You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.15
Question 1.
Graph the following quadratic equations and state their nature of solutions,
(i) x2 – 9x + 20 = 0
Solution:
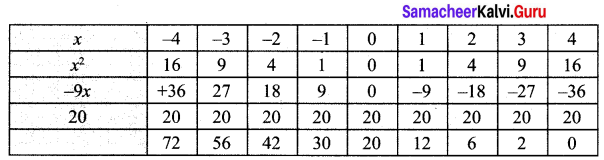
Step 1:
Points to be plotted : (-4, 72), (-3, 56), (-2, 42), (-1, 30), (0, 20), (1, 12), (2, 6), (3, 2), (4, 0)
Step 2:
The point of intersection of the curve with x axis is (4, 0)
Step 3:
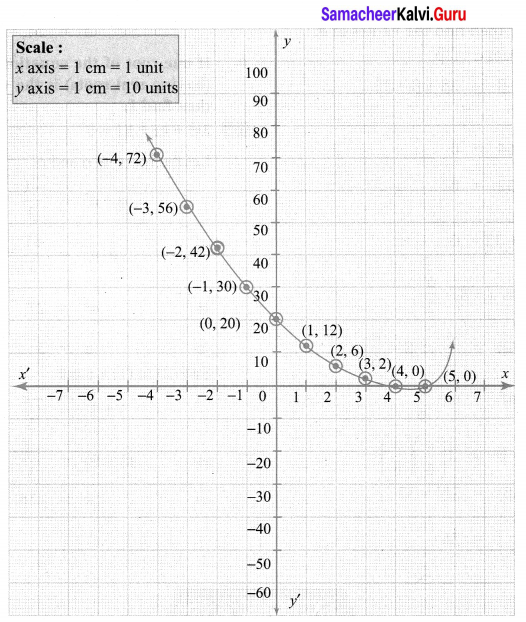
The roots are real & unequal
∴ Solution {4, 5}
(ii) x2 – 4x + 4 = 0
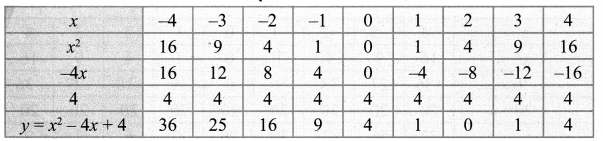
Step 1: Points to be plotted : (-4, 36), (-3, 25), (-2, 16), (-1, 9), (0, 4), (1, 1), (2, 0), (3, 1), (4, 4)
Step 2: The point of intersection of the curve with x axis is (2, 0)
Step 3:
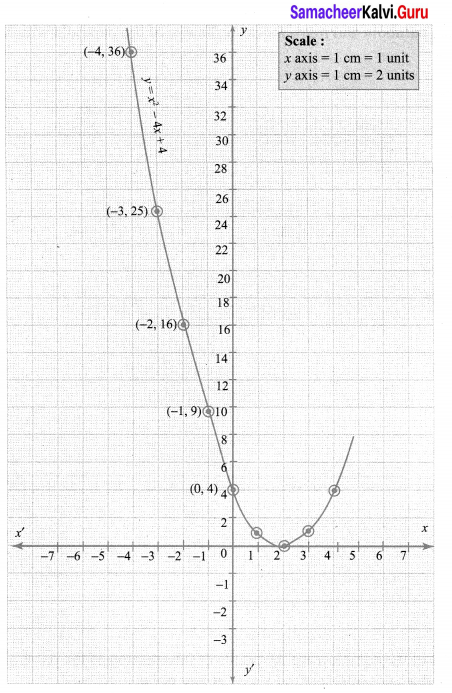
Since there is only one point of intersection with x axis, the quadratic equation x2 – 4x + 4 = 0 has real and equal roots.
∴ Solution{2, 2}
(iii) x2 + x + 7 = 0
Let y = x2 + x + 7
Step 1:
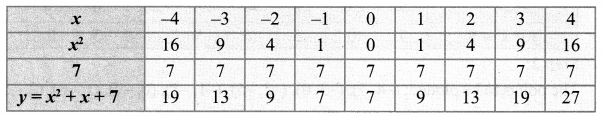
Step 2:
Points to be plotted: (-4, 19), (-3, 13), (-2, 9), (-1, 7), (0, 7), (1, 9), (2, 13), (3, 19), (4, 27)
Step 3:
Draw the parabola and mark the co-ordinates of the parabola which intersect with the x-axis.
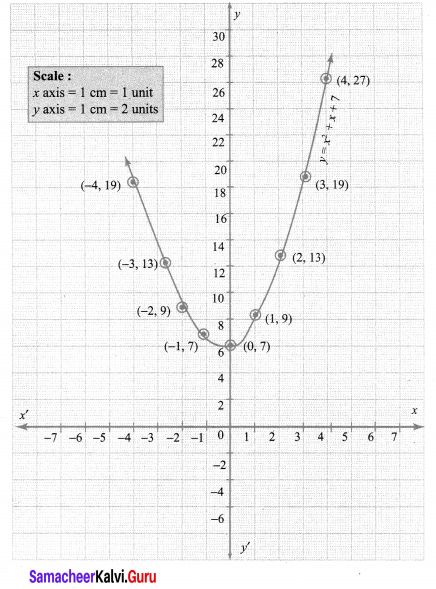
Step 4:
The roots of the equation are the points of intersection of the parabola with the x axis. Here the parabola does not intersect the x axis at any point.
So, we conclude that there is no real roots for the given quadratic equation,
(iv) x2 – 9 = 0
Let y = x2 – 9
Step 1:
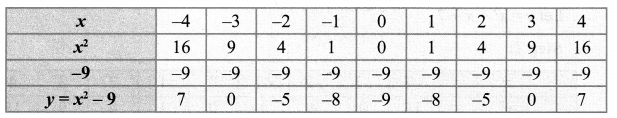
Step 2:
The points to be plotted: (-4, 7), (-3, 0), (-2, -5), (-1, -8), (0, -9), (1,-8), (2, -5), (3, 0), (4, 7)
Step 3:
Draw the parabola and mark the co-ordinates of the parabola which intersect the x-axis.
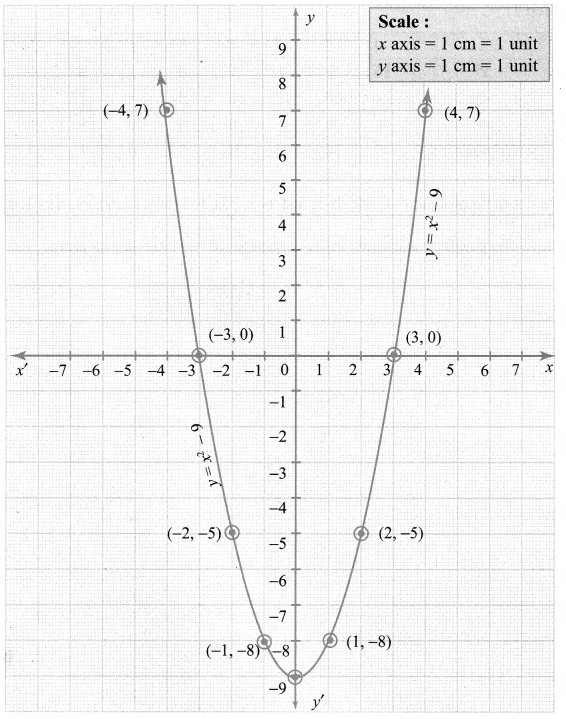
Step 4:
The roots of the equation are the co-ordinates of the intersecting points (-3, 0) and (3, 0) of the parabola with the x-axis which are -3 and 3 respectively.
Step 5:
Since there are two points of intersection with the x axis, the quadratic equation has real and unequal roots.
∴ Solution{-3, 3}
(v) x2 – 6x + 9 = 0
Let y = x2 – 6x + 9
Step 1:
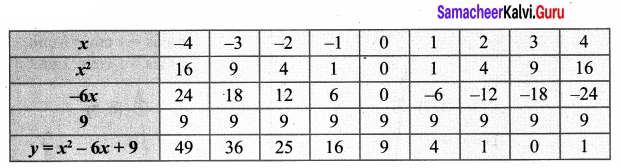
Step 2:
Points to be plotted: (-4, 49), (-3, 36), (-2, 25), (-1, 16), (0, 9), (1, 4), (2, 1), (3, 0), (4, 1)
Step 3:
Draw the parabola and mark the co-ordinates of the intersecting points.
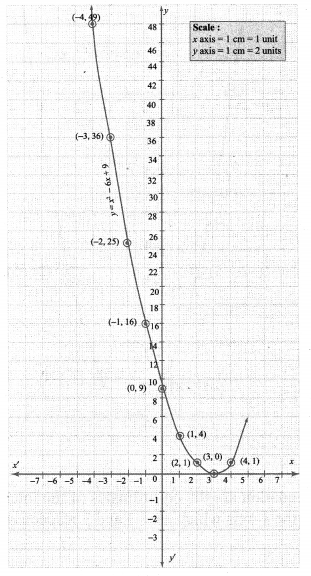
Step 4:
The point of intersection of the parabola with x axis is (3, 0)
Since there is only one point of intersection with the x-axis, the quadratic equation has real and equal roots. .
∴ Solution (3, 3)
(vi) (2x – 3)(x + 2) = 0
2x2 – 3x + 4x – 6 = 0
2x2 + 1x – 6 = 0
Let y = 2x2 + x – 6 = 0
Step 1:
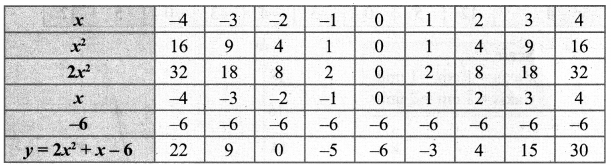
Step 2:
The points to be plotted: (-4, 22), (-3, 9), (-2, 0), (-1, -5), (0, -6), (1, -3), (2, 4), (3, 15), (4, 30)
Step 3:
Draw the parabola and mark the co-ordinates of the intersecting point of the parabola with the x-axis.
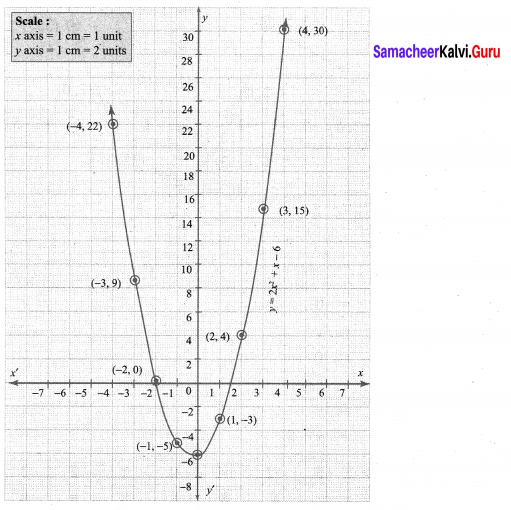
Step 4:
The points of intersection of the parabola with the x-axis are (-2, 0) and (1.5, 0).
Since the parabola intersects the x-axis at two points, the, equation has real and unequal roots.
∴ Solution {-2, 1.5}
Question 2.
Draw the graph of y = x2 – 4 and hence solve x2 – x – 12 = 0
Solution:
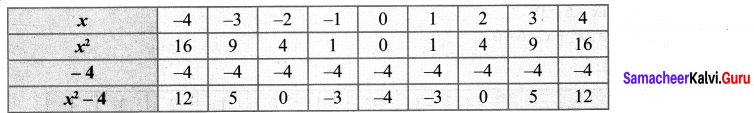
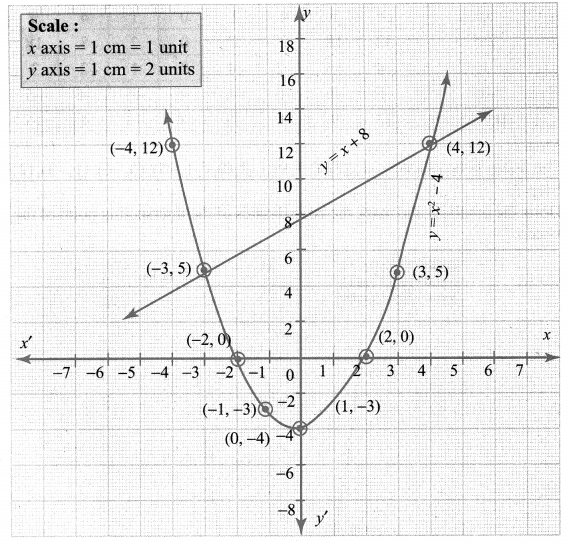
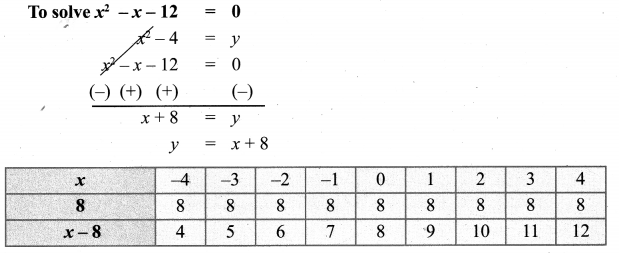
Point of intersection (-3, 5), (4, 12) solution of x2 – x – 12 = 0 is -3, 4
![]()
Question 3.
Draw the graph of y = x2 + x and hence solve x2 + 1 = 0.
Solution:
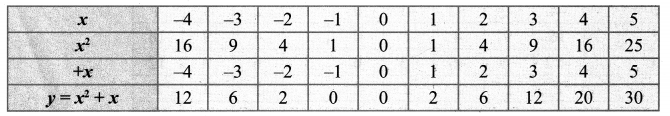
Draw the parabola by the plotting the points (-4, 12), (-3, 6), (-2, 2), (-1, 0), (0, 0), (1, 2), (2, 6), (3, 12), (4, 20), (5, 30)
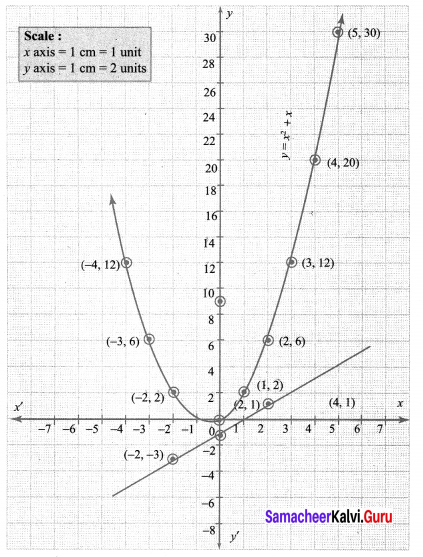
To solve: x2 + 1 = 0, subtract x2 + 1 = 0 from y = x2 + x.
x2 + 1 = 0 from y = x2 + x
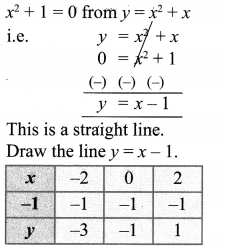
Plotting the points (-2, -3), (0, -1), (2, 1) we get a straight line. This line does not intersect the parabola. Therefore there is no real roots for the equation x2 + 1 = 0.
Question 4.
Draw the graph of y = x2 + 3x + 2 and use it to solve x2 + 2x + 1 = 0.
Solution:
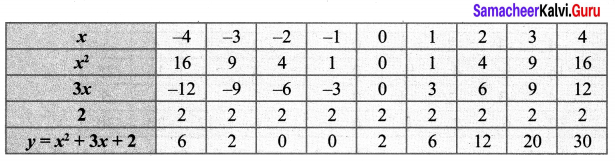
Draw the parabola by plotting the point (-4, 6), (-3, 2), (-2, 0), (-1, 0), (0, 2), (1, 6), (2, 12), (3, 20), (4, 30).
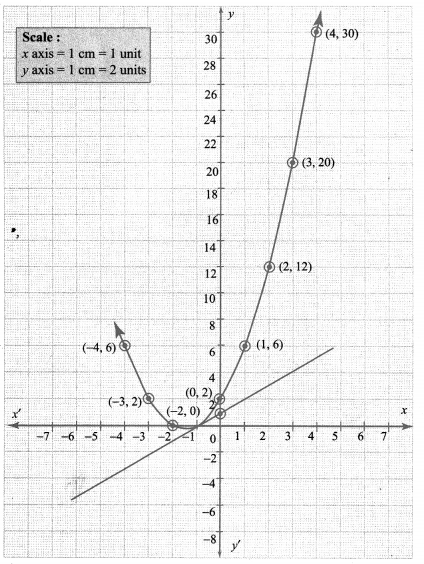
To solve x2 + 2x + 1 = 0, subtract x2 + 2x + 1 = 0 from y = x2 + 3x + 2
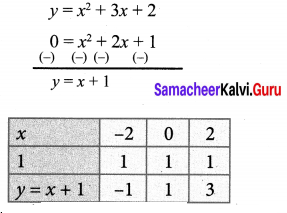
Draw the straight line by plotting the points (-2, -1), (0, 1), (2, 3)
The straight line touches the parabola at the point (-1,0)
Therefore the x coordinate -1 is the only solution of the given equation
Question 5.
Draw the graph of y = x2 + 3x – 4 and hence use it to solve x2 + 3x – 4 = 0. y = x2 + 3x – 4
Solution:
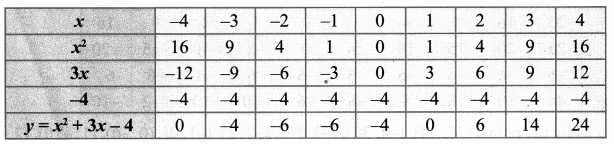
Draw the parabola using the points (-4, 0), (-3, -4), (-2, -6), (-1, -6), (0, -4), (1, 0), (2, 6), (3, 14), (4, 24).
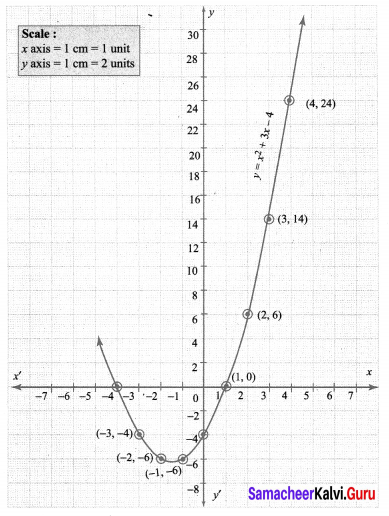
To solve: x2 + 3x – 4 = 0 subtract x2 + 3x – 4 = 0 from y = x2 + 3x – 4 ,
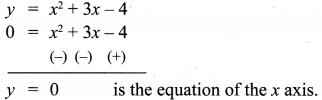
The points of intersection of the parabola with the x axis are the points (-4, 0) and (1, 0), whose x – co-ordinates (-4, 1) is the solution, set for the equation x2 + 3x – 4 = 0.
Question 6.
Draw the graph of y = x2 – 5x – 6 and hence solve x2 – 5x – 14 = 0.
Solution:
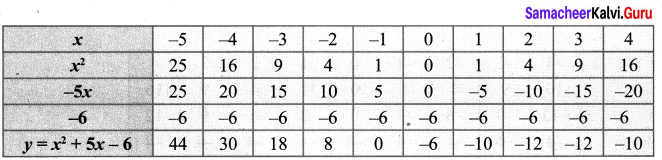
Draw the parabola using the points (-5, 44), (-4, 30), (-3, 18), (-2, 8), (-1, 0), (0, -6), (1, -10), (2, -12), (3, -12), (4, -10)
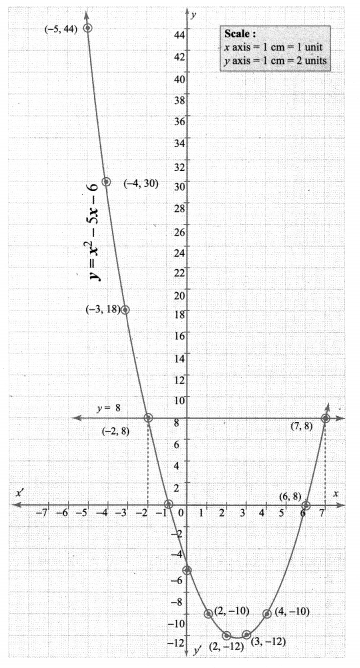
To solve the equation x2 – 5x – 14 = 0, subtract x2 – 5x – 14 = 0 from y = x2 – 5x – 6.

The co-ordinates of the points of intersection of the line and the parabola forms the solution set for the equation x2 – 5x – 14 = 0.
∴ Solution {-2, 7}
![]()
Question 7.
Draw the graph of y = 2x2 – 3x – 5 and hence solve 2x2 – 4x – 6 = 0. y = 2x2 – 3x – 5
Solution:
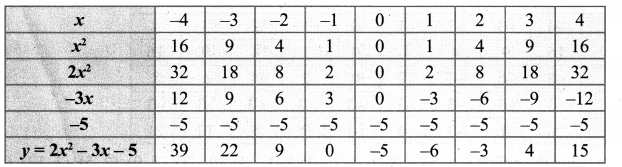
Draw the parabola using the points (-4, 39), (-3, 22), (-2, 9), (-1, 0), (0, -5), (1, -6), (2, -3), (3, 4), (4, 15).
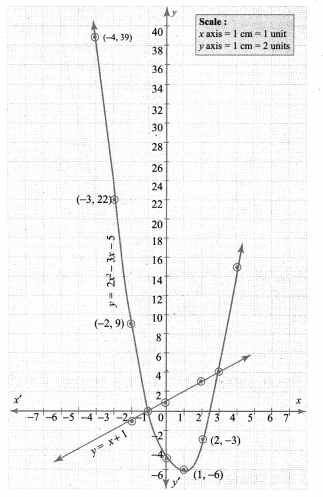
To solve 2x2 – 4x – 6 = 0, subtract it from y = 2x2 – 3x – 5
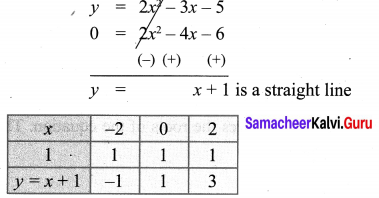
Draw a straight line using the points (-2, -1), (0, 1), (2, 3). The points of intersection of the parabola and the straight line forms the roots of the equation.
The x-coordinates of the points of intersection forms the solution set.
∴ Solution {-1, 3}
Question 8.
Draw the graph of y = (x – 1)(x + 3) and hence solve x2 – x – 6 = 0.
Solution:
y = (x – 1)(x + 3) = x2 – x + 3x – 3 = 0
y = x2 + 2x – 3
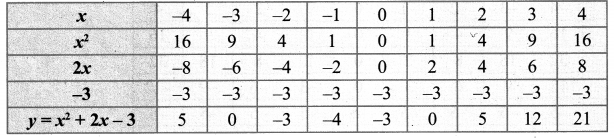
Draw the parabola using the points (-4, 5), (-3, 0), (-2, -3), (-1,-4), (0, -3), (1, 0), (2, 5), (3, 12), (4, 21)
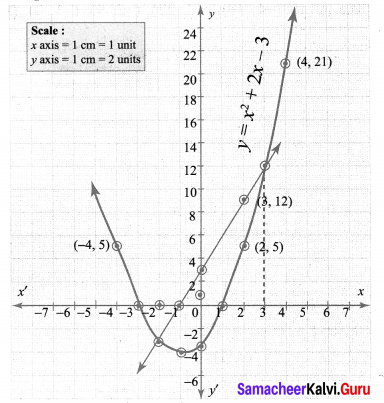
To solve the equation x2 – x – 6 = 0, subtract x2 – x – 6 = 0 from y = x2 – 2x – 3.

Plotting the points (-2, -3), (-1, 0), (0, 3), (2, 9), we get a straight line.
The points of intersection of the parabola with the straight line gives the roots of the equation. The co¬ordinates of the points of intersection forms the solution set.
∴ Solution {-2, 3}