You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science History Solutions Chapter 1 Outbreak of World War I and Its Aftermath
Outbreak of World War I and Its Aftermath Textual Exercise
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
What were the three major empires shattered by the end of First World War?
(a) Germany, Austria Hungary, and the Ottomans
(b) Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Russia
(c) Spain, Portugal and Italy
(d) Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy
Answer:
(a) Germany, Austria Hungary, and the Ottomans
Question 2.
Where did the Ethiopian army defeat the Italian army?
(a) Delville
(b) Orange State
(c) Adowa
(d) Algiers
Answer:
(c) Adowa
Question 3.
Which country emerged as the strongest in East Asia towards the close of nineteenth century?
(a) China
(b) Japan
(c) Korea
(d) Mongolia
Answer:
(b) Japan
![]()
Question 4.
Who said “imperialism is the highest stage of capitalism”?
(a) Lenin
(b) Marx
(c) Sun Yat-sen
(d) Mao Tsetung
Answer:
(a) Lenin
Question 5.
What is the Battle of Marne remembered for?
(a) air warfare
(b) trench warfare
(c) submarine warfare
(d) ship warfare
Answer:
(b) trench warfare
Question 6.
Which country after World War I took to a policy of isolation?
(a) Britain
(b) France
(c) Germany
(d) USA
Answer:
(d) USA
![]()
Question 7.
To which country did the first Secretary-General of League of Nations belong?
(a) Britain
(b) France
(c) Dutch
(d) USA
Answer:
(a) Britain
Question 8.
Which country was expelled from the League of Nations for attacking Finland?
(a) Germany
(b) Russia
(c) Italy
(d) France
Answer:
(b) Russia
II. Fill in the blanks
1. Japan forced a war on China in the year …….
2. The new state of Albania was created according to the Treaty of ……. signed in May 1913.
3. Japan entered into an alliance with England in the year ……….
4. In the Balkans ……… had mixed population.
5. In the battle of Tannenberg …….. suffered heavy losses.
6. ……… as Prime Minister represented France in Paris Peace Conference.
7. ……… became Prime Minister leading a new coalition of liberals and moderate Socialists before Lenin established the Bolshevik government.
8. Locarno Treaty was signed in the year ……….
Answers:
1. 1894
2. London
3. 1902
4. Macedonia
5. Russia
6. Clemenceau
7. Kerensky
8. 1925
III. Choose the correct statement
Question 1.
(i) Italy remained a neutral country when the World War broke out.
(ii) Italy was much disappointed over the peace settlement at Versailles.
(iii) The Treaty of Sevres was signed with Italy.
(iv) Italy was denied even small places such as Trieste, Istria and the south Tyrol.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (iii) is correct
(c) (iv) is correct
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv) are correct
Answer:
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
Question 2.
(i) The Turkish Empire contained many non-Turkish people in the Balkans
(ii) Turkey fought on the side of the central powers
(iii) Britain attacked Turkey and captured Constantinople
(iv) Turkey’s attempt to attack Suez Canal but were repulsed.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (i) and (iii) are correct
(c) (iv) is correct
(d) (i), (ii) and (iv) are correct.
Answer:
(d) (i), (ii) and (iv) are correct.
![]()
Question 3.
Assertion: Germany and the United States were producing cheaper manufactured goods and capturing England’s markets.
Reason: Both the countries produced required raw material for their industries.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is right but R is not the correct reason
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) R is right but it has no relevance to A.
Answer:
(c) Both A and R are wrong
Question 4.
Assertion: The first European attempts to carve out colonies in Africa resulted in bloody battles.
Reason: There was stiff resistance from the native population.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is right but R is not the correct reason
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) R is right but it has no relevance to A.
Answer:
(b) A is right but R is not the correct reason
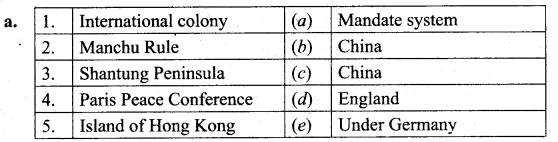
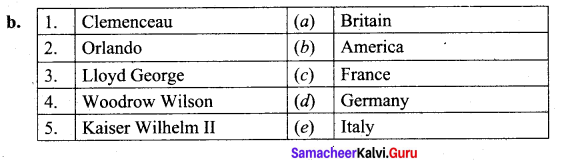
IV. Match the following.

Answers
1. (c)
2. (d)
3. (b)
4. (e)
5. (a)
V. Answer briefly.
Question 1.
How do you assess the importance of the Sino-Japanese War?
Answer:
The Sino-Japanese War proved that Japan was the strongest nation of the East Asia.
Question 2.
Name the countries in the Triple Entente.
Answer:
The countries of Triple-Entente were Britain, France and Russia.
Question 3.
What were the three militant forms of nationalism in Europe?
Answer:
England’s jingoism, France’s chauvinism and Germany’s Kultur were militant forms of nationalism in Europe.
Question 4.
What do you know of trench warfare?
Answer:
Trenches or ditches dug by troops enabled soldiers to safely stand and protect themselves from enemy fire. During the first world war the battle of Mame (between French and Germans) is a memorable one for trench warfare.
Question 5.
What was the role of Mustafa Kemal Pasha?
Answer:
It was Mustafa Kemal Pasha whose efforts caused Turkey’s rebirth as a nation. Not only did Kemal Pasha win freedom for the country but he modernised it and changed it out of all recognition. He put an end to the Sultanate and the Caliphate.
Question 6.
Highlight the global influence of Russian Revolution?
Answer:
In many countries, communist government were formed. Debates over issues like land reforms, social welfare, workers rights and gender equality started taking place in the global context.
Question 7.
List out any two causes for the failure of the League of Nations.
Answer:
Here are the two causes for the failure of the League of Nations:
a. The League appeared to be an organisation of those who were victorious in the First World War. Though it had a world-wide membership. It became very much the centre of European diplomacy.
b. The unanimity of members was required for all its decisions on political issues. Since it lacked the military power of its own, it could not enforce its decisions
![]()
VI. Answer all the questions given under each caption.
Question 1.
Imperialism
(а) What do you know of monopoly capitalism?
Answer:
Monopoly capitalism is a capitalist system typified by tread monopolies in the hands of a few people. After 1870, the capitalism of free competition (based on the principle of free trade without any control or regulation by the state) became the capitalism of monopolies.
(b) How did Japan emerge as an imperial power?
Answer:
Japan took to Western education and machinery with a modem army and navy had emerged as an advanced industrialised power. It also followed the imperialistic aggression policy of the European powers faithfully. It surprised the world by giving a crashing defeat to China in the Sino-Japanese War during the period of 1894-95. Japan also defeated Russia in Russo-Japanese War in 1904 and got back Port Arthur from it. In this way it emerged as an imperial power.
(c) Why did the industrial countries need colonies in the nineteenth century?
Answer:
An ever-growing demand for markets and raw materials made the industrial countries hungry for colonies in the nineteenth century.
(d) What were the contrasts capitalism produced?
Answer:
Capitalism produced huge contrasts. Those contrasts were: extreme poverty and extreme wealth, slum and skyscraper, empire-state and dependent exploited colony.
Question 2.
German Emperor
(a) What was the nature of Emperor Kaiser Wilhelm II of Germany?
(b) What was the violent form of Germany called?
(c) Why did Kaiser Wilhelm intervene in the Morocco affair?
(d) What happened to Germany’s colonies in Africa?
Answer:
(a) He was ruthlessly assertive and aggressive. He proclaimed that Germany would be the leader of the world.
(b) The violent form of Germany is called Kultur.
(c) The British agreement with France to occupy Morocco was not consented by Germany.
(d) The colonies of Germany in Africa were attacked by the allies and therefore had to surrender to them.
Question 3.
Balkan Wars
(а) Why was Balkan League formed?
Answer:
Balkan League was formed to attack and defeat Turkish forces in the first Balkan War in 1912-13.
(b) What was the outcome of the first Balkan War?
Answer:
The new state of Albania was created and the other Balkan states divided up Macedonia , between them. Turkey was reduced the area around Constantinople.
(c) Who were defeated in this war?
Answer:
The Turkish forces were defeated in the first Balkan War.
(d) What was the name of the Treaty signed at the end of this second Balkan War?
Answer:
The name of the Treaty signed at the end of the second Balkan War was the Treaty of Bucharest
VII. Answer the following in detail.
Question 1.
Discuss the main causes of the First World War.
Answer:
- European great powers were divided into two armed camps.
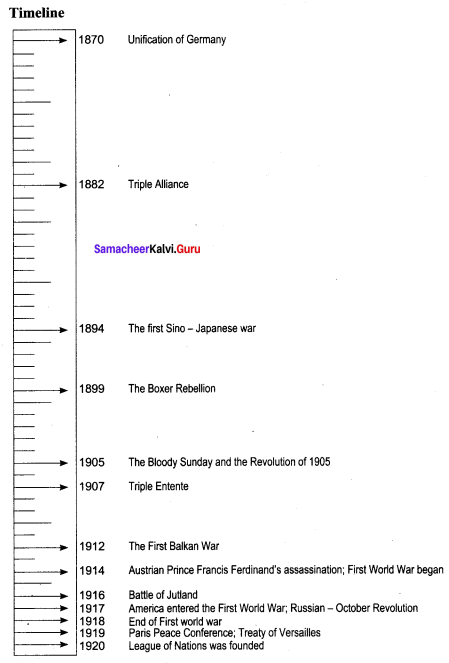
- One camp consisted of central powers namely Germany, Austria-Hungary Bulgaria and Turkey which was called Triple Alliance formed in 1882.
- Another camp consisted of Ally powers namely Britain, France, and . Russia which was called Entente cordiale formed in 1904.
- The aggressive nature of German Emperor Kaiser Wilhelm II who proclaimed that Germany would be the leader of the world.
- The emergence of militant forms of nationalism like England’s Jingoism, France’s Chauvinism and Germany’s Kulthur contributed to the outbreak of the war.
- Kaiser Wilhelm II of Germany wanted declare Morocco an International ‘ colony instead of France occupying it with the support of Britain. Thus France was hostile under German.
- Balkan countries like Greece, Serbia, Bulgaria and Montenegro was succeeding each other in occupying Balkan regions from Turks. So, to control them Balkan League was formed.
- The Balkan League defeated the Turks in the first Balkan war in 1912.
- When dispute arose in sharing the spoils of the war with Bulgaria, the second Balkan war broke out in 1913 against it and Bulgaria was defeated. Turks and Bulgaria approached Germany for help.
- Austrian crown prince Ferdinand was killed by Princip a Serbian lad of Bosnia.
- Austria could get support from Germany while Serbia from Russia.
- Germany therefore declared war on Russia on 1 August 1914.
- The Franco – Russian Alliance forced Germany to wage war against France when Britain also Supported them.
- Thus, the first world war broke out between central powers and Allies in 1914.
Question 2.
Highlight the provisions of the Treaty of Versailles relating to Germany.
Answer:
- Germany was found guilty of starting the War and therefore was to pay reparations for the losses suffered. The Reparation Commission set up for deciding the compensation decided on 6,600 million pounds to be paid in installments. All Central Powers were directed to pay war indemnity.
- The German army was to be limited to 100,000 men. A small navy was allowed, but there were to be no submarines and no air force.
- The union of Austria and Germany was forbidden and Germany was to acknowledge and respect the Independence of Austria.
- Germany was forced to give up all the rights and titles over her overseas possessions to the allies. All German colonies became mandated territories under the League of Nations.
- Germany was forced to revoke the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (with Russia) and Bucharest (Bulgaria).
Question 3.
Explain the course of the Russian Revolution under the leadership of Lenin.
Answer:
- Lenin gained the support of a small majority known as Bolsheviks which became the Bolshevik party. His opponents were called as Mensheviks.
- In October, Lenin persuaded the Bolshevik central committee to decide on immediate revolution.
- The revolutionary troops and armed factory workers seized the government buildings including the winter palace, the Prime Minister’s headquarters on 7th November 1917.
- The next day, 8th November, the new communist government was formed headed by Lenin.
- He renamed, the Bolshevik party into Russian communist party.
- The Russian communist party developed agriculture and Industry, and eliminated Illiteracy and poverty within a record time.
- Women were given equal rights and right to vote.
- Land was distributed to poor peasants.
- Lenin appealed for peace and opted for withdrawing from the war and concentrated on the formation of new government.
- Therefore, In March 1918, the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was signed.
- The communist government encouraged the colonies to fight for their freedom.
- It led to debates over key issues, land reforms, social welfare, worker’s rights and gender equality started taking place in a global context.
Question 4.
Estimate the work done by the League of Nations, pointing out the reasons for its failure?
Answer:
Reasons for the failure of the League of Nations:
- The League had been successful until signing of the Locarno Treaty in 1925. It was the year when European powers were confronted with a problem—how to achieve disarmament. The Council of the League set up a commission to hold a Disarmament Conference to sort out the problem.
- The proposed conference materialised only in February 1932. In this conference, Germany’s demand of equality of arms with France was rejected. In October Hitler withdrew Germany from the conference and the League.
- In September 1931, Japan attacked Manchuria and the League condemned its action. So Japan resigned from the League.
- Italy also resigned from the League in 1937. Thereafter the League was a passive witness to events, taking no part in the crises over the Rhineland. Austria, Czechoslovakia and Poland.
- The last decisive action it took was in December 1939 when Russia was expelled for her attack on Finland. The Assembly did not meet again and the League of Nations was finally dissolved in 1946.
![]()
VIII. Activity
Question 1.
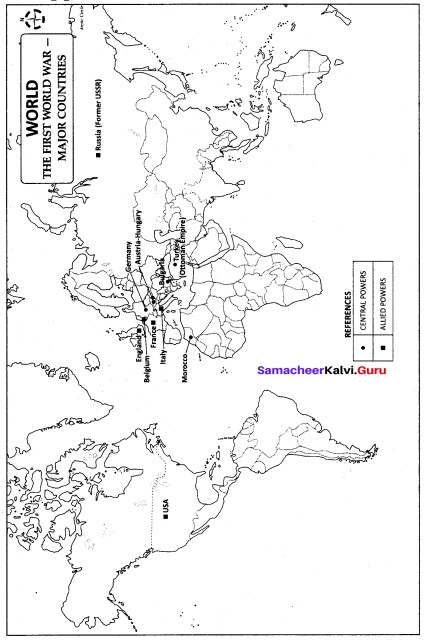
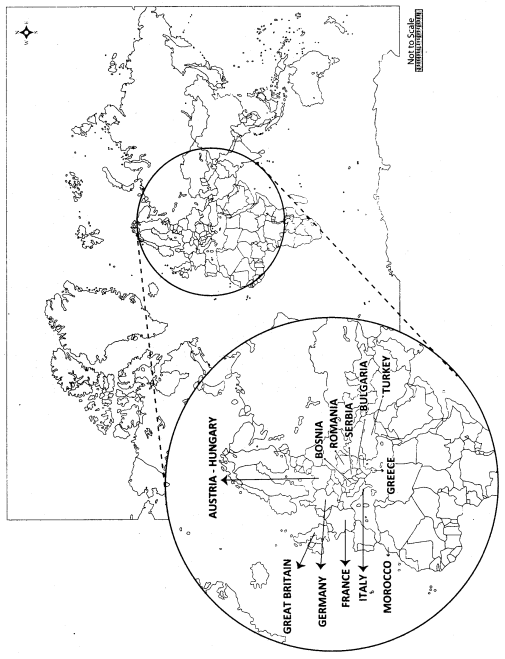
Students can be taught to mark the places of battles and the capital cities of the countries that were engaged in the War.
Question 2.
An assignment or a project work on the role of Indian soldiers in different battle fields across the globe and the casualties they suffered during the War be attempted by the students.
Answer:
British Indian Army: A Military department was created within the government of the East India company at Kolkata in the year 1776.
The British Indian Army was a critical force for the primacy of the British empire both in India and across the world.
Participation:
- Maintaining the internal security of the British Raj
- Anglo-Burmese war
- First and second Anglo-Sikh war
- First, Second and Third Anglo Afghan war
- First and Second Opium wars in China
- Boxer Rebellion in China
World War I (1914-1918): Indian soldiers 1.3 million Indian soldiers served with Allies in which, 74,187 Indian troops were killed. Indian Army fought against German empire in western front.
World War II (1939-1945): Indian soldiers 1,30,000 men along with 44,000 men in British units in India . Some 87,000 Indian soldiers died in the war.
First Kashmir war (1947): Tensions between Indian and Pakistan largely over Kashmir have never been entirely eliminated.
Indo-Pakistani war (1965): India lost a total of 150-190 tanks during the conflict. Over 3,000 soldiers were killed.
Sino-Indian conflict (1967): Conflict between Indian troops and members of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army on 1st Oct 1967. Indian losses were 88 killed and 163 wounded.
Indo-Pakistani war (1971): The war began with aerial strikes on eleven Indian air stations. Indian forces captured around 5,795 sq.miles land in the west but returned in 1972 Simla agreement.
Kargil war (1999): The war broke out at the Himalayan heights in the Kargil district of India. There was heavy casualties in India.
UN peace keeping mission: In 2014, India is the third largest troop contributor with 7,860 personnel deployed. Nearly 157 Indians have been killed during such operations. The Indian army provided paramedical units to help the sick and the wounded.
IX. Map Work
Mark the following countries on the world map.
1. Great Britain
2. Germany
3. France
4. Italy
5. Morocco
6. Turkey
7. Serbia
8. Bosnia
9. Greece
10. Austria-Hungary
11. Bulgaria
12. Rumania
Outbreak of World War I and Its Aftermath Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
……. was in competition with Germany and United States.
(a) Japan
(b) England
(c) Africa
Answer:
(b) England
![]()
Question 2.
The outcome of the first world war is the:
(a) French
(b) Russian
(c) American
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Russian
Question 3.
China was politically independent under the ……..
(a) Chin rule
(b) Chou rule
(c) Manchu rule
Answer:
(c) Manchu rule
Question 4.
Chauvinism means:
(a) extreme patriotism
(b) thinking high
(c) blind patriotism
(d) quality of the state
Answer:
(a) extreme patriotism
Question 5.
In 1876, barely 10% of Africa was under rule.
(a) Austria
(b) European
(c) China
Answer:
(b) European
Question 6.
The International court of Justice was set up at ……………. with ……………. judges.
(a) Greece, 10
(b) Hague, 15
(c) Austria,20
(d) America
Answer:
(b) Hague, 15
Question 7.
The term ………. denotes control or rule by a country over the Political and Economical life of another country.
(a) Imperialism
(b) Capitalism
(c) Socialism
Answer:
(a) Imperialism
Question 8.
The event of police and soldiers fired on th peaceful processions against Tsar in Russia was called:
(a) Bloody Sunday
(b) Petrograd problem
(c) Worst incident
(d) Militant action
Answer:
(a) Bloody Sunday
Question 9.
The industrial revolution created a need for …….
(a) Peace
(b) War
(c) Raw materials
Answer:
(c) Raw materials
Question 10.
The years of the first world war is:
(a) 1914-1918
(b) 1914-1916
(c) 1914-1917
(d) 1914-1920
Answer:
(a) 1914-1918
Question 11.
“Germany alone was competent to rule the whole world”, was said by
(a) Bismark
(b) Kaiser Wilhelm II
(c) Hitler
Answer:
(b) Kaiser Wilhelm II
![]()
Question 12.
France wanted to get back
(a) Alsace and Lorraine
(b) Bosnia and Herzegovina
(c) Estonia and Latvia
Answer:
(a) Alsace and Lorraine
Question 13.
Austria declared war on Serbia on
(a) 28th July 1914
(6) 28th June 1914
(c) 28th August 1914
Answer:
(a) 28th July 1914
Question 14.
Germany invaded France by crossing
(a) Luxemburg
(b) Rhineland
(c) Belgium
Answer:
(c) Belgium
II. Fill in the blanks :
1. The First World War started in ……….
2. Turkey extended her support to the ……….
3. ……… expedition was an utter failure for the British.
4. …….. an American ship was torpedoed by a German submarine.
5. In Russia, the Tsarist government was overthrown by ……..
6. Germany was sued for peace on November ………
7. The League of Nations was officially founded in January ……..
8. Japan captured Manchuria in …………
9. The turning point of the First World War was the ……….
10. The Bolshevik Party was renamed as ……….
11. The Treaty of Versailles abolished ……… in Germany, Austria and Russia.
12. The League had its headquarters in ……….
13. In March 1918, the …… was signed.
Answers:
1. 1914
2. Central Powers
3. Dardanelles
4. Lusitania
5. Lenin
6. 11,1918
7. 20,1920
8. 1931
9. entry of America
10. Russian Communist Party
11. Monarchy
12. Geneva
13. Treaty of Brest- Litovsk
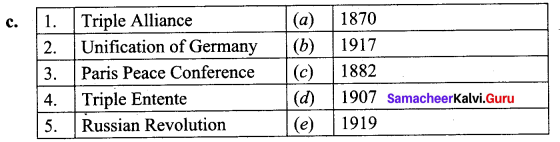
III. Match the following
Answers:
1. (b)
2. (e)
3. (c)
4. (a)
5. (d)
Answers:
1. (c)
2. (e)
3. (a)
4. (b)
5. (d)
Answers:
1. (c)
2. (a)
3. (e)
4. (d)
5. (b)
IV. Answer briefly:
Question 1.
Define Imperialism.
Answer:
The word‘imperialism’is defined in three ways:
- The term imperialism refers to the policy of extending a country’s rule over the others.
- It is a policy of aggressive behaviour of one state against another.
- It also refers to a country’s domination over the political and economic interest of another nation to exploit its natural resources.
![]()
Question 2.
Name the countries of Triple Alliance? When was it formed?
Answer:
Germany, Austria-Hungary and Bulgaria and Turkey were the countries of Triple Alliance. It was formed under the guidance of Bismarck in 1882.
Question 3.
Industrial Revolution is an important cause for the rise of Imperialism – Explain it.
Answer:
- Industrial Revolution in European countries resulted in a great increase in production. So there was a need for raw materials and new markets.
- It also instructed a great progress in the means of transport and communication.
- Due to the “Protective trade policy” of Europe, they could not sell their finished goods in their local markets.
- These causes forced the Europeans to find new markets in Asian and African continents which led to the rise of Imperialism.
Question 4.
Write a note on Balkan League.
Answer:
Balkan is a region in South-eastern Europe between the Mediterranean sea and the Black sea.
Turkey extended her empire over the Balkans. Taking advantage of the political instability of the Turkish empire, Greece, Serbia, Bulgaria and later Montenegro tried control over it and formed the Balkan League in March 1912.
Question 5.
Why did Germany needed colonies?
Answer:
- Germany needed colonies as a sign of her world importance.
- She needed colonies for her growing population.
- To get raw materials and markets for its finished products.
Question 6.
What do you mean by Pravada.
Answer:
Pravada is a Russian word meaning ‘Truth’. It was the official newspaper of the communist party of the soviet union from 1918 to 1991.
Question 7.
Why did America enter into First World War?
Answer:
- In 1917, Germany drowned four merchant ships of America including Lusitania with her submarines.
- More than hundred Americans died in this incident.
- This incident made the American President Woodrow Wilson angry and he declared war on Germany on the 6th April of 1917.
Question 8.
What is the significance of the Treaty of Portsmouth?
Answer:
In the Russo-Japanese war, of 1904, Japan defeated Russia. By the Treaty of Portsmouth, got back Port Arthur, also entered the circle of great powers.
![]()
Question 9.
What are the organs of the League of Nations?
Answer:
The League of Nations consisted of: The General Assembly, The Council, The Secretariat, The International Court of Justice, and The International Labour Organisation.
Question 10.
Write any two incidents of violations by the member countries of the League.
Answer:
- Japan attacked Manchuria in September 1931 and when the League condemned Japan, it resigned from the League.
- Russia attacked Finland in 1939.
Question 11.
Name the prominent industrial areas in the Russian Empire?
Answer:
St. Petersburg and Moscow.
Question 12.
Who led the procession of workers to the event “Bloody Sunday” in Russia?
Answer:
Father Gapon
Question 13.
Write a note on Trusts and Cartels.
Answer:
- A Trust is an Industrial organization in USA engaged in production, distribution of a commodity and control over its supply and price.
- A Cartel was an association in Germany which was based upon a contractual agreement between people doing same type of business.
V. Answer all the questions given under each caption:
Question 1.
Causes for the rise of Imperialism
(a) What became the fashion of the later part of the 19th century?
Answer:
Imperialism became the fashion of the later part of the 19th century.
(b) What was the “White man’s burden”?
Answer:
To civilise the backward and uncivilised native people of Africa and Asia.
(c) Why were the European nations forced to acquire new colonies?
Answer:
The European nations were forced to acquire new colonies to get the Balance of power with their neighbours and competitors.
(d) What promoted the spirit of imperialism?
Answer:
The discovery of new routes to African and Asian continents.
Question 2.
Rise of Japan
(a) Which incident of Japan surprised the whole world?
Answer:
The crushing defeat of China by little Japan in the Sino-Japanese war of (1894-95) surprised the world.
(b) Why did Japan entered an alliance with England?
Answer:
Japan developed hostile towards Russia because Franch was the ally of Russia. Therefore, it entered into an alliance with Britain.
(c) What was the result of the Russo-Japanese war?
Answer:
In the Russo-Japanese war of 1904, Japan defeated Russia and the Treaty of Portsmouth was signed thereby got back Port Arthur.
(d) What was the position of Japan after this war?
Answer:
Japan after this war, entered the charmed circle of the great powers.
Question 3.
Balkan Problem
(a) Name the Balkan countries.
Answer:
Serbia, Bulgaria, Albania, Greece and Montenegro.
(b) How did the First Balkan War come to an end?
Answer:
The First Balkan War came to an end by the “Treaty of London”.
(c) Why did the other Balkan countries declare war on Bulgaria?
Answer:
Dispute arose between Serbia and Bulgaria in sharing the spoils of the war.
(d) What was the result of the Second Balkan war?
Answer:
Bulgaria was defeated and Serbia gained more territories.
![]()
Question 4.
Violent Form Of Nationalism
(a) What was the attitude developed with the growth of Nationalism?
Answer:
The attitude of “ My country right or wrong, I support it” developed.
(b) What is meant by Jingoism, Chauvinism, Kulthur.
Answer:
Jingoism – England – Blind patriotism.
Chauvinism – France – Extreme Patriotism.
Kulthur – Germany – Thinking high.
(c) Why did hatred developed towards other countries?
Answer:
The love for one country demanded hatred for another country.
(d) What did the newspapers do?
Answer:
Newspapers whipped up nationalist feelings by twisting the situation obtained in other countries.
Question 5.
War in the Near East front
(a) When did Turkey enter the war?
Answer:
In October 1914.
(b) Why was it considered a terrible blow?
Answer:
Because communications between Russia and the Allies were cut off.
(c) Why did Britain wanted to capture Gallipoli Peninsula?
Answer:
To control the Dardanelles and to capture Constantinople.
(d) What was the result of Dardanelles expedition?
Answer:
It was an utter failure to Britain.
Question 6.
League of nations
(a) When was the covenant of the League of nations formed?
Answer:
The Covenant of the League was formed at the Paris peace conference in 1919.
(b) Who helped in its formation?
Answer:
President ofU.S.A Woodrow Wilson.
(c) What was the structure of the League?
Answer:
The League consisted of Assembly,, the council, the Secretariat, Court of Justice and the International Labour organization.
(d) What were the privileges Enjoyed by the member countries?
Answer:
Each member had one vote and even the small nations possessed the right of Veto (The vote that blocks a decision).
Question 7.
League of Nations:
(a) Name the organisations which were found before the League of Nation.
Answer:
- The League of Nations society 1915.
- The World League for Peace 1917
- The League of Free Nations Association 1918.
(b) Where was the League of Nation’s headquarters situated?
Answer:
The League of Nation’s headquarters was situated at Geneva in Switzerland.
(c) How should the member nations solve the problems?
Answer:
The member nations should solve the problems only through the League of Nations.
(d) When did Japan capture Manchuria?
Answer:
Japan captured Manchuria in 1931.
VI. Answer the following in detail.
Question 1.
What were the effects of Imperialism?
Answer:
Positive effects:
- The powerful nations developed the transport and communication facilities in the weaker nations.
- The formers gave the latter education, medical care and better methods of sanitation.
- They introduced new farming methods to get increased food production.
- These changes meant less death in the colonies and overall improvement in the standard of living.
- It promoted order, discipline and unity in countries.
- Clemenceau of trance, Orlando of Italy, Lloyd George of Britain and Woodrow Wilson of America were the main personalities of the conference.
The Treaty of Versailles:
- The peace treaty with Germany was signed and it was called the Treaty of Versailles.
- A huge war indemnity was imposed or Germany and German army was reduced.
- The overseas possessions of Germany were divided among the victorious nations.
- Germany surrendered Alsace and Lorraine to France.
- The saar coal field was to be occupied by France for 15 years.
Other important treaties:
- The Treaty of Germaine was concluded in Austria.
- The Treaty of Trianon was concluded with Hungary.
- The Treaty of Nevilly was concluded with Bulgaria.
- The Treaty of Severes was concluded with Turkey.
New Nations created:
- In many countries, monarchies gave place to Democracies.
- New Republics of Czechoslovakia and Poland were born.
- The Republic of Austria and Hungary was recognized.
Negative effects:
- The colonies had no freedom. They were exploited and treated as slaves.
- Imperialism led to the exploitation of the natural resources of the colonies.
- The colonies were used as the suppliers of raw materials and markets for finished products.
- The colonies plunged into poverty and unemployment due to the disappearance of indigenous industries.
- The traditional pattern of agriculture was completely changed as the natives were forced to cultivate raw materials rather than food crops.
- The introduction of western culture and education led to the loss of traditional culture, of the colonies.
- It also led to the extinction of some native races of Africa due to slave trade.
- The policy of racial discrimination was practiced in some colonies.
Question 2.
What were the criticisms raised against the peace settlement?
Answer:
- The defeated powers were absent from the negotiations.
- Self-determination was the principle for restoring peace among nations, but Germany alone did not follow it.
- Austria was not allowed to unite with Germany.
- Germany was thus left with total injustice.
- Germany had to pay 6,600 million pounds for reparation which was beyond her capacity.
- Germany was newly bordered by small weak states.
- In 1920, the United States took a policy of Isolation.
- Italy was given merely small places like Trieste, Istria and the south Tyrol.
- The peace settlement created many national minorities and countries gave promises to respect the rights of minorities.
- Separate treaties were drawn up and signed by the allies with Austria, Hungary, Bulgaria and Turkey.
- Though, it was largely due to the pressure from President of USA, Woodrow Wilson, League was formed but could not become the member of the League.
Question 3.
What were the achievements of League of Nations?
Answer:
The League of Nations succeeded in solving many problems during its existence for about 20 years.
- It settled the dispute between Sweden and Finland regarding the ownership of Aaland island.
- It solved a boundary dispute in Silesia between Poland and Germany.
- It solved a dispute between Greece and Italy over the Island of Corfu.
- It avoided a war between Greece and Bulgaria over the border disputes.
- In 1926, Germany was admitted as a member of the League of Nations. In 1934, Russia was also admitted in the League.
- It solved a border issue between Peru and Columbia.
- Through its other organs, the League prevented the spread of many diseases.
- It extended its helping hand in solving the problems of refugees and lepers.
- It whole heartedly promoted cultural co-operation among the nations.
- It attempted to raise the standard of education in various states.
- The International Court of Justice handled more than thirty cases. It delivered judgement in some cases and in some others gave advisory opinions.