Students can Download Computer Science Chapter 3 Computer Organization Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Solutions Chapter 3 Computer Organization
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Computer Organization Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – 1
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
Which of the following is said to be the brain of a computer?
(a) Input devices
(b) Output devices
(c) Memory device
(d) Microprocessor
Answer:
(d) Microprocessor
Question 2.
Which of the following is not the part of a microprocessor unit?
(a) ALU
(b) Control unit
(c) Cache memory
(d) register
Answer:
(c) Cache memory
Question 3.
How many bits constitute a word?
(a) 8
(b) 16
(c) 32
(d) determined by the processor used
Answer:
(d) determined by the processor used
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following device identifies the location when address is placed in the memory address register?
(a) Locator
(b) encoder
(c) decoder
(d) multiplexer
Answer:
(c) decoder
Question 5.
Which of the following is a CISC processor?
(a) Intel P6
(b) AMD K6
(c) Pentium III
(d) Pentium IV
Answer:
(c) Pentium III
Question 6.
Which is the fastest memory?
(a) Hard disk
(b) Main memory
(c) Cache memory
(d) Blue – Ray disc
Answer:
(c) Cache memory
Question 7.
How many memory locations are identified by a processor with 8 bits address bus at a time?
(a) 28
(b) 1024
(c) 256
(d) 8000
Answer:
(c) 256
Question 8.
What is the capacity of 12 cm diameter DVD with single sided and single layer?
(a) 4.7 GB
(b) 5.5 GB
(c) 7.8 GB
(d) 2.2 GB
Answer:
(a) 4.7 GB
![]()
Question 9.
What is the smallest size of data represented in a CD?
(a) blocks
(b) sectors
(c) pits
(d) tracks
Answer:
(c) pits
Question 10.
Display devices are connected to the computer through.
(a) USB port
(b) PS/2 port
(c) SCSI port
(d) VGA connector
Answer:
(d) VGA connector
PART – 2
II. Short Answers
Question 1.
What are the parameters which influence the characteristics of a microprocessor?
Answer:
It depends on (a) Clock speed (b) Instruction set (c) Word size
Question 2.
What is an instruction?
Answer:
Instruction is a command which is given to the computer to perform an operation on a piece of data.
Question 3.
What is a program counter?
Answer:
A program counter (PC) is a CPU register in the computer processor which has the address of the next instruction to be executed from memory. It is a digital counter needed for faster execution of tasks as well as for tracking the current execution point.
![]()
Question 4.
What is HDMI?
Answer:
HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface is an audio/video interface which transfer the the uncompressed video and audio data from a video controller, to a compatible computer monitor, LCD projector, digital television, etc.
Question 5.
Which source is used to erase the content of a EPROM?
Answer:
Ultra violet rays are used to erase the contents of EPROM. EPROM retains its contents until it is exposed to ultraviolet light. The ultraviolet light clears its contents making it possible to reprogram the memory.
PART – 3
III. Explain in Brief
Question 1.
Differentiate Computer Organisation from Computer Architecture.
Answer:
Differences between computer organisation and Computer Architecture:
Computer Organisation:
- Often called micro architecture (low level).
- Transparent from programmer (example: a programmer does not worry much how addition is implemented in hardware).
- Physical components (Circuit design. Adders, Signals, Peripherals).
Computer Architecture:
- Computer architecture (a bit higher level)
- Programmer viewfi.e. Programmer has to be aware of which instruction set used)
- Logic (Instruction set, Addressing modes, Data types, Cache optimization)
Question 2.
Classify the microprocessor based on the size of the data.
Answer:
Depending upon the size of the data the microprocessor can be classified as
- 8 bit microprocessor
- 16 bit microprocessor
- 4 bit microprocessor
- 32 bit microprocessor
- 64 bit microprocessor.
![]()
Question 3.
Write down the classifications of microprocessors based on the instruction set.
Answer:
Classification of Microprocessor based on the Instruction set:
- RISC- Reduced Instruction Set Computers.
- CISC- Complex Instruction set Computers.
Question 4.
Differentiate PROM and EPROM.
Answer:
PROM:
- Can be Programmed only once.
- This has Permanent memory.
- Enclosed in plastic package so that not visible to UV light.
- Uses high Voltage.
EPROM:
- It is reusable and can be programmed multiple times.
- EPROMs memory can be erased using UV light.
- EPROMs are fused with quartz window.
- Also use high Voltage but not enough to alter the semiconductor layer permanently.
Question 5.
Write down the interfaces and ports available in a computer.
Answer:
Interfaces are HDMI interface port, USB 3.0 port, Ports available in the computer: Serial Port. Parallel port, USB ports, VGA connector. Audio plugs, PS/2 port, SCSI Port.
Question 6.
Differentiate CD and DVD.
Answer:
CD:
- CD stands for Compact Disc.
- Can store up to 700 MB.
- CD’s are single sided.
- Due to capacity constraint, CD’s cannot store movies of good quality.
- CD players cannot play DVD’s.
DVD:
- DVD stands for Digital Versatile Disc.
- Capacity of DVD is 4.7 GB of data.
- DVD’s are single or double sided.
- DVD’s are used for storing movies with good quality.
- DVD players can play CD’s.
Question 7.
How will you differentiate a flash memory and an EEPROM?
Answer:
Flash memory:
- It is faster.
- Flash memory is read/write memory.
- Flash memory can store 4GB to 2TB of data.
- Flash memory is used in PDA’S, Digital camera to store data.
EEPROM:
- It is slower.
- EEPROM is read only memory.
- EEPROM can store only less data.
- It is used to store critical programs.
PART – 4
IV. Explain in Detail
Question 1.
Explain the characteristics of a microprocessor.
Answer:
(a) Clock speed – Each microprocessor has an internal clock that regulates the speed at which it executes instructions. The speed at which the microprocessor executes instructions is called clock speed. It is measured in MHz or in GHz.
(b) Instructions set – The set of machine level instructions that a microprocessor is designed to execute is called as an instruction set. This carries 4 types of operations. They are
- Data transfer
- Arithmetic operations
- Logical Operations
- Control flow
- Input/output
(c) Word size – The number of bits that can be processed by a processor in a single instruction is called as its word size. It determines the amount of RAM that can be accessed at one time and the total number of pins on the microprocessor. Total number of input and output pins in turn determines the architecture of the microprocessor.
Question 2.
How the read and write operations are performed by a processor? Explain.
Answer:
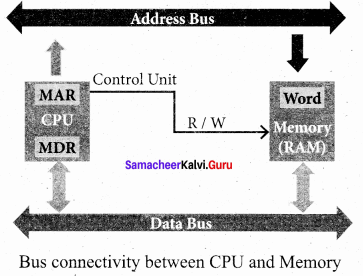
- The Central Processing Unit(CPU) has a Memory Data Register (MDR) and a Memory Address Register (MAR).
- The Memory Data Register (MDR) keeps the data which is transferred between the Memory and the CPU. The Program Counter (PC) is a special register in the CPU which always keeps the address of the next instruction to be executed.
- The Arithmetic and Logic unit of CPU places the address of the memory to be fetched, into the Memory Address Register.
- A bus is a collection of wires used for communication between the internal components of a computer.
- The address bus is used to point a memory location. A decoder, a digital circuit is used to point to the specific memory location where the word can be located.
- The address register is connected with the address bus, which provides the address of the instruction. A data bus is used to transfer data between the memory and the CPU.
- The data bus is bidirectional and the address bus is unidirectional. The control bus controls both read ana write operations.
- The read operation fetches data from memory and transfers to MDR. A single control line performs two operations like Read/Write using lor 0.
- Also, the write operation transfers data from the MDR to memory. This organisation is shown below.
- The word in the RAM has the same size (no. of bits) as the Memory Data Register (MDR). If the processor is an 8-bit processor like Intel 8085, its MDR and the word in the RAM both have 8 bits.
- If the size of the MDR is eight bits, which can be connected with a w7ord in the memory which is also eight bits size. The data bus has eight parallel wires to transfer data either from MDR to word or word to MDR based on the control(Read or write).
- This control line is labeled as R/W, which becomes 1 means READ operation and 0 means WRITE operation.
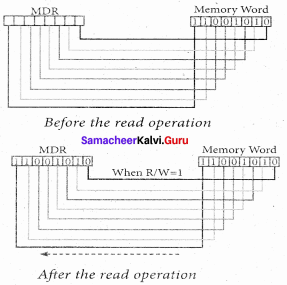
- These pictures show the contents of MDR and the word before and after the READ operation.
- The read operation transfers the data(bits) from word to Memory Data Register.
- The write operation transfers the data(bits) from Memory Data Register to word.
Question 3.
Arrange the memory devices in ascending order based on the access time.
Answer:
A memory is just like a human brain. It is used to store data and instructions. Computer memory is the storage space in the computer, where data and instructions are stored. There are two types of accessing methods to access (read or write) the memory. They are sequential access and random access. In sequential access, the memory is accessed in an orderly manner from starting to end. But, in random access, any byte of memory can be accessed directly without navigating through previous bytes. Different memory devices are arranged according to the capacity,
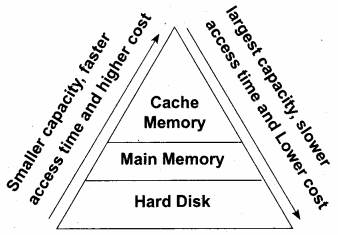
Question 4.
Explain the types of ROM.
Answer:
Types of Rom:
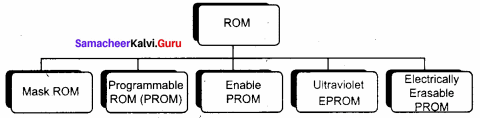
Read Only Memory (ROM):
- Read Only Memory refers to special memory in a computer with pre-recorded data at manufacturing time which cannot be modified.
- The stored programs that start the computer and perform diagnostics are available in ROM’s. ROM stores critical programs such as the program that boots the computer.
- Once the data has been written onto a ROM chip, it cannot be modified or removed and can only be read.
- ROM retains its contents even when the computer is turned off. So, ROM is called as a non – volatile memory.
Programmable Read Only Memory (PROM):
- Programmable read only memory is also a non – volatile memory on which data can be written only once. Once a program has been written onto a PROM, it remains there forever.
- Unlike the main memory, PROM’s retain their contents even when the computer is turned off.
- The PROM differs from ROM. PROM is manufactured as a blank memory, whereas a ROM is programmed during the manufacturing process itself.
- PROM programmer or a PROM burner is used to write data to a PROM chip. The process of programming a PROM is called burning the PROM.
Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EPROM):
- Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory is a special type of memory which serves as a PROM, but the content can be erased using ultraviolet rays.
- EPROM retains its contents until it is exposed to ultraviolet light. The ultraviolet light clears its contents, making it possible to reprogram the memory.
- An EPROM differs from a PROM, PROM can be written only once and cannot be erased.
- EPROMs are used widely in personal computers because they enable the manufacturer to change the contents of the PROM to replace with updated versions or erase the contents before the computer is delivered.
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM):
- Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory is a special type of PROM that can be erased by exposing it to an electrical charge.
- Like other types of PROM, EEPROM retains its contents even when the power is turned off.
- Comparing with all other types of ROM, EEPROM is slower in performance.
Samacheer kalvi 11th Computer Science Computer Organization Additional Questions and Answers
PART – 1
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The ………………. is the major component of a computer, which performs all taks.
(a) CPU
(b) MDR
(c) MAR
(d) RISC
Answer:
(a) CPU
Question 2.
The speed at which the microprocessor executes instructions is called ……………….
(a) Instruction set
(b) word size
(c) clock speed
(d) control flow
Answer:
(c) clock speed
Question 3.
The number of bits that can be processed by a processor in a single instruction is called ……………….
(a) word size
(b) CPU
(c) Data transfer
(d) CISC
Answer:
(a) word size
![]()
Question 4.
The main memory is otherwise called as ……………….
(a) cache memory
(b) main memory
(c) hard disk
(d) random access memory
Answer:
(d) random access memory
Question 5.
………………. is a magnetic disk on which you can store data.
(a) compact disc
(b) hard disk
(c) DVD
(d) flash memory devices
Answer:
(b) hard disk
Question 6.
………………. is a high – density optical disc similar to DVD.
(a) Blu – Ray disc
(b) digital versatile disc
(c) flash memory devices
(d) compact disc
Answer:
(a) Blu – Ray disc
Question 7.
………………. connect the hard disk drives and network connectors.
(a) PS/2 port
(b) SCSI port
(c) USB port
(d) serial port
Answer:
(b) SCSI port
Question 8.
………………. is an electronic (solid – state) non – volatile computer storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed.
(a) main memory
(b) flash memory
(c) Blu – Ray disc
(d) USB
Answer:
(b) flash memory
Question 9.
The micro processors were first introduced in early ……………….
(a) 1976
(b) 1975
(c) 1970
(d) 1978
Answer:
(c) 1970
Question 10.
………………. is commonly used to measure wave frequencies.
(a) Hertz
(b) internal memory
(c) RAM
(d) ALU
Answer:
(a) Hertz
Question 11.
Which one of the following deals with hardware components of a computer system.
(a) Computer organisation
(b) Computer architecture
(c) System software
(d) Application software
Answer:
(a) Computer organisation
Question 12.
Computer architecture deals with ……………….
(a) designing the computer
(b) input devices
(c) output devices
(d) memory
Answer:
(a) designing the computer
![]()
Question 13.
The first general purpose microprocessor was ……………….
(a) IBM 2002
(b) IBM 1620
(c) Intel 4004
(d) Intel 4002
Answer:
(c) Intel 4004
Question 14.
Which one of the following is a programmable multipurpose silicon chip and are driven by clock pulses?
(a) Hardware
(b) Memory
(c) Microprocessor
(d) Clock
Answer:
(c) Microprocessor
Question 15.
Which of the following temporarily holds the instructions and data for execution of the processor.
(a) ALU
(b) CU
(c) Registers
(d) RAM
Answer:
(c) Registers
Question 16.
How many types of system buses are available?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(b) 3
Question 17.
System bus is a collection of ……………….
(a) address bus
(b) data bus
(c) control bus
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Question 18.
Which one of the following bus serves as a communication channel between the microprocessor and other devices.
(a) Address bus
(b) Data bus
(c) Control bus
(d) Process bus
Answer:
(c) Control bus
Question 19.
MHz arid GHz are the units of ……………….
(a) clock speed
(b) instruction set
(c) Word size
(d) system bus
Answer:
(a) clock speed
Question 20.
An average human ear can detect sound waves between ……………….
(a) 20 to 200 Hz
(b) 20 to 2000 Hz
(c) 20 to 20000 Hz
(d) 20 to 200000 Hz
Answer:
(c) 20 to 20000 Hz
Question 21.
One hertz is equal to ………………. cycles per second.
(a) 1
(b) 10
(c) 2
(d) 20
Answer:
(a) 1
Question 22.
Which among the following is not an operation carried out Instruction set?
(a) Arithmetic operations
(b) Logical operations
(c) Control flow
(d) Bitwise operations
Answer:
(d) Bitwise operations
Question 23.
The architecture of the microprocessor is determined by ……………….
(a) total no. of input and output pins
(b) clock speed
(c) word size
(d) instruction set
Answer:
(a) total no. of input and output pins
Question 24.
The amount of RAM that can be accessed by a microprocessor at one time is determined by ……………….
(a) clock speed
(b) word size
(c) instruction
(d) software
Answer:
(b) word size
Question 25.
Intel 8085 is a ………………. bit processor.
(a) 8
(b) 16
(c) 32
(d) 64
Answer:
(a) 8
Question 26.
What will be the value of of control line for read operation from RAM to MDR?
(a) 1
(b) 0
(c) 1
(d) 2
Answer:
(a) 1
Question 27.
Which bus is unidirectional?
(a) Control
(b) System
(c) Data
(d) Address
Answer:
(d) Address
Question 28.
Which of the following digital circuit is used to point to the specific memory location where the word can be located?
(a) Logic gate
(b) Transistor
(c) Encoder
(d) Decoder
Answer:
(d) Decoder
Question 29.
How many classifications of microprocessors are there based on data width?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(c) 4
![]()
Question 30.
Which one of the following is not a RISC processor?
(a) Pentium IV
(b) AMD K6
(c) Intel P6
(d) AMD K8
Answer:
(d) AMD K8
Question 31.
Which one of the following is not a CISC processor?
(a) Pentium II
(b) Pentium III
(c) Pentium IV
(d) Pentium
Answer:
(c) Pentium IV
Question 32.
Which of the following memory is of higher cost?
(a) Hard disk
(b) Main memory
(c) Cache memory
(d) Floppy
Answer:
(c) Cache memory
Question 33.
Which of the following needs refreshing very often?
(a) ROM
(b) Static RAM
(c) Dynamic RAM
(d) EPROM
Answer:
(c) Dynamic RAM
Question 34.
In which of the following memory, contents can be erased by exposing to ultraviolet rays?
(a) ROM
(b) EPROM
(c) PROM
(d) RAM
Answer:
(b) EPROM
Question 35.
Identify the wrong statement.
(i) Dynamic RAM have to be refreshed frequently.
(ii) SRAM is faster.
(iii) SRAM is cheap.
(iv) SRAM is to be refreshed less often.
(a) (iv)
(b) (iii)
(c) (ii)
(d) (i)
Answer:
(b) (iii)
Question 36.
The time taken to respond to a read/write operation is ………………….
(a) response time
(b) access time
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) sequential time
Answer:
(c) both (a) and (b)
Question 37.
CD data represented as tiny indentations are called ………………….
(a) tracks
(b) sectors
(c) stacks
(d) pits
Answer:
(d) pits
Question 38.
Which one of the following has the stacked arrangement of disks?
(a) CD
(b) DVD
(c) Blu – Ray
(d) Hard disk
Answer:
(d) Hard disk
Question 39.
A 12 cm diameter DVD with single sided, single layer has the storage capacity of ………………….
(a) 4.7 GB
(b) 8.7 GB
(c) 8.5 GB
(d) 1.5 GB
Answer:
(a) 4.7 GB
Question 40.
What is the colour of double layered sides DVD?
(a) Silver
(b) Green
(c) Gold
(d) Brown
Answer:
(c) Gold
Question 41.
Which type of disc is : used for playing High-Definition movies?
(a) CD
(b) DVD
(c) Flash Devices
(d) Blu – Ray Disc
Answer:
(d) Blu – Ray Disc
Question 42.
DVD uses a …………………. colour laser to read and write data.
(a) red
(b) green
(c) blue
(d) orange
Answer:
(a) red
Question 43.
Blu – ray uses a …………………. laser to write data.
(a) red
(b) green
(c) blue – violet
(d) violet
Answer:
(c) blue – violet
Question 44.
USB 3.0 can transfer data up to ………………….
(a) 3 GB/sec
(b) 5GB/sec
(c) 5GB/min
(d) 3GB/min
Answer:
(b) 5GB/sec
Question 45.
Match the following.

(a) (1) (2) (3) (4)
(b) (4) (3) (2) (1)
(c) (2) (3) (4) (1)
(d) (3)(4) (2) (1)
Answer:
(c) (2) (3) (4) (1)
Question 46.
Which port is used to LCD projector.
(a) SCSI
(6) PS/2
(c) Audio
(d) VGA port
Answer:
(d) VGA port
![]()
Question 47.
The areas between the pits in CD’s are called ………………….
(a) memory
(b) bus
(c) buffer
(d) lands
Answer:
(d) lands
Question 48.
Which one of the following uses magnetic disk to store the data?
(a) DVD
(b) HD
(c) CD
(d) FD
Answer:
(b) HD
Question 49.
How are sound waves close to 20 Hz with low pitch called?
(a) Treble
(b) Tremble
(c) Bass
(d) Accumulator
Answer:
(c) Bass
Question 50.
Which of the following interface transfers the uncompressed audio and video data to monitor, projector?
(a) CD
(b) DVD
(c) HDMI
(d) FDD
Answer:
(c) HDMI
PART – 2
II. Short Answers
Question 1.
Which is the first commercial microprocessor?
Answer:
Intel 4004 is a 4-bit processor.
Question 2.
What are the components of CPU?
Answer:
The CPU has a Memory Data Register (MDR) and a Memory Address Register (MAR). The MDR keeps the data which is to be transferred between memory and the CPU. The ALU of CPU places the address of the memory to be fetched into MAR.
Question 3.
What is Program counter?
Answer:
Program counter is a special Register in the CPU which always keeps the address of the next instruction to be executed.
![]()
Question 4.
Define a BUS?
Answer:
- A bus is a collection of wires used for communication between the internal components of a computer.
- The three types of buses are: address bus, data bus and control bus.
Question 5.
What is the use of cache memory?
Answer:
- Cache memory is a very high speed and expensive memory.
- It is used to speed up the memory retrieval process.
- Cache memory comes with smaller size.
Question 6.
What is meant by Hard Disk?
Answer:
- Hard disk is a magnetic disk on which user can store data.
- The hard disks has the stacked arrangement of disks accessed by a pair of heads for each of the disk.
- The hard disks come with a single or double sided disk.
Question 7.
Write notes on Blu-Ray Disc.
Answer:
- Blu – Ray disc is a high density optical disc used for playstation games and HD movies.
- A double layer Blu-Ray disc can store up to 50 GB of data.
- Blu – Ray disc uses a blue-violet laser to write data.
Question 8.
Why the Blu – Ray disc is called so?
Answer:
Since it uses a blue – violet laser to write, hence it is called so.
Question 9.
What is meant by word size?
Answer:
- The number of hits that can be processed by a processor in a single instruction is called its Word Size.
- Word size determines the amount of RAM that can be accessed by a microprocessor at one time and the total number of pins on the microprocessor.
Question 10.
Expand RISC, CISC
Answer:
RISC stands for Reduced Instruction Set Computers CISC stands for Complex Instruction Set Computers.
Question 11.
What is Cache Memory?
Answer:
The cache memory is a very high speed and expensive memory, which is used to speed up the memory retrieval process.
Question 12.
Expand HDMI
Answer:
HDMI – High Definition Multimedia Interface
![]()
Question 13.
What are the main units of a microprocessor.
Answer:
The three major units of a microprocessor are:
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): To perform arithmetic and logical instructions.
- Control Unit (CU): To control the overall operation of the computer through signals.
- Registers (Internal Memory): They are used to hold the data and instruction for the execution of the processor.
Question 14.
Name the types of operations performed by the Instruction Set.
Answer:
- Data transfer
- Arithmetic operations
- Logical operations
- Control flow
- Input/output
Question 15.
Mention the criteria on which microprocessors are classified.
Answer:
Microprocessors are classified based on the following criteria:
- The width of the data that can be processed.
- The instruction set.
Question 16.
What is RISC?
Answer:
RISC stands for Reduced Instruction Set Computers. They have small set of highly optimised instructions. Example Pentium IV, intel P6, AMD K6 and K7.
Question 17.
What is CISC?
Answer:
CISC stands for Complex Instruction Set Computers. They support hundreds of instructions. It is ideal for personal computers. Example Intel 386486, Pentium, Pentium II and III, Motorola 68000.
Question 18.
What are the two types of accessing methods to access the memory?
Answer:
The two types of accessing methods are:
- In sequential access, the memory is accessed in an orderly manner from starting to end.
- In random access, any byte of memory can be accessed directly without navigating through previous bytes.
Question 19.
Give the Block diagram of microprocessor based system.
Answer:
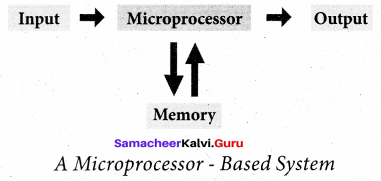
Question 20.
Write note on secondary storage devices.
Answer:
To store data and programs permanently, secondary storage devices are used. Secondary storage devices serve as a supportive storage to main memory and they are non-volatile in nature. Secondary storage is also called as back up storage.
PART – 3
III. Explain in Brief
Question 1.
What is memory?
Answer:
A memory is just like a human brain. It is used to store data and instructions. Computer memory is the storage space in the computer, where data and instructions are stored.
Question 2.
What is RAM?
Answer:
The main memory is otherwise called as Random Access Memory. This is available in computers in the form of Integrated Circuits (ICs). It is the place in a computer where the Operating System, Application Programs and the data in current use are kept temporarily so that they can be accessed by the computer’s processor.
Question 3.
What is ALU?
Answer:
Arithmetic and Logic unit (ALU):
To perform arithmetic and logical instructions based on computer instructions.
![]()
Question 4.
What is control unit?
Answer:
Control unit: To control the overall operations of the computer through signals.
Question 5.
What is microprocessor?
Answer:
The microprocessor is a programmable multipurpose silicon chip. It is driven by clock pulses. It accepts input as a binary data and after processing, it provides the output data as per the instructions stored in the memory.
PART – 4
IV. Explain in Detail
Question 1.
Explain the ports and interfaces.
Answer:
Ports and Interfaces:
The Motherboard of a computer has many I/O sockets that are connected to the ports and interfaces found on the rear side of a computer. The external devices can be connected to the ports and interfaces. The various types of ports are given below:
Serial Port:
To connect the external devices, found in old computers.
Parallel Port:
To connect the printers, found in old computers.
USB Ports:
To connect external devices like cameras, scanners, mobile phones, external, hard disks and printers to the computer. USB 3.0 is the third major version of the Universal Serial Bus (USB) standard to connect computers with other electronic gadgets. USB 3.0 can transfer data up to 5 Giga byte/second. USB 3.1 and USB 3.2 are also released.
SCSI Port:
To connect the hard disk drives and network connectors.
VGA Connector:
To connect a monitor or any display devices like LCD projector.
Audio plugs:
To connect sound speakers, microphone and headphones
PS/2 Port:
To connect mouse and keyboard to PC.
High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI):
High Definition Multimedia Interface is an audio/video interface which transfers the uncompressed video and audio data from a video controller to a compatible computer monitor, LCD projector, digital television.
Question 2.
Explain the flash memory devices and Blu-ray disc.
Answer:
Flash Memory Devices:
Flash memory is an electronic (solid – state) non – volatile computer storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. They are either EEPROM or EPROM. Examples for Flash memories are pendrives, memory cards etc. Flash memories can be used in personal computers, Personal Digital Assistants (PDA), digital audio players, digital cameras and mobile phones. Flash memory offers fast access times. The time taken to read or write a character in memory is called access time. The capacity of the flash memories vary from 1 Gigabytes (GB) to 2 Terabytes (TB).
Blu – Ray Disc:
Blu – Ray Disc is a high – density optical disc similar to DVD. Blu-ray is the type of disc used for PlayStation games and for playing High – Definition (HD) movies. A double – layer Blu – Ray disc can store up to 50 GB (gigabytes) of data. This is more than 5 times the capacity of a DVD, and above 70 times of a CD. The format was developed to enable recording, rewriting and playback of high – definition video, as well as storing large amount of data. DVD uses a red laser to read and write data. But, Blu – ray uses a blue-violet laser to write. Hence, it is called as Blu – Ray.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain various types of microprocessors.
Answer:
Microprocessors can be classified based on the following criteria:
- The width of data that can be processed
- The instruction set
Classification of Microprocessors based on the Data Width
Depending on the data width, microprocessors can process instructions. The microprocessors can be classified as follows:
- 8 – bit microprocessor
- 16 – bit microprocessor
- 32 – bit microprocessor
- 64 – bit microprocessor
Classification of Microprocessors based on Instruction Set:
The size of the instruction set is another important consideration while categorizing microprocessors. Initially, microprocessors had very small instruction sets because complex hardware was expensive as well as difficult to build. As technology had developed to overcome these issues, more and more complex instructions were added to increase the functionality of microprocessors. Let us learn more about the two types of microprocessors based on their instruction sets.
Reduced Instruction Set Computers (RISC):
RISC stands for Reduced Instruction Set Computers. They have a small set of highly optimized instructions. Complex instructions are also implemented using simple instructions, thus reducing the size of the instruction set.
Examples of RISC processors are Pentium IV, Intel P6, AMD K6 and K7.
Complex Instruction Set Computers (CISC):
CISC stands for Complex Instruction Set Computers. They support hundreds of instructions. Computers supporting CISC can accomplish a wide variety of tasks, making them ideal for personal computers.
Examples of CISC processors are Intel 386 & 486, Pentium, Pentium II and III, and Motorola 68000.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the secondary storage devices.
Answer:
Secondary Storage Devices:
A computer generally has limited amount of main memory which is expensive and volatile. To store data and programs permanently, secondary storage devices are used. Secondary storage devices serve as a supportive storage to main memory and they are non – volatile in nature, secondary storage is also called as Backup storage
Hard Disks:
Hard disk is a magnetic disk on which you can store data. The hard disk has the stacked arrangement of disks accessed by a pair of heads for each of the disks. The hard disks come with a single or double sided disk.
Compact Disc (CD):
A CD or CD – ROM is made from 1.2 millimeters thick, polycarbonate plastic material. A thin layer of aluminum or gold is applied to the surface. CD data is represented as tiny indentations known as “pits”, encoded in a spiral track moulded into the top of the polycarbonate layer. The areas between pits are known as “lands”. A motor within the CD player rotates the disk. The capacity of an ordinary CD – ROM is 700 MB.

Digital Versatile Disc (DVD)
A DVD (Digital Versatile Disc or Digital Video Disc) is an optical disc capable of storing up to 4.7 GB of data, more than six times what a CD can hold. DVDs are often used to store movies at a better quality. Like CDs, DVDs are read with a laser.
The disc can have one or two sides, and one or two layers of data per side; the number of sides and layers determines how much it can hold. A 12 cm diameter disc with single sided, single layer has 4.7 GB capacity, whereas the single sided, double layer has 8.5 GB capacity. The 8 cm DVD has 1.5 GB capacity. The capacity of a DVD-ROM can be visually determined by noting the number of data sides of the disc. Double – layered sides are usually gold – coloured, while single – layered sides are usually silver – coloured, like a CD.

Fash Memory Devices:
Flash memory is an electronic (solid – state) non – volatile computer storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. They are either EEPROM or EPROM. Examples for Flash memories are pendrives, memory cards etc. Flash memories can be used in personal computers, Personal Digital Assistants (PDA), digital audio players, digital cameras and mobile phones. Flash memory offers fast access times. The time taken to read or write a character in memory is called access time. The capacity of the flash memories vary from 1 Gigabytes (GB) to 2 Terabytes (TB).
Blu – Ray Disc
Blu – Ray Disc is a high-density optical disc similar to DVD. Blu-ray is the type of disc used for PlayStation games and for playing High-Definition (HD) movies. A double – layer Blu-Ray disc can store up to 50GB (gigabytes) of data. This is more than 5 times the capacity of a DVD, and above 70 times of a CD. The format was developed to enable recording, rewriting and playback of high-definition video, as well as storing large amount of data. DVD uses a red laser to read and write data. But, Blu-ray uses a blue-violet laser to write. Hence, it is called as Blu-Ray.
Question 5.
Explain the cache memory.
Answer:
Cache Memory:
The cache memory is a very high speed and expensive memory, which is used to speed up the memory retrieval process. Due to its higher cost, the CPU comes with a smaller size of cache memory compared with the size of the main memory. Without cache memory, every time the CPU requests the data, it has to be fetched from the main memory which will consume more time. The idea of introducing a cache is that, this extremely fast memory would store data that is frequently accessed and if possible, the data that is closer to it. This helps to achieve the fast response time, Where response time, (Access Time) refers to how quickly the memory can respond to a read / write request. Arrangement of cache memory between the CPU and the main memory is shown below
![]()
Question 6.
Explain main memory and its types.
Answer:
The main memory is otherwise called as Random Access Memory. This is available in computers in the form of Integrated Circuits (ICs). It is the place in a computer where the Operating System, Application Programs and the data in current use are kept temporarily so that they can be accessed by the computer’s processor. The smallest unit of information that can be stored in the memory is called as a bit. The memory can be accessed by a collection of 8 bits which is called as a byte. The bytes are referred by ‘B\ If a computer has 1 megabyte of memory, then it can store 10,48,576 bytes (or characters) of information. [Hence 1MB is 1024KB and 1 KB is 1024 Bytes, So 1024 X 1024 =10,48.576 Bytes],
Types of RAM:
There are two basic types of”RAM
- Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
- Static RAM (SRAM)
These two types differ in the technology they use to hold data. Dynamic RAM being a common type needs to be refreshed frequently. Static RAM needs to be refreshed less often, which makes it .faster. Hence, Static RAM is more expensive than Dynamic RAM.