acid undergoes electrophilic substitution. The carboxyl group is a deactivating and meta directing group.
1. Halogenation.
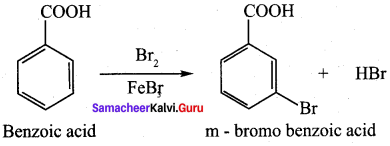
2. Nitration
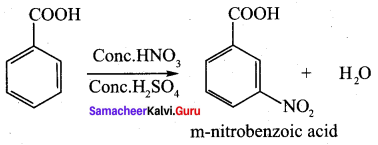
3. Sulphonation
Quesiton 27.
Formic acid act as reducing agent. Prove this statement.
Answer:
1. Formic acid contains both an aldehyde as well as an acid group. Hence, like other aldehydes, formic acid can easily be oxidised and therefore acts as a strong reducing agent.
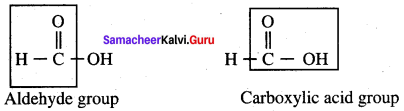
2. Formic acid reduces Tollen’s reagent (ammonical silver nitrate solution) to metallic silver.
![]()
3. Formic acid reduces Fehling’s solution. It reduces blue coloured cupric ions to red coloured cuprous ions.

Question 28.
Give three test for carboxylic acid.
Answer:
- In aqueous solution, carboxylic acid turn blue litmus red.
- Carboxylic acids give brisk effervescence with. sodium bicarbonate due to the evolution of carbon – di – oxide.
- When carboxylic acid is warmed with alcohol and conc H2SO4 it forms an ester, which is detected by its fruity odour.
Question 29.
Write a note about acidity of carboxylic acids.
Answer:
1. Carboxylic acids undergo ionisation to produce W and carboxylate ions in aqueous solution. The carboxylate ion is stabilised by resonance which make the Carboxylic acid to donate the proton easily.

2. The resonance structure of carboxylate ion are given below.

3. The strength of carboxylic acid can be expressed in terms of the dissociation constant(Ka):

The stronger the acid, the large will be its Ka value.
PKa = – log Ka
A strong acid will have higher ka value but smaller pKa value, the reverse is true for weak acid.
![]()
Question 30.
Formic acid is more stronger than acetic acid. Justify this statement. The electron releasing groups (+I groups) increase the relative charge on the carboxylate ion and destabilise it and hence the loss of proton becomes difficult.
+ I groups are CH3, – C2H5, – C3H7
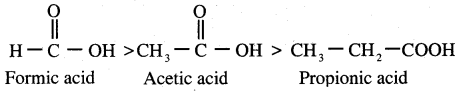
Question 31.
Explain the order of relative reactivity of acid derivatives.
Answer:
1. The reactivity of the acid derivatives follows the order
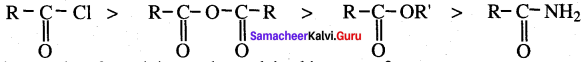
2. The above order of reactivity can be explained in terms of
Basicity of the leaving group
(b) Resonance effect
3. Weaker bases are good leaving groups. Hence acyl derivatives with weaker bases as leaving groups (L) can easily rupture the bond and are more reactive. The correct order of the basicity of the leaving group is
![]()
Hence the reverse is the order of reactivity.
4. Lesser the electronegativity of the group, greater would be the resonance stabilization as shown below.
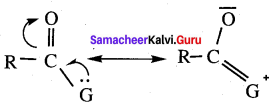
This effect makes the molecule more stable and reduces the reactivity of the acyl compound. The order of electronegativity of the leaving groups follows the order – Cl > – OCOR > – OR > – NH2. Hence the order of reactivity of the acid derivatives with nucleophilic reagent follows the order
Acid halide > Acid anhydride> esters> Acid amides
Question 32.
Explain the following reaction with acetyl chloride
- ammonolysis.
Answer:
Reaction with ammonia is known as arninonolysis
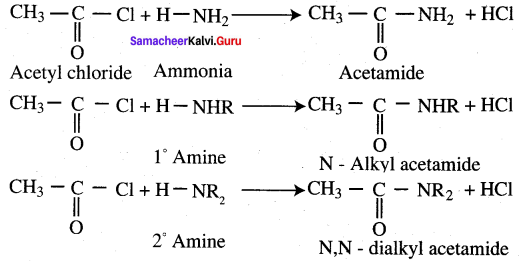
Question 33.
Explain the action of the following reagents with acetyl chloride?
- Pd / BaSO4
- LiAIH4
Answer:
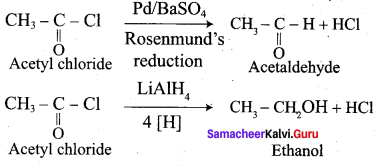
Question 34.
Describe about Claisen condensation.
Answer:
Esters containing at least one α – hydrogen atom undergo self condensation in the presence of a strong base such as sodium ethoxide to form β – keto ester. This reaction is known as Claisen condensation.
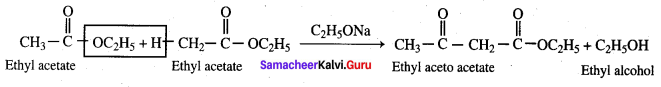
Question 35.
Acid amides are generally amphoteric in nature. Justify this statement.
Answer:
1. Amides behave both as weak acid as well as weak base and thus show amphoteric character. This can be proved by the following reactions.
2. Acetamide (as base) reacts with hydrochloric acid to form salt
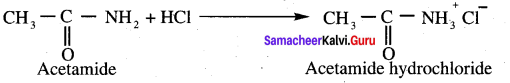
3. Acetamide (as acid) reacts with sodium to form sodium salt and hydrogen gas is liberated
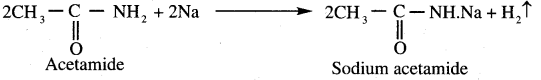
Question 36.
Mention the uses of formic acid?
Answer:
Formic acid. It is used
- for the dehydration of hides.
- as a coagulating agent for rubber latex
- in medicine for treatment of gout
- as an antiseptic in the preservation of fruit juice
Question 37.
What are the uses of acetic acid?
Answer:
Acetic acid is used
- as table vinegar
- for coagulating rubber latex
- for manufacture of cellulose acetate and poiy vinylacetate
![]()
Question 38.
Indicate the uses of Benzoic acid.
Answer:
Benzoic acid is used
- as food preservative either in the pure form or in the form of sodium benzoate
- in medicine as an urinary antiseptic
- for manufacture of dyes
Question 39.
What are the uses of acetic anhydride?
Answer:
Acetic anhydride is used
- acetylating agent
- in the preparation of medicine like aspnn and phenacetin
- for the manufacture plastics like cellulose acetate and poly vinyl acetate.
Question 40.
Mention the uses of Ethyl acetate?
Answer:
Ethyl acetate is used
- in the preparation of artificial fruit essences.
- as a solvent for lacquers.
- in the preparation of organic synthetic reagent like ethyl acetoacetate.
Question 41.
Give reasons for the following.
- Carboxylic acids do not give characteristic reactions of carboxyl group
- Treatment of benzaldehyde with HCN gives a mixture of two isomers which cannot be separated even by careful fractional distillation.
- Sodium bisuiphite is used for the purification of aldehydes and ketones.
Answer:
1. It is due to reasonance
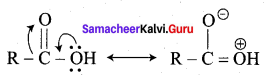
2. It is because we get two optical isomers which have same physical properties, therefore, cannot be separated by fractional distillation.
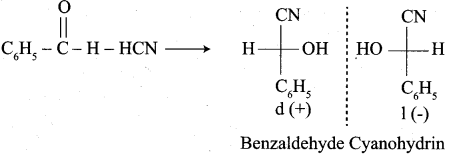
3. Aldehydes and ketones form addition compounds with NaHSO3 whereas any impurities do not. On hydrolysis, we get pure aldehydes and ketones back again.
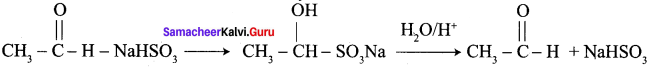
Question 42.
(i) Describe the preparation of acetic acid from acetylene.
(ii) How can the following be obtained from acetic acid:
(a) Acetone
(b) Acetaldehyde
(iii) In what way can acetic acid be distinguished from acetone?
(iv) Why carboxylic acid do not give the characteristic reactions of a carbonyl group?
Answer:
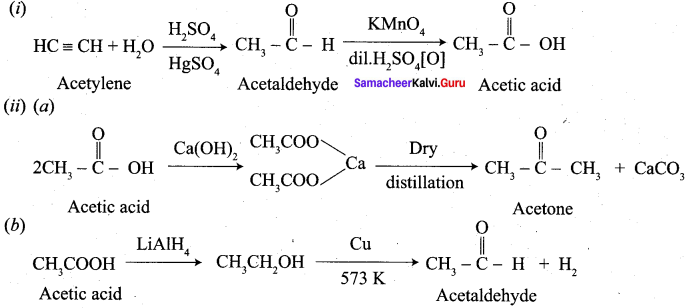
(iii). Add I2 and NaOH. Acetone will give yellow precipitate of iodoform whereas acetic acid does not react to give any yellow precipitate.(or) Add sodium bicarbonate solution Acetone will not react, but acetic acid will give brisk effervescence due to the evolution of CO2.
(iv). Carboxylic acid does not give the characteristic reactions of carbonyl group due to reasonance effect by the virtue of which it does not have free
![]()
carbonyl group.
Question 43.
Account for the following
- Cl – CH2COOH is a stronger acid than CH3COOH
- Carboxylic acids do not give reactions of carbonyl group.
Answer:
1. MonochLoroacetic acid is comparatively stronger acid than acetic acid. This is due to – Cl as a – I group
2. Carboxylic acids do not give reactions of carbonyl group because the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen attached to hydrogen in the – COOH group are involved in resonance, which makes the carbon less electrophilic.
Question 44.
A group of students were given to study the properties of aldehydes and ketones in the lab. They recorded a few observation of their physical properties.
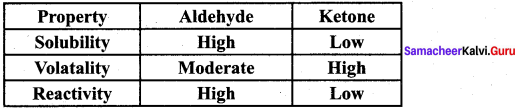
- Why are aldehydes more reactive and moreioiuble than ketones?
- What values of students are seen from the above act?
Answer:
- Aldehydes are more soluble in water because they form hydrogen bond with water molecule.
- Critical thinking
![]()
Question 45.
How will you distinguish between methanol and ethanol?
Answer:
By Iodoform test:
Ethanol having α – methyl group will give yellow ppt of iodoform whereas methanol, which do not have α – methyl group, will not give ppt. of iodoform.
Question 46.
There are two – NH2 group in semicarbazide. However, only one is involved in the formation of semicarbazone. Why?
Answer:
Although semicarbazide has two – NH2 groups but only one of them is involved in resonance as shown below.
As a result, e density on one of the – NH2 group is reduced and hence it does not act as nucleophile. One pair of the other – NH2 group is not involved in resonance and hence it is available for nucleophilic attack.
Question 47.
Explain why o – hydroxybenzaldehyde is a liquid at room temperature while p – hydroxybenzaldehyde is a high melting solid?
Answer:
Due to intramolecular H – bonding orthohydroxy benzaldehyde exists as discrete molecule whereas due to intermolecular H – bonding, p – hydroxybenzaldehyde exists as associated molecules. To break these intermolecular H – bonds, a large amount of energy is needed.
Consequently, p – hydroxybenzaldehyde has a much higher m.pt. and b.pt. than that of o – hydroxy benzaldehyde. As a result, o -hydroxy benzaldehyde is a liquid at room temperature while p – hydroxy benzaldehyde is a high melting solid.
Question 48.
A compound ‘X’ (C2H4O) on oxidation gives ‘Y’ (C2H4O2), ‘X’ undergoes haloform reaction. On treatment with HCN ‘X’ form a product ‘Z’ which on hydrolysis gives 2 – hydroxy propanoic acid.
- Write down the structures of ‘X’ and ‘Y’
- Name the product when ‘X’ reacts with dii NaOH.
- Write down the equations for the reaction involved.
Answer:
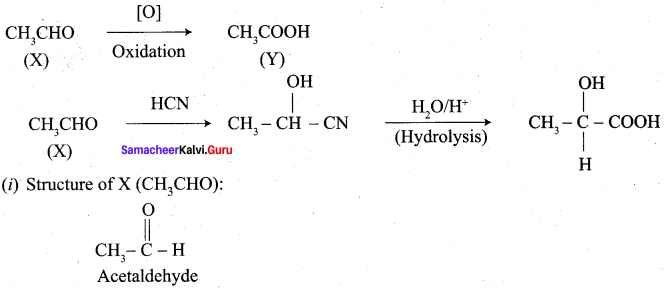
Structure of Y (CH3COOH)
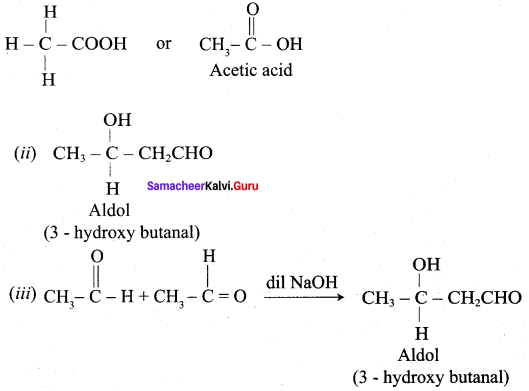
Question 49.
1. How will you prepare
- Acetic anhydride and
- Acetyl chloride from acetic acid?
Write the reactions involved in each case.
2. Why is the boiling point of an acid anhydride higher than the acid from which it is derived?
Answer:
1.
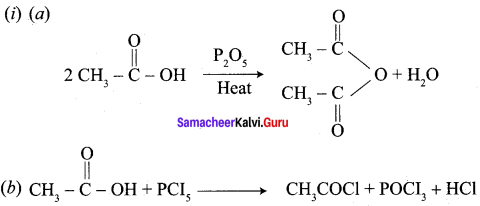
2. Acid anhydrides are bigger sized molecules than the corresponding acids, therefore have more surface area, more van der Waals’ forces of attraction and hence higher boiling points.
![]()
Question 50.
Suggest a reason for the large difference in the boiling point of butanol and butanal, although they have the same solubility in water.
Answer:
The b.pt. of butanol is higher than that of butanal because butanol has strong intermolecular H – bonding while butanal has weak dipole – dipole interactions. However both of them will form H – bond with water and hence are soluble.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids 5 Mark Questions and Answers
Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
Explain the action of ammonia with the following compounds.
Answer:
(i). Formaldehyde reacts with ammonia to form hexa methylene tetramine, which is also known as UrotroDine.
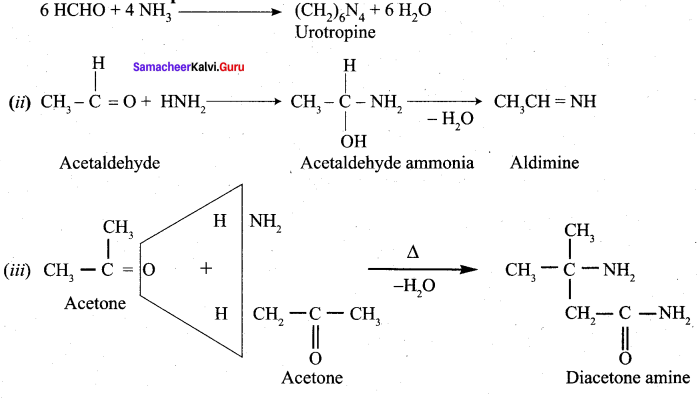
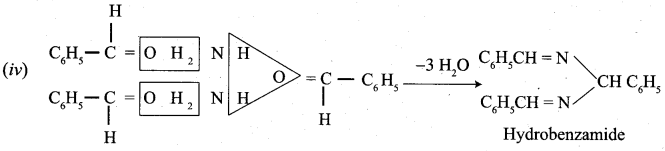
Question 2.
Explain the mechanism of aldol condensation.
Answer:
In presence of dilute base NaOH, or KOH, two molecules of an aldehyde or ketone having α – hydrogen add together to give 3 – hydroxyl aldehyde (aldol) or – hydroxyl ketone (ketol). The reaction is called aldol condensation reaction.
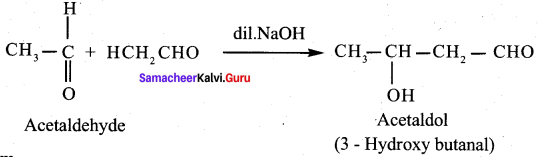
Mechanism
The mechanism of aldol condensation of acetaldehyde takes place in three steps.
Step 1:
The carbanion is formed as the α – hydrogen atom is removed as a proton by the base.

Step 2:
The carbanion attacks the carbonyl carbon of another unionized aldehyde to form an alkoxide ion.
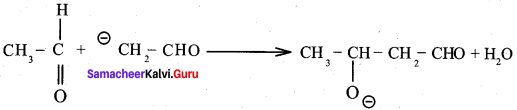
Step 3:
The alkoxide ion formed is protonated by water to form aldol.
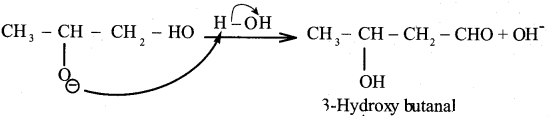
The aldol rapidly undergoes dehydration on heating with acid to form a, f3 unsaturated aldehyde.
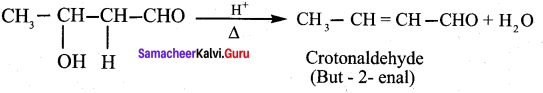
Question 3.
Explain the mechanism of Cannizaro reaction.
Answer:
1. In the presence of concentrated aqueous or alcoholic alkali, aldehydes which do not have α – hydrogen atom undergo self oxidation and reduction to give a mixture of alcohol and a salt of carboxylic acid. This reaction is called Cannizaro reaction.
2. Benzaldehyde on treatment with concentrated NaOH (50%) gives benzyl alcohol and sodium benzoate.
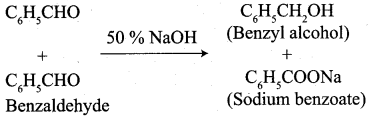
Mechanism
Cannizaro reaction involves three steps.
3. Step 1:
Attack of OH– on the carbonyl carbons.
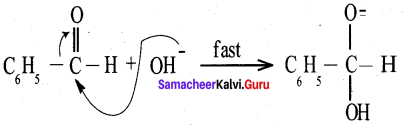
4. Step 2:
Hydride ion transfer
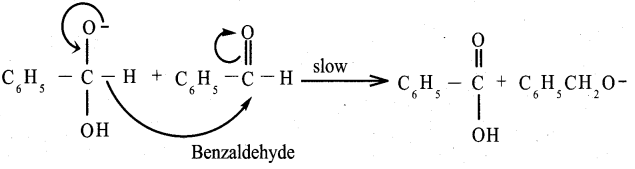
5. Step 3:
Acid – base reaction
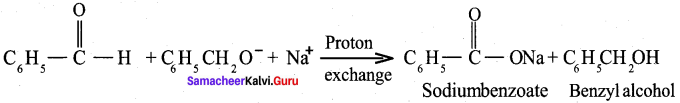
Question 4.
Explain
- Perkin’s reaction
- Knocvenagal reaction.
Answer:
1. Perkin’s reaction
When an aromatic aldehyde is heated with an aliphatic acid anhydride in the presence of the sodium salt of the acid corresponding to the anhydride, condensation takes place and an α, β unsaturated acid is obtained. This reaction is known as Perkin’s reaction.
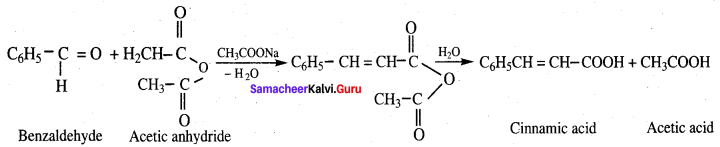
2. Knoevenagal reaction
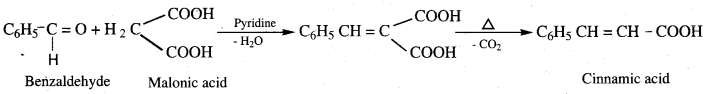
Question 5.
Explain about electrophilic substitution reactions of Benzaldehyde and acetophenone.
Answer:
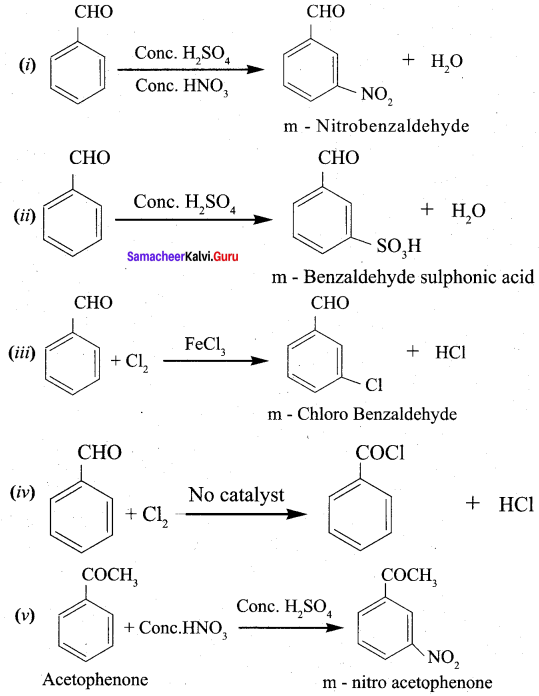
Question 6.
How would you prepare acetic acid from the following compounds.
- Ethyl alcohol
- Methyl cyanide
- Ethyl acetate
Answer:
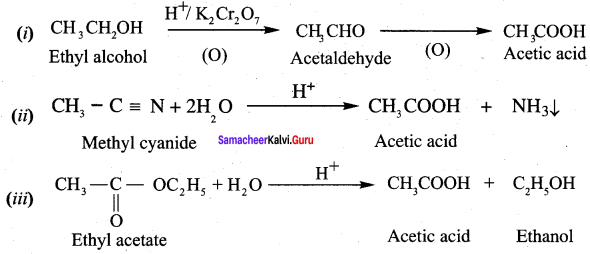
Question 7.
What is esterification? Explain the mechanism of esterification.
Answer:
When carboxylic acids are heated with alcohols in the presence of conc. HCI (or) dry HCI gas, esters are formed. This reaction is reversible and is called esterification.
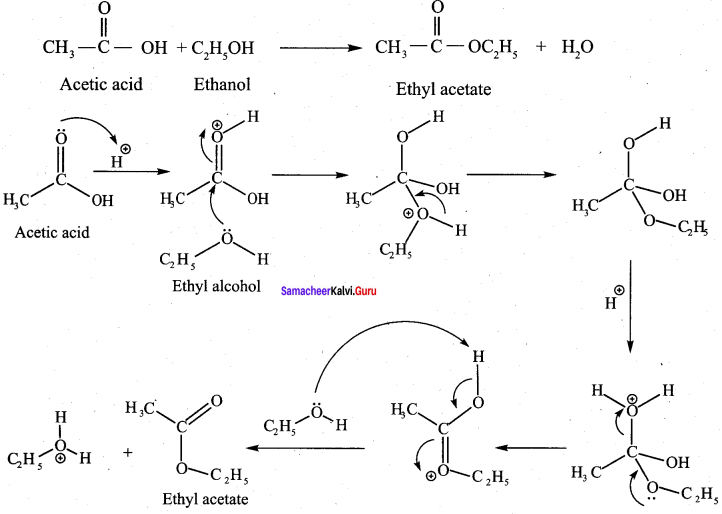
Question 8.
An organic compound (A) (molecular formula C8H16O2) was hydrolysed with dilute sulphuric acid to give a carboxylic acid (B) and an alcohol (C). Oxidation of (C) with chromic acid produced (B). (C) on dehydration gives but -1-ene. Write equations for the reactions involved.
Answer:
The relevant equations for all the reactions involved may be explained as follows.
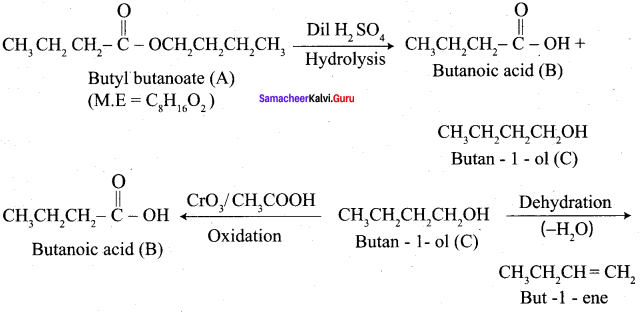
Question 9.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula CH6 reacts with Br2 in the presence of FeCI3 gives (B) of formula C6HBr. B on treatment with mg in the presence of dry ether gives (C) compound (C) on treatment with dry ice followed by hydrolysis gives a compound (D) of molecular formula C7H6O2. Identify A,B,C,D and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
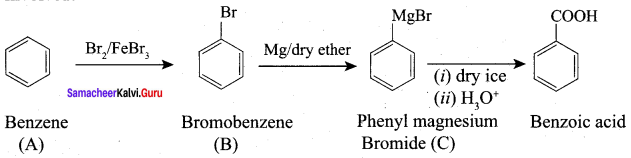
Question 10.
A simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (A) reacts with methyl chloride in the presence of AICI3 gives (B) C7H8. Compound (B) reacts with Br2 along with light gives (C) of molecular formula C7H7Br (C) reacts with alcohol KCN gives (D) (C8H7N) (D) on acid hydrolysis gives (E) of formula C8H8O2. Identify A,B,C,D,E and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
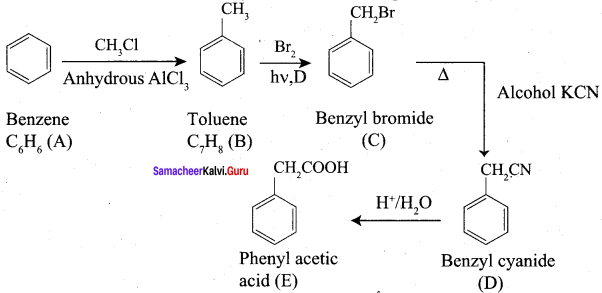
Question 11.
An organic compound (A) is a calcium salt of acetic acid. (A) on dry distillation gives (B) of formula C3H6O. (B) on reaction with LiAIH4 gives (C) of formula C3H8O (C) on heating with conc. H2SO4 gives (D) of molecular formula C3H6. Identify A,B,C,D and explain the reaction involved.
Answer:
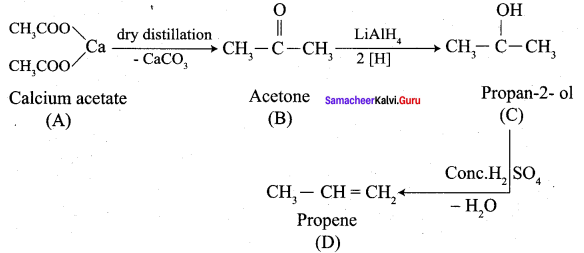
Question 12.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C7H8O on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 gives (B) of formula C7H6O. (B) on reaction with CI2 in the presence of catalyst FeCl3 gives (C) of formula C7HOCl. (B) on reaction with CI2 in the absence of catalyst gives C7H5OCI. Identify A,B, C,D and explain the reaction involved.
Answer:
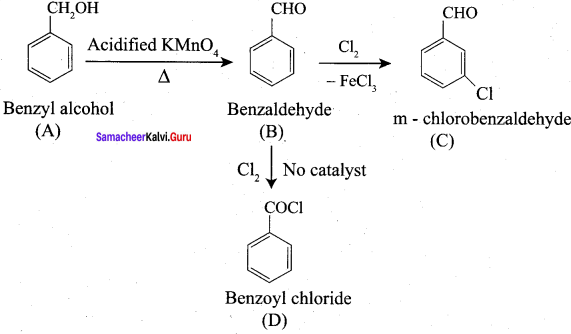
Question 13.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C7H6O reacts with acedaldehyde In the presence of sodium ethoxide gives (B) of formula C9H8O an unsaturated aldehyde. Compound (A) reacts with acetic anhydride in the presence of sodium acetate gives (C) and (D) of formula C9HO2 & C2H4O2 respectively. Identify AB,C,D and explain the reaction involved.
Answer:
1. From the molecular formula (A) is identified as Benzaldehyde C6H5CHO.Benzaldehyde reacts with acetaldehyde to give cinnamaldehyde as B in Claisen condensation reaction.
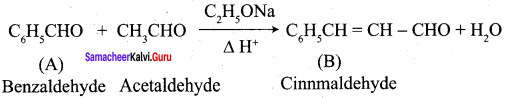
2. Benzaldehyde reacts with acetic anhydride (Oerkin’s reaction) to give cinnamic acid (C) as product.
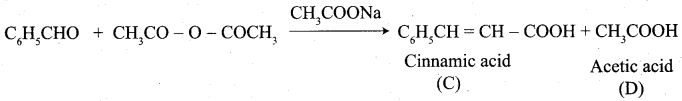
Question 14.
An aromatic aldehyde (A) of molecular C7H6O reacts with acidified KMnO4 to give (B) of molecular formula C7H6O2 calcium salt of compound (B) on dry distillation gives (C) of molecular formula C13H10O Compound (C) on Clemmenson’s reduction, gives (D) of formula C13H12O. Identify A,B,C,D and explain the reaction involved.
Answer:
1. From the molecular formula (A) is identified as Benzaldehyde C6H5CHO.Benzaldehyde on reaction with acidified KMnO4 undergoes oxidation to give Bcnzoic acid as compound (B)
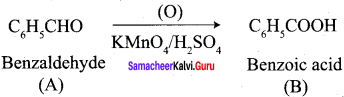
2. Calcium salt of Benzoic acid on dry distillaiton gives Benzophenone as compound (C)
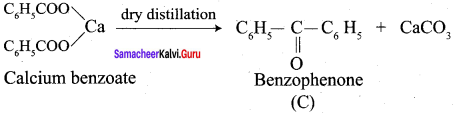
3. Benzophenone undergoes Clemmenson reduction in the presence Zn amalgam and HCI gives Diphenyl methane as (D)
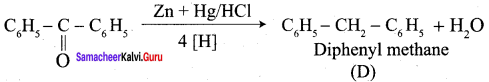
Question 15.
A simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (A) of formula C6H6 reacts with Bromine to gives (B) of molecular formula C6H5Br. (B) on treatment with magnesium metal in the presence of dry ether gives (C) . (C) on reaction with formaldehyde followed by acid hydrolysis gives (D) of formula C7H8O. Identify AB,C,D and explain the reaction involved.
Answer:
1. From the molecular formula (A) is identified as Benzene C6H6, Benzene reacts with Bromine to give bromobenzene as (B)
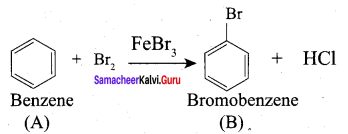
2. Bromobenzene reacts with Mg in the presence of dry ether gives phenyÍ magnesium bromide (Grignard reagent) as compound (C)
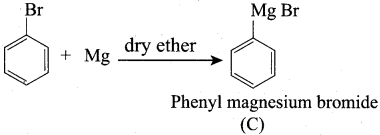
3. Phenyl magnesium bromide react with formaldehyde followed by acid hydrolysis gives Benzyl alcohol as product (D)
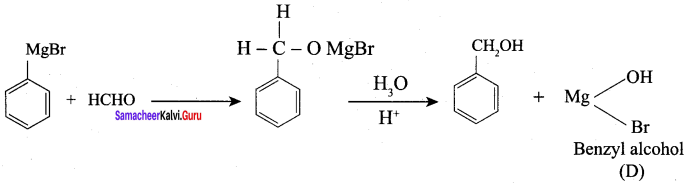
Question 16.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C2H3N on acid hydrolysis gives (B) of molecular formula C2H4O2 calcium salt of (B) gives (C) of molecular formula C3H6O. Compound (C) on reduction of hydrazine and sodium ethoxide gives (D) of molecular formula C3H8. Identify A,B,C,D and explain the reaction involved.
Answer:
1. 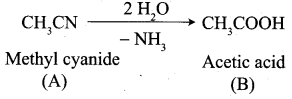
2. 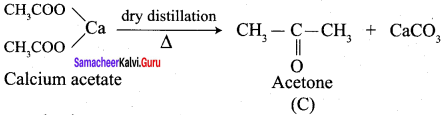
3. Wolf – Kishner reduction
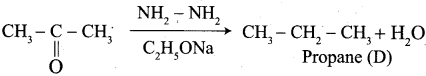
Question 17.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C7H8 on reaction with hot alkaline KMnO4 gives (B) of formula C7H6O2 which gives brisk effervescence with NaHCO3 solution. (B) on reaction with sodium hydroxide gives (C) of formula C7H5O2Na. Compound (C) on treatment with sodalime gives (D) the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon.
Answer:
1. From the molecular formula (A) is identified as Toluene. Toluene on treatment with hot alkaline KMnO4, oxidation take place and the product (B) formed is Benzoic acid.
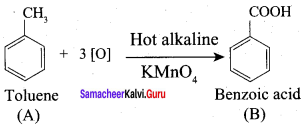
2. Benzoic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to give sodium benzoate as compound (C)
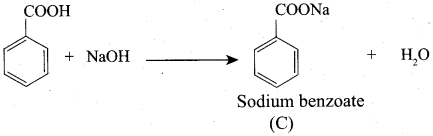
3. Sodium benzoate on reaction with sodalime (NaOH + CaO) decarboxylation take place and the product (D) formed is Benzene.
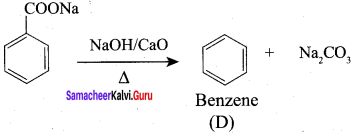
Question 18.
An organic compound (A) molecular formula C3H6O is resistant to oxidation but form a compound (B) (C3H8O) on reduction (B) reacts with HBr to form a bromide (C) which on treatment with alcoholic KOH forms an alkene (D) (C3H6). Deduce the structures of A,B,C and D.
Answer:
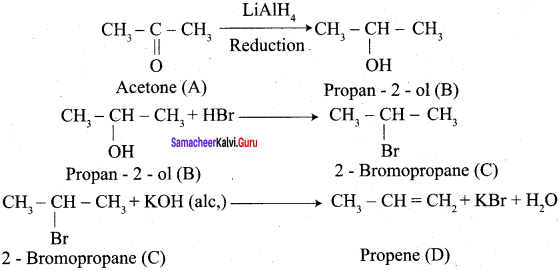
Question 19.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C6H6O gives violet colour with neutral FeCI3. (A) on reaction with zinc dust gives (B) of formula C6H6 (B) on treatment with acetvl chloride in the presence of anhydrous AICI3 gives (C) of formula C8HO. (C) on Clemmenson reduction gives (D) of formula C8H10O. Identify A,B,C,D and explain the reaction involved.
Answer:
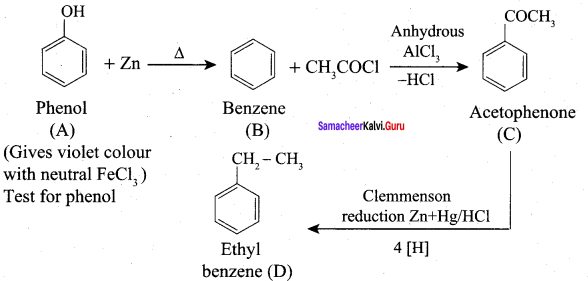
Question 20.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C3H6O reduces Tollen’s reagent on reaction with methyl magnesium bromide followed by acid hydrolysis gives (B) of formula C4H10O. (B) gives blue colour in victor meyer test. (B) on reaction with Cu at 573 K gives (C) of formula C4H8O (C) on reaction with hydrazine and sodium ethoxide gives (D) of molecular formula C4H10. identify A,B,C,D and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
1. An organic compound (A) reduces Tollen’s reagent it must be an aldehyde. From the formula, it is identified as CH3 – CH2 – CHO propanal.
2. Propanal on reaction with methyl magnesium bromide followed by acid hydrolysis gives (B) as Butan – 2 – ol. It must be a secondary alcohol and gives blue colour with victor meyer’s test. H
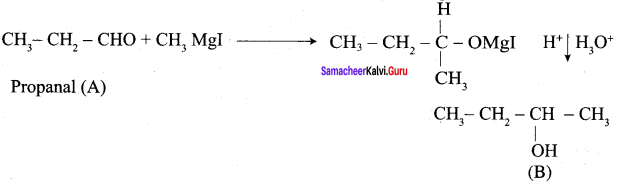
3. 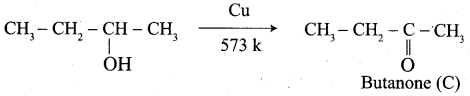
4. Wolf – Kishner reduction.
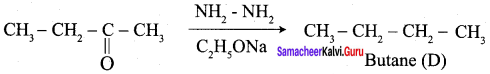
Question 21.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C7H6O2 reacts with PCI5 to give (B) of formula C7H5OCl (B) on treatment with ammonia gives (C) of formula C7H7NO (C) on treatment with phosphorous pentoxide gives (D) of formula C7H5N. Identify A,BC,D and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
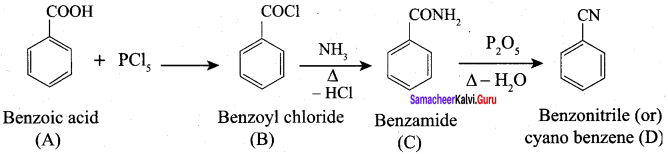
Question 22.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C3H6 on hydration in the presence of H2SO4 gives (B) C3H5O which gives blue colour In victor meyer’s test. (B) on treatment with Cu at 573 K gives C3H6O a compound (C) on self condensation in the presence of magnesium amalgam and water gives (D) of formula C6H14O2. Identify A,B,C,D and explain the reaction involved.
Answer:
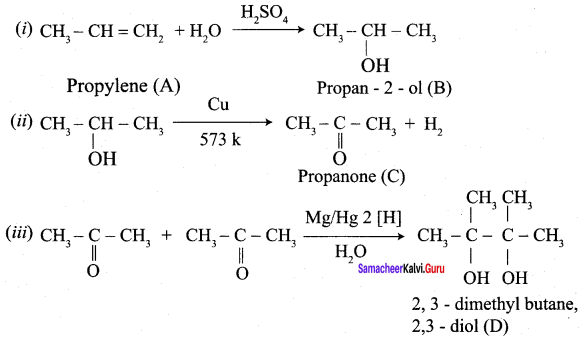
Question 23.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C2H4O reduces tollen’s reagent to silver mirror. (A) on treatment with C2H5MgBr followed by acid hydrolysis gives (B) of formula C4H10O. (B) on reaction with Cu at 573 K gives (C) of formula C4H8O which does not reduce tollen’s reagent but answers iodoform test. Identify A,B,C,D and explain the reaction involved.
Answer:
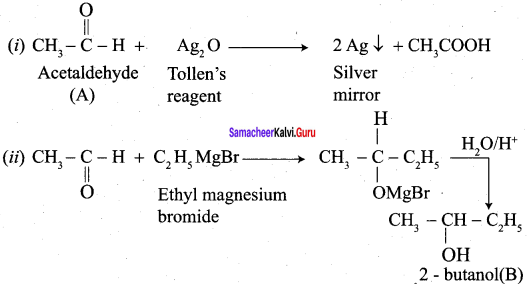
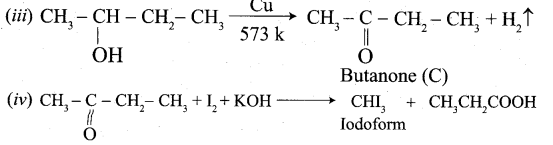
Question 24.
An unknown aldehyde ‘A’ on reacting with alkali gives a b – hydroxy – aldehyde, which loses water to form an unsaturated aldehyde, 2 – butenal. Another aldehyde ‘B’ undergoes disporportionation reaction in the presence of conc. alkali to form products C and D. C is – an aryl alcohol with formula C7H8O.
- Identify A and B.
- Write the sequence of reactions involved
- Name the product, when ‘B’ reacts with Zn amalgam and hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
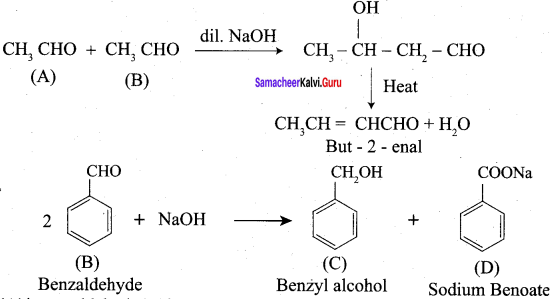
1. ‘A’ is acetaldehyde ‘B’ is Benzaldehyde
2. reactuib are shown above.
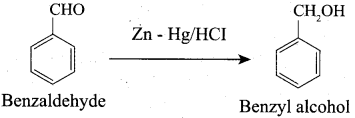
Question 25.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C4H8 is symmetric alkene. (A) on ozonolysis gives 2 moles (B) of molecular formula C2H4O. (B) on reaction with ammonia gives (C) of molecular formula C2H5N.
Answer:
1. (A) is a symmetric alkene. From the molecular formula, it is identified as But – 2 – ene
2. But – 2 – ene on ozonolysis gives 2 moles of acetaldehyde as product (B)
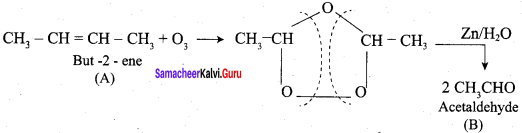
3. 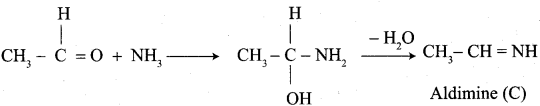
Question 26.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C2H4O2 gives brisk effervescence with sodium carbonate. (A) on reaction with thiony chloride gives (B) of formula C2H3OCI. (B) on reaction with Pd/BaSO4 gives (C) of molecular formula C2H4O that reduces Tollen’s reagent to silver mirror. (C) on reaction with dilute NaOH gives (D) of molecular formula C4H8O2. identify A,B,C,D and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
1. (A) gives brisk effervescence with Na2CO3 means it must be a carboxylic acid. So (A) must be CH3COOH Acetic acid.
2. Acetic acid reacts with thionyl chloride to give acetyl chloride CH3COCI as (B)
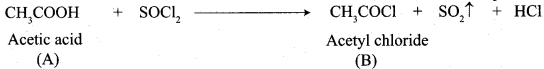
3. Acetyl chloride reacts with Pd/BaSO4, it undergoes Rosenmund’s reduction to give acetaldehyde as (C)
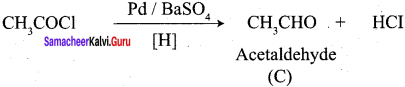
4. When acetaldehyde is warmed with dilute NaOH, it undergoes aldol condensation to
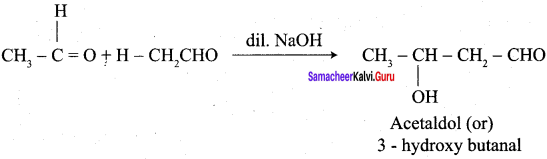
Question 27.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C7H8 reacts with CI2 in the presence of ho light gives (B) of formula C7H6C12. (B) on hydrolysis at 373 k gives (C) of formula C7H6O. (C) on treatment with 50% NaOH gives (D) and (E). Identify A,B,CD,E and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
1. From the molecular formula (A) is identified as Toluene. ToÍuene reacts with Cl2 in the presence of light gives Benzal chloride as (B)
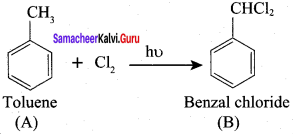
2. Benzal chloride on hydrolysis at 373 k gives Benzaldehyde as (C)
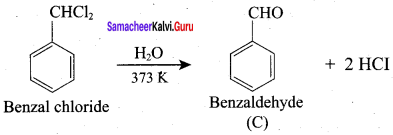
3. Benzaldehyde when warmed with dilute NaOH undergoes cannizaro reaction to give Benzyl alcohol (D) and sodium benzoate (E)
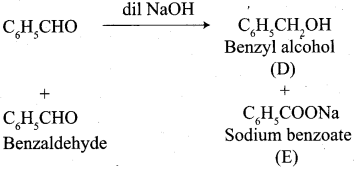
Question 28.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C2H3OCI on reaction with pd and BaSO4 gives (B) of formula C2H4O. (B) on reaction with LiAIH4 gives (C) of formula C2H6O. (B) on reaction with 12 and NaOH gives (D) of formula CH2ONa and iodoform. identify A,B,CD and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
1. From the molecular formula (A) is identified as CH3COCl (Acetyl chloride)
2. Acetyl chloride on treatment with Pd and BaSO4 gives acetaldehyde CH3CHO as (B)
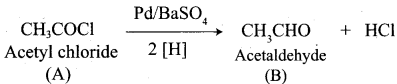
3. Acetaldehyde on reaction with LiAIH4 gives ethyl alcohol as (C)
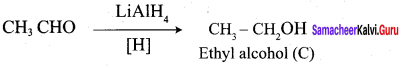
4. Acetaldehyde when treated with I2 and NaOH gives sodium formate (D) and iodoform CHI3 as products.
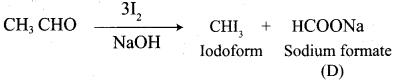
Question 29.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C7H6O gives brisk effervescence with Na2CO3. Sodium salt of (A) on treatment with sodalime gives (B) a simplest aromatic hydrocarbon. (B) on reaction with acetyichioride in the presence of anhydrous AICI3 gives (C) of formula C8H8O. (C) on treatment with conc. nitric acid and conc. sulphuric acid gives (D) of formula C8H7NO3. Identify A,BC,D,E and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
1. (A) gives brisk effervescence with Na2CO3 solution and it must be a carboxylic acid. (A) gives brisk effervescence with NNa2CO3 solution and it must be a carboxylic acid. (A) is C6H5COOH benzoic acid.
2. Sodium salt of benzoic acid on reaction with sodalime (decarboxylation) produces benzene as (B)
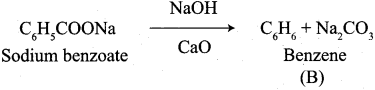
3. Benzene on treatment with acetyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 gives acetophenone as (C)
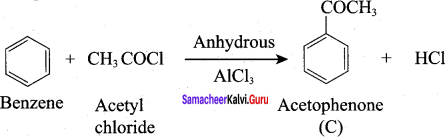
4. Acetophenonc on reaction with conc. HNO3 and cone. H2SO4 gives m – nitro acetophenone as (D)
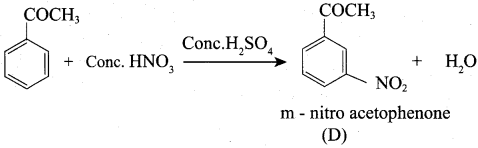
Question 30.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C2H6O on reaction with acidified K2Cr2O7 gives (B) of molecular formula C2H4O which on further oxidation gives (C) of molecular formula C2H4O2. Compound (C) reacts with (A) in the presence of conc. H2SO4 gives (D) of molecular formula C4H8O2. Identify A,B,C,D and explain the reaction Involved.
Answer:
1. An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C2H6O is identified as ethanol.
2. Ethanol on oxidation with acidified K2Cr2O7 gives first acetaldehyde as (B) which on further oxidation gives acetic acid as (C)
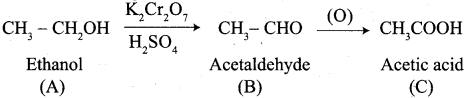
3. Ethanol reacts with acetic acid in the presence of conc. H2SO4, esterification take place to give ethyl acetate as product (D)
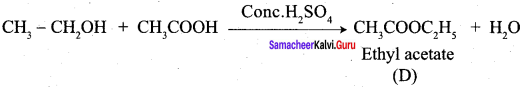
Question 31.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C2H4O2 gives brisk effervescence with Na2CO3. Acetyl chloride reacts with sodium acetate to give C4H6O3 as (B). (B) on reaction with PCI5 gives (C) of formula C2H10CI. (C) on reaction with ammonia gives (D) of molecular formula C2H5NO. Identify A,B,C,D and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
1. Compound (A) gives brisk effervescence with Na2CO3 and so it must be a carboxylic acid. CH3COOH (acetic acid) is compound A.
2. Acetyl chloride on heating with sodium acetate to give acetic anhydride as (B)
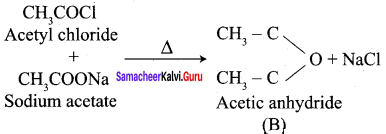
3. Acetic anhydride reacts with PCI5 to give acetyl chloride CH3COCI as (C)
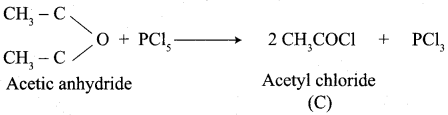
4. Acetyl chloride on treatment with ammonia gives acetamide as (D)
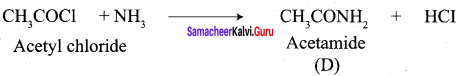
Question 32.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C2H4O2 reacts with PCI5 to give (B) of formula C2H3OCI. (B) on treatment with ammonia gives (C) of formula C2H5NO. (C) on reaction with Br2 and KOH gives CH5N as (D). Identify A,B,C,D and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
1. The organic compound (A) is identified as CH3COOH (Acetic acid).
2. Acetic acid reacts with PCI5 to form acetyl chloride as (B)
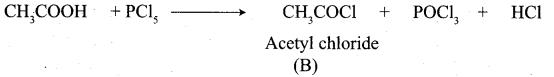
3. Acetyl chloride on reaction with ammonia gives acetamide as (C)

4. Acetamide on treatment with Br2, and KOH gives methylamine as (D)
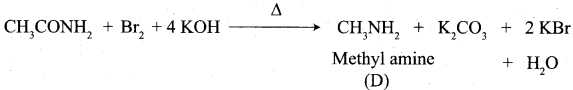
Question 33.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C2H5NO on treatment with LiAIH4 gives (B) of formula C2H7N. (A) on treatment with Br2 and excess of caustic alkali gives (C) of formula CH5N. (A) on treatment with phosphorous pentoxide gives (D) of molecular formula C2H3N Identify A,B,C,D and explain the reaclions involved.
Answer:
1. The organic compound (A) is identified as CH3CONH2 acetamide.
2. Acetamide on treatment with LiAlH4 gives ethylamine as product (B)
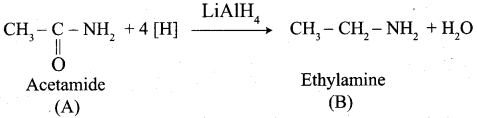
3. Acetamide on reaction with Br2 and caustic alkali gives methyl amine as (C)

4. Acetamide on treatment with P2O5 gives Aceto nitrile (or) methyl cyanide as (D)
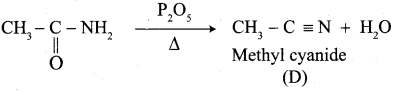
Question 34.
An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C2H5NO on reaction with P2O5 gives C2H3N(B). (B) on hydrolysis gives (C) of formula C2H4O2 (C) on reaction with LiMB4 gives (D) formula C2H6O. Identify A,B,C,D and explain the reactions involved.
Answer:
1. (A) is identified as CH3CONH2 acetarnide.
2. Acetamide on reaction with P2O5 gives methyl cyanide as (B)
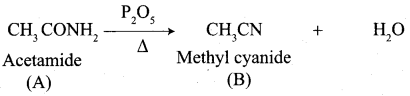
3. Methyl cyanide on acid hydrolysis gives acetic acid CH3COOH as (C)
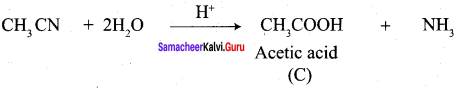
4. Acetic acid on reaction with LiAlH4 gives ethanol as (D)
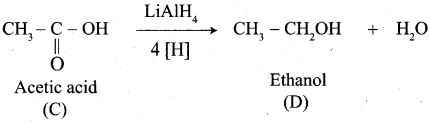
Errors
- Aldehydes IUPAC names
- Ketone – IUPAC name
- Ozonolysis – easy way to remember the products. Students may feel difficult in writing equation
- Clemmenson reduction and Wolf – Kishner reduction may get confused
Rectifications
1. The name should end with the word – al, HCHO – methanal, Aldehyde – Al, Alcohol – ol
2. The name should end with the word – one.  Propanone
Propanone
3. By the either side of = bond, add one oxygen atom as products
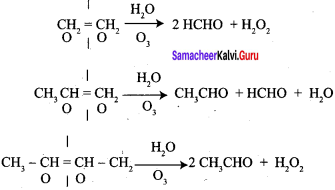
4. The products are same, only catalyst are different