Students can Download Bio Zoology Chapter 2 Kingdom Animalia Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 2 Kingdom Animalia
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Kingdom Animalia Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The symmetry exhibited in cnidarians is-
(a) Radial
(b) Bilateral
(c) Pentamerous radial
(d) Asymmetrical
Answer:
(a) Radial
Question 2.
Sea anemone belongs to phylum-
(a) Protozoa
(b) Porifera
(c) Coelenterata
(d) Echinodermata
Answer:
(c) Coelenterata
![]()
Question 3.
The excretory cells that are found in platyhelminthes are –
(a) Protonephridia
(b) Flame cells
(c) Solenocytes
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 4.
In which of the following organisms, self-fertilization is seen?
(a) Fish
(b) Round worm
(c) Earthworm
(d) Liver fluke
Answer:
(d) Liver fluke
Question 5.
Nephridia of Earthworms are performing the same functions as –
(a) Gills of prawn
(b) Flame cells of Planaria
(c) Trachea of insects
(d) Nematoblasts of Hydra
Answer:
(b) Flame cells of Planaria
Question 6.
Which of the following animals has a true coelom?
(a) Ascaris
(b) Pheretima
(c) Sycon
(d) Taenia solium
Answer:
(b) Pheretima
Question 7.
Metameric segmentation is the main feature of –
(a) Annelida
(b) Echinodermata
(c) Arthropoda
(d) Coelenterata
Answer:
(a) Annelida
![]()
Question 8.
In Pheretima locomotion occurs with help of –
(a) circular muscles
(b) longitudinal muscles and setae
(c) circular, longitudinal muscles and setae
(d) parapodia
Answer:
(c) circular, longitudinal muscles and setae
Question 9.
Which of the following have the highest number of species in nature?
(a) Insects
(b) Birds
(c) Angiosperms
(d) Fungi
Answer:
(a) Insects
Question 10.
Which of the following is a crustacean?
(a) Prawn
(b) Snail
(c) Sea anemone
(d) Hydra
Answer:
(a) Prawn
Question 11.
The respiratory pigment in cockroach is –
(a) Haemoglobin
(b) Haemocyanin
(c) Haemoerythrin
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Haemoerythrin
Question 12.
Exoskeleton of which phylum consists of chitinous cuticle?
(a) Annelida
(b) Porifera
(c) Arthropoda
(d) Echinodermata
Answer:
(a) Annelida
Question 13.
Lateral line sense organs occur in –
(a) Salamander
(b) Frog
(c) Water snake
(d) Fish
Answer:
(d) Fish
![]()
Question 14.
The limbless amphibian is –
(a) Icthyophis
(b) Hyla
(c) Rana
(d) Salamander
Answer:
(a) Icthyophis
Question 15.
Four chambered heart is present in –
(a) Lizard
(b) Snake
(c) Scorpion
(d) Crocodile
Answer:
(d) Crocodile
Question 16.
Which of the following is not correctly paired?
(a) Humans – Ureotelic
(b) Birds – Uricotelic
(c) Lizards – Uncotelic
(d) Whale – Ammonotelic
Answer:
(d) Whale – Ammonotelic
Question 17.
Which of the following is an egg laying mammal?
(a) Deiphinus
(b) Macropus
(c) Ornitho rhynchus
(d) Equus
Answer:
(c) Ornitho rhynchus
![]()
Question 18.
Pneumatic bones are seen in –
(a) Mammalia
(b) Aves
(c) Reptilia
(d) Sponges
Answer:
(b) Aves
Question 19.
Match the following columns and select the correct option.
|
Column – I |
Column – II |
|
(P) Pila |
(i) Devil fish |
|
(q) Dentalium |
(ii) Chiton |
|
(r) Chaetopleura |
(iii) Apple snail |
|
(s) Octopus |
(iv) Tusk shell |
(a) p – (ii), q – (i), r – (iii), s – (iv)
(b) p – (iii), q – (iv), r – (ii), s – (i)
(c) p – (ii), q – (iv), r – (i), s – (iii)
(d) p – (i), q – (ii), r – (iii), s – (iv)
Answer:
(b) p – (iii), q – (iv), r – (ii), s – (i)
Question 20.
In which of the following phyla, the adult shows radial symmetry but the larva shows bilateral symmetry?
(a) Mollusca
(b) Echinodermata
(c) Arthropoda
(d) Annelida
Answer:
(b) Echinodermata
![]()
Question 21.
Which of the following is correctly matched?
(a) Physalia – Portugese man of war
(b) Pennatula – Sea fan
(c) Adamsia – Sea pen
(d) Gorgonia – Sea anemone
Answer:
(a) Physalla – Portugese man of war
Question 22.
Why are spongin and spicules important to a sponge?
Answer:
- Choanocytes or collar cells are special I flagellated cells lining the spongocoel and the canals.
- The body is supported by a skeleton made of spicules or spongin or both.
- The spicules are made up of calcium and silica.
Question 23.
What are the four characteristics common to most animals?
Answer:
The characteristics common to most animals are the arrangement of cell layers.
- The levels of organization.
- Nature of coelom.
- The presence or absence of segmentation and notochord.
- Organization of the organ system.
Question 24.
list the features that all vertebrates show at some point in their deelopnwnt.
Answer:
1. Embryonic germ layer
a) Endoderm, b) Ectoderm – Two germinal layers.
2. a) Ectoderm, b) Endoderm, c) Mesoderm – Three germinal layers,
3. Organogenesis
- Ectoderm – Skin, Hair, Nerve, Tooth, Nail
- Endoderm – Intestine lung, Liver
- Mesoderm – Muscle, Bones, Heart
Question 25.
Compare closed and opened circulatory systems.
Answer:
Closed circulatory system:
- The circulation in which blood is present inside the blood vessels is called closed circulatory’ system
- It is found in higher organisms, e.g. annelids, cephalochordates and vertebrates.
Open circulatory system:
- The circulation in which blood remains filled in tissue spaces due to the absence of blood vessels is called open circulatory system.
- It is found in lower organisms. e.g. arthropods, molluscs and echinoderms.
Question 26.
Compare schizocoelom with enterocoeloni.
Schizocoelom:
- The coelom which is formed by splitting of Mesoderm is called schizocoelom.
- It is found in lower invertebrates like annelids, arthropods and molluscs.
Enterocoeloni:
- The coelom which is formed from the Mesodermal pouches of archenteron is called enteroceolem.
- It is found in echinoderms, hemichordates and chordates.
Question 27.
Identify the structure that the archenteron becomes in a developing animal.
Answer:
The true coelom called enterocoel formed from the archenteron.
![]()
Question 28.
Observe the animal below and answer the following questions
(a) Identify the animal
(b) What type of symmetry does this animal exhibit?
(c) Is this animal Cephalized?
(d) How many germ layers does this animal have?
(e) How many openings does this animal’s digestive system have?
(f) Does this animal have neurons?

Answer:
(a) Sea anemone (Adarnasia)
(b) Radial symmetry
(c) No
(d) Two (ectoderm and endoderm)
(e) One
(f) No.
Question 29.
Choose the term that does not belong in the following group and explain why it does not belong?
Answer:
The notochord, cephalization, dorsal nerve cord, and radial symmetry Unrelated characters:
Radial Symmetry Notochord, Cephalization dorsal nerve chord, are characteristic features of chordate animals. Radial Symmetry This is the feature of the invertebrate organism.
Question 30.
Why flat worms are called acoelomates?
Answer:
Flat worms are called acoelomate because they do not possess a body cavity.
Question 31.
What are flame cells?
Answer:
Specialized excretory cells present in flatworms called flame cell helps in Osmoregulation and excretion.
Question 32.
Concept Mapping – Use the following terms to create a concept map that shows the major characteristic features of the phylum nematoda: Round worms, pseudocoelomates, digestive tract, cuticle, parasite and sexual dimorphism.
Answer:
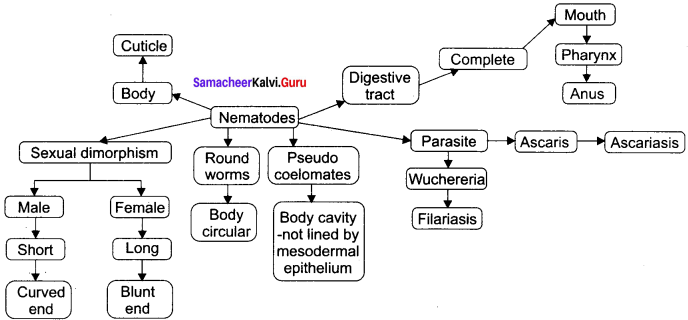
Question 33.
In which phyla is the larva trochopore found?
Answer:
Trochopore larva is seen in the Phylum – Annelida.
Question 34.
Which of the chordate characteristics do tunicates retain as adults?
Answer:
- Presence of notochord below the nerve cord and above the alimentary canal.
- The dorsal nerve cord lies above the notochord and below the dorsal body wall.
- Pharyngeal gill slits at some stage of their life cycle.
![]()
Question 35.
List the characteristic features that distinguish cartilaginous fishes with living jawless fishes.
Answer:
Cartilaginous Fishes:
- These have powerful jaws which help in predation.
- These are free living predatory fishes.
- These are advanced over jawless fishes.
- These have a tough skin covered by dermal
- Respiration is by lamelliform gills without operculum.
- Paired fins are present.
- Fertilization is internal
- Viviparous e.g. Scoliodon
Living Jawless Fishes:
- They do not have jaws and the mouth is circular and suctorial.
- These are ectoparasites on fishes.
- These are primitive over cartilaginous fishes.
- The skin is soft and devoid of scales.
- These have six to fifteen pair of gills slits.
- Paired fins are absent.
- Fertilization is external
- Oviparous, e.g. Lamprey
Question 36.
List three features that characterize bony fishes.
Answer:
- The body is spindle-shaped skin is covered by ganoid cycloid or Ctenoid scales.
- They have four pairs of filamentous gills with operculum on either side.
- Air bladder helps in gaseous exchange and for maintaining buoyancy.
- Sexes are separate.
- They have lateral line sense organs. The kidney is mesonephric.
Question 37.
List the functions of air bladder in fishes.
Answer:
- Air bladder helps in gaseous exchange.
- It helps in maintaining buoyancy.
Question 38.
Write the characteristics that contributes to the success of reptiles on land.
Answer:
- The body of the reptile is covered by dry and cornified skin with epidermal scales or scutes.
- All are poikilotherms.
- Most reptiles lay cleidoic eggs.
- Excretion is by metanephric kidneys and is uricotelic.
- They are monoecious.
- Internal fertilization is taking place
Question 39.
List the unique features of bird’s endoskeleton.
Answer:
- The endoskeleton of birds is bony
- The long bones are hollow with air cavities (pneumatic)
- The body is covered by feathers.
Question 40.
Could the number of eggs or young ones produced by an oviparous and viviparous female be equal? Why?
Answer:
- Each female gamete from a female unites with a male gamete (spermatozoa) of a male through internal or external fertilization and form a zygote that will become an individual.
- The number of female gametes produced is united with that much number of male gametes and produced that much number of individuals. Hence the egg or young ones produced by the oviparous or viviparous females are equal.
Entrance Examination Questions Solved
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Classification of sponges is primarily based on the …………. (JCECE-2003)
(a) body organization
(b) body plan
(c) skeleton
(d) canal system
Answer:
(c) skeleton
Question 2.
Symmetry is cnidaria is …………. (AMU-2009)
(a) radial
(b) bilateral
(c) pentamerous
(d) spherical
Answer:
(a) radial
Question 3.
Cavity of coelenterates is called …………. (BHU-2008)
(a) coelenteron
(b) coelom
(c) cavity
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) coelenteron
![]()
Question 4.
Sea anemone belongs to phylum …………. (BCECE-2005)
(a) protozoa
(b) Porifera
(c) Coelenterata
(d) Echinodermata
Answer:
(c) Coelenterata
Question 5.
Medusa is the reproductive organ of …………. (BHU-2008)
(a) Hydra
(b) Aurelia
(c) Obelia
(d) Sea anemone
Answer:
(b) Aurelia
Question 6.
The excretory cells, that are found in Platyhelminthes …………. (J & K CET-2007)
(a) Protonephridia
(b) Flame cells
(c) Solenocytes
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) Flame cells
Question 7.
In which of the following organisms, self-fertilization is seen? (CCET-2007)
(a) Fish
(b) Round worm
(c) Earthworm
(d) Liver fluke
Answer:
(d) Liver fluke
![]()
Question 8.
Nephridia of Earthworms are performing same function as …………. (J & KCET-2003)
(a) gills of prawn
(b) flame cells of Planaria
(c) trachea of insects
(d) nematoblasts of Hydra
Answer:
(b) flame cells of Planaria
Question 9.
Phylum of Taenia solium is …………. (BCECE-2004)
(a) Aschelminthes
(b) Annelids
(c) Platylelminthes
(d) Mollusca
Answer:
(c) Platylelminthes
Question 10.
Ascaris is found in …………. (RPMT-2004)
(a) body cavity
(b) lymph nodes
(c) tissue
(d) alimentary canal
Answer:
(d) alimentary canal
Question 11.
Which of the following animals has a true coelom? (J & K CET-2007)
(a) Ascaris
(b) Pheretima
(c) Sycon
(d) Taenia solium
Answer:
(b) Pheretima
Question 12.
Metameric segmentation is the main feature of ………….
(a) Annelida
(b) Echinodermata
(c) Arthropoda
(d) Coelenterata
Answer:
(a) Annelida
Question 13.
Body cavity lined by mesoderm is called …………. (J & T CET-2005)
(a) coelenteron
(b) pseudocoel
(c) coelom
(d) blastocoel
Answer:
(c) coelom
![]()
Question 14.
Which of the following have the highest number of species in nature? (AIPMT-2011)
(a) Insects
(b) Birds
(c) Angiosperms
(d) Fungi
Answer:
(a) Insects
Question 15.
Which of the following is a crustacean? (Guj-CET-2011)
(a) Prawn
(b) Snail
(c) Sea anemone
(d) Hydra
Answer:
(a) Prawn
Question 16.
The respiratory pigment present in cockroach is …………. (OJEE-2010)
(a) Haemoglobin
(b) Haemocyanin
(c) Oxyhaemoglobin
(d) None of these
Answer:
(d) None of these
Question 17.
Book lungs are respiratory organs in …………. (AMU-2008)
(a) Insects
(b) Arachnids
(c) Molluscans
(d) Echinoderms
Answer:
(b) Arachnids
Question 18.
The excretory organ in cockroach is …………. (Kerala-CEE-2007)
(a) Malpighian corpuscle
(b) Malpighian tubules
(c) Green gland
(d) Metanephridia
Answer:
(b) Malpighian tubules
Question 19.
The exoskeleton of which phylum consists of chitinous cuticle? (J & KCET-2007)
(a) Annelida
(b) Porifera
(c) Arthropoda
(d) Echinodermata
Answer:
(c) Arthropoda
Question 20.
In cockroach, vision is due to …………. (PMET-2005)
(a) one compound eye
(b) two compound eyes
(c) two simple eyes
(d) two compound and two simple eyes.
Answer:
(b) two compound eyes
![]()
Question 21.
Which of the following respires through gills? (J & K CET-2005)
(a) Whale
(b) Turtle
(c) Frog
(d) Prawns
Answer:
(d) Prawns
Question 22.
Animals active at night are called …………. (J & K CET-2004)
(a) diurnal
(b) nocturnal
(c) parasites
(d) nocto – diumal
Answer:
(b) nocturnal
Question 23.
Salient features of Arthropoda is ……….. (RPMT-2003)
(a) aquatic and free living
(b) chitinous exoskeleton and jointed appendages
(c) radulla
(d) none of those
Answer:
(b) chitinous exoskeleton and jointed appendages
Question 24.
The second-largest number of species containing phylum in the animal kingdom is ……….. (J & K CET-2008)
(a) Annelida
(b) Arthropoda
(c) Mollusca
(d) Chordata
Answer:
(c) Mollusca
Question 25.
Mollusca is ………… (JCECE-2006)
(a) Triploblastic, acoelomate
(b) Triploblastic, coelomate
(c) Diploblastic, acoelomate
(d) Diploblastic, coelomate
Answer:
(b) Triploblastic, coelomate
Question 26.
Tube feet are the locomotory organs of ………….
(a) Platyhelminthes
(b) Echinodermata
(c) Mollusca
(d) Arthropoda
Answer:
(b) Echinodermata
![]()
Question 27.
Given below are four matchings of a animal and its kind of respiratory organ …………. (PMT 2003)
(A) Silver fish – Trachea
(B) Scorpion – Book lung
(C) Sea squirt – Pharyngeal gills
(D) Dolphin – Skin
The correct matchings are
(a) A and B
(b) A, B, and C
(c) B and D
(d) C and D
Answer:
(b) A,B and C
Question 28.
Which one of the following is a matching pair of an animal and a certain phenomenon it exhibits? (PMT 2003)
(a) Pheretima – Sexual dimorphism
(b) Rana – Complete metamorphosis
(c) Chameleon – Mimicry
(d) Taenia – Polymorphism
Answer:
(b) Rana – Complete metamorphosis
Question 29.
Two common characters found in centipede, cockroach and crab …………. (PMT 2006)
(a) book lungs and antennae
(b) compound eyes and anal cerci
(c) joint legs and chitinous exoskeleton
(d) green gland and tracheae
Answer:
(c) joint legs and chitinous exoskeleton
Question 30.
Which one of the following groups of animals is bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic? (PMT 2009)
(a) Aschelminthes (round worms)
(b) Ctenophores
(c) Sponges
(d) Coelenterates (cnidarians)
Answer:
(a) Aschelminthes (round worms)
Question 31.
Which one feature is common to leech, cockroach and scorpion? (AIIMS 2004)
(a) Nephridia
(b) Ventral nerve cord
(c) Cephalization
(d) Antennae
Answer:
(b) Ventral nerve cord
Question 32.
Which one of the following features is common in silverfish, scorpion, dragonfly and prawn?
(a) Three pairs of legs and segmented body
(b) Chitinous cuticle and two pairs of antennae
(c) Jointed appendages and chitinous exoskeleton
(d) Cephalothorax and trachea
Answer:
(c) Jointed appendages and chitinous exoskeleton
Question 33.
Peripatus is known as a connecting link because it has the characters of both …………. (BHU 1993)
(a) Fishes & amphibians
(b) Reptiles & birds
(c) Aves & fishes
(d) Arthropoda & annelids
Answer:
(d) Arthropoda & annelids
Question 34.
Osphradium of Pila globosa is ………… (BHU 1994, 2000, 2007)
(a) thermoreceptor
(b) Pheretima
(c) chemoreceptor
(d) tangoreceptor
Answer:
(c) chemoreceptor
Question 35.
Green glands present in some arthropods help in …………. (BHU 1998, 2007)
(a) respiration
(b) excretion
(c) digestion
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) excretion
![]()
Question 36.
Squid, cuttlefish, and Octopus belongs to a class of …………. (BHU 1998, 2001)
(a) Decapoda
(b) Scaphopoda
(c) Cephalopoda
(d) apods
Answer:
(c) Cephalopoda
Question 39.
The canal system is a characteristic feature of …………. (BHU 1999, 2002)
(a) sponges
(b) echinoderms
(c) helminths
(d) coelenterates
Answer:
(a) sponges
Question 40.
Malpighian tubules are …………. (BHU 2006)
(a) excretory organs of insects
(b) excretory organs of the frog
(c) respiratory organs of insects
(d) endocrine glands of insects
Answer:
(a) excretory organs of insects
Question 41.
Caterpillar and maggot are …………. (BHU 2007)
(a) larvae
(b) nymphs
(c) adults
(d) pupa
Answer:
(a) larvae
Question 42.
The excretory organ of Platyhelminthes is …………. (BHU 2008)
(a) gills
(b) flame cells
(c) nephridia
(d) trachea
Answer:
(b) flame cells
Question 43.
Water vascular system is a characteristic of …………. (BHU 2008)
(a) ctenophore
(b) annelid
(c) echinodermata
(d) arthropoda
Answer:
(c) Echinodermata
Question 44.
Tube feet are the characteristic structures of …………. (DPMT 1993, 2008)
(a) jellyfish
(b) starfish
(c) cuttlefish
(d) crayfish
Answer:
(b) starfish
![]()
Question 45.
Hormone, which helps in metamorphosis in insects is …………. (DPMT 1996)
(a) pheromone
(b) ecdysone
(c) thyroxine
(d) all of these
Answer:
(b) ecdysone
Question 46.
The muscles associated with the heart of insects are …………. (DPMT 1996, 2006)
(a) alary
(b) striped
(c) radial
(d) pericardial
Answer:
(a) alary
Question 47.
Which of the following organisms is pseudocoelomate? (DPMT 2001, 2006)
(a) Hookworm
(b) Liver fluke
(c) Jellyfish
(d) Leech
Answer:
(a) Hookworm
Question 48.
Which of the following is not reported to have any freshwater forms? (DPMT 2003)
(a) Mollusca
(b) Sponges
(c) Coelenterates
(d) Echinoderms
Answer:
(d) Echinoderms
Question 49.
Pseudocoelom is not found in ………… (DPMT 2004)
(a) Ascaris
(b) Ancylostoma
(c) Fasciola
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) Fasciola
Question 50.
Animals devoid of respiratory, excretory, and circulatory organs belong to phylum ………… (DPMT 2004)
(a) echinodermata
(b) platyhelminthes
(c) porifera
(d) mollusca
Answer:
(c) Porifera
Question 51.
Cilia of gills of bivalve mollusks help in …………. (DPMT 2005)
(a) protection
(b) respiration
(c) excretion
(d) feeding
Answer:
(b) respiration
Question 52.
All flatworms differ from all roundworms in having …………. (DPMT 2009)
(a) triploblastic body
(b) solid mesoderm
(c) bilateral symmetry
(d) metamorphosis in the life history
Answer:
(b) solid mesoderm
Question 53.
Parthenogenesis can be seen in …………. (UPCPMT 1995)
(a) frog
(b) honey bee
(c) moth
(d) all of these
Answer:
(b) honey bee
Question 54.
The endocrine gland of insects, which secretes the juvenile hormone, is …………. (UP-CPMT 1995)
(a) corpora allata
(b) corpora Albicans
(c) corpora myecaena
(d) all of these
Answer:
(a) corpora allata
![]()
Question 55.
Malpighian tubules are …………. (UP – CPMT 1996, 2008)
(a) excretory organs of insects
(b) respiratory organs of insects
(c) excretory organs of the frog
(d) endocrine glands of insects
Answer:
(a) excretory organs of insects
Question 56.
In Mollusca, the eye is present over a stalk called …………. (UP-CPMT 2000, 2007)
(a) osphradium
(b) ostracum
(c) ommatophore
(d) operculum
Answer:
(c) ommatophore
Question 57.
Which of the following symmetries is found in adult sea anemone? (UP – CPMT 2004)
(a) Radial
(b) Biradial
(c) Bilateral
(d) Spherical
Answer:
(a) Radial
Question 58.
Feeding in sponges takes place through …………. (UP-CPMT 2005)
(a) choanocytes
(b) nurse cells
(c) Ostia
(d) osculum
Answer:
(a) choanocytes
Question 59.
Osphradium is meant for …………. (UP-CPMT 2005)
(a) excretion
(b) nutrition
(c) selection and rejection of food
(d) grinding of food
Answer;
(c) selection and rejection of food
Question 60.
Excretory product of spider is …………. (UPCPMT 2007)
(a) uric acid
(b) ammonia
(c) guanine
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) guanine
Question 61.
Which of the following is not the character of Taenia soliuml …………. (UPCPMT 2007)
(a) Polysis
(b) Proglottid
(c) Metamerism
(d) Strobila
Answer:
(c) Metamerism
Question 62.
Daphnia is commonly known as …………. (UP-CPMT 2007)
(a) clam shrimp
(b) fairy shrimp
(c) water fleas
(d) tadpole shrimp
Answer:
(c) water fleas
Question 63.
Wuchereria is found in …………. (UP-CPMT 2007)
(a) lymph nodes
(b) lungs
(c) eye
(d) gonds
Answer:
(a) lymph nodes
Question 64.
“Turbellarians” are free-living …………. (UP-CPMT 2008)
(a) flatworms
(b) trematodes
(c) nematodes
(d) cesrtodes
Answer:
(a) flatworms
![]()
Question 65.
Polyp phase is absent in …………. (UP-CPMT 2008)
(a) Physalia
(b) Obselia
(c) Hydra
(d) Aurelia
Answer:
(d) Aurelia
Question 66.
Animals having pseudocoelomate and triploblastic nature are present in phyla …………. (UP-CPMT 2008).
(a) annelida
(b) arthropoda
(c) aschelminthes
(d) platyhelminthes
Answer:
(c) aschelminthes
Question 67.
Primitive nervous system is formed in …………. (UP-CPMT 2009)
(a) sponge
(b) cnidaria (coelenterate)
(c) echinodermata
(d) annelida
Answer:
(b) cnidaria (coelenterate)
Question 68.
Tissues are absent in the body of …………. (UP-CPMT 2009)
(a) sponge
(b) annelida
(c) platyhelminthes
(d) arthropoda
Answer:
(a) sponge
Question 69.
Linmulus belongs to class ………….
(a) onychophora
(b) insect
(c) merostomata
(d) Crustacea
Answer:
(c) merostomata
Question 70.
Ambulacral system is mainly useful for ………….
(a) locomotion
(b) feeding
(c) circulation
(d) defence
Answer:
(b) feeding
Question 71.
Which of the following is an excretory organ in Mollusca?
(a) Keber’s organ
(b) nephridia
(c) Malpighian organ
(d) Flame cells
Answer:
(a) Keber’s organ
Question 72.
Mouthparts of housefly are ………….
(a) Piercing and sucking type
(b) Biting and sucking type
(c) Sponging and sucking type
(d) biting and chewing type
Answer:
(c) Sponging and sucking type
Question 73.
Anus is absent in
(a) Periplaneta
(b) Unio
(c) Fasciola
(d) Pheretima
Answer:
(c) Fasciola
Question 74.
Asymmetry in Gastropoda is due to ………….
(a) twisting
(b) torsion
(c) coiling
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) torsion
![]()
Question 75.
The pigment hemocyanin is found in ………….
(a) mollusca
(b) chordate
(c) echinodermata
(d) annelida
Answer:
(a) Mollusca
Question 76.
The development of adult characteristics in a moulting insect is promoted by ………….
(a) pheromone
(b) thyroxine
(c) juvenile hormone
(d) ecdysone
Answer:
(d) ecdysone
Question 77.
If you are given an insect, a spider, a Peripatus, and a crab, based on which character you can identify an arachnid from others?
(a) one pair of legs
(b) sense organs
(c) four pairs of legs
(d) number of wings
Answer:
(c) four pairs of legs
Question 78.
Choanocytes perform ………….
(a) reproduction
(b) nutrition
(c) discretion of spicules
(d) excretion
Answer:
(b) nutrition
Question 79.
Common characteristics of cockroach, housefly and mosquito are ………….
(a) one pair each of wings and halters
(b) three pairs of legs and one pair of developed wings
(c) two pair of legs and two compound eye
(d) compound and simple eyes
Answer:
(a) one pair each of wings and halters
Question 80.
The secondary host of Taenia is ………….
(a) snail
(b) pig
(c) man
(d) dog
Answer:
(b) pig
Question 81.
The exoskeleton of insect is made up of ………….
(a) pectin
(b) lignin
(c) chitin
(d) suberin
Answer:
(c) chitin
Question 82.
Collar cells are found in ………….
(a) aschelminthes
(b) cnidaria
(c) Arthropoda
(d) sponges
Answer:
(d) sponges
Question 83.
Ommatidia are the units that constitute the compound eyes in …………. (AMU 1995).
(a) Fish ‘
(b) Insects
(c) Mammals
(d) Birds
Answer:
(b) Insects
Question 84.
Which of the following animals possesses ink gland?(AMU 2003)
(a) Blue Whale
(b) Scorpion
(c) Sea Urchin
(d) Cuttle Fish
Answer:
(d) Cuttle Fish
Question 85.
Comb plates are present in …………. (AMU 2004)
(a) echinoderms
(b) ctenophores
(c) annelids
(d) molluscs
Answer:
(b) ctenophores
![]()
Question 86.
Which of the following does not belong to phylum cnidaria?(AMU 2004)
(a) Sea pen
(b) Sea lily
(c) Sea-fan
(d) Sea anemone
Answer:
(b) Sea lily
Question 87.
Protonephridia are the excretory structures present in …………. (AMU 2005)
(a) Planaria
(b) Roundworm
(c) Tapeworm
(d) Prawn
Answer:
(a) Planaria
Question 88.
Which of the following is not an annelid? (AMU 2007)
(a) Leech
(b) Earthworm
(c) Sea mouse
(d) Sea cucumbers
Answer:
(d) Sea cucumbers
Question 89.
Blood worms are the larvae of …………. (AMU 2007)
(a) Hirudinaria
(b) Chironomus
(c) Limulus
(d) Daphnia
Answer:
(b) Chironomus
Question 90.
Pick the odd pair …………. (AMU 2008)
(a) Porifera : spicules
(b) Scyphozoan : coral reef
(c) Nematode : pseudocoelomate
(d) Cestoda : proglottid
Answer:
(b) Scyphozoan : coral reef
Question 91.
Insect metamorphosis having larval stage is called …………. (AFMC 1994)
(a) Incomplete metamorphosis
(b) Retrogressive metamorphosis
(c) Heteromorphosis
(d) Complete metamorphosis
Answer:
(d) Complete metamorphosis
Question 92.
Which of the following is not an insect? (AFMC 1996)
(a) Cockroach
(b) Spider
(c) Mosquito
(d) Bedbug
Answer:
(b) Spider
Question 93.
Which of the following enters intestine by penetrating through skin? (AFMC 2003)
(a) Hook worm
(b) Ascaris
(c) Pin worm
(d) Filarialworm
Answer:
(a) Hook worm
Question 94.
In nemathelminthes the coelom is not lined by peritoneum is …………. (AFMC 2004)
(a) acoelom
(b) pseudocoelom
(c) enterocoelom
(d) haemocoel
Answer:
(b) pseudocoelom
Question 95.
Leech secretes which of the following anticoagulant? (AFMC 2004)
(a) Hirudin
(b) Heparin
(c) Serotonin
(d) Histamine
Answer:
(a) Hirudin
Question 96.
Canal system in porifera is not concerned with …………. (AFMC 2005)
(a) respiration
(b) nutrition
(c) sexual reproduction
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) sexual reproduction
![]()
Question 97.
Johnston’s organ is present in …………. (AFMC 2007)
(a) antenna of insect
(b) head of cockroach
(c) abdomen of housefly
(d) abdomen of spider
Answer:
(a) antenna of insect
Question 98.
Which of the following is not an arachnid? (AFMC 2007)
(a) Spider
(b) Itchmite
(c) Louse
(d) Tick
Answer:
(c) Louse
Question 99.
Fasciola hepatica is …………. (AFMC 2007)
(a) hermaphrodite self fertilizing
(b) hermaphrodite, cross fertilizing
(c) unisexual
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) both (a) and (b)
Question 100.
Match the excretory organs listed under column I with the animals given under column II. Choose the answer which gives the correct combination of alphabets of the column.
|
Column I |
Column II |
| A. Nephridia |
p. Hydra |
| B. Malpighian tubules |
q. Leech |
| C. protonephridia |
r. Shark |
| D. kidneys |
s. Round worms |
|
t. Cockroach |
(a) A – q; B -1; C – s; D – r
(b) A = s ; B= q; C= p; D= t
(c) A -1; B – q; C – s; D – r .
(d) A = q; B = s ; C =t; D= p
Answer:
(a) A – q; B -1; C- s; D – r
Question 101.
Entomology is concerned with the study of ………….
(a) formation and properties of soil
(b) agricultural practices
(c) various aspects of human life
(d) various aspects of insects.
Answer:
(d) various aspects of insects.
Question 102.
Which phylum of the animal kingdom is exclusively marine? (Orissa 2003, 2006)
(a) Porifera
(b) Arthropoda
(c) Echinodermata
(d) Molluscs
Answer:
(c) Echinodermata
Question 103.
Study of ticks and mites is ………….
(a) Acarology
(b) Entomology
(c) Malacology
(d) Carcinology
Answer:
(a) Acarology
Question 104.
Larva of mosquito is ………….
(a) maggot
(b) caterpillar
(c) grub
(d) none of these
Answer:
(d) none of these
Question 105.
Transparent hairs on catkins and caterpillars function to?
(a) Trap heat
(b) Trap moisture
(c) Reflect light
(d) Drink water
Answer:
(b) Trap moisture
Question 106.
Which of the following traits is not the characteristic of Echinodermata?
(a) Water vascular system
(b) Trochophore larva
(c) Aristotle’s lantern
(d) Radial and indeterminate cleavage
Ans.
(b) Trochophore larva
Question 107.
Which of the following is pseudocoelomate?
(a) Nematode
(b) Chordate
(c) Echinodermata
(d) Arthropoda
Answer:
(a) Nematode
![]()
Question 108.
Which is not correct for sponges?
(a) Internal fertilization
(b) External fertilization
(c) Gemmule formation
(d) Gametes are formed from epidemial cells.
Answer:
(b) External fertilization
Question 109.
Triploblastic, schizocoelic, and unsegmented soft-bodied animals belong to the phylum ……….. (J&K 1998)
(a) annelid
(b) Mollusca
(c) nemathelminthes
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) mollusca
Question 110.
Which one of the following animals belongs to the phylum cnidaria? (J&K 1998)
(a) Silver fish
(b) Squid
(c) Jelly fish
(d) Echidna
Answer:
(c) Jelly fish
Question 111.
Palaemon (prawn) is a …………. (J & K 2000)
(a) fish
(b) insect
(c) soft shell mollusca
(d) crustacean
Answer:
(d) crustacean
Question 112.
Tapeworm occurs as a parasite in …………. (J&K 2001)
(a) liver
(b) stomach
(c) intestine
(d) all of these
Answer:
(c) intestine
Question 113.
What distinguishes an insect from a crustacean? (J&K 2002. 2005)
(a) number of eyes
(b) arrangement of nerve cords
(c) number of appendages
(d) presence of wings.
Answer:
(c) number of appendages
Question 114.
Leeches are usually …………. (J&k 2005)
(a) herbivorous
(b) insectivorous
(c) carnivorous
(d) sanguivorous
Answer:
(d) sanguivorous
Question 115.
Wuchereria bancrofti is a common filarial worm. It belongs to the phylum …………. (J&K 2007)
(a) Platyhelminthes
(b) Nemathelminthes
(c) Annelid
(d) Coelenterate
Answer:
(b) Nemathelminthes
Question 116.
The dioecius animal is …………. (J&K 2008)
(a) Liver fluke
(b) Aurelia
(c) Tapeworm
(d) Earthworm
Answer:
(b) Aurelia
Question 117.
Malpighian tiihuies remove excretory products from ………….
(a) Mouth
(b) Haemolymph
(c) Oesophagus
(d) Alimentary canal
Answer:
(b) Haemolymph
Question 118.
Which of the following cell type is capable of giving rise to other ccli types in sponges?
(a) Pinacocytes
(b) Archaeocytes
(c) Thesocytes
(d) Collencytes
Answer:
(b) Archaeocytes
Question 119.
The infective stage of Entarnoeba histolytica is ………….
(a) cyst
(b) spore
(c) egg
(d) trophozoite
Answer;
(d) trophozoite
Question 120.
Gonads of Obelia occur in ………….
(a) on blastocyst
(b) in hydrula stage
(c) radial canals of medusa
(d) bases of entacies of medusa
Answer:
(c) radial canals of medusa
Question 121.
Which one of the following features is common to leech, cockroach and scorpion?
(a) nephridia
(b) ventral nerve cord
(c) cephalization
(d) antennae
Answer:
(b) ventral nerve cord
Question 122.
Excretory organs of flatworms are ………….
(a) Malpighian tubules
(b) Neprons
(c) Protonephridia
(d) Nnepridia
Answer:
(c) Protonephridia
![]()
Question 123.
Sea cucumbers belong to class ………….
(a) Echinoidea
(b) Ilolothuroidea
(c) Ophiuroidea
(d) Asteroidean
Answer:
(b) Holothuroidea
Question 124.
One of the following is a very unique feature of the mammals …………. (PMT2004, DPMT 1996. 1998)
(a) Homeothermy
(b) Presence of diaphragam
(c) Four chambered heart
(d) Rib cage
Answer:
(b) Presence of diaphragam
Question 125.
Uricotelisum is found in …………. (PMT 2004)
(a) Mammals and birds
(b) Fishes and fresh water protozoans
(c) Birds, reptiles and insects
(d) Frogs and toads
Answer:
(c) Birds, reptiles and insects
Question 126.
Which one of the following characters is not typical of the class mammalian? (PMT 2004)
(a) Thecodont dentition
(b) Alveolar lungs
(C) Ten pairs of cranial nerves
(d) Seven cervical vertebrate
Answer:
(c) Ten pairs of cranial nerves
Question 127.
Which one of the following in birds, indicates their reptilian ancestry? (PMT 2008)
(a) Two special chambers crop and gizzard in their digestive tract
(b) Eggs with a calcareous shell
(c) Scales on their hind limbs
(d) Four – chambered heart
Answer:
(e) Scales on their hind limbs
Question 128.
Which one of the following pairs of animals comprises ‘Jawless fishes’? (PMT2009)
(a) Mackerals and rohu
(b) Lampreys and hag fishes
(c) Guppies and hag fishes
(d) Lampreys and eels
Answer:
(b) Lampreys and hag fishes
Question 129.
Camouflage of chameleon is associated with …………. (AIIMS 1995)
(a) Chromoplast
(b) Chromosome
(c) Chromatophore
(d) Chromomere
Answer:
(c) Chromatophore
Question 130.
In fast swimming fishes, propulsion is due to …………. (A1IMS 2000)
(a) Pelvic fin
(b) Pectoral fin
(c) Dorsal fin
(d) Caudal fin
Answer:
(d) Caudal fin
Question 131.
Body temperature of cold-blooded animals …………. (AIIMS 2000)
(a) Is constant
(b) Fluctuates with surrounding temperature
(c) Becomes very low (a) times
(d) Is very cold
Answer:
(b) Fluctuates with surrounding temperature
Question 132.
Which of the following is an egg-laying mammal? (AUMS 2001)
(a) Kangaroo
(b) Platypus
(c) Penguin
(d) Whale
Answer:
(b) Platypus
![]()
Question 133.
Which of the following are uricotelic animals? (AIIMS 2002)
(a) rohu and frog
(b) camel
(c) lizard and crow
(d) earthworm and eagle
Answer:
(c) lizard and crow
Question 134.
Which of the following does not come under the class mammals? (AIIMS 2007)
(a) flying fox
(b) hedgehog
(c) manatee
(d) lamprey
Answer:
(d) lamprey
Question 135.
Which of the following is concerned with the formation of urea in rabbits? (BHU 1994,2007)
(a) spleen
(b) kidney
(c) blood
(d) liver
Answer:
(d) liver
Question 136.
The lateral line is present in …………. (BHU 1996)
(a) dogfish
(b) jellyfish
(c) starfish
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) dogfish
Question 137.
The largest and heaviest mammals in the world is …………. (BHU 1994)
(a) blue whale
(b) elephant
(c) lion
(d) tiger
Answer:
(a) blue whale
Question 138.
Ichthyophis is a member of …………. (AIIMS 1997)
(a) amphibian
(b) Mollusca
(c) reptilian
(d) annelid
Answer:
(a) amphibian
Question 139.
The renal portal system is absent in …………. (AIIMS 1998,2008)
(a) reptiles
(b) amphibians
(c) reptiles and amphibians
(d) birds
Answer:
(b) amphibian
Question 140.
Bone marrow is absent in …………. (AIIMS 2000)
(a) reptilian
(b) amphibian
(c) fishes
(d) birds
Answer:
(d) birds
Question 141.
Urea is formed in which organ of rabbit? (AIIMS 2001)
(a) liver
(b) kidney
(c) spleen
(d) lung
Answer:
(a) liver
Question 142.
Which of the following is not classified as an amphibian? (AIIMS 2003)
(a) frog
(b) salamander
(c) tortoise
(d) ichthiophis
Answer:
(c) tortoise
![]()
Question 143.
The excretory material of bony fish is …………. (AIIMS 2004)
(a) urea
(b) protein
(c) ammonia
(d) amino acid
Answer:
(c) ammonia
Question 144.
Limbless amphibians belong to the order …………. (AIIMS 2007)
(a) anura
(b) urodela
(c) gymnophiona
(d) lissamphibia
Answer:
(c) gymnophiona
Question 145.
Which of the following snakes is non-poisonous?…………. (AIIMS 2007)
(a) cobra
(b) krait
(c) viper
(d) python
Answer:
(d) python
Question 146.
Placoid scales are found in …………. (AIIMS 2008)
(a) reptilia
(b) bony fishes
(c) cartilaginous fishes
(d) amphibians
Answer:
(c) cartilaginous fishes
Question 147.
Which of the following is a correct sequence of decreasing order of a number of species? (AIIMS 2008)
(a) aves, Pisces, reptiles, amphibians, mammals
(b) Pisces, aves, reptiles, mammals, amphibians
(c) Pisces, mammals, reptiles, amphibians, aves
(d) amphibians, aves, Pisces, mammals, reptiles
Answer:
(b) Pisces, aves, reptiles, mammals, amphibians
Question 148.
The excretory organ in Balanoglossus is…………. (DPMT 1991, 2008)
(a) nephridia
(b) antennary gland
(c) collar cord
(d) probosci’s gland
Answer:
(d) probosci’s gland
Question 149.
Reptiles share which of the following character with birds and mammals? (DPMT 1994)
(a) Amnion
(b) Homeothermy
(c) Diaphragm
(d) Hippie
Answer:
(a) Amnion
Question 150.
Cowper’s gland is present in …………. (DPMT 1996)
(a) Frog
(b) Earthworm
(c) Rabbit
(d) Cockroach
Answer:
(c) Rabbit
Question 151.
Which of the following pairs belong to the category of cold-blooded animals? (DPMT 1998)
(a) bat & rat
(b) snakes & birds
(c) frog & snakes
(d) birds & monkey
Answer:
(c) frog & snakes
Question 152.
The character of birds without exception is …………. (UP-CPMT 1995)
(a) omnivorous
(b) beak without teeth
(c) flying wings
(d) lay eggs with calcareous shells
Answer:
(b) beak without teeth
![]()
Question 153.
Quill feathers (a) the base of quill wings are called …………. (UP-CPMT 1995)
(a) remiges
(b) coverts
(c) barbules
(d) down feathers
Answer:
(a) remiges
Question 154.
Which of the following pair of organisms is uricotelic? (UP-CPMT 2000)
(a) cartilaginous fishes and mammals
(b) reptiles and mammals
(c) birds and insects
(d) bony fishes and lizards
Answer:
(c) birds and insects
Question 155.
In the urinogenital organs of rabbit which one of the following parts is present in males but not in females? (UP-CPMT 2005)
(a) Urethra
(b) Fallopian tube
(c) Vagina
(d) Vas deferens
Answer:
(d) Vas deferens
Question 156.
Which one of the following features is present in some stage of the life history of all chordates? (UP-CPMT 2000)
(a) Blood flowing forward in dorsal blood vessel
(b) Pharyngeal gill slits
(c) A ventral hollow nerve cord
(d) Heart lying dorsally
Answer:
(b) Pharyngeal gill slits
Question 157.
Thoracic cage in rabbit is made up of …………. (UP-CPMT 2006)
(a) Ribs, vertebral column & diaphragm
(b) Ribs, diaphragm & sternum
(c) Vertebral column, diaphragm & sternum
(d) Ribs, vertebral column & sternum
Answer:
(d) Ribs, vertebral column & sternum
Question 158.
Which of the following has an exoskeleton of scales and paired copulatory organ or penis? (UP-CPMT 2007)
(a) Sharks
(b) Lizards
(c) Urodela
(d) Urochordata
Answer:
(b) Lizards
Question 159.
The laterally compressed tail is found in ………….
(a) Freshwater snakes
(b) Terrestrial snakes
(c) Marine non-poisonous snakes
(d) Marine poisonous snakes
Answer:
(d) Marine poisonous snakes
Question 160.
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of fishes?
(a) Tail and venous heart
(b) Epidermal scales and tail
(c) Venous heart and gills
(d) Epidermal scales and gills
Answer:
(c) Venous heart and gills
Question 161.
The similarity between fish and tadpole is ………….
(a) Scales
(b) Legs
(c) Lateral line
(d) Fins
Answer:
(c) Lateral line
![]()
Question 162.
The four-chambered heart is present in ………….
(a) frog
(b) crocodile
(c) shark
(d) lizard
Answer:
(b) crocodile
Question 163.
The right aortic arch is present in ………….
(a) reptiles only
(b) mammals only
(c) birds only
(d) both birds and mammals
Answer:
(c) birds only
Question 164.
The kidney of adult reptiles are …………. (AMU 1996)
(a) mesonephric
(b) metanephric
(c) pronephnc
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(b) metanephric
Question 165.
Marine fishes drink seawater to …………. (AMU 2001)
(a) meet their body salt requirements
(b) compensate the loss of water from their body
(c) flush out nitrogenous wastes from their body
(d) achieve all of the above
Answer:
(d) achieve all of the above
Question 166.
In which of the following fishes the males have brood pouch, where eggs laid by the female remain till they hatch? (AMU 2002)
(a) Lungfish
(b) Climbing perch
(c) Salmon
(d) Sea horse
Answer:
(d) Sea horse
Question 167.
Match the names of branches of science listed under column-I with the field study given under column-II choose the choice which gives the correct combination of the alphabets …………. (AMU 2000)
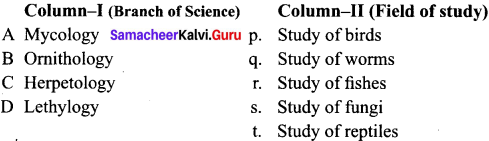
(a) A – s, B – p, C – q, D – r
(b) A – q, B – s , C – r, D – q
(c) A – s, B – q, C – p, D – r
(d) A – p, B – s, C – r, D – q
Answer:
(a) A – s, B – p, C – q, D – r
Question 168.
Identify the edible fresh water teleosts …………. (AMU 2001)
(a) Sharks
(b) Rays and skates
(c) Hilsa ilisha
(d) Catla catla
Answer:
(d) Catla catla
Question 169.
Turtles are …………. (AMU 2002)
(a) Pisces
(b) Reptiles
(c) Molluscans
(d) Arthropods
Answer:
(b) Reptiles
![]()
Question 170.
Harversian systems are found in the bones of …………. (AMU 2002)
(a) Pigeon
(b) Panther
(c) Pipe fish
(d) Python
Answer:
(b) Panther
Question 171.
Choose the correct combination of alphabets which matches the zoological names given under column I with their common names given under column-II

(a) A – F,B – G,C – E,D – H
(b) A – G,B – E,C – H,D – F
(c) A – F,B – E,C – H,D – G
(d) A – F,B – E,C – G,D – H
Answer:
(c) A – F,B – E,C – H,D – G
Question 172.
Which of the following statements is true? (AMU 2003)
(a) All chordates are vertebrates
(b) All vertebrates are chordates
(c) Invertebrates possess a tubular nerve cord
(d) Non-chordates have a vertebral column
Answer:
(b) All vertebrates are chordates
Question 173.
Choose the cat fish from the following. (AMU 2004)
(a) Cirrhina mriga / a
(b) Wa / logo atiti
(c) Lobeo rohita
(d) Catia calla
Answer:
(b) Wallago allu
Question 174.
A four chambered heart is not found in …………. (AMU 2004)
(a) Mammals
(b) Birds
(c) Snake
(d) Crocodile
Answer:
(c) Snake
Question 175.
Calotes versicolor is a …………. (AMU 1997)
(a) House lizard
(b) Rock lizard
(c) Garden lizard
(d) Flying lizard
Answer:
(c) Garden lizard
Question 176.
Scientific name of king cobra is …………. (AMU 2002)
(a) Naja naja
(b) Amphibians
(c) Naja Hannah
(d) Vipera russelli
Answer:
(c) Naja Hannah
![]()
Question 177.
Branch of zoology dealing with the study of amphibians and reptiles is called …………. (AMU 2003)
(a) Ichthyology
(b) Ornithology
(c) Herpetology
(d) Malacology
Answer:
(c) Herpetology
Question 178.
Adaptation of colour vision is found in …………. (AMU 2006)
(a) Mammals
(b) Aves
(c) Reptiles
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 179.
Epidemial scale is the characteristic feature of class reptilian, which of the following class is without epidermal scale? (AMU 2006)
(a) Fish
(b) Aves
(c) Mammals
(d) Amphibians
Answer:
(d) Amphibians
Question 180.
Duck-billed platypus is a connecting link between …………. (AMU 2007)
(a) Reptile and bird
(b) Living and non-living
(c) Reptile and mammal
(d) Echinodermata and chordate
Answer:
(c) Reptile and mammal
Question 181.
Which of the following is a egg laying mammal? (J&K 2005)
(a) Dolphin
(b) Platypus
(c) Whale
(d) Walrus
Answer:
(b) Platypus
Question 182.
In sharks, one of the following is absent …………. (J&K 2008)
(a) Claspers
(b) Placoid scales
(c) Cartilaginous endoskeleton
(d) Air bladder
Answer:
(d) Air bladder
Question 183.
Which one of the following animals belongs to cyclostomata? (J&K2008)
(a) Channa
(b) Loris
(c) Dodo
(d) Pertomyzon
Answer:
(d) Pertomyzon
Question 184.
Which of the following is dominant in desert?
(a) Lizard
(b) Tiger
(c) Leopard
(d) Hyla
Answer:
(a) Lizard
Question 185.
Two examples in which the nitrogenous wastes are excreted from the body in the form of uric acid are ………….
(a) birds and lizards
(b) insects and bony fishes
(c) mammals and molluscs
(d) frogs and cartilaginous fishes
Answer:
(a) birds and lizards
Question 186.
The arrangement of ear ossicles in mammalian ear is ………….
(a) stapes, malleus, incus
(b) malleus, incus, stapes
(c) incus, malleus, stapes
(d) columella, inatleus, incus
Answer:
(b) malleus, incus, stapes
Question 187.
Snake has ………….
(a) movable eyelids
(b) immovable eyelids
(c) no cyclids
(d) eyelids in pouches
Answer:
(b) immovable eyelids
Question 188.
Which among these is correct combination of aquatic mammals? (NEET 2017)
(a) Dolphins, Seals, Trygon
(b) Whales, Dolphin, Seals
(c) Trygon, Whales, Seals
(d) Seals, Dolphin, Sharks
Answer:
(b) Whales, Dolphin, Seals
![]()
Question 189.
In case of poriferance, the spongocoel is lined with flagellated cells called …………. (NEET 2017)
(a) Oscula
(b) Coenocytes
(c) Mesenchymal cells
(d) Ostia
Answer:
(b) Coenocytes
Question 190.
Which is the National Aquatic animal of India? (NEET 2016)
(a) River Dolphin
(b) Blue whale
(c) Sca horse
(d) Gangetic shark
Answer:
(a) River Dolphin
Question 191.
An important characteristic that Hernichordates share with chordates is …………. (NEET2O17)
(a) Ventral tubular nerve chord
(b) Pharynx with gill slits
(c) Pharynx without gill slits
(d) Absence of notochord
Answer:
(a) Ventral tubular nerve chord
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Kingdom Animalia Additional Questions & Answers
Multiple Choice Question And Answer
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Which of the following has loose aggregates of cells without tissues?
(a) cnidarians
(b) flatworms
(c) sponges
(d) echinodenns
Answer:
(c) sponges
Question 2.
Which of the following has open type of circulation?
(a) frogs
(b) garden lizard
(c) man
(d) cockroach
Answer:
(d) cockroach
Question 3.
Which of the following is advantageous for the animals in locomotion, food capture etc.?
(a) asymmetrical
(b) radially symmetrical
(c) biradially symmetrical
(d) bilaterally symmetrical
Answer:
(d) bilaterally symmetrical
Question 4.
Which of the following restricts the free movement of internal organs?
(a) acoelom
(b) pseudocoelom
(c) schizocoelom
(d) enterocoelom
Answer:
(a) acoelom
Question 5.
Radiata include
(a) Diploblastic and bilaterally symmetrical animals
(b) Triploblastic and radially symmetrical animals
(c) Diploblastic and radially symmetrical animals
(d) Triploblastic and bilaterally symmetrical animals
Answer:
(c) Diploblastic and radially symmetrical animals.
Question 6.
The minute pores on the body of sponges are called
(a) oseuliem
(b) ostia
(c) choanocytes
(d) spongocoel
Answer:
(b) ostia
Question 7.
Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Polyp forms are free-living
(b) Medusa forms are sessile
(c) Medusa produces gametes
(d) Polyp reproduces sexually
Answer:
(c) Medusa produces gametes
Question 8.
Which of the following is the adaptation of flatworms for the endoparasitic mode of life?
(a) They are dorsoventrally flattened
(b) They have hooks, suckers or both
(c) Their body is not segmented
(d) They reproduce sexually
Answer:
(b) They have hooks, suckers or both
Question 9.
Sexual dimorphism is seen in –
(a) Sycon
(b) Hydra
(c) Liver flukes
(d) Ascaris
Answer:
(d) Ascaris
Question 10.
Which of the following shows metamerically segmented body?
(a) Aschelminthes
(b) Annelida
(c) Arthropoda
(d) Platyhelminthes
Answer:
(b) Annelida
Question 11.
Which of the following is the characteristic feature of the phylum Arthropoda?
(a) They have segmented legs
(b) They have collablasts for food capture
(c) They are end oparasites of animals
(d) They do not have chitinous exoskeleton
Answer:
(a) They have segmented legs
Question 12.
Which of the following is the rasping organ of molluscs found in the mouth?
(a) radula
(b) pallium
(c) misceral mass
(d) mantle
Answer;
(a) radula
Question 13.
Which of the following is bilaterally symmetrical in larval stages and radially symmetrical in adult?
(a) Molluscs
(b) Echinoderms
(c) Arthropods
(d) Annelids
Answer:
(b) Echinoderms
Question 14.
Which of the following has the anterior proboscis, collar and trunk?
(a) Ascidian
(b) Star fish
(c) Sea cucumber
(d) Balanoglossus
Answer:
(d) Balanoglossus
![]()
Question 15.
Urochordate means
(a) Chordates which have notochord in the head region
(b) Chordates which have notochord in the tail region of larval forms
(c) Chordates which have notochord in the tail region of adults
(d) Chordates which have no notochord
Answer:
(b) Chordates which have notochord in the tail region of larval forms.
Question 16.
Which of the following loses all the chordate characters in the adult stage?
(a) Cephalochordates
(b) Hemichordates
(c) Tunicates
(d) Chordates
Answer:
(c) Tunicates
Question 17.
Which of the following has cartilaginous endoskeleton with notochord?
(a) Exocoetus
(b) Labeo
(c) Hyla
(d) Scolidon
Answer:
(d) Scolidon
Question 18.
Which is the class of animals adapted for dual mode of life?
(a) Pisces
(b) Amphibia
(c) Reptilia
(d) Mammalia
Answer:
(b) Amphibia
Question 19.
Which of the following is the flight adaptation of birds?
(a) Pneumatic bones and strong flight muscles
(b) Homeothermic condition
(c) Migration to distant places
(d) Presence of homy covering on the beak
Answer:
(a) Pneumatic bones and strong flight muscles
Question 20.
Which of the following are truly terrestrial animals?
(a) Lung fishes
(b) Amphibians
(c) Mammals
(d) Reptiles
Answer:
(d) Reptiles
II Give Reasons
Question 1.
Closed type of circulation is advanced.
Answer:
Closed type of circulation is found in higher organisms like prochordates and vertebrates. The invertebrates have open type of circulation except annelids. The closed type of circulation is advanced because blood flows in blood vessels. There is a clear separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Question 2.
Pseudocoelomates are more advanced than acoelomates.
Answer:
Acoelomates do not have body cavity. Their body is solid and hence the movement of internal organs is restricted. Pseudocoelomates have pseudocoelomic fluid in the pseudocoelom. It acts as a hydrostatic skeleton and allows free movement of visceral organs and circulation of nutrients.
Question 3.
Sponges are primitive animals.
Answer:
Sponges have cellular grade of organisation. Tissues are not formed. The cells are loosely arranged. The division of labour is found among the group of cells.
Question 4.
Bioluminescence is advantageous to ctenophores.
Answer:
Ctenophores are exclusively marine. They emit light. It helps the animals in finding food, mate and escape from the predators.
![]()
Question 5.
Tapeworm and liver fluke are not destroyed by the digestive juices secreted by human beings.
Answer:
The body of helminth parasites is covered by a thick covering called tegument. This protects the worms. They have hooks, suckers or both for attachment.
Question 6.
All vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates.
Answer:
All Vertebrates have notochord during embryonic development. Later it is replaced by the vertebral column. But in lower chordates like prochordates, vertebral column is not present. They have only notochord in the adult or larval stage. Hence it is said that all vertebrates are chordates but all chordates do not have vertebrate characters
Answer the following
Questions 1.
What are pinococytes?
Answer:
In sponges, the outer surface is formed of plate-like cells that maintain the size and structure of the sponges are called pinococytes.
Question 2.
Distinguish between invertebrates and vertebrates.
Answer:
Invertebrates:
- The major group of animals which do not have notochord or vertebral column are Invertebrates.
- These are lower animals.
Vertebrates:
- The major group of animals which have vertebral column are vertebrates
- These are higher animals.
Question 3.
What are choanocytes?
Answer:
The inner layer of sponges have a special type of cells called choanocytes. These flagellated collar cells create and maintain water flow through the sponge. It helps in respiration and digestion.
Question 4.
Distinguish between open type of circulation and closed type of circulation.
Answer:
Open Type of circulation:
- The circulation in which blood remains filled in tissue spaces is known as open type of circulation.
- This is seen in lower organisms, e.g. arthropods, molluscs echinoderms and urochordates.
Closed type of circulation:
- The circulation in which blood flows inside the blood vessels is known as closed type of circulation.
- This is seen in higher organisms, e.g. Annelids, cephalochordates and vertebrates.
Question 5.
Distinguish between Diploblastic animals and triploblastic animals.
Answer:
Diploblastic animals:
- The animals in which the cells are arranged in two embryonic layers, the ectoderm and endoderm are called diploblastic animals.
- These are lower organisms, e.g. Cnidaria and ctenophora
Triploblastic animals:
- The animals in which the cells are arranged in three embryonic layers, the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm are called triploblastic animals.
- These are higher organisms, e.g. Platyhelminthes to Mammalia.
Question 6.
What are asymmetrical animals?
Answer:
The animals which lack a definite body plan and any plane passing through the center of the body does not divide them into two equal halves are known as asymmetrical animals, e.g. Sponges.
Question 7.
What is segmentation?
Answer:
In some animals, the body is externally and internally divided into a series of repeated units called segments with a serial repetition of some organs. (Eg.) Annelida.
![]()
Question 8.
What is bilateral symmetry?
Answer:
The symmetry in which the animals have two similar halves on either side of the central place is bilateral symmetry, e.g. Flatworms and annelids.
Question 9.
What is biradial symmetry?
Answer:
The symmetry in which the animals have two planes of symmetry, longitudinal and sagittal axis and longitudinal and transverse axis is biradial symmetry, e.g. Ctenophores.
Question 10.
What is a water vascular or ambulacral system? What is its function?
Answer:
Tube feet or podia are present in Echinodermata. Through this structure, the water enters and comes out. This system is known as the water vascular system or ambulacral system.
Uses Locomotion capture and transport of food and respiration.
Question 11.
What are acoelomates?
Answer:
The animals which do not possess a body cavity are called acoelomates. The body is solid without perivisceral cavity. These have restricted free movement of internal organs, e.g. Flatworms.
Question 12.
What are pseudocoelomates?
Answer:
The animals which have the body cavity that is not fully lined by the mesodermal epithelium are called pseudocoelomates. The pseudocoel is filled with pseudocoelomic fluid. It acts as a hydrostatic skeleton and allows free movement of visceral organs and circulation of nutrients e.g. Roundworms.
Question 13.
What are eucoelomates?
Answer:
Eucoelomates are the animals which have true coelom that develops with the mesoderm and is lined by mesodermal epithelium called peritoneum.
Question 14.
Distinguish between schizocoelomates and enterocoelomates
Answer:
Schizocoelomates:
In schizocoelometes, the body cavity is formed by splitting of mesoderm, e.g. Annelids, arthropods and molluscs.
Enterocoelomates:
In enterocoelomates, the body cavity is formed from the mesodermal pouches of archenteron. e.g. Echinoderms, hemichordates and chordates.
Question 15.
Distinguish between parazoa and eunietazoa.
Answer:
Parazoa:
These include multicellular animals whose cells are loosely arranged without the formation of tissues or organs, e.g. Sponges
Eumetazoa:
These include multicellular animals with well defined tissues, organs and organ systems.
Question 16.
Distinguish between radiata and bilateria.
Answer:
Radiata:
- These include radially symmetrical animals.
- There are diploblastic e.g., Cnidarians and ctenophores
Bilateria:
- These include bilaterally symmetrical animals.
- There are triploblastic. e.g. Flatworms
Question 17.
Distinguish between protostomes and deuterostomes.
Answer:
Protostomia:
- These include the eumetazoans in which embryonic blastopores develops into mouth.
- Acoelomata, pseudocoelomata and schizocoelomata are the three subdivisions of this division.
Deuterostomia:
- These include the cutnetazoans in which embryonic blastopore develops into anus.
- Enterocoelmata is the only one subdivision of this division.
Question 18.
What is canal system?
Answer:
The water transport system in sponges through which water enters through minute opores and goes out through the large opening called osculum. It helps in nutrition, circulation, respiration and excretion.
Question 19.
Distinguish between ostia and osculum.
Answer:
Ostia:
- The minute pores lining the body wall of sponges are called ostia.
- Water enters through ostia.
Osculum:
- The large opening in sponges is called osculum.
- Water goes out through osculum.
Question 20.
What spongocoel?
Answer:
The central cavity of the sponges is called spongocoel.
Question 21.
What are choanocytes?
Answer:
Choanocytes are the collar cells lining the spongocoel and the canals of sponges. These are helpful in creating water current in sponges.
![]()
Question 22.
Distinguish between asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
Answer:
Asexual Reproduction:
- The reproduction without involvement of gametes is called Asexual Reproduction.
- Zygote is not formed.
Sexual Reproduction:
- The reproduction with the involvement of gametes is called sexual reproduction.
- Zygote is formed by the process called fertilization.
Question 23.
Name the larvae of sponges.
Answer:
Parenchymula and amphiblastula.
Question 24.
What is indirect development?
Answer:
The development with different types of larval stages is called indirect development.
Question 25.
What is holozoic nutrition?
Answer:
The nutrition in which solid food materials are taken in by animals is called holozoic nutrition.
Question 26.
What are cnidocytes or cnidoblasts or nematocysts?
Answer:
The stinging cells found on the tentacles of cnidarians are called cnidocytes or cnidoblasts or nematocysts. They are useful for anchorage, defense and capturing prey.
Question 27.
What is coelenteron?
Answer:
The central visceral cavity of cnidarians is called coelenteron.
Question 28.
Distinguish between polyp and medusa.
Answer:
Polyp:
- The sessile body form of cnidarians is called a polyp.
- It is the asexual generation.
Medusa:
- The free-living body form of cnidarians is called medusa.
- It is the asexual generation.
Question 29.
What is metagenesis or Alternation of generation?
Answer:
The cnidarians exhibit sexual and asexual forms that alternate with each other. This is called metagenesis or Alternation of generation.
Question n 30.
Name the larva of cnidarians?
Answer:
Planula larva.
Question 31.
What are lasso cells or colloblasts?
Answer:
The special cells of ctenophores which helps in food capture are lasso cells or colloblasts.
Question 32.
Name the larva of ctenophores?
Answer:
Cydippid larva.
Question 33.
What are solanocytes?
Answer:
The specialized excretory cells of flatworms, flame cells are called solanocytes.
Question 34.
What are the larvae of flatworms?
Answer:
Miracidium, Sporocyst, redia, cercaria and metacercaria.
Question 35.
What is regeneration?
Answer:
The ability to regrow the lost parts is called regeneration, e.g. Planaria.
Question 36.
What is metamerism? –
Answer:
The body of annelids are divided into segments. This phenomenon is known as metamerism.
Question 37.
Name the respiratory pigments of annelids?
Answer:
Haemoglobin and chlorocruorin.
Question 38.
Name the larva of annelids.
Answer:
Trochophore larva.
Question 39.
What is moulting or ecdysis?
Answer:
The chitinous exoskeleton of arthropods is shed periodically. This process is known as moulting or ecdysis.
![]()
Question 40.
What are the respiratory organs of arthropods?
Answer:
Gills, Book gills, Book lungs, and trachea.
Question 41.
Name the sensory organs of arthropods?
Answer:
Antennae, Simple and compound eyes, and statocysts.
Question 42.
What are ctenidia?
Answer:
The feather-like gills of molluscs are called ctenidia.
Question 43.
What is radula?
Answer:
The rasping organ found in the mouth of molluscs is called radula.
Question 44.
What is the function of ospharidium?
Answer:
Ospharidium is helpful to test the purity of water.
Question 45.
Name the respiratory pigment of molluscs.
Answer:
Haemocyanin, a copper-containing pigment.
Question 46.
Name the larva of molluscs?
Answer:
Veliger larva.
Question 47.
What is a water vascular system?
Answer:
The system which helps in nutrition and respiration in echinoderms is called the water vascular system. Water enters into the body through special organs.
Question 48.
Name the larva of hemichordates?
Answer:
Tornaria larva.
Question 49.
What are urochordates?
Answer:
The chordates which have notochord only in the tail region of the larval stage are called urochordates e.g. Ascidian.
![]()
Question 50.
Distinguish between Agnatha and Gnathostomata.
Answer:
Agnatha:
- These include jawless fish-like aquatic vertebrates.
- They do not have paired appendages.
Gnathostomata:
- These include jawed vertebrates.
- They have paired appendages.
Question 51.
What are poikilothermic?
Answer:
The animals which change their body temperature according to the environment are called poikilothermic.
Question 52.
What is anadromous migration?
Answer:
The migration of marine fishes to freshwater body like rivers for spawning is known as anadromous migration.
Question 53.
Distinguish between oviparous and viviparous animals.
Answer:
Oviparous animals:
- The egg-laying animals are known as oviparous animals.
- They lay eggs containing yolk for embryonic development e.g. birds.
Viviparous animals:
- The animals which give birth to young ones are called viviparous animals.
- The developing embryo derives nutrients from the parent, e.g. man
Question 54.
What are Ammonotelic animals?
Answer:
The animals which excrete ammonia dissolved in water are called ammonotelic animals. More water is spent, e.g. fishes.
Question 55.
What are ureotelic animals?
Answer:
The animals which excrete urea along with water are called ureotelic animals. Less water is spent e.g. man.
Question 56.
What are urecotelic animals?
Answer:
The animals which excrete uric acid in the form of pellets are called urecotelic animals. Very less water is spent e.g. birds.
Question 57.
What are the characteristic features of the phylum Ctenophora?
Answer:
- They are exclusively marine.
- They are radially symmetrical and diploblastic animals.
- In mesogica arnoebocytes and smooth muscles are present.
- Bioluminescence is well marked in ctenophores.
- They have collohiasts which help in food capture.
- They reproduce only by sexual means.
Question 58.
Distinguish between cleidoic eggs and non-cleidoic eggs.
Answer:
Cleidoic eggs:
- The eggs which have a thick and hard outermost shell are cleidoic eggs.
- This is a terrestrial adaptation, e.g., Reptiles and birds.
Non Cleidoic eggs:
- The eggs Which do not have a protective shell are non – Cleidoic eggs
- This is seen in aquatic animals, e.g., fish, amphibians.
Question 59.
What is rhamphotheca?
Answer:
The homy covering on the beak of birds is called rhamphotheca.
Question 60.
Name some flightless birds.
Answer:
Ostrich, kiwi, and penguin.
Question 61.
Distinguish between poikilothermic and homeothermic.
Answer:
Poikilothermic:
- The animals which change their body temperature according to the environment are called poikilothermic animals.
- These cold-blooded animals, e.g., fishes, amphibians and reptiles.
Homeothermic:
- The animals which maintain constant body temperature irrespective of environmental changes are called homeothermic animals.
- These are warm-blooded animals, e.g., birds and mammals.
Question 62.
What is symmetry? Describe its type with examples.
Answer:
Symmetry is the body arrangement in which parts that lie on the opposite side of an axis are identical
- A Symmetrical: If any plane passing through the centre of the body does not divide them into two equal halves. (Eg.) Sponges.
- Radial Symmetry: When any plane passing through the central axis of the body divides an organism into two identical parts it is called radial symmetry. (Eg.) Sea anemone
- Bilateral Symmetry: Animals which have two similar halves on either side of the central plane show bilateral symmetry. (Eg.) Man
- Biradial Symmetry: It is a combination of radial and bilateral symmetry. (Eg.) Comb jellyfish
Question 63.
Explain symmetry in animals.
Answer:
Symmetry is the body arrangement in which parts lie on opposite side of the axis are identical. If the animals lack a definite body plane or irregular shaped and any plane passing through the center of the body does not divide them into two equal halves, these are known as asymmetrical, e.g., sponges, adult gastropods.
When any plane passing through the central axis of the body divides an organism into two equal parts, it is known as radial symmetry. They have a top and bottom side, e.g., cnidarians. Echinoderms have five planes of symmetry and show pentamerous radial symmetry. Animals which have two pairs of symmetrical sides are biradially symmetrical. Animal which have two similar halves on either side of the control plane show bilateral symmetry.
![]()
Question 64.
List the characteristics features of the phylum Arthropoda?
Answer:
- They are bilaterally symmetrical triploblastic animals.
- They have jointed appendages which are used for locomotion.
- The body is covered by a chitinous exoskeleton.
- There is moulting during its life cycle.
- The body cavity is filled with haemocoel.
- Their respiratory organs are gills book gills trachea.
- They have an open type of circulatory system.
- Eyes are compound and simple.
- Excretion takes place through malpighian tubules green glands coxal glands.
- They are dioecious and life history includes metamorphosis.
Question 65.
Classify the animal kingdom.
Answer:
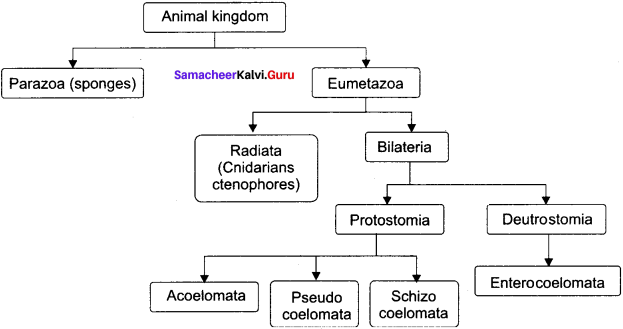
Question 66.
Write the general characters of the phylum porifera.
Answer:
- They are aquatic, asymmetrical.
- They have pores all over the body.
- They are multicellular with cellular level of organisation. Tissues are not formed.
- They have canal system for circulation of water.
- They have skeleton made of calcareous or siliceous spicules.
- Nutrition is holozoic and digestion intracellular.
- Asexual reproduction by fragmentation and gemmule formation.
- Indirect development with parenchymula and amphiblastula larvae, e.g., Sycon and Spongilla.
Question 67.
What are the general characters of class aves?
Answer:
- The forelimbs are modified into wings. (Eg.) Ostrich, Kiwi penguin
- The hind limbs are adapted for walking, running, swimming and perching.
- Tail has a preen gland at its base.
- The long bones are hollow with air cavities.
- They have pectoralis major and minor muscles for flying.
- Respiration is by spongy lungs that are continuous with air sacs.
- The heart is four-chambered.
- In males the testes are paired bu t in females only one ovary is present.
- All birds are oviparous. Eggs are megalecithal.
- Migration and parental care are well marked.
Question 68.
Write the general characters of the phylum ctenophora.
Answer:
- The animals are marine, diploblastic and radially symmetrical.
- They have eight external rows of ciliated comb plates which help in locomotion.
- Bioluminescence is seen.
- They lack nematocysts but have lasso cells which help in food capture.
- Digestion is by both extracellular and intracellular.
- Sexual reproduction is seen.
- Fertilization is external and development is indirect.
- Cydippid larva is seen, e.g., Pleurobrachia.
Question 69.
Write the general characters of flatworms.
Answer:
- The flatworms are flat, bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic animals.
- These are acoelomates with organ system level of organisation.
- They are endoparasites. They have hooks or suckers or both.
- They show pseudosegmentation.
- Flame cells or solanocytes are excretory cells.
- Sexes are not separate.
- Fertilization is internal. Development is indirect with many larval stages like miracidium sporocyst, redia, cercaria and metacercaria. e.g., Taenia and liver fluke.
Question 70.
Write the general characters of the phylum aschelminthes.
Answer:
- The body of these worms is circular.
- They are free-living or parasites.
- They are triploblastic, pseudocoelomates with organ system level of organisation.
- Body is covered by a cuticle.
- Digestive system is complete with the mouth, pharynx, and anus.
- Excretory system consists of rennet glands.
- Sexes are separate. Sexual dimorphism is seen.
- Fertilization is internal.
- Development may be direct or indirect, e.g., Ascaris.
Question 71.
Write the general characters of the phylum Annelida.
Answer:
- They are aquatic or terrestrials, free-living or parasitic.
- They are triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical, schizocoelomates with organ system level of organisation.
- The body is metamerically segmented.
- Longitudinal and circular muscles help in locomotion.
- A closed type of circulation is seen.
- Respiratory pigments are present.
- Sexual reproduction is seen. Development is direct or indirect with a trochophore larva e.g., the earthworm.
Question 72.
Write the general characters of the phylum Arthropoda.
Answer:
- These are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, schizocoelomate, segmented animals.
- They have an organ system grade of organisation.
- They have jointed appendages.
- Body is covered by a chitinous exoskeleton. The body is divided into the head, thorax, and abdomen.
- Body cavity is filled with colourless blood. It is called haemocoel.
- Respiratory organs are gills, book gills, book lungs, trachea.
- Open type circulation is seen.
- Sense organs are present.
- Fertilization is internal, e.g., Limulus and insects.
Question 73.
Write the general characters of the phylum Mollusca.
Answer:
- Molluscs are terrestrial or aquatic with an organ system level of organisation.
- They are triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical, coelomate animals.
- Body is divided into head, foot, and visceral hump.
- The digestive system is complete.
- Nephridia are the excretory organs.
- Open type of circulatory system is seen.
- Blood contains a copper-containing respiratory pigment called hemocyanin.
- They are oviparous.
- Development is indirect with a veliger larva, e.g., Pila and Octopus.
Question 74.
Write the general characters of the phylum Echinodermata.
Answer:
- The adults are radially symmetrical but the larvae are bilaterally symmetrical.
- They have a mesodermal endoskeleton of calcareous ossicles called spines.
- A water vascular system is present.
- Tube feet are the organs of locomotion, respiration, and capture of food.
- The digestive system is complete with a mouth on the ventral side and anus on the dorsal side.
- Excretory organs are absent.
- An open type of circulatory system is present.
- Reproduction is by a sexual method.
- Fertilization is external.
- Indirect development with bilaterally symmetrical larval forms, e.g., starfish.
Question 75.
Write the general characters of hemichordata.
Answer:
- The Hemichordates have both invertebrate and vertebrate characters.
- They are worm-like, tuberculous animals.
- They are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic coelomate animals with organ system level of organisation.
- The body is divided into proboscis, collar, and trunk.
- They are ciliary feeders.
- The circulatory system is simple and open.
- Excretion is by a single probosci’s gland or glomerulus situated in the proboscis.
- Sexes are separate.
- Fertilization is external.
- Development is indirect with tomaria larva, e.g., Balanoglossus.
Question 76.
Write the general characters of urochordates or tunicates.
Answer:
- They are marine, sessile, pelagic or free-swimming.
- Body is unsegmented and covered by a test or tunic.
- Ault forms are sac-like.
- Coelom is absent.
- Notochord is present only in the tail region of the larval stage.
- Heart is ventral and tubular.
- Nerve cord is present only in the larval stage.
- They are hermaphrodites and development is indirect with a free-swimming tadpole larva.
- Retrogressive metamorphosis is seen e.g. Ascidia.
Question 77.
Write the general characters of cephalochordates.
Answer:
- They are marine found in shallow waters.
- They lead a burrowing mode of life.
- They are fish-like with a notochord, nerve cord, and pharyngeal gill slits throughout their life.
- A closed type of circulatory system is seen without a heart.
- Excretion is by protonephridia.
- Sexes are separate.
- Fertilization is external.
- Development is indirect with a larva e.g. Amphioxus.
Question 78.
Write the general character of the subphylum Vertebrata.
Answer:
- The vertebrates have a notochord during the embryonic stage. In adults, it is replaced by the vertebral column.
- They have paired appendages.
- The skin is covered by protective skeleton-like scales, feathers, hairs, claws, nails, etc.
- Respiration is by gills, skin, buccopharyngeal cavity, and lungs.
- They have a ventral heart with two or three or four chambers.
Question 79.
Classify the subphylum Vertebrata.
Answer:
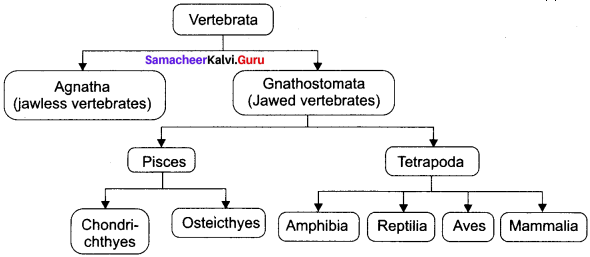
Question 80.
Write the general characters of the class Cyclostomata.
Answer:
- They are primitive, poikilothermic, jawless aquatic vertebrates.
- Body is slender and eel-like with six to fifteen pairs of gill slips.
- The mouth is circular without jaws and suctorial.
- Heart is two-chambered. Closed types of circulation are seen.
- No paired appendages.
- Cranium and vertebral column are cartilaginous, e.g. Petromyzon.
Question 81.
Write the general characters of the class Chondrichthyes.
Answer:
- They are cartilaginous marine fishes. .
- The notochord is persistent throughout life.
- The skin is covered by dermal placoid. scales.
- Caudal fin is heterocercal.
- Jaws are powerful.
- Respiration is by lamelliform gills without operculum.
- Mesonephric kidneys are present.
- They have two-chambered hearts.
- They are ureotelic.
- They are poikilothermic and viviparous.
- Sexes are separate and fertilization is internal, e.g., Scoliodon.
Question 82.
Write the general characters of the class Osteichthyes.
Answer:
- They are marine or freshwater fishes.
- They have a bony endoskeleton.
- The body is spindle-shaped.
- The skin is covered by ganoid, cycloid or ctenoid scales.
- Respiration is by four pairs of gills covered by an operculum.
- The air bladder is present which helps in gaseous exchange (lungfishes) for maintaining buoyancy.
- They have two-chambered hearts.
- They have mesonephric kidneys and ammonotelic.
- The lateral line sense organ is present.
- External fertilization is seen and most forms are oviparous e.g. Labeo and Catla.
Question 83.
Write the general characters of the class Amphibia.
Answer:
Amphibians are adapted to live both in water and on land.
- They are poikilothermic.
- The body is divisible into the head and trunk.
- They have two pairs of limbs.
- The skin is smooth or rough, moist, pigmented, and glandular.
- Eyes have eyelids.
- Respiration is by gills, lungs, and through the skin.
- The heart is three-chambered.
- Kidneys are mesonephric and ureotelic.
- Sexes are separate and fertilization is external.
- They are oviparous and development is indirect, e.g. Bufo and Rana.
Question 84.
Write the general characters of the class Reptilia.
Answer:
- They are mostly terrestrial.
- The body is covered by dry and cornified skin with scales.
- They have a three-chambered heart.
- They are poikilothermic.
- They are oviparous and they lay cleidoic eggs.
- They have metanephric kidneys and are uricotelic.
- Fertilization is internal, e.g. Chelone and Chameleon.
Question 85.
Write the general characters of the class Aves.
Answer:
- They have feathers on the body.
- The forelimbs are modified into wings.
- The hind limbs are adapted for walking, running, swimming, and perching.
- The skin has an oil gland.
- The exoskeleton consists of feathers, scales, claws on legs.
- The bones are pneumatic.
- Respiration is by lungs with air sacs.
- The heart is four-chambered with a right systemic arch.
- They are homeothermic.
- Migration and parental care are seen.
- The urinary bladder is absent.
- Females have only left ovaries.
- They are oviparous. The eggs are cleidoic.
Question 86.
Write the general characters of the class Mammalia.
Answer:
- The body is covered by hair.
- They have mammary glands.
- They have two pairs of limbs adapted for walking, running, climbing, burrowing, swimming, and flying.
- The skin has sweat glands, scent glands, and sebaceous glands.
- Exoskeleton includes homy epidermal horns, spines, claws, nails, hooves, and bony dermal plates.
- They have the thecodont, heterodont and diphyodont teeth.
- External ears or pinnae are present.
- The heart is four-chambered with a left systemic arch.
- RBCs are non-nucleated.
- They have metanephric kidneys and they are ureotelic.
- They are homeothermic.
- Sexes are separate and fertilization is internal e.g. Platypus, kangaroo, elephants and man.