Students can Download Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Exploring Continents – North America and South America Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Geography Solutions Term 3 Chapter 1 Exploring Continents – North America and South America
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Exploring Continents – North America and South America Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
The ______ separates North America from Asia
(a) Bering Strait
(b) Palk Straits
(c) Malacca Strait
(d) Gibraltar straits
Answer:
(a) Bering Strait
Question 2.
__________ is known as the “sugar bowl of the world”
(a) Mexico
(b) USA
(c) Canada
(d) Cuba
Answer:
(d) Cuba

Question 3.
__________ are the longest rivers in North America
(a) The Mississippi and Missouri rivers
(b) The Mackenzieriver
(c) The St. Lawrence river
(d) The Colorado river
Answer:
(a) The Mississippi and Missouri rivers
Question 4.
__________ is the longest mountain chain in the world.
(a) The Andes
(b) TheRockies
(c) The Himalayas
(d) The Alps
Answer:
(a) The Andes
Question 5.
__________ basin gets rainfall every day because of its equatorial location
(a) The Mackenzie
(b) The Orinoco
(c) The Amazon
(d) The Parana
Answer:
(c) The Amazon
II. Fill in the blanks.
- _______ 86 m below the sea level is the lowest part of the continent of North America.
- _______ is one of the worlds best fishing grounds.
- The highest peak in the Andes is ______ on the Chile – Argentina border.
- _______ of the equatorial regions are called the “lungs of the world”.
- _______ is also known as the “coffee pot” of the world.
Answer:
- Death valley is
- Grand Bank
- Mt Aconcagua
- The Selvas
- Brazil
III. Match the following
| Mount McKinley |
– |
Tropical forests |
| Grand Canyon |
– |
The flightless bird |
| Ebony |
– |
The Colorado River |
| 4’o Clock Rains |
– |
6194 m |
| Rhea |
– |
The equatorial regions |
Answer:
| Mount McKinley |
– |
6194 m |
| Grand Canyon |
– |
The Colorado River |
| Ebony |
– |
The equatorial regions |
| 4’O Clock Rains |
– |
Tropical forests |
| Rhea |
– |
The flightless bird |
IV. Give Reasons.
Question 1.
The eastern coast of North America particularly the USA enjoys a mild climate.
Answer:
The South and east is usually warm all the year-round and the regions around the mouth of the Mississippi-Missouri and the Gulf Coast have summer rain from the North East Trades which blow on-shore in summer.
Question 2.
The United States of America is known as “Melting Pot”.
Answer:
The United States of America is known as “Melting Pot” where hundreds of different cultures meet, blend, and creating a new culture.

Question 3.
Though Quito and Amazon basin are in the same latitude Quito enjoys eternal Spring. Whereas the Amazon basin is hot.
Answer:
- The climate of the continent of South America has been closely influenced by the latitudes, attitudes, and proximity of the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.
- It is hot in the Amazon basin as the equator passes through it whereas Quito, situated almost on the same latitude on the Andes, has “Eternal Spring”.
- That is, it has a pleasant climate throughout the year because of its high altitude at 9,350 feet or2849.88 meters above the sea level.
Question 4.
Peru is one of the world’s largest producers of tropical fish.
Answer:
- Peru is one of the world’s largest producers of tropical fish. Here the cool Humboldt Current helps in bring plankton, which is the main food for fishes.
- Commercial deep-sea fishing off of Peru’s coastal belt of over 3000 km.
- Peruvian waters normally abound with sword fish, mackerel, yellow fin, pompano and shark.
- More than 50 species are caught commercially. –
- There are over 40 fishing ports on the Peruvian coast.
- Paita and Callao are being the most important centers in Peru.
V. Distinguish between
Question 1.
The Rocky Mountain and the Appalachian mountain.
Answer:
| S.No. |
Rocky mountain |
Appalachian mountain |
| 1. |
The western part of North America is occupied by long ranges of young fold mountains known as Rocky mountains. |
The eastern part of North America is formed of old fold Appalachian which are not continuous like Rockies. |
| 2. |
The width varies from 110 to 480 kms. |
There are few peaks more than 1800m high. |
| 3. |
The Rocky mountains are west of the Mississippi River. |
The Appalachian Mountains are east of the river. |
Question 2.
The Prairies and the Pampas grassland.
Answer:
| S.No. |
Prairies grassland |
Pampas grassland |
| 1. |
The temperate grasslands of North America are known as Prairies. |
The temperate grasslands of South America are known as Pampas. |
| 2. |
Region – Central USA and Central Canada. |
Region – North of Eastern part of Argentina, Uruguay and Southernmost Brazil. |
| 3. |
Winter is very cold, Summer is hot and rainfall is moderate. |
Summer is quite warm and winter is cold and moderate rainfall. |
| 4. |
Flora – Grasses |
Flora – short grass. |
| 5. |
Fauna – Coyote, Gophers, Rabbits Prairie Dogs and Bison. |
Fauna – Rhea, Pampas Deer, Jaguar, Camel, Stag etc. |
Question 3.
Tundra and Taiga.
Answer:
| S.No. |
Tundra |
Taiga |
| 1. |
Region – Northern coast of Canada and the Northern Islands. |
Region – The coniferous forests are found in Alaska and Canada, South Central Alaska and North Eastern Canada. |
| 2. |
Climate – Winter is long and severely cold, Summer is short and cool. Rainfall is scanty. |
Climate – Winter is very cold, Summer is warm and short. Heavy snowfall in winter. |
| 3. |
Flora – Mosses, Lichens and Dwarf willows. |
Flora – Pine, Fir, Cedar and Spruce. |
| 4. |
Fauna – Arctic fox, Reindeer, Musk ox, Polar bears, Sable and Blue fox. |
Fauna – Beaver, Fox, Sable, Ermine, Skunk, Caribou and Grizzly Bears. |
VI. Put (✓) for the correct option
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Cotton grows well in southern and western states of North America.
Reason (R): Warm summer with frequent rainfall and the fertile soil which provide favourable condition.
(a) Both A and R is correct.
(b) A is correct and R is wrong,
(c) A is wrong and R is correct.
(d) Both A and R is wrong
Answer:
(a) Both A and R is correct

Question 2.
Assertion (A) industries in South America have developed rapidly.
Reason (R): The continent lacks infrastructure (especially transport) need for industrialization,
(a) Both A and R are correct.
(b) A is correct and R is wrong,
(c) A is wrong and R is correct.
(d) Both A and R are wrong
Answer:
(c) A is wrong and R is correct
VII. Answer the following.
Question 1.
Name the boundaries of North America.
Answer:
- North America is surrounded by the Pacific Ocean in the West, the Atlantic Ocean in the east, the Arctic Ocean in the north, and South America in the south.
- North America is joined with South America by the Isthmus of Panama.
- The Bering Strait separates North America from Asia.
Question 2.
Write a note on Mackenzie River.
Answer:
The Mackenzie River is the second-largest drainage basin of North America. It has it source from Great Slave Lake and drains into Arctic Ocean.
Question 3.
What type of fruits are cultivated in North America? Name some of them.
Answer:
- Mainly Citrus Fruits are cultivated in Texas, California, Great Lakes regions, and St. Lawrence Valley.
- The important Fruits of North America are Cranberries, Blueberries, Concord Grapes, Strawberries, Gooseberries, and other fruits.
Question 4.
Give a short note about the lifestyle of Eskimos.
Answer:
- Eskimos live in a very cold and inhospitable region where plenty of fish varieties are available.
- They were able to dress in thick warm clothes made of fur, they live in igloos.
- Their lives were very simple and they could not alter the environment to any extent.
- The specially designed house by ice and is known as igloos.
Question 5.
Which are the densely populated areas of North America?
Answer:
Densely populated areas: Eastern part of North America, Great Lakes region, Florida, California, Mexico and Central America are the most densely populated areas.

Question 6.
Name the physiographic divisions of South America.
Answer:
On the basis of topographical features, the continent may be divided into the following physiographic divisions:
- The Andes Mountains
- The River Basin or Central Plains
- The Eastern Highlands
Question 7.
What is called “4’o clock rains”?
Answer:
In equatorial regions, convectional rain occurs almost daily in the afternoons. It generally occurs at 4 pm that’s why it is known as 4’o Clock Rain.
Question 8.
Name the flora and fauna of equatorial forest in South America.
Answer:
- Flora: Rubber, Mahogany, Ebony, Logwood, Brazil nuts, and Ceiba.
- Fauna: Anaconda, Armadillo, Piranha, Monkey, Snake, Crocodile, and Parrots.
Question 9.
What is known as “Estancias”?
Answer:
The Breeds raised on large pasture lands is known as Estancias. These are divided into several paddocks. Besides this, there are small yards known as corrals where animals are sorted and branded. The owner is the Estanciera who has a number of gauchos.
Question 10.
Name the major export of South America.
Answer:
South America’s major exports are mostly primary commodities such as sugar, coffee, cocoa, tobacco, beef, corn, wheat, petroleum, natural gas, linseed, cotton, iron ore, tin, and copper. South America’s products include mostly exported to North America and Europe.
VIII. Answer the following in a paragraph
Question 1.
Give an account of the climate of North America.
Answer:
- The vast latitudinal extent from the Tropics to the Polar Regions makes the climate of North America as varied as that of Asia.
- Unlike the Himalayas, the Rockies run north to south which does not form a climatic barrier and does not prevent the icy winds from the Arctic region and penetrating the central plains which therefore have a very long cold winter and very short hot summer.
- Precipitation occurs due to cyclonic storms.
- The Arctic region is cold and mostly dry and has very short summers and a very long bitterly cold winter.
- As one proceeds southwards the short summers become warm but the winters are very cold.
- The central plains have extreme climates from freezing conditions in winter to tropical heat in summer.
- The South is usually warm all the year-round and the regions around the mouth of the Mississippi-Missouri and the Gulf Coast have summer rain from the North East Trades which blow on-shore in summer.
- The warm moist South Westerlies not only bring rainfall to the North West coast and also keep it warm.
- The warm Alaskan Current keeps the North West coast ice-free.
- The State of California in the USA has a Mediterranean Climate with moist winter and dry summers.
Question 2.
Describe the Heavy Engineering Industries in North America.
Answer:
Heavy Engineering Industries:
- Industries which require heavy and bulky raw materials using enormous amounts of power, the involvement of huge investment, and large transport costs are called heavy industries.
- These industries depend heavily on the Iron and Steel industry.
- The important Heavy Industries are automobile industries, aircraft industries, shipbuilding industries, Railway Wagon industries, and farm equipment industries.
- The USA is the largest producer of automobiles.
- The important Centers of heavy engineering industries are Detroit, Chicago, Buffalo, Indianapolis, Los Angeles, Saint Louis, Philadelphia, New York, Baltimore, and Atlanta in the USA and Windsor in Canada.
Question 3.
Describe the drainage system in South America.
Answer:
- Owing to the position of the Andes all the great rivers of the continent drain into the Atlantic.
- The Pacific streams are short and swift but along the coastlands of Peru their waters are used for irrigation and to some extent for hydro-electric power. Amazon is the longest river of South America (6,450km) and is the largest river system in the world.
- This river has over a thousand of tributaries.
- The rivers Rio Negro, Madeira and Tapajos are important tributaries.
- At the point where it enters the sea the river is so wide and powerful that it flows even at a distance of 80 km into the high seas.
- The Orinoco River originates in the Guiana Highlands and flows northwards into the Caribbean Sea.
- The river Paraguay has the Parana and Uruguay rivers as the main tributaries which together form and known as the Platte River system.
- All the rivers are navigable for quite some distance in the interior.
Question 4.
Write briefly about the major races in South America.
Answer:
- South America contains the world s most mixed population.
- Many people in South America are descended from Europeans, especially the Spanish and Portuguese, who begin to arrive during the 15th century.
- The descendants of African slaves brought over by the Europeans. Native people still live in the mountain and the rainforests and keeping their own languages and traditions.
- There are three major races found in South America and are
- American Indian
- European
- Blacks.
- The mixed population of Native Indians and Europeans is known as ‘Mestizo’.
- The mixed population of Europeans and Blacks is called ‘Mulato’ and the mixture of Native Indians and Blacks is called ‘Zambo’.
- The current population of South America is 429, 115, 060 (42.25 cores). The population density of South America is 21 persons per square kilometer.
- South America is positioned 5th rank in total population among the continents.
IX. Map skill
Question 1.
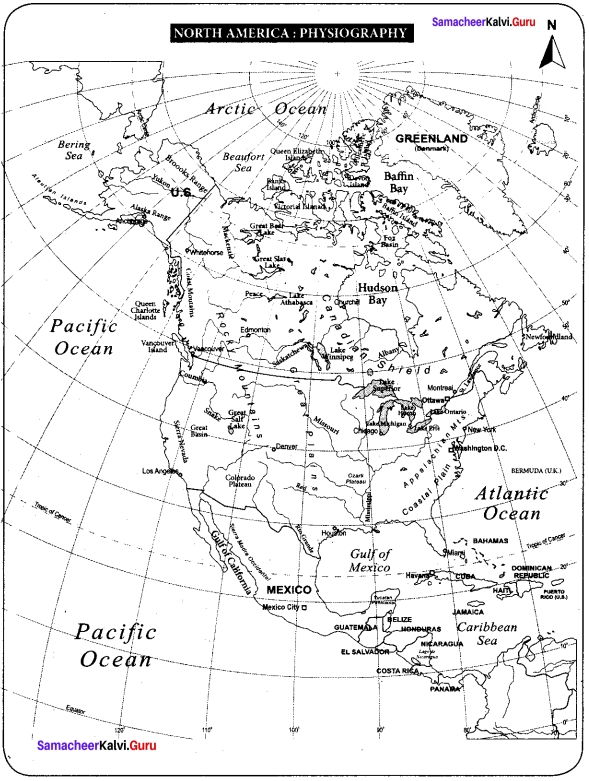
With the help of the map given in the text and an atlas, name the seas and bays in North America
Answer:
Question 2.
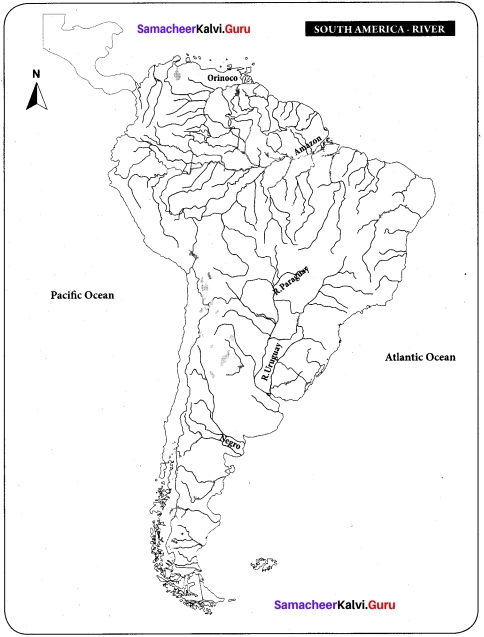
Mark the rivers Amazon, Orinoco, Negro, Paraguay, Uruguay on a map of South America.
Answer:
X. Activity
Question 1.
Given below are some important cities with industries placed in brackets. Pick out the correct answer from them.
- Pittsburgh (Textile, Iron and steel, Shipping)
- Chicago (Meat Packing, Woolen textile, Heavy Engineering)
- Ontario (Automobile, Paper, Cement)
- Chile (Oil refinery, Sugar, Cotton textile)
- Uruguay (Leather processing, Copper smelting, Dairy products)
Answer:
- Iron and steel
- Meat Packing
- Paper
- Oil refinery
- Dairy products
Question 2.
Write down the answers to the question given in blocks:
(a) Name the highest peak in South America.
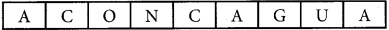
(b) An active volcano in South America

(c) The combined Parana and Paraguay river.

(d) The highest falls in the world.
(e) The largest river in the world.

Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Exploring Continents – North America and South America Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
In _______ North America was discovered by Christopher Columbus.
(a) 1492
(b) 1491
(c) 1498
(d) 1496
Answer:
(a) 1492

Question 2.
The landmass was named America in _____ after Italian explorer America Vespucci.
(a) 1506
(b) 1507
(c) 1508
(d) 1509
Answer:
(b) 1507
Question 3.
North America is the __________ largest continent next to Asia and Africa
(a) second
(b) third
(c) fourth
(d) fifth
Answer:
(b) third
Question 4.
North America has _____ time zones
(a) 6
(b) 8
(c) 7
(d) 9
Answer:
(c) 7
Question 5.
The _____ small countries which lie to the south of Mexico are referred to as central America
(a) six
(b) seven
(c) eight
(d) nine
Answer:
(b) seven
Question 6.
Death Valley is about _______ m below the sea level and is the lowest part of the continent of North America.
(a) 86
(b) 90
(c) 95
(d) 100
Answer:
(a) 86
Question 7.
Mount McKinley is about m _______ above the sea level and is the highest peak of North America.
(a) 6194
(b) 6195
(c) 6180
(d) 6185
Answer:
(a) 6194
Question 8.
The width of Rocky mountains varies from _______ to _______ kms.
(a) 100 to 500
(b) 110 to 480
(c) 115 to 485
(d) 120 to 490
Answer:
(b) 110 to 480

Question 9.
Mississippi and Missouri together form the _______ longest river system in the world.
(a) sixth
(b) fourth
(c) fifth
(d) third
Answer:
(b) fourth
Question 10.
The warm Alaskan Current keeps the _______ coast ice-free.
(a) Northwest
(b) Northeast
(c) Southwest
(d) Southeast
Answer:
(a) North West
Question 11.
Approximately _____ percentage of the total land area is under forest cover.
(a) 10
(b) 30
(c) 40
(d) 50
Answer:
(b) 30
Question 12.
North America accounts for approximately ________ Percentage of the world’s production of timber
(a) 20
(b) 30
(c) 40
(d) 50
Question 13.
Wheat was introduced by ________ settlers in North America.
(a) European
(b) Spanish
(c) Italian
(d) Dutch
Answer:
a) European

Question 14.
North America is the largest producer of meat and about ________ of world production.
(a) one fourth
(b) one-sixth
(c) half
(d) three fourth
Answer:
(a) one fourth
Question 15.
North America produces about ________ percent of the world total milk and dairy products.
(a) 30
(b) 35
(c) 25
(d) 40
Answer:
(c) 25
Question 16.
The New England region contains ________ % woolen textile industries.
(a) 70
(b) 80
(c) 50
(d) 40
Answer:
(a) 70
Question 17.
North America is the ________ largest producer of synthetic fibers.
(a) second
(b) third
(c) fourth
(d) fifth
Answer:
(a) second
Question 18.
The population density in North America is about ________ present per sq.km.
(a) 20
(b) 19
(c) 18
(d) 17
Answer:
(a) 20

Question 19.
North America population is equivalent to ________ % of the world total population.
(a) 4.75
(b) 4.76
(c) 4.77
(d) 4.78
Answer:
(c) 4.77
Question 20.
________ has the biggest railway yard in the world.
(a) Chicago
(b) Vancouver
(c) Newyork
(d) San Francisco
Answer:
(a) Chicago
Question 21.
There are ________ great rivers in south America that drain into the Atlantic Ocean.
(a) three
(b) four
(c) five
(d) six
Answer:
(a) three
Question 22.
The ________ is grown extensively on the Pampas of Argentina.
(a) maize
(b) wheat
(c) millets
(d) sugarcane
Answer:
(b) wheat

Question 23.
Brazil stands ________ in the production of Coffee and in Cocoa in the world.
(a) first, third
(b) third, first
(c) fourth, sixth
(d) fifth, sixth
Answer:
(a) first, third
Question 24.
South America has ________ varieties of fish that inhabit this river.
(a) 750
(b) 850
(c) 950
(d) 550
Answer:
(a) 750
Question 25.
There are over ________ fishing ports on the Peruvian coast.
(a) 50
(b) 45
(c) 40
(d) 55
Answer:
(c) 40
Question 26.
River Amazon has ________ varieties of fish.
(a) 700
(b) 750
(c) 800
(d) 850
Answer:
(b) 750
Question 27.
South America contains ________ of the world’s iron ore reserves.
(a) one-seventh
(b) one fifth
(c) one-sixth
(d) one third
Answer:
(b) one fifth

Question 28.
Brazil and Chile both have massive deposits of ________
(a) iron ore
(b) copper
(c) coal
(d) gypsum
Answer:
(a) iron ore
Question 29.
Brazil is estimated to have about ________ % of the world export of iron ore.
(a) 10
(b) 15
(c) 16
(d) 14
Answer:
(b) 15
Question 30.
South America is positioned ________ rank in total population among the continents
(a) 4th
(b) 3rd
(c) 5th
(d) 8th
Answer:
(c) 5th
Question 31.
Population density of south America is ________ personal per square kilometer.
(a) 20
(b) 22
(c) 21
(d) 24
Answer:
(c) 21
Question 32.
Chile is the ________ largest producer of copper in the world.
(a) second
(b) third
(c) fourth
(d) fifth
Answer:
(b) third
II. Fill in the blanks:
- ______ is a continent of great physical diversity.
- The _______ mountain range extends for about. the Panama Strait in the south.
- The_______ and ______ rivers are the longest rivers in North America.
- The ______ river is the second-largest drainage basin in North America.
- St. Lawrence has its origin in ______
- The ______ river forms the boundary between USA and Mexico.
- Lake ______ is the largest freshwater lake in the world.
- ______ is a well-developed industry particular in Canada.
- Cuba is known as ______
- Edible oil is extracted from ______ .
- Cattle and pigs are fed with ______ and ______
- The ______ current brings plenty of plankton which provides food for fish.
- ______ is the largest producer and exporter of all kinds of paper in the world.
- Rayon and other synthetic fibers are made up of cellulose obtained from ______
- The important ports in the west coast of North America are ______ and ______
- The Great Lakes region along ______ waterway is the most important inland waterway in North America.
- The USA has the best-laid ______ in the world.
- The Andes are rich in minerals like ______ and ______
- The longest river in South America is ______
- The Geo-climatic condition of ______ are ideal for agriculture
- Brazil is the largest producer of in ______ south America
- Maize is also known as ______
- _____and_____ are the most important crops of South America
- Barley is a member of the ______ family.
- The extensive tropical grasslands of South America are ______ and ______
- Quebracho tree yields ______
- South America is rich in ______
- Northern Chile has the world s only natural deposits of ______
- Venezuela is rice in ______ products
- Peru has some of the biggest _____ mines of the world
- The ______ and ______ river of south America Provide cheap water transport
- The temperate grasslands of South America are Knows as ______
Answer:
- North America
- Rocky,4800
- Mississippi and Missouri
- Mackenzie
- Lake Ontario
- Rio Grande
- Superior
- Lumbering
- sugar bowl of the world”
- Soya beans
- Potato and Sugar beet
- Cold labrador
- Canada
- Wood pulp
- Vancouver and San Francisco
- St. Lawrence
- roadways
- Copper and Tin
- Amazon
- Pampas
- Sugar
- Corn
- Coffee and Cocoa
- grass
- Lianos and Campos
- tannis
- Mineral
- Sodium nitrate
- Petroleum
- copper
- Amazon, plate
- Pampas
III. Match the following:
Question 1.
| Continent |
|
Peaks |
| Asia |
(a) |
Mount Kilimanjaro |
| South America |
(b) |
Mount McKinley |
| North America |
(c) |
Mount Elbrus |
| Africa |
(d) |
Mount Aconcagua |
| Europe |
(e) |
Mount Everest |
Answer:
- e
- d
- b
- a
- c
Question 2.
| Forest |
|
Flora |
| Thundra |
(a) |
Grasses |
| Prairies |
(b) |
Mahogany |
| Desert |
(c) |
Pine |
| Tropical Rainforest |
(d) |
Cactus |
| Coniferous forest |
(e) |
Mosses |
Answer:
- e
- a
- d
- b
- c
Question 3.
| Mineral |
|
Area |
| Iron ore |
(a) |
Appalachians |
| Copper |
(b) |
Mexico |
| Silver |
(c) |
Lake superior |
| Gold |
(d) |
Great lakes |
| Coal |
(e) |
California |
Answer:
- c
- d
- b
- e
- a
Question 4.
| Country |
|
Population Density |
| USA |
(a) |
3 persons |
| Canada |
(b) |
51 persons |
| Mexica |
(c) |
30 persons |
| Central Highland |
(d) |
Densly Populated |
| Central America |
(e) |
Moderate Population |
Answer:
- c
- a
- b
- e
- d
IV. Give reason.
Question 1.
Mississippi River has been given the nickname “The Big Muddy”.
Answer:
- The Mississippi River has been given the nickname “The Big Muddy” because it erodesa lot of sand and mud as it rushes down the Mountains.
- Some of the States of the United States are named after the tributaries of two mighty rivers the Mississippi and Missouri.

Question 2.
The Climate of North America is as varied as that of Asia.
Answer:
The vast latitudinal extent from the Tropics to the Polar Regions makes the climate of North America as varied as that of Asia.
Question 3.
South America is also known as Latin America.
Answer:
Together with Central America, South America is also known as Latin America, having been discovered and colonized mostly by the Latins, i.e., The Spanish and the Portuguese.
Question 4.
Cordilleras come under the pacific ring of fire.
Answer:
The Cordilleras are also part of the Fire Ring of the Pacific. Because there are a number of active volcanoes and this area is also subject to earthquakes.
Question 5.
The selvas of the equatorial regions are called the lungs of the world.
Answer:
They are thick forests and provide fresh oxygen so are known as the lungs of the world.
V. Distinguish between,
Question 1.
Rocky Mountain and Andes Mountain.
Answer:
| S.No. |
Rocky Mountain |
Andes Mountain |
| 1. |
Young fold mountains found in North America. |
Young fold mountains found in South America. |
| 2. |
The highest peak is Mt. Mckinley. |
The highest peak is Mt. Aconcagua. |
Question 2.
Mississippi River and Amazon river.
Answer:
| S.No. |
Mississippi river |
Amazon river |
| 1. |
The Source of the Mississippi river is lake Itasca. |
The Source of the Amazon river is the high Andes mountains. |
| 2. |
The important tributaries are Arkansas, Illinois, Missouri etc. |
The important tributaries Rio Negro, Madeira and Tapajos. |
| 3. |
The river drains into the Gulf of Mexico. |
The river drains into the Atlantic ocean ore the North-Eastern coast of Brazil. |
Question 3.
Bear Lake and Lake Titicaca.
Answer:
| S.No: |
Bear Lake |
Lake Titicaca |
| 1. |
Found in North America. |
Found in South America. |
| 2. |
It is located in the Rocky mountains. |
It is located in the High Andes Mountains. |
| 3. |
Found at an elevation of 1806m. |
The highest lake in the world. |
VI. Answer in one or two sentences
Question 1.
Name the prominent intermontane plateaus of North America.
Answer:
There are high intermontane plateaus between the ranges. The prominent ones are the Mexican plateau, the Colorado Plateau and the Columbian plateau.

Question 2.
Name the fold mountains of North America.
Answer:
Rockies and Appalachians.
Question 3.
What are westerlies?
Answer:
The Westerlies or anti-trades are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude.
Question 4.
Write a note on Grand Banks.
Answer:
Grand Banks: The Grand Banks is among the world’s largest and richest resource areas, renowned for both their valuable fish stocks and petroleum reserves.
Question 5.
Write a note on heavy industries of North America.
Answer:
Industries which require heavy and bulky raw materials using enormous amounts of power, the involvement of huge investment, and large transport costs are called heavy industries.
Question 6.
Name the important centers of heavy engineering industries.
Answer:
The important Centers of heavy engineering industries are Detroit, Chicago, Buffalo, Indianapolis, Los Angeles, Saint Louis, Philadelphia, New York, Baltimore, and Atlanta in the USA and Windsor in Canada.

Question 7.
Name the world’s important ports found in North America.
Answer:
Quebec City, Montreal, Boston, New York, Philadelphia, Charleston and New Orleans are the Worlds largest ports.
Question 8.
Write a note on the Panama canal.
Answer:
- Panama Canal: In 1914 a Canal was cut across the Isthmus of Panama for 80 kms long which connects the Atlantic with the Pacific Ocean.
- It greatly reduced the distance between Europe and the West Coast of North and South America.
Question 9.
Name the busiest international airports of the world found in North America.
Answer:
New York, Chicago, Los Angeles, Atlanta, Toronto, Montreal and Mexico City are some of the busiest international airports in the World.
Question 10.
Write about Trade in North America.
Answer:
- North America trades mainly with Asia, Europe, and Latin America.
- Though Alaska belongs to the USA, it has to import practically every resource. It is being developed now due to its mineral wealth.
- North America’s exports are mainly manufactured goods such as Industrial Machinery, Automobile, Paper, Fish, Arms and Ammunition, Aircraft, Telecom Equipments, Chemical, Plastics, Fertilizers, Wood Pulp, Timber, Crude Oil, Petroleum, Natural Gas, Aluminum, Nickel and Lead, etc.,
- The countries of North America Imports Tropical goods and Textiles from Asia and Africa. The countries of Europe, Japan, China, and India are the major trading partners.
Question 11.
What are the main natural vegetation areas of South America?
Answer:
There are four main natural vegetation areas of South America and are the Amazon basin (the Selvas), the Eastern Highlands, the Gran Chaco and the slopes of the Andes.
Question 12.
Write a note on the coniferous forest of South America.
Answer:
The forests on the slopes of the Andes have coniferous such as pine, fir, and spruce. These forests are also called Montana. They yield valuable softwood for the paper and pulp industry.

Question 13.
Write a note on Orinoco and Paraguay rivers.
Answer:
- The Orinoco River originates in the Guiana Highlands and flows northwards into the Caribbean Sea.
- The river Paraguay has the Parana and Uruguay rivers as the main tributaries which together form and known as the Platte River system.
- All the rivers are navigable for quite some distance in the interior.
Question 14.
Write a note on the Amazon river.
Answer:
- Amazon is the longest river in South America (6,450km) and is the largest river system in the world. This river has over a thousand tributaries.
- The rivers Rio Negro, Madeira, and Tapajos are important tributaries.
- At the point where it enters the sea, the river is so wide and powerful that it flows even at a distance of 80 km into the high seas.
Question 15.
Define
- Isthmus
- Strait
- Igloo
- Selvas
- Pampas.
Answer:
- Isthmus – A narrow stretch of land joining two large landmasses
- Strait – A narrow stretch of water joining two large water bodies
- Igloo – The specially designed house by ice
- Selvas – A tract of land covered by dense equatorial forest in the Amazon basin.
- Pampas – A temperate grassland of South America.
VII. Answer in Detail.
Question 1.
Explain about the Rocky mountains.
Answer:
The Rocky Mountains:
- The western part of the continent is occupied by long ranges of young folded mountains interspersed with high plateaus, narrow valleys, and broad interior basins.
- This mountain range extends for about 4800 km from Alaska in the North to the Panama Strait in the South.
- The width varies from 110 to 480 Kms.
- They are parallel ranges and are known as the Rockies in the east and the Coast Range Mountains in the west.
- In Mexico, they are called the Sierra Madre.
- The Rockies and the Coast Range are together called the “Western Cordilleras”.
- There are high intermontane plateaus between the ranges.
- The prominent ones are the Mexican plateau, the Colorado Plateau, and the Columbian plateau.

Question 2.
Write in detail about the drainage of North America.
Answer:
Drainage:
- Many rivers flow across this land and some of them following the valleys are formed by the glaciers.
- The Mississippi and Missouri rivers are the longest rivers in North America.
- The Mackenzie River is the second-largest drainage basin of North America. It has its source from Great Slave Lake and drains into the Arctic Ocean.
- St. Lawrence has its origin in Lake Ontario which flows northeast and drains into the Atlantic Ocean.
- The plateau of the west has been cut deeply by the River Columbia and its tributary which forms many gorges called Canyons.
- The most famous is the Grand Canyon cut by the River Colorado which all flows over the plateau of Columbia.
- The River Yukon rising in the north-west of the Western mountain system is frozen for eight months in the year. .
- The River Rio Grande flows into the Gulf of Mexico and forms the boundary between the USA and Mexico.
- The most important chain consists of five lakes. The biggest is Lake Superior and it is the largest freshwater lake in the world.
- Lake Winnipeg, Great Bear Lake, and Lake Athabasca are some of the other lakes in Canada.
Question 3.
Write in detail about the crops grown in North America.
Answer:
(i) Agriculture:
Though the least proportion of the total workforce is engaged in agriculture America’s agriculture is the most productive in the world. Wheat, Corn (Maize), Oats, Soybean, Barley, and many other food crops are grown throughout the vast interior plains.
(ii) Wheat:
Wheat was introduced by European settlers in North America. It is grown extensively in the Prairies of North America. North America is the largest exporter in North America produces more than half of the world’s total Maize.
(iii) Barley and Oats:
These are temperate crops that withstand the cold climate and need less water. The Barley is grown in the United States and are produced in Minnesota, North Dakota, and Washington. Barley and Oats is used as cattle fodder.
(iv) Cotton:
Cotton grows well in Southern and Western States and it is dominated in Texas, California, Mississippi, South of the Prairies, and Mexico. Warm summer with frequent rainfall and fertile soil are favorable conditions for the growth of the cotton crops.
(v) Sugar cane:
Sugar cane is cultivated along the Gulf of Mexico, Parts of Central America and the West Indies. It is an important Cash Crop of the West Indies. Cuba is known as the “sugar bowl of the world” and it is the world’s largest exporter of sugar.
(vi) Soya beans:
It is raised in the same area where Maize is grown. It is used for the extraction of edible ml.
(vii) Potatoes and Sugar beet:
Prairie Region, North Dakota, and Minnesota are the producers of Sugar Beets and Potatoes. Sugar beet is used for making Sugar. Potato and Sugar Beet are used to feed cattle and pigs.
Question 4.
Write about population density in North America.
Answer:
The density of the population in North America is 19 people/Sq. km.
Population and Density of North America
| S. No |
Country |
Population (in Millions) |
Density |
| 1. |
United States |
327.16 |
30 persons |
| 2. |
Canada |
36.95 |
3 persons |
| 3. |
Mexico |
123.00 |
51 persons |
- Densely populated areas: Eastern part of North America, Great Lakes region, Florida, California, Mexico and Central America are the most densely populated areas.
- Moderately populated areas: Central part of United States, Central Highland, Highlands of Mexico, Central and western Canada are the Moderately populated areas.
- Sparsely populated areas: Northern Canada, Alaska, Rocky Mountain regions and desert regions are sparsely populated areas.

Question 5.
Explain in detail the physiographic divisions of south America.
Answer:
On the basis of topographical features, the continent may be divided into the following physiographic divisions:
The Andes Mountains:
- The Andes are Fold Mountains like the Himalayas.
- The highest peak in the Andes is Mount Aconcagua (an extinct volcano) on the Chile- Argentina border which reaches at an elevation of 6,961 m. In Chile, the mountains run very close to the coast.
- The slopes are steep on the western side and gentle on the eastern side like the Rockies in North America.
- There are some active volcanoes like Cotopaxi (5,991m) on the Andes range. The Andes are rich in minerals like Copper, Tin and Precious Gems including Emerald.
The River Basins (or) the Central Plains:
- Nearly half of the Continent is covered by the plains. Three great rivers drain into the Atlantic Ocean.
- The biggest of them is Amazon.
- The Amazon basin consisting mainly of the alluvial deposits is the thickly forested part of the world.
The Eastern Highlands:
- These are considerably older than the Andes and are mainly Plateau which is cut by many rivers.
- They lie to the north and south of the Amazon River.
- The Brazilian Highlands are found to the south of the Amazon basin.
- They are gently rolling plateaus with steep cliffs along the east coast.
Question 6.
Explain the mineral deposits of South America.
Answer:
Minerals:
- South America is rich in minerals. These mineral deposits are unevenly distributed.
- South America has many valuable deposits of minerals particularly iron ore, manganese, petroleum, copper and bauxite. There are some active mines producing silver and gold.
- Northern Chile has the world’s only natural deposits of sodium nitrate an important ingredient of fertilizers.
Iron ore:
- South America contains about one-fifth of the world s iron ore reserves.
- Brazil and Chile both have massive deposits of iron ore.
- Brazil has the second-largest iron ore deposits in the world after Russia, Brazil is estimated to have about 15% of the world export of iron ore.
Manganese:
- Brazil also has large deposits of Manganese.
- Manganese ore is mined at Lafaiete, Minas Gerais, and in the Northern State of Amapa.
Petroleum:
- Venezuela is rich in petroleum deposits.
- Argentina, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Chile, and Bolivia are the other valuable oilfields. Petroleum is the only mineral produced in substantial quantity.
Copper:
- Chile is the third-largest producer of copper in the world.
- Copper provides over 40% of exports by value. Some of the biggest copper mines in the world are located in Peru.
- It is found in the Atacama Desert.
Bauxite:
- Brazil is the third-largest bauxite producing country.
- An important bauxite mining centre is located near the mouth of the Amazon River. Bauxite is used for aluminum production.

Question 7.
Explain the industries of South America.
Answer:
Industries:
- Industries in South America have developed slowly Argentina, Brazil, and Chile are the most highly developed industrial countries in this continent.
- The continent lacks infrastructure (especially transport) which is an essential need for Industrialisation. Railways and the roads could not be developed sufficiently owing to rugged terrain.
- In spite of having an abundance of natural resources, industrialisation started quite late in South America.
| S.no |
Country |
Industries |
| 1. |
Brazil |
Iron and steel, cotton textiles, sugar, food processing, oil refining, chemicals and automobiles |
| 2. |
Argentina |
Meat processing and Canning, dairy products, food processing, leather processing, woolen textiles, sugar and oil refining |
| 3. |
Chile |
Oil refining, chemical fertilizers and copper smelting |
| 4 |
Peru |
Mining and the processing of minerals, chemicals, fertilizers, sugar, coffee, and wool textiles |
| 5. |
Uruguay |
Dairy products, meat processing, and woolen textiles |
| 6. |
Venezuela |
Oil refining, chemical fertilizers and copper smelting |
Question 8.
Explain about the Transport of South America.
Answer:
Transport:
Unlike North America, South America still does not have an adequately integrated transportation network. Significant efforts have been made to improve both the connection within the countries and the linkages between them.
Roadways:
- South America has an extensive and rapidly expanding network of roads.
- A Road linking Venezuela and Brazil allows north to south movement through the Amazon Basin.
- Brazil continues to have the largest network of roads belonging to the Pan American Highway System which extends throughout the Americas.
Railways:
- In most South American countries, railways have lost their dominant position of the major mode of transportation and have been replaced by the road networks that have developed rapidly since the 1960 s.
- Moreover, rail transport is plagued by operational problems as well as by obsolete equipment.
- Many countries have two or more track gauges which impede the efficient integration of the rails system.
Waterways:
- Seaways have long been a vital component of the transport systems of South American countries.
- The majority of imports and exports to and from the continent are moved by ship. South America has a number of outstanding natural harbours.
- There is two inland waterways system of international importance. They are
- The Paraguay – Uruguay basin includes territory in four countries and
- The Amazon basin includes six countries. Each has several thousand miles of navigable waterways..
Airways:
- Airways have developed rapidly since World War II.
- The increase is particularly significant with respect to passenger traffic and also handling of bulky freights.
- All the South American capitals and most of the large cities are linked by direct air services to the major traffic centres of the United States and Europe.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()