You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 4 Electric Charge and Electric Current
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Electric Charge and Electric Current Textbook Exercises
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
In current electricity, a positive charge refers to,………………
(a) presence of electron
(b) presence of proton
(c) absence of electron
(d) absence of proton
Answer:
(c) absence of electron
Question 2.
Rubbing of comb with hair ……………………
(a) creates electric charge
(b) transfers electric charge
(c) either (a) or (b)
(d) neither (a) nor (b)
Answer:
(c) either (a) or (b)
![]()
Question 3.
Electric field lines ………….. from positive charge and ………. in negative charge.
(a) start; start
(b) start; end
(c) start: end
(d) end; end
Answer:
(b) start; end
Question 4.
Potential near a charge is the measure of its ………… to bring a positive charge at that point.
(a) force
(b) ability
(c) tendency
(d) work
Answer:
(d) work
Question 5.
In an electrolyte the current is due to the flow of …………. .
(a) electrons
(b) positive ions
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) neither (a) nor (b)
Answer:
(a) electrons
Question 6.
Heating effect of current is called
(a) Joule heating
(b) Coulomb heating
(c) Voltage heating
(d) Ampere heating
Answer:
(a) Joule heating
![]()
Question 7.
Electroplating is an example for
(a) heating effect
(b) chemical effect
(c) flowing effect
(d) magnetic effect
Answer:
(b) chemical effect
Question 8.
Resistance of a wire depends on
(a) temperature
(b) geometry
(c) nature of material
(d) all the above
Answer:
all the above
II. Match the following.
| Column-I |
Column-II |
| 1. Electric Charge | (a) ohm |
| 2. Potential difference | (b) ampere |
| 3. Electric field | (c) coulomb |
| 4. Resistance | (d) newton per coulomb |
| 5. Electric current | (e) volt |
Answer:
- (c)
- (e)
- (d)
- (a)
- (b)
III. True or False.
Question 1.
Electrically neutral means it is either zero or equal positive and negative charges
Answer:
True
![]()
Question 2.
Ammeter is connected in parallel in any electric circuit
Answer:
False
Correct Statement: An ammeter is connected in series with a device to measure its current.
Question 3.
The anode in electrolyte is negative
Answer:
False
Correct Statement: The anode in electrolyte is positive.
Question 4.
Current can produce magnetic field
Answer:
True
IV. Fill in the blanks.
- Electrons move from ………….. potential to …………….. potential.
- The direction opposite to the movement of electron is called ……………….. current.
- The e.m.f of a cell is analogous to ……………. of a pipe line.
- The domestic electricity in India is an ac with a frequency of ………… Hz.
- Trip switch is an …………. safety device.
Answer:
- higher, lower
- Conventional
- a pump
- 50
- electromechanical
V. Conceptual questions.
Question 1.
A bird sitting on a high power electric line is still safe. How?
Answer:
Birds can sit on power lines and not get electric shocks because the electricity is always looking for a way to get to the ground (i.e.) the current is not flowing out of its body to any other material.
Current flows in a loop (which means the circuit is closed). A bird sitting on a transmission line does not complete the circuit. If the same bird keeps one leg on one line and another leg or any part of its body on another line or the neutral points, then it will get burnt.
Question 2.
Does a solar cell always maintain the potential across its terminals constant? Discuss.
Answer:
The electro-chemical process inside a battery provides electrons at the negative terminal and draws electrons from the positive terminal to maintain the current being drawn. By providing energy to the electrons, the cell is capable of maintaining an electric potential difference across the two ends of the external circuit.
Question 3.
Can electroplating be possible with the alternating current?
Answer:
The heating effect and the chemical effect experiments have to be performed only with a dc cell of around 9V. The 9V dc cell will not give any electrical shock.
At any cost, we should not use the main domestic electric supply which is 220V ac voltage. If it is used it will give a heavy electric shock leading to severe damage to our body.
VI. Answer the following.
Question 1.
On what factors does the electrostatic force between two charges depend?
Answer:
The numerical value (magnitude) of electric force between two charges depend on the,
- value of charges on them,
- distance between them and
- nature of medium between them.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the electric lines of force?
Answer:
The direction of the electric field is the direction of the force that would act on a small positive charge. Therefore the lines representing the electric field are called ‘electric lines of force’.
Question 3.
Define electric field.
Answer:
The electric field is the region around a charged body within which its influence can be experienced (i.e) within which it can attract or repel another charged body.
Question 4.
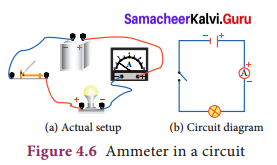
Define electric current and give its unit.
Answer:
Current is the rate at which charges flow past a point on a circuit. Current (I) is represented as, I = \(\frac { q }{ t }\)
The standard SI unit for current is ampere with symbol A.
Question 5.
State Ohm’s law.
Answer:
Ohm’s law states that the current passing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across its ends, provided the physical conditions like temperature, density, etc. remain unchanged. V α I or V = IR.
Question 6.
Name any two appliances which work under the principle of heating effect of current.
Answer:
The principle of all-electric heating appliances like an iron box, water heater, toaster, etc. works under the principle of heating effect of current.
![]()
Question 7.
How are the home appliances connected in general, in series or parallel? Give reasons.
Answer:
In a household electric circuit, different home appliances are connected in parallel to one another due to the following reasons:
- The appliances can be operated independently. If one appliance is switched off, others remain unaffected.
- Each appliance gets the same constant voltage.
- In parallel connection of electrical appliances, the overall resistance of the circuit is reduced due to which the current from the power supply is high.
Question 8.
List the safety features while handling electricity.
Safety features to be followed are:
- Ground connection
- Trip switch
- Fuse.
VII. Exercises.
Question 1.
Rubbing a comb on hair makes the comb get -0.4C.
(a) Find which material has lost an electron and which one gained it.
Answer:
The material is a comb that gained electrons and the hair gained it.
(b) Find how many electrons are transferred in this process.
Answer:
Charge on 1 electron, e = 1.6 × 10– 19C
q = ne or n = \(\frac { q }{ e }\)
n = \(\frac { 0.4 }{ 1.6 }\) × 10– 19 = 0.25 × 1019 = 2.5 × 1018
Question 2.
Calculate the amount of charge that would flow in 2 hours through an element of an electric bulb drawing a current of 2.5A.
Answer:
Given: Time ‘t’ = 2 hours = 2 × 60 × 60s
t = 7200s
I = 2.5A
Amount of charge, Q = I × t
= 2.5 × 7200
Q = 18000C
Question 3.
The values of current I flowing through a resistor for various potential differences V across the resistor are given below. What is the value of resistor?
Answer:
| I (ampere) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 |
| V (volt) | 1.6 | 3.4 | 6.7 | 10.2 | 13.2 |
[Hint: plot V-I a graph and take slope].
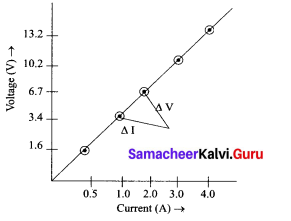
Resistance(R) = \(\frac { ∆V }{ ∆I }\)
= 10.2 – \(\frac { 6.7 }{ 3 }\) – 2 = 3.5/1
R = 3.5Ω
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Electric Charge and Electric Current In Text Problems
Question 1.
How many electrons will be there in one coulomb of charge?
Solution:
Charge on 1 electron, e = 1.6 × 10– 19C
q = ne or n = \(\frac { q }{ e }\)
number of electrons in 1 coulomb = \(\frac{1}{1.6 \times 10^{-19}}\) = 6.25 × 1018 electrons
![]()
Question 2.
If, 25 C of charge is determined to pass through a wire of any cross-section in 50 s, what is the measure of current?
Solution:
I = \(\frac { q }{ t }\) = \(\frac { (20C) }{50s}\) = 0.5 \(\frac { C }{ s }\) = 0.5 A
Question 3.
The current flowing through a lamp is 0.2A. If the lamp is switched on for one hour, what is the total electric charge that passes through the lamp?
Solution:
I = \(\frac { q }{ t }\);q = I × t
1hr = 1 × 60 × 60 s = 3600 s
q = I × t = 0.2A × 3600s = 720C
Question 4.
The e.m.f of a cell is 1.5 V. What is the energy provided by the cell to drive 0.5 C of charge around the circuit?
Solution:
ℰ = 1.5V and q = 0.5C
ℰ = \(\frac { W }{ q }\); W= ℰ × q ; Therefore W = 1.5 × 0.5 = 0.75J
Question 5.
A charge of 2 × 104 C flows through an electric heater. The amount of electrical energy converted into thermal energy is 5 MJ. Compute the potential difference across the ends of the heater.
Solution:
V = \(\frac { W }{ q }\) that is 5 × 106 \(\frac { J }{ 2 }\) × 104 C = 250 V
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Electric Charge and Electric Current Additional Questions
I. Short answers questions.
Question 1.
What is a positive and a negative ion?
Answer:
If an electron is removed from the atom, it becomes positively charged. Hence it is called a positive ion. When an electron is added to an atom, it becomes negatively charged. Hence it is called a negative ion.
![]()
Question 2.
Define Electric potential.
Answer:
Electric potential is a measure of work done on the unit positive charge to bring it to that point against all electrical forces. It is represented as ‘V’.
Question 3.
What are the effects of electric current?
Answer:
When current flows in a circuit, it exhibits various effects. The main effects are; heating, chemical, and magnetic effects.
Question 4.
What is resistance?
Answer:
The resistance (R) is the measure of opposition offered by the component to the flow of electric current through it.
Question 5.
What is common to both direct and alternating current?
Answer:
Joule’s heating effect of current is common to both direct and alternating current.
Question 6.
What is a trip switch?
Answer:
It is an electromechanical device which does not allow a current beyond a particular value by automatically switching off the connection.
![]()
Question 7.
What are the advantages of AC over DC?
Answer:
Advantages of AC over DC are;
- The voltage of an AC can be varied easily using a transformer.
- The AC can be carried over long distances using step-up transformers.
- The loss of energy while distributing current in the form of AC is negligible.
- DC cannot be transmitted as such, but AC can be easily converted to DC.
- Generating AC is easier than DC, AC can produce electromagnetic induction which is useful in several ways.
Question 8.
What is the ground connection?
Answer:
A ground connection is a safety feature. The metal bodies of all electrical appliances are connected to the ground by a third wire, apart from the two wires used for electrical connection. The ground connection wire is green in colour, All the ground wires from various electrical sockets are connected together finally to a thick copper wire, hurried deep in the ground, so that excess current flows down instead of entering our body.
Question 9.
Write a short note on the different electrical circuits.
Answer:
There are two types of electrical circuits – Series circuit and Parallel circuit.
- Series circuit – A series circuit has only one path for electricity to flow from one point to another. The amount of electricity in the circuit is constant throughout the circuit. When electricity flows through the circuit, there will be no fluctuation in its speed.
- Parallel circuit – A parallel circuit has multiple paths for electricity to flow, horizontally and vertically. The components of the parallel circuit will have the same voltage across their ends.
Question 10.
What is the difference between electromagnetic force and potential difference?
Answer:
The e.m.f. refers to the voltage developed across the terminals of an electrical source when it does not produce current in the circuit.
Potential difference refers to the voltage developed between any two points in an electric circuit when there is current in the circuit.
II. Long Answers Questions.
Question 1.
Draw and explain the electric circuit diagram.
Answer:
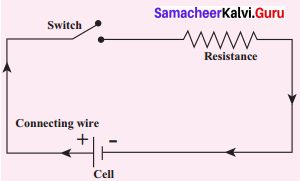
To represent an electrical wiring or solve problem involving electric circuits, the circuit diagrams are made. The four main components of any circuits namely the,
- cell,
- connecting wire,
- switch and
- resistor or load are given above. In addition to the above many other electrical components are also used in an actual circuit. A uniform system of symbols has been evolved to describe them. It is like learning a sign language, but useful in understanding circuit diagrams.
![]()
Question 2.
What is the magnetic effect of electricity?
Answer:
A wire or a conductor carrying current develops a magnetic field perpendicular to the direction of the flow of current. This is called magnetic effect of current. The discovery of the scientist Oersted and the ‘right hand thumb rule’ are detailed in the chapter on Magnetism and Electromagnetism in this book. Direction of current is shown by the right hand thumb and the direction of magnetic field is shown by other fingers of the same right hand.
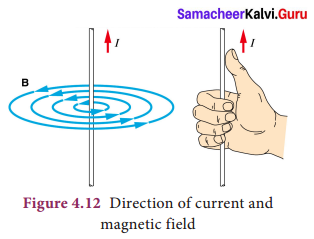
Question 3.
Explain fuse.
Answer:

A fuse is another safety mechanism which works on the joule heating principle. Fuse is a wire made up of a Nickel and Chromium alloy which has a definite melting point. If current passes through the fuse beyond a particular desired value, the excess heat produced melts the fuse wire, thus the electrical connection is cut-off. Fuse has to be kept in tight a ceramic enclosure to avoid the melting heat from producing fire accidents.
Question 4.
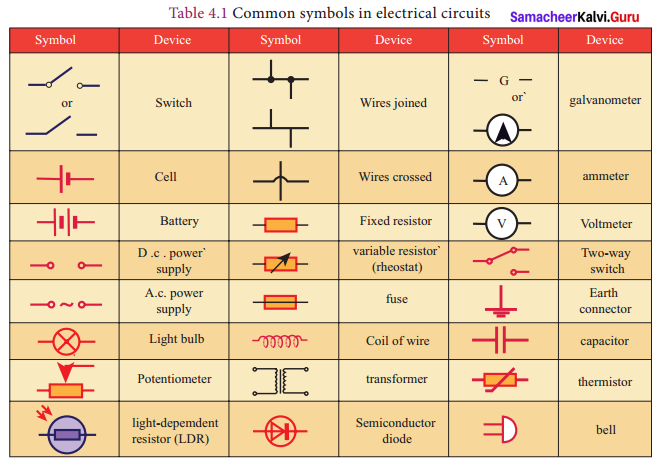
Name any ten symbols with a diagram.
Answer: