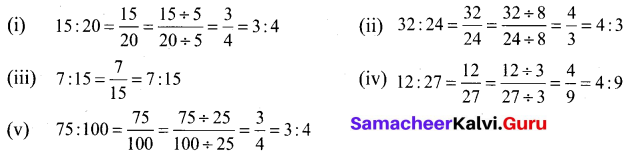
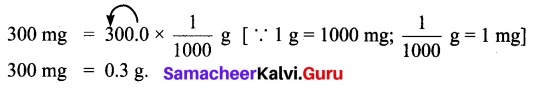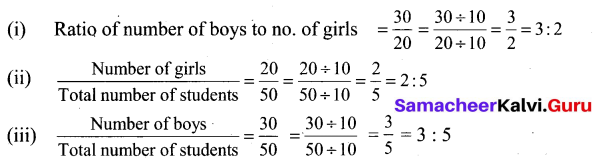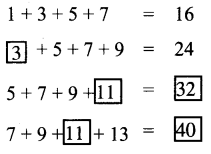Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 1 Chapter 4 The Living World of Plants
You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 1 Chapter 4 The Living World of Plants
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science The Living World of Plants Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the appropriate answer
Question 1.
Pond is an example of ______ ecosystem.
(a) Marine
(b) Freshwater
(c) Deserts
(d) Mountain
Answer:
(b) Freshwater
Question 2.
The important function of stomata is ……….
(a) conduction
(b) Transpiration
(c) Photosynthesis
(d) Absorption
Answer:
(c) Photosynthesis
Question 3.
Organ of absorption is ______
(a) Root
(b) Stem
(c) Leaf
(d) Flower
Answer:
(a) Root
Question 4.
The habitat of water hyacinth is
(a) Aquatic
(b) Terrestrial
(c) Desert
(d) Mountain
Answer:
(a) Aquatic
![]()
II. True or False
Question 1.
Plants can live without water.
Answer:
False. Plants cannot live without water.
Question 2.
All plants have chlorophyll.
Answer:
True.
Question 3.
Plants have three parts: the root, the stem and leaves.
Answer:
False. Plants have several parts: Such as the root, the stem, leaves, flowers, fruits and seeds.
Question 4.
Mountain is an example for freshwater habitat.
Answer:
False. Rivers, ponds, lakes and pools are the example for freshwater habitat. (OR) Mountain is an example for Terrestrial habitat.
Question 5.
Root is modified into spines.
Answer:
False. Leaves are modified into spines.
Question 6.
Green plants need sunlight.
Answer:
True.
![]()
III. Fill in the Blanks.
- Earth’s surface is covered by __________ % of water.
- The driest places on Earth are __________
- Fixation and absorption are the main functions of __________
- Primary organs of photosynthesis are __________
- Tap root system is present in __________ plants.
Answers:
- More than 70%
- deserts
- root
- leaves
- dicotyledonous
![]()
IV. Match the following.

Answer:

V. Arrange in correct sequence.
Question 1.
Leaves – Stem Root – Flower.
Answer:
Root, Stem, Leaves, Flower.
Question 2.
Transpiration-Conduction-Absorption-Fixation
Answer:
Fixation-Absorptiori-Conduction-Transpiration
![]()
VI. Very short answer.
Question 1.
Classify the plants on the basis of their habitats.
Answer:
The two major habitats.
(a) Aquatic habitat
(b) Terrestrial habitat
(a) Aquatic habitat classified into two. They are
- Fresh water habitat
- Marine water habitat
(b) Terrestrial habitat classified into three.
- Forest habitat
- Grassland habitat
- Desert habitat.
Question 2.
Identify the Desert plants from the following-
Cactus, Hydrilla, Mango and Rose
Answer:
Cactus plants – grow in deserts, and are able to store water in their stem.
Question 3.
Define the term habitat.
Answer:
A dwelling place of an animal, plant, or another organism, to live and reproduce is called a habitat.
Question 4.
Relate the terms leaves and photosynthesis.
Answer:
The green leaves are essential for preparing food. Because it contains a green pigment called chlorophyll. The preparation of food is known as photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is essential for plant growth.
![]()
VII. Short Answer.
Question 1.
Why do you call jasmine plant, a twiner?
Answer:
Jasmine plant has a weak stem. It cannot stand straight on its own. It must climb on any support to survive. So jasmine plant is called as twiner.
Question 2.
Compare the taproot and fibrous root systems.
Answer:
Taproot:
Single root-grow straight with smaller roots arise from the taproot.
eg. Dicot plants- Bean, mango
Fibrous root:
Cluster of roots arising from base of the stem, tin and uniform in size.
eg. Monocots, grass, paddy
Question 3.
Distinguish between terrestrial and aquatic habitats.
Answer:
Terrestrial habitats:
- They are found on land
- They include desert, grassland, forest, farms, towns and cities
- They are classified into 3 types, such as Desert habitat, Grassland habitat & Forest habitat.
- Eg. Rubber tree, teak tree, neem tree
Aquatic habitats:
- They are found in water.
- They include the areas, permanently as well as occasionally covered by water.
- They are classified into 2 types, such as Fresh water habitat, & Marine water habitat.
- Eg. Lily, lotus, marine algae, sea grasses.
Question 4.
List out the plants present in your school garden.
Answer:
Shoe Flower, Ferns, Crotons, Roses, Lilies, Cactus, Coconut Trees, Royal Palm, Clitoria, Cycas, Agave, Allamanda, Tomato, Brinjal, Lady’s Finger etc in Terrace garden.
![]()
VIII. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
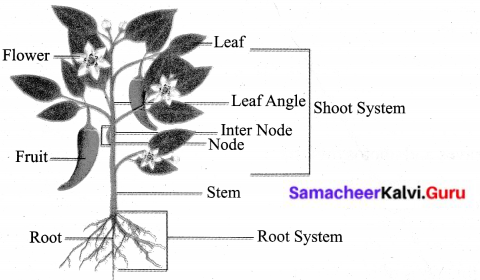
Make a list of the functions of root and stem.
Answer:
Roots:
- Fixation – Fixes plants to the soil.
- Absorption – Absorbs water and minerals from the soil and conduct them to other parts.
- Storage – Some plants store food in the roots. Eg. Carrot
Functions of the stem:
Support: Supports the branches leaves flowers and the fruits
Conduction:
- Transports water and minerals from roots to upper aerial plants parts
- Transports the prepared food from leaves to all parts
- Some stems like sugarcane store food.
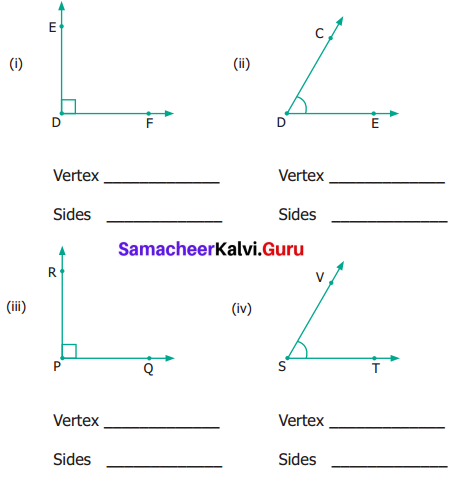
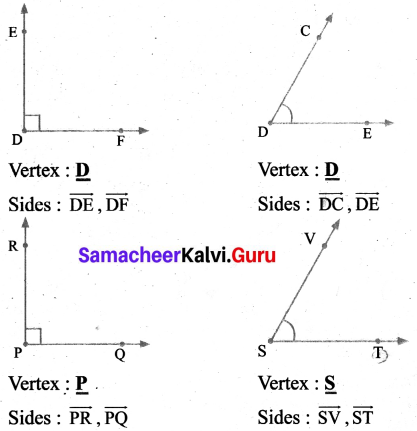
![]()
Question 2.
Study the given concept map. Connect them correcting by drawing arrow marks. Complete the map by filling the blanks.
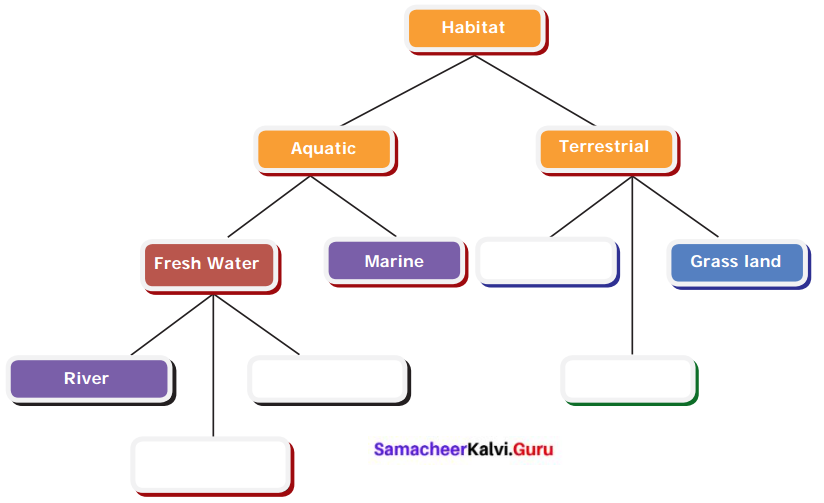
Answer:
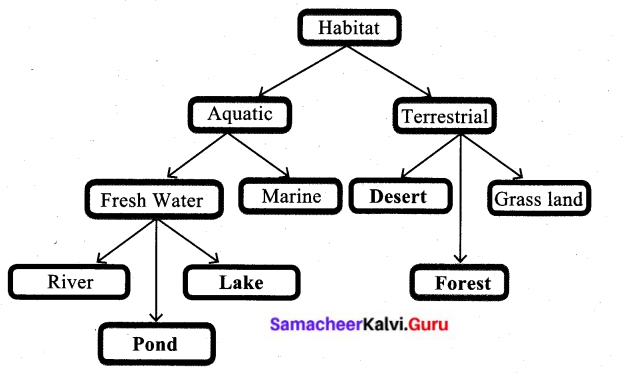
Guess it :
Ginger: Is it a Root or stem?

Answer:
Ginger is often mistaken for a root. In fact, it is actually an underground stem from a tropical herb plant Zingiber Officinale.
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science The Living World of Plants Intext Activities
Activity – 1
Water absorption by Root
Aim:- To observe the absorption of water by root
Question 1.
What do you need?
Answer:
A carrot, a glass of water, and blue ink.
Question 2.
What to do?
Answer:
Place a carrot in a glass of water with a few drops of blue ink. Leave the carrot in water for two to three days. Then cut the carrot into half lengthwise and observe.
Question 3.
What do you learn?
Answer:
Blue colour appears in carrot which indicates the upward movement of water in the carrot showing that root conducts water.
Activity – 2
Conduction of water
Aim:- To observe conduction of water by stem.
Question 1.
What do you need?
Answer:
A small twig of balsam plant, a glass of water, and a few drops of red ink.
Question 2.
What to do?
Answer:
Place the small twig in the water with red ink.
Question 3.
What do you see?
Answer:
The stem becomes reddish.
Question 4.
What do you learn?
Answer:
This is because red coloured water is being absorbed by the stem upwards.
![]()
Activity – 3
Question:
The teacher will divide students into four groups. Each group leader will pull a plant part from a “hat” (roots, stems, leaves, and flowers). The teacher will take students around campus to search for their assigned plant parts. They have to locate different types of plants discussed in the classroom. The learner will return to the class, follow a process sheet given to create a poster with their group, and identify correctly each type of root, stem, or leaf observed. The flower group will create a poster by identifying correctly each part of the flower. Each group will share their posters within the class.
Answer:
Activity did by the students themselves.
Activity – 4
Question 1.
Read the following story along with your friend
Once, I was a happy monkey. I lived in a beautiful thick forest with my mother and two brothers. We ran and played in the lush grass. On one hot day, I fell fast asleep in the cool shade of a tree. Suddenly the bright sun woke me up. I opened my eyes and could not believe what I saw everything has changed. Everything had been destroyed. I stood and looked at the stumps that used to be trees. Nothing was left apart from hard dry ground and only streets and buildings. I saw a deer that looked very sad, “where have all the trees gone and where are all the other animals?” I asked her.
She explained how humans had chopped down all the trees but had not planted new ones to replace them. After a while, I said goodbye to the deer. My home had gone. I didn’t know where my family was, and I was hungry and thirsty, day and night. I walked in search of water, food, and a safe place to sleep. Whenever I stopped, to rest humans drove me away with sticks and angry voices. I could feel my body getting weak and tired. One day when I had almost given all the hope, I came across a cool and dark forest. As I walked through it, I found plenty of food and water. The forest was safe for me. There were no signs of humans visiting it.
- Why did the deer feel sad?
- Who chopped the trees?
- Which is the safest place for monkeys to live?
- What is a habitat?
Answer:
- The deer felt sad because humans had chopped down all the trees and there was no place to live.
- People had chopped the trees.
- A forest is the safest place for monkeys to live.
- The dwelling place of an animal, plant, or other organism is called a habitat.
![]()
Activity – 5
Visit a nearby nursery. Choose any ten varieties of plants and place them under the appropriate habitats.
Answer:

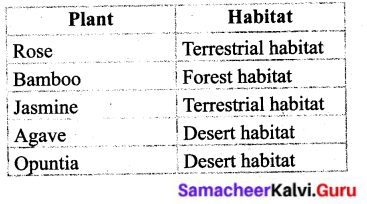
Activity – 6
Field Investigation
Name of the student :
Date :
Location :
Plant types to be observed
1. A tendril climber
2. A twiner
3. A plant with thorn
Tabulate the modification that you have observed in these plants.
Answer:
Field Investigation
Name of the student: Ramesh
Date : 28 – 07 – 2018
Location: Thekkady

![]()
Hots
The Cactus plant is green in colour and performs photosynthesis. Which part of the plant does photosynthesis?
Answer:
The stem part of the cactus plant performs photosynthesis.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science The Living World of Plants Additional Questions
I. Choose the appropriate answer.
Question 1.
______ is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms.
(a) Chemistry
(b) Biology
(c) Zoology
(d) Physics
Answer:
(b) Biolog
Question 2.
The part of a stem from where a leaf arises is
(a) node
(b) internode
(c) terminal bud
(d) lateral bud
Answer:
(a) node
Question 3.
Main axis of the shoot system Is called ______
(a) stem
(b) root
(c) Leaf
(d) buds
Answer:
(a) stem
Question 4.
The green colour of the leaf is due to the presence of
(a) chloronchyma
(b) chlorophyll
(c) lamina
(d) stomata
Answer:
(b) chlorophyll
Question 5.
World habitat day is observed on the first Monday of ______
(a) October
(b) November
(c) September
(d) December
Answer:
(a) October
Question 6.
______ is one of the fast-growing plants during the active growth phase.
(a) Mango
(b) Neem
(c) Hibiscus
(d) Bamboo
Answer:
(d) Bamboo
Question 7.
______ is the longest river in the world.
(a) Sutlej
(b) Yellow
(c) the Nile
(d) Congo
Answer:
(c) the Nile
Question 8.
Length of Nile river is ______
(a) 6560 km
(b) 6650 km
(c) 6506 km
(d) 5606 km
Answer:
(b) 6650 km
Question 9.
Air spaces in stems and petioles of ______ plant are useful for floating in the water.
(a) lotus
(b) waterlily
(c) water hyacinth
(d) agave
Answer:
(a) lotus
Question 10.
The first land plants are ______
(a) neem and pine
(b) hibiscus and lotus
(c) banyan and peepal
(d) mosses and liverworts
Answer:
(d) mosses and liverworts
Question 11.
The ______ forest in South America produces half of the world’s oxygen supply.
(a) Taiga
(b) Congo rain
(c) Amazon rain
(d) Dry deciduous
Answer:
(c) Amazon rain
![]()
II. True or False – If False gives the correct answer.
Question 1.
The living world comprises plants and animals.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
Root has nodes and internodes.
Answer:
False. The stem has nodes and internodes.
Question 3.
Taproot consists of a cluster of roots arising from the base of the stem.
Answer:
False. The fibrous root consists of a cluster of roots arising from the base of the stem.
Question 4.
The buds at the axils of the leaves are called terminal buds.
Answer:
False. The buds at the axils of the leaves are called auxiliary buds.
Question 5.
In the case of sugarcane, food is stored in the stem region.
Answer:
True.
Question 6.
The longest river in India is the Ganges river.
Answer:
True
Question 7.
The Amazon rain forest in Canada produces half of the world’s oxygen supply.
Answer:
False.
The Amazon rain forest in South America produces has of the world’s oxygen supply.
![]()
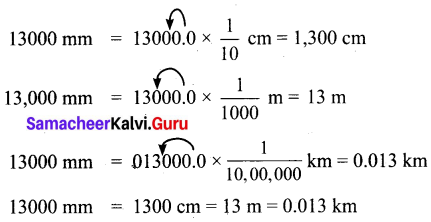
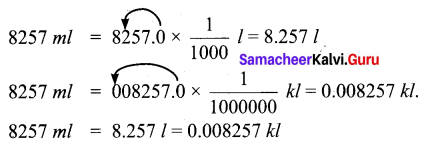
III. Fill in the blanks.
- Plants can prepare _______
- _______ are positively geotropic in nature.
- Mango plant is a _______ plant.
- _______ plants store food in their roots.
- The aerial part of the plant body above the ground is known as _______
- The part of the stem between two successive nodes is called _______
- The flat portion of the leaf is called _______
- The green colour of the leaf is due to the presence of a green coloured pigment called _______
- _______ plant’s leaves grow up to 3 metres across.
- _______ are free-floating Algae.
- _______ desert is called as Great Indian desert.
- River Ganges is _______ km long.
- Marine plants perform about _______ of all photosynthesis that occurs on the planet.
Answers:
- food
- Roots
- dicotyledonous
- Carrot and beetroot
- shoot system
- internode
- Leaf Lamina
- Chlorophyll
- Victoria amazonica
- Phytoplanktons
- Thar
- 2525
- 40%
![]()
IV. Complete the given analogy.
Question 1.
The aerial part above the ground: Shoot system
The underground part of the axis of a plant: _______
Answer:
Root system
Question 2.
Dicotyledonous plants: Bean, Mango
Monocotyledonous plants : _______
Answer:
Grass, paddy
Question 3.
Carrot, beetroot: store food in roots.
Sugarcane : _______
Answer:
Stores food in shoot
Question 4.
Photosynthesis : _______
Transpiration : Stomata.
Answer:
chlorophyll
Question 5.
Flowering plant : Sunflower
Non-flowering plant : _______
Answer:
Riccial
Question 6.
Mango : Angiosperm
Cycas : _______
Answer:
Gymnosperm
Question 7.
Water lily : Freshwater habitat
Marine Algae : _______
Answer:
Marine water habitat
Question 8.
Rainfall 25 – 200 cm : Forest habitat
Rainfall below 25 cm : _______
Answer:
Desert habitat
Question 9.
Sweet Peas : Tendril Climber
Clitoria : _______
Answer:
Twiners
Question 10.
Leaves are modified into spines : Opuntia
Stem has sharp thorns : _______
Answer:
Bougainvillea
![]()
V. Match the following.
- Tap root – (a) Grass
- Aquatic plant – (b) Teak tree
- Desert plant – (c) Neem
- Grassland – (d) Opuntia
- Terrestrial plant – (e) Water lily
Answer:
- – (c)
- – (e)
- – (d)
- – (a)
- – (b)
VI. Short Answers.
Question 1.
What are the uses of plants?
Answer:
Plants are used as food, medicine, wood, and shelter.
Question 2.
Classify plants on the basis of flowers.
Answer:
Plants can be classified into 2 on the basis of flowers
- Non-flowering plants – Eg. Riccia
- Flowering plants – Eg. Mango
Question 3.
What are the properties of root?
Answer:
- The root lies below the surface of the soil.
- It does not have nodes and internodes.
- It has a root cap at the tip.
- Roots are positively geotropic in nature.
Question 4.
Notes on cactus.
Answer:
- Cactus – desert plant ( where there is less or no rainfall)
- Stem – store water
- Leaves – modified to spines
- Roots – well developed, go deep down into soil to get water.
Question 5.
Answer:
- The shoot system is the aerial part of the plant body above the ground.
- It consists of stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits.
- It grows towards the sunlight.
- It has nodes and internodes.
Question 6.
List the functions of leaves.
Answer:
- The green leaves prepare food by the process of photosynthesis.
- They help in respiration
- They carryout transpiration.
Question 7.
Classify the plants on the basis of (i) flower and (ii) position of seed.
Answer:
Based on the flower:
They are classified into
- Flowering plants
- Non-flowering plants
Based on the position of seed:
They are classified into
- Gymnosperms
- Angiosperms
Question 8.
List the characters of aquatic plants.
Answer:
In aquatic plants, roots are very much reduced in size. Stem and leaves have air chambers that allow floating in the water.
Question 9.
Give some examples of freshwater habitat and marine water habitat plants.
Answer:
Freshwater habitat: Water hyacinth, water lily, lotus.
Marine water habitat: Marine Algae, Seagrasses, Marsh grass, Phytoplanktons.
Question 10.
Name the part which is modified into tendril in Sweet Peas and Bitter Gourd?
Answer:
In Sweet Peas: Leaflets are modified.
In Bitter Gourd: Auxiliary buds are modified.
Question 11.
Define Thorns.
Answer:
Leaves of some plants become wholly or partially modified into sharply pointed structures called thorns or spines.
Question 12.
Name the part which is modified into Thorns or Spines in Agave, Opuntia, and Bougainvillea.
Answer:
In Agave: The leaf apex and margins are modified into thorns.
In Opuntia: The leaves are modified into spines.
In Bougainvillea: The stem has sharp thorns.
![]()
VII. Long Answer.
Question 1.
Describe the Structure of Leaf.
Answer:
- The leaf is a green, flat expanded structure.
- It has a stalk called a petiole.
- The flat portion of the leaf is called leaf lamina or leaf blade.
- On the lamina, there is a main vein called the midrib.
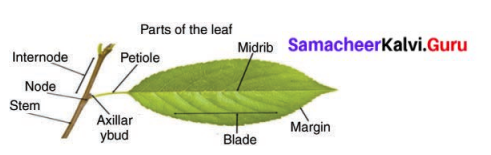
- The portion of the leaf connected in the nodal region of the stem is known as the leaf base.
- The green colour is due to the presence of a green coloured pigment called chlorophyll.
- On the lower side of the leaf, there are tiny pores or openings known as stomata.
Question 2.
Draw a diagram of a plant and label its parts.
Answer: