Students can Download Economics Chapter 8 Indian Economy Before and After Independence Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Solutions Chapter 8 Indian Economy Before and After Independence
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Indian Economy Before and After Independence Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part – A
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The arrival of Vasco da Gama in Calicut, India
(a) 1498
(b) 1948
(c) 1689
(d) 1849
Answer:
(a) 1498
Question 2.
In 1614 Sir Thomas Roe was successful in getting permission from
(a) Akbar
(b) Shajakan
(c) Jahangir
(d) Noorjakhan
Answer:
(c) Jahangir
![]()
Question 3.
The power for governance of India was transferred from the East India Company (EIC) to the British crown in
(a) 1758
(b) 1858
(c) 1958
(d) 1658
Answer:
(b) 1858
Question 4.
Ryotwari system was initially introduced in _______
(a) Kerala
(b) Bengal
(c) Tamil Nadu
(d) Maharastra
Answer:
(c) Tamil Nadu
Question 5.
First World War started in the year _______
(a) 1914
(b) 1814
(c) 1941
(d) 1841
Answer:
(a) 1914
Question 6.
When did the Government of India declared its first Industrial Policy ?
(a) 1956
(b) 1991
(c) 1948
(d) 2000
Answer:
(c) 1948
Question 7.
The objective of the Industrial Policy 1956 was
(a) Develop heavy industries
(b) Develop agricultural sector only
(c) Develop private sector only
(d) Develop cottage industries only
Answer:
(a) Develop heavy industries
Question 8.
The industry which was de-reserved in 1993 ?
(a) Railways
(b) Mining of copper and zinc
(c) Atomic energy
(d) Atomic minerals
Answer:
(b) Mining of copper and zinc
Question 9.
The father of Green Revolution in India was _______
(a) M.S. Swaminathan
(b) Gandhi
(c) Visweswaraiah
(d) N.R. Viswanathan
Answer:
(a) M.S. Swaminathan
Question 10.
How many commercial banks were nationalised in 1969 ?
(a) 10
(b) 12
(c) 14
(d) 16
Answer:
(c) 14
Question 11.
The main objective of nationalisation of banks was _______
(a) Private social welfare
(b) Social welfare
(c) To earn
(d) Industries monopoly
Answer:
(b) Social welfare
Question 12.
The Planning Commission was setup in the year _______
(a) 1950
(b) 1955
(c) 1960
(d) 1952
Answer:
(a) 1950
Question 13.
In the first five year plan, the top priority was given to _______ Sector.
(a) Service
(b) Industrial
(c) Agriculture
(d) Bank
Answer:
(c) Agriculture
Question 14.
Tenth Five year plan period was _______
(a) 1992-1997
(b) 2002-2007
(c) 2007-2012
(d) 1997-2002
Answer:
(b) 2002-2007
![]()
Question 15.
According to HDR (2016), India ranked _______ out of 188 countries.
(a) 130
(b) 131
(c) 135
(d) 145
Answer:
(b) 131
Question 16.
Annual Plans formed in the year _______
(a) 1989-1991
(b) 1990-1992
(c) 2000-2001
(d) 1981-1983
Answer:
(b) 1990-1992
Question 17.
The Oldest large scale industry in India ________
(a) cotton
(b) jute
(c) steel
(d) cement
Answer:
(a) cotton
Question 18.
Human development index (HDI) was developed _________
(a) Jawaharlal Nehru
(b) M.K.Gandhi
(c) Amartiya Sen
(d) Tagore
Answer:
(c) Amartiya Sen
Question 19.
The main theme of the Twelth Five Year Plan __________
(a) faster and more inclusive growth
(b) growth with social Justice
(c) socialistic pattern of society
(d) faster, more inclusive and sustainable growth
Answer:
(d) faster, more inclusive and sustainable growth
Question 20.
The PQLI was developed by _______
(a) Planning Commission
(b) Nehru
(c) Morris
(d) Morris
Answer:
(c) Morris
Part – B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences
Question 21.
What are the Phases of colonial exploitation of India?
Answer:
- India was a colony for a long time. Colonialism refers to a system of political and social relations between two countries, of which one is the ruler and the other is its colony.
- The ruling country not only has political control over the colony, but it also determines the economic policies of the subjugated country.
- The people living in a colony cannot take independent decisions in respect of the utilization of the country’s resources and important economic activities.
- India had the bitter experience of colonialism.
![]()
Question 22.
Name out the different types of land tenure that existed in India before Independence.
Answer:
- Zamindari system
- Mahalwari system
- Ryotwari system
Question 23.
State the features that distinguish a land tenure system from other systems.
Answer:
- Land Tenure refers to the system of land ownership and management.
- The features that distinguish a land tenure system from the others relate to the following:
- Who owns the land;
- Who cultivate the land;
- Who is responsible for paying the land revenue to the government.
- Based on these questions, three different types of land tenure existed in India before Independence. They were Zamindari System, Mahalwari System, and Ryotwari System.
Question 24.
List out the weaknesses of the Green Revolution.
Answer:
- Indian agriculture was still a gamble of the monsoons.
- This strategy needed heavy investment.
- The income gap has increased
- Increased unemployment among agricultural labourers.
- Reduced the soil fertility and spoiled human wealth.
Question 25.
What are the objectives of the Tenth five-year plan?
Answer:
Tenth Five Year Plan [2002 – 2007]
- This plan aimed to double the per capita income of India in the next 10 years.
- It aimed to reduce the poverty ratio to 15% by 2012.
- Its growth target was 8.0% but it achieved only 7.2%
Question 26.
What is the difference between HDI and PQLI?
Answer:
- Human Development Index: It is constructed based on life expectancy index, Education index, and GDP per capita.
- Physical quality of life index: The PQLI is a measure to calculate the quality of life.
Question 27.
Mention the indicators which are used to calculate HDI.
Answer:
HDI is based on the following three indicators:
- Longevity is measured by life expectancy at birth.
- Educational attainments.
- Standard of living is measured by real GDP per capita [PPP $].
Part – C
Answer the following questions in one Paragraph
Question 28.
Explain the Period of Merchant Capital.
Answer:
- The period of merchant capital was from 1757 to 1813.
- The only aim of the East India company was to earn profit by establishing monopoly trade.
- During this period, India had been considered as the best hunting ground for capital
- The objective of monopoly trade was fulfilled by achieving political control.
- The company administration succeeded in generating huge surpluses which were repatriated to England.
Question 29.
The Handicrafts declined in India in British Period. Why?
Answer:
- The Indian handicrafts products had a worldwide market.
- Indian exports consisted chiefly of hand weaved cotton and silk fabrics, calicoes, artistic wares, wood carving, etc.
- Through discriminatory tariff policy, the British Government purposefully destroyed the handicrafts.
- With the disappearance of nawabs and kings, there was no one to protect Indian handicrafts.
- Indian handicraft products could not compete with machine-made products.
- The introduction of railways in India increased the domestic market for British goods.
Question 30.
Elucidate the different types of land tenure systems in colonial India.
Answer:
The three types of land tenure systems are Zamindari, Mahalwari, and Ryotwari systems.
1. Zamindari system or the landlords: This system was created in 1793, after the introduction of the permanent settlement act. Under this system, the landlords were declared as the owners of the land. They were responsible to pay the land revenue. The share of the rent to the government is fixed at 10/11th and the balance is zamindar’s remuneration.
2. Mahalwari system or communal farming: The ownership of the land was maintained by the collective body of villagers which served as a unit of management. They distribute the land and collect revenue and pay it to the state.
3. Ryotwari or the owner – cultivator system: The ownership rights of use and control of land were held by the tiller himself.
![]()
Question 31.
State the reasons for the nationalization of commercial banks.
Answer:
- After Independence, the Government of India adopted planned economic development.
- Five-year plans came into existence in 1951.
- The main objective of economic planning aimed at social welfare.
- Before Independence commercial banks were in the private sector.
- These commercial banks failed in helping the Government to achieve social objectives of planning.
- Therefore, the government decided to nationalize 14 major commercial banks on 19 July 1969.
- In 1980, again the government took over another 6 commercial banks.
Question 32.
Write any three objectives of Industrial Policy 1991.
Answer:
- Ensuring rapid industrial development in a competitive environment.
- Enhancing support to the small scale sector.
- Providing more incentives for industrialization of the backward areas.
Question 33.
Give a note on Twelfth Five Year Plan.
Answer:
- Its main theme is “Faster, More Inclusive and Sustainable Growth”.
- Its growth rate target is 8%.
- The Indian Independence the Five Year Plans of India played a very prominent role in the economic development of the country.
- These plans had guided the Government as to how it should utilize scarce resources so that maximum benefits can be gained.
- It is worthy to mention here that the Indian Government adopted the concept of five-year plans from Russia.
Question 34.
What is PQLI?
Answer:
Morris D Morris developed the physical quality of life index (PQLI). The PQLI is a measure to calculate the quality of life.
PQLI includes three indicators life expectancy, infant mortality rate, and literacy rate. A scale of each indicator ranges from the number 1 to 100. Represents the worst performance and 100 is the best performance.
HDI includes income while PQLI does not. PQLI has only the physical aspects of like.
Part – D
Answer the following questions in about a page
Question 35.
Discuss the Indian economy during the British Period.
Answer:
- India’s sea route trade to Europe started only after the arrival of Vasco da Gama in Calicut, India on May 20, 1498.
- The Portuguese had traded in Goa as early as 1510.
- In 1601 the East India Company was chartered, and the English began their first inroads into the Indian ocean.
- In 1614 Sir Thomas Roe was successful in getting permission from Jahangir for setting up factories and slowly moved all parts of India.
- Hundred years after the Battle of Plassey, the rule of the East India Company finally did come to an end.
- In 1858, British Parliament passed a law through which the power for the governance of India was transferred from the East India Company [EIC] to the British Crown.
- Even the transfer of power from the East India Company to the British Crown did not materially alter the situation.
- Britain had exploited India over a period of two centuries of its colonial rule.
- On the basis of the form of colonial exploitation, economic historians have divided the whole period into three phases:
- The period of merchant Capital
- The period of Industrial Capital
- The period of Finance Capital
Question 36.
Explain the role of SSIs in economic development?
Answer:
1. SSIs provide employment:
- SSIs use labor-intensive techniques thus reduce the problem of unemployment to a great extent.
- They provide employment to people in villages and unorganized sectors.
- The employment – capital ratio is high for the SSIs.
2. SSIs bring balanced regional development: SSIs remove regional disparities by industrializing rural and backward areas and bring balanced regional development.
3. Help in the mobilization of local resources: SSIs help to mobilize and utilize local resources like small savings, entrepreneurial talent etc.,
4. Pave for optimization of capital: SSIs require less capital per unit of output. They function as a stabilizing force by providing output-capital ratio as well as high employment capital ratio.
5. Promote exports: SSIs earn valuable foreign exchange through exports from India.
6. Complement large scale industries: SSIs serve as ancillaries to large scale units.
7. Meet consumer demands: SSIs serves as an anti-inflationary force by providing goods of daily use.
8. Develop entrepreneurship: They promote self-employment and a spirit of self-reliance in society. They help to increase the per capita income. They help in distributing national income in a more efficient and equitable manner.
![]()
Question 37.
Explain the objectives of the nationalization of commercial banks.
Answer:
The Government of India nationalized the commercial banks to achieve the following objectives:
- The main objective of nationalization was to attain social welfare. Sectors such as agriculture, small and village industries were in need of funds for their expansion and further economic development.
- The nationalization of banks helped to curb private monopolies in order to ensure a smooth supply of credit to socially desirable sections.
- In India, nearly 70% of population lived in rural areas. Therefore it was needed to encourage the banking habit among the rural population.
- Nationalization of banks was required to reduce the regional imbalances where the banking facilities were not available.
- Before Independence, the numbers of banks were certainly inadequate. After nationalization, new bank branches were opened in both rural and urban areas.
- Banks created credit facilities mainly to the agriculture sector and its allied activities after nationalization.
After New Economic Policy 1991, the Indian banking industry has been facing new horizons of competition, efficiency, and productivity.
Question 38.
Describe the performance of the 12th five-year plan in India.
Answer:
Economic planning is the process in which the limited natural resources are used skillfully so as to achieve the desired goals.
1. First five-year plan (1951 – 56): Main focus was on agricultural development it achieved a growth rate of 3.6%.
2. Second five-year plan (1956 – 61): Focus was on the industrial development of the country and achieved a growth rate of 4.1%.
3. Third five-year plan (1961 – 66): To make the economy independent and to reach take off.
4. Plan holiday (1966 – 69): Equal priority was given to agriculture, its allied sectors, and the industrial sectors during annual plans.
5. Fourth five-year plan (1969 – 74): Growth with stability and progressive achievement of self-reliance was the goal but the plan failed.
6. Fifth five-year plan (1975 – 79): A successful plan prioritized agriculture and then industry and mines.
7. Rolling plan: This plan was started with an annual plan for 1978-79.
8. Sixth five-year plan (1980 – 85): Based on investment yojana, its objective was poverty eradication and technological self-reliance.
9. Seventh five-year plan (1985 – 90): Establishment of the self-sufficient economy and opportunities for productive employment. Private sector got the priority over the public sector.
10. Annual plans: Two annual plans were formed in 1990 – 91 & 1991 -92.
11. Eighth five-year plan (1992 – 97): Priority was given to the development of human resources. A new economic policy was introduced.
12. Ninth five-year plan (1997 – 02):
- Aimed to double the per capita income in the next 10 years.
- Aimed to reduce the poverty ratio to 15% by 2012.
13. Tenth five-year plan (2002 – 07): Growth with justice and equity was the focus but the plan failed with a growth rate of 5.6%. Aimed to double the per capita income in the next 10 years. Aimed to reduce the poverty ratio to 15% by 2012.
14. Eleventh five-year plan (2007 – 12): The main theme was faster and more inclusive growth.
15. Twelfth five-year plan (2012 – 17): The main theme was faster more inclusive and sustainable growth. The five-year plans played a very prominent role in the economic development of the country. These plans had guided the government as to how it should utilize scarce resources so that maximum benefits can be gained.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Indian Economy Before and After Independence Additional Questions and Answers
Part – A
Choose the best options
Question 1.
Lord Cornwallis introduced “Permanent Settlement Act in” _______
(a) 1793
(b) 1794
(c) 1795
(d) 1796
Answer:
(a) 1793
![]()
Question 2.
In the year _______ green revolution started in India.
(a) 1950
(b) 1951
(c) 1948
(d) 1960
Answer:
(d) 1960
Question 3.
KGN. Daber established Mumbai’s spinning and weaving co. in _______
(a) 1810
(b) 1854
(c) 1845
(d) 1948
Answer:
(b) 1854
Question 4.
The oil well of Digboi, Assam was dug in.
(a) 1889
(b) 1898
(c) 1988
(d) 1810
Answer:
(a) 1889
Question 5.
The period of twelfth five year plan _______
(a) 2010 – 15
(b) 2011 – 16
(c) 2012 – 17
(d) 2013 – 18
Answer:
(c) 2012 – 17
Question 6.
NITI Aayog replaced the planning commission in _______
(a) 2013
(b) 2015
(c) 2014
(d) 2016
Answer:
(b) 2015
Question 7.
Human development index is _______
(a) HDI
(b) UNDP
(c) PQLI
(d) HID
Answer:
(a) HDI
![]()
Question 8.
Physical Quality of Life Index (PQLI) was developed by _______
(a) HDI
(b) PQLI
(c) UNDP
(d) HID
Answer:
(c) UNDP
Question 9.
In the _______ system, the ownership rights of use and control of land were held by the tiller himself.
(a) Zamindari
(b) Mahalwari
(c) Ryotwari
(d) Green revolution
Answer:
(c) Ryotwari
Question 10.
The period of industrial capital is _______
(a) 1757 – 1813
(b) 1813 – 1858
(c) 1757 – 1858
(d) 19th century
Answer:
(b) 1813 – 1858
Match the following and choose the answer using the codes given below
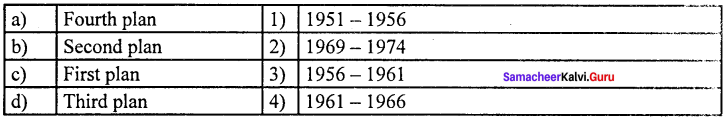
Question 1.
(a) 12 3 4
(b) 2 4 3 1
(c) 2 3 1 4
(d) 4 3 2 1
Answer:
(c) 2 3 1 4
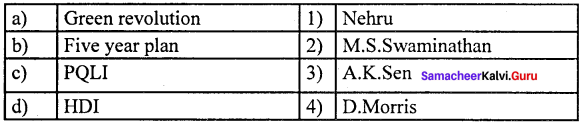
Question 2.
(a) 12 3 4
(b) 2 1 4 3
(c) 4 3 2 1
(d) 2 3 1 4
Answer:
(b) 2 1 4 3
Choose the correct option
Question 3.
The period of merchant capital is _______
(a) 1842 – 1857
(b) 1918 – 1920
(c) 1757 – 181
(d) 1721 – 1838
Answer:
(c) 1757 – 181
Question 4.
How many types of land tenure systems were there before independence?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) 5
Answer:
(b) 3
Question 5.
The first Indian modernized cotton cloth mill was established _______
(a) Chennai
(b) Calcutta
(c) Mumbai
(d) Bengaluru
Answer:
(b) Calcutta
Fill in the blanks with the suitable option given below
Question 6.
The plan holiday was _______
(a) 1951-53
(b) 1966-69
(c) 2001 -02
(d) 1976-79
Answer:
(b) 1966-69
Question 7.
The planning commission was replaced by _______
(a) NITI Aayog
(b) Planning group
(c) Finance commission
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) NITI Aayog
Question 8.
NITI Aayog was formed in _______
(a) 2001
(b) 2014
(c) 2015
(d) 2016
Answer:
(c) 2015
Choose the incorrect statement
Question 9.
(a) Ryotwari system was first established in Tamilnadu.
(b) Zamindari system was established by the British East India Company
(c) Mahalwari system was also called the owner – cultivator system
(d) Zamindari system was created in 1793
Answer:
(c) Mahalwari system was also called as the owner – cultivator system
![]()
Question 10.
(a) The investment of small service enterprises should be more than ₹ 10 lakhs.
(b) The investment of microservice enterprises should not exceed ₹ 10 lakhs.
(c) The investment of medium service enterprises should be more than ₹ 2 crores,
(d) The investment of medium service enterprises should not exceed ₹ 10 crores.
Answer:
(d) The investment of medium service enterprises should not exceed ₹ 10 crores.
Choose the incorrect pair
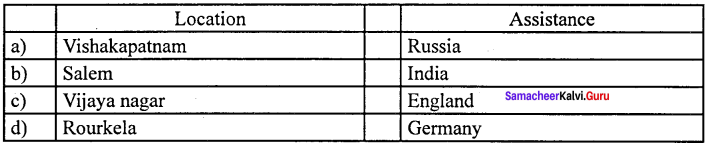
Question 11.
Answer:
(c) Vijaya Nagar (iii) England
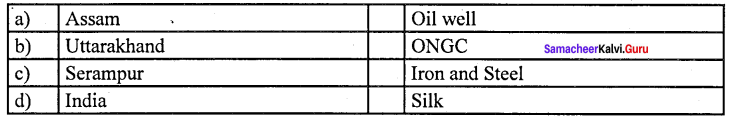
Question 12.
Answer:
(c) Serampur (iii) Iron and steel
Chooose the correct pair
Question 13.
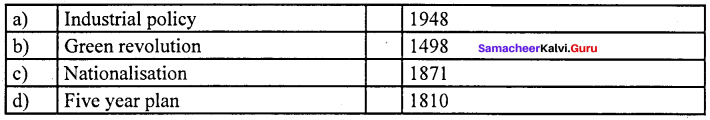
Answer:
(a) Industrial policy (i) 1948
Question 14.
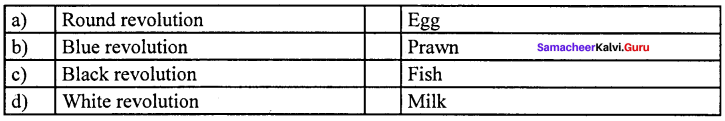
Answer:
(d) White revolution (iv) Milk
Analyze the reason for the following
Question 15.
Assertion (A): Before the advent of the British, the Indian economy was self-sufficient.
Reason (R): Before the advent of the British, India lived in the village.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true
(b) (A) is true (R) is false
(c) Both (A) and (R) are false.
(d) (A) is false (R) is true.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true
Choose the incorrect statement
Question 16.
(a) The industrial policy resolutions in India ushered in a socialistic economy
(b) The high yielding varieties programme was called a pilot project of the green revolution
(c) The aim of the seventh five-year plan is ‘Garibi Hatao’
(d) Finance commission replaced the planning commission.
Answer:
(b) The high yielding varieties programme was called a pilot project of the green revolution
![]()
Question 17.
(a) Switzerland ranks first in HDI.
(b) PQLI includes income whereas HDI excludes income
(c) The process of transforming private assets to government ownership is called privatization
(d) The third plan was called as ‘Gadgil plan’.
Answer:
(d) The third plan was called as ‘Gadgil plan’.
Pick the odd one out
Question 18.
(a) The period of revenue capital
(b) The period of industrial capital
(c) The period of merchant capital
(d) The period of financial capital
Answer:
(c) The period of merchant capital
Question 19.
(a) Investment system
(b) Zamindari system
(c) Mahalwari system
(d) Ryotwari system
Answer:
(a) Investment system
Question 20.
(a) Black revolution
(b) Red revolution
(c) White revolution
(d) Violet revolution
Answer:
(d) Violet revolution
Part – B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences
Question 1.
Name the classification of industries in India?
Answer:
- Public sector
- Public-cum-private sector
- Controlled private sector
- Private and co-operative sectors.
Question 2.
What is the resolution of industrial policy 1948?
Answer:
The first industrial policy was declared on 6th April 1948. Its main importance was introducing the system of mixed economy in India.
Question 3.
What is the resolution of industrial policy 1956?
Answer:
The policy was shaped by the Mahalanobis model of growth with an emphasis on heavy industries which would lead to a higher growth path.
Question 4.
Write a note on micro-manufacturing enterprises.
Answer:
In micro-enterprises, the investment in plant and machinery does not exceed Rs. 25 lakhs.
![]()
Question 5.
Write a note on small manufacturing enterprises
Answer:
The investment in plant and machinery is more than twenty-five lakh rupees but does not exceed Rs. 5 crores.
Question 6.
Write a note on medium manufacturing enterprises.
Answer:
The investment in plant and machinery is more than Rs. 5 crores but not exceeding Rs. 10 crores.
Question 7.
Name the classification of public sector banks.
Answer:
- Nationalized Banks.
- State Bank and its associates
Part – C
Answer the following questions in One Paragraph
Question 1.
Describe the problems of British rule in the Indian economy?
Answer:
- The British rule stunted the growth of Indian enterprise. It retarded the capital formation in India.
- The drain of wealth financed capital development in Britain.
- Indian agricultural sector became stagnant and deteriorated.
- Indian handicraft industries were collapsed.
- The system of capitalist firms with profit motives led to the drain of resources from India.
Question 2.
Mention the achievements of the green revolution.
Answer:
- The production of major cereals wheat and rice were boosted. India became a food surplus exporting food grains to European countries.
- It was confined to high yielding variety cereals.
- Production of commercial crops was increased.
- Per hectare productivity of all crops had increased due to better seeds.
- The revolution had a positive effect on the development of industries manufacturing agricultural tools.
- It brought prosperity to rural people.
- Demand for labor increased.
- Financial resources were provided by banks and co-operative societies.
Question 3.
Examine the requirements of the second green revolution.
Answer:
- Introduction of genetically modified (GM) seeds which double the per average production.
- Contribution of the private sector to market the usage of GM foods.
- The government can play a key role in expediting irrigation schemes and managing water resources.
- Linking of rivers to transfer surplus water to deficient areas.
![]()
Question 4.
Write a note on the iron and steel industry.
Answer:
- First steel industry at Kulti, near Jharia, West Bengal – Bengal ironworks company in 1870.
- First large-scale steel plant TISCO at Jamshedpur in 1907.
- Steel Authority of India Ltd. (SAIL) was established in 1974 and was made responsible for the development of the steel industry.
- India is the eighth-largest steel producing country in the world.
Question 5.
Write a note on petrol and natural gas.
Answer:
- The first successful oil well was dug in India in 1889 at Digboi, Assam.
- At present, a number of regions with oil reserves have been identified and oil is being extracted in these regions.
- For exploration purposes, the Oil and Natural Gas Commission (ONGC) was established in 1956 at Dehradun, Uttarakhand.