You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Set Language Ex 1.5
Question 1.
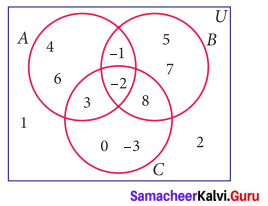
Using the adjacent venn diagram, find the following sets:
(i) A – B
(ii) B – C
(iii) A’ ∪ B’
(vi) A’ ∩ B’
(v) (B ∪ C)’
(vi) A – (B ∪ C)
(vii) A – (B ∩ C)
Solution:
(i) A – B = {3, 4, 6}
(ii) B – C = {-1, 5, 7}
(iii) A’ ∪ B’
A’ = {1, 2, 0, -3, 5, 7, 8}
B’ = {-3, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6)
A’ ∪ B’ = {-3, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8)
(iv) A’ ∩ B’
A’ ∩ B’ = {-3, 0, 1, 2}
(v) B ∪ C = {-3, -2, -1, 0, 3, 5, 7, 8}
(B ∪ C)’ = U – (B ∪ C)
= {-3, -2, -1, 0, 1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} – {-3, -2, -1, 0, 3, 5, 7, 8}
(B ∪ C)’ = {1, 2, 4, 6}
(vi) A – (B ∪ C) = {-2, -1, 3, 4,6} – {-3, -2, -1, 0, 3, 5, 7, 8} = {4, 6}
A – (B ∩ C)
B ∩ C = {-2, 8}
A- (B ∩ C) = {-2, -1, 3, 4, 6} – {-2, 8} = {-1, 3, 4, 6}
Question 2.
If K = {a, b, d, e,f}, L = {b, c, d, g} and M {a, b, c, d, h} then find the following:
(i) K ∪ (L ∩ M)
(ii) K ∩ (L ∪ M)
(iii) (K ∪ L) ∩ (K ∪ M)
(iv) (K ∩ L) ∪ (K ∩ M) and verify distributive laws.
Solution:
K = {a, b, d, e, f}, L = {b, c, d, g} and M {a, b, c, d, h}
(i) K ∪ (L ∩ M)
L ∩ M = {b, c, d, g} ∩ {a, b, c, d, h} = {b, c, d}
K ∪ (L ∩ M) = {a, b, d, e, f } ∪ {b, c, d) = {a, b, c, d, e, f}
(ii) K ∩(L ∪ M)
L ∪ M = {a, b, c, d, g, h}
K ∩ (L ∪ M) = {a, b, d, e, f} ∩ {a, b, c, d, g, h} = {a, b, d}
(iii) (K ∪ L) ∩ (K ∪ M)
K ∪ L = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g}
K ∪ M = {a, b, c, d, e, f, h}
(K ∪ L) ∩ (K ∪ M) = {a, b, c, d, e,f}
(iv) (K ∩ L) ∪ (K ∩ M)
(K ∩ L) = {b, d)
(K ∩ M) = {a,b,d}
(K ∩ L) ∪ (K ∩ M) = {b, d} ∪ {a, b, d} = {a, b, d}
Distributive laws
K ∪ (L ∩ M) = (K ∪ L) ∩ (K ∪ M)
{a, b, c, d, e, f) = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g} ∩ {a, b, c, d, e, f, h}
= {a, b, c, d, e, f}
Thus Verified.
K ∩ (L ∪ M) = (K ∩ L) ∪ (K ∩ M)
{a, b, d} = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g} ∪ {a, b, c, d, e, f, h}
= {a, b, d}
Thus Verified.
Question 3.
If A = {x : x ∈ Z, -2 < x ≤ 4}, B = {x : x ∈ W, x ≤ 5}, C ={-4, -1, 0, 2, 3, 4}, then verify A ∪ (B ∩ C) = (A ∪ B) ∩ (A ∪ C).
Solution:
A = {x : x ∈ Z, -2 < x ≤ 4} = {-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4}
B = {x : x ∈ W, x ≤ 5} = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
C = {-4, -1, 0, 2, 3, 4}
A ∪ (B ∩ C)
B ∩ C = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} ∩ {-4, -1, 0, 2, 3, 4} = {0, 2, 3, 4}
A ∪ (B ∩ C) = {-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4} ∪ (0, 2, 3, 4} ={-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4} …………. (1)
(A ∪ B) ∩ (A ∪ C)
A ∩ B = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4}
A ∩ C = {-1, 0, 2, 3, 4}
(A ∩ B) ∪ (A ∩ C) = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4} ∪ {-1, 0, 2, 3, 4}= {-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4} …………. (2)
From (1) and (2), it is verified that
A ∪ (B ∩ C) = (A ∪ B) ∩ (A ∪ C)
![]()
Question 4.
Verify A ∪ (B ∩ C) = (A ∪ B) ∩ (A ∪ C) using Venn diagrams.
Solution:
L.H.S A ∪ (B ∩ C)
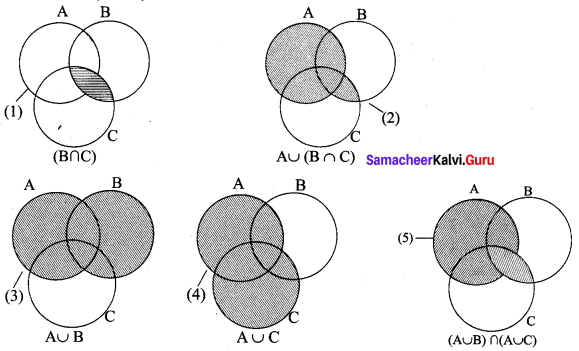
From (2) and (5), it is verified that A ∪ (B ∩ C) = (A ∪ B) ∩ (A ∪ C)
Question 5.
If A = {b, c, e, g, h}, B = {a, c, d, g, i} and C = {a, d, e, g, h}, then show that A – (B ∩ C) = (A – B) ∪ (A – C).
Solution:
A = {b, c, e, g, h}
B = {a, c, d, g, i}
C = {a, d, e, g, h}
B ∩ C = {a, d, g}
A – (B ∩ C) = {b, c, e, g, h} – {a, d, g} = {b, c, e, h} ……..… (1)
A- B = {b, c, e, g, h} – {a, c, d, g, i} = {b, e, h}
A – C = {b, c, e, g, h} – {a, d, e, g, h} = {b, c}
(A – B) ∪ (A – C) = {b, c, e, h} ………..… (2)
From (1) and (2) it is verified that
A – (B ∩ C) = (A – B) ∪ (A – C)
Question 6.
If A = {x : x = 6 n ∈ W and n < 6}, B = {x : x = 2n, n ∈ N and 2 < n ≤ 9} and C = {x : x = 3n, n ∈ N and 4 ≤ n < 10}, then show that A – (B ∩ C) = (A – B) ∪ (A – C)
Solution:
A = {x : x = 6n, n ∈ W, n < 6}
x = 6n
n = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
⇒ x = 6 × 0 = 0
x = 6 × 1= 6
x = 6 × 2 = 12
x = 6 × 3 = 18
x = 6 × 4 = 24
x = 6 × 5 = 30
∴ A = {0, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30}
B = { x : x = 2n, n ∈ N, 2 < n ≤ 9}
n = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
x = 2 n
⇒ x = 2 × 3 = 6
2 × 4 = 8
2 × 5 = 10
2 × 6 = 12
2 × 7 = 14
2 × 8 = 16
2 × 9 = 18
∴ B {6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18}
C = { x : x = 3n, n ∈ N, 4 ≤ n < 10}
N = { 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
x = 3 × 4 = 12
⇒ x = 3 × 5 = 15
x = 3 × 6 = 18
x = 3 × 7 = 21
x = 3 × 8 = 24
x = 3 × 9 = 27
x = 2 × 9 = 18
∴ C = {12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27}
A – (B ∩ C) = (A – B) ∪ (A – C)
L.H.S R.H.S
B ∩ C = {12,18}
A – (B ∩ C) = {0, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30} – {12, 18} = {0, 6, 24, 30} ……….…. (1)
(A – B) = {0, 24, 30}
(A – C) = {0, 6, 30}
(A – B) ∪ (A – C) = {0, 6, 24, 30} …………. (2)
From (1) and (2), it is verified that
A – (B ∩ C) = (A – B) ∪ (A – C).
Question 7.
If A = {-2, 0, 1, 3, 5}, B = {-1, 0, 2, 5, 6} and C = {-1, 2, 5, 6, 7}, then show that A – (B ∪ C) = (A – B) ∩ (A – C).
Solution:
A = {-2, 0, 1, 3, 5},
B = {-1, 0, 2, 5, 6}
C ={-1, 2, 5, 6, 7}
B ∪ C = {-1, 0, 2, 5, 6, 7}
A – (B ∪ C) = {-2, 1, 3} …………. (1)
(A – B) = {-2, 1, 3}
(A – C) = {-2, 0, 1, 3}
(A – B) ∩ (A – C) = {-2, 1, 3} ………..… (2)
From (1) and (2), it is verified that . A – (B ∪ C) = (A – B) ∩ (A – C)
![]()
Question 8.
if A={y: y = \(\frac{a+1}{2}\), a ∈ W and a ≤ 5},B = {y: y=\(\frac{2 n-1}{2}\),n ∈ W and n < 5} and C={−1,\(-\frac{1}{2}\), 1, \(\frac{3}{2}\), 2} then show that A – (B ∪ C) = (A – B) ∩ (A – C).
Solution:
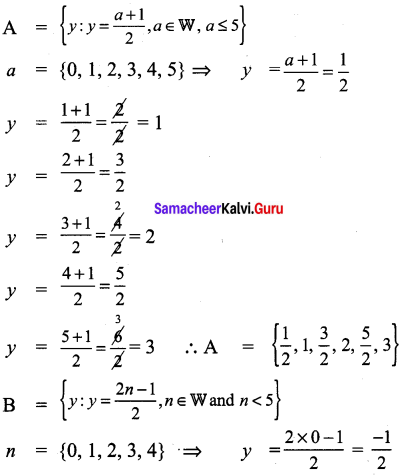
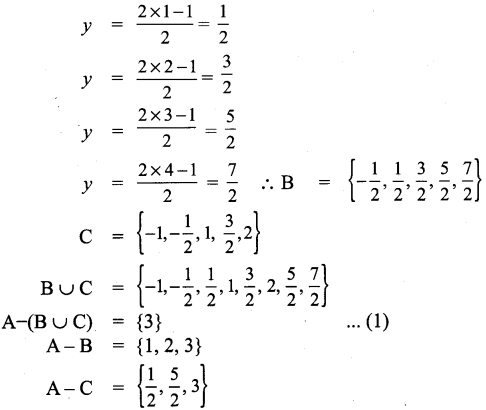
(A – B) ∩ (A – C) = {3} …………. (2)
From (1) and (2), it is verified that A – (B ∪ C) = (A – B) ∩ (A – C).
Question 9.
Verify A – (B ∩ C) = (A – B) ∪ (A – C) using Venn diagrams.
Solution:
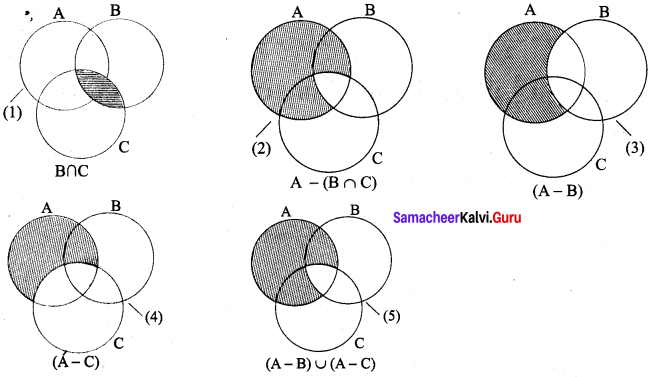
∴ A – (B ∩ C) = (A – B) ∪ (A – C)
Hence it is proved.
Question 10.
If U = {4, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 15, 16}, A = {7, 8, 11, 12} and B = {4, 8, 12, 15}, then verify De Morgan’s Laws for complementation.
U = {4, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 15, 16}
A = {7, 8, 11, 12}, B = {4, 8, 12, 15}
De Morgan’s Laws for complementation.
(A ∪ B)’ = A’ ∩ B’
A ∪ B = {4, 7, 8, 11, 12, 15}
(A ∪ B)’ = {4, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 15, 16} – {4, 7, 8, 11, 12, 15}
= {10, 16} ……………. (1)
A’ = {4, 10, 15, 16}
B’ = {7, 10, 11, 16}
A’ ∩ B’ = {10, 16} ………………(2)
From (1) and (2) it is verified that (A ∪ B)’ = A’ ∩ B’.
![]()
Question 11.
Verify (A ∩ B)’ = A’ ∪ B’ using Venn diagrams.
Solution:
(A ∩ B)’ = A’ ∪ B’
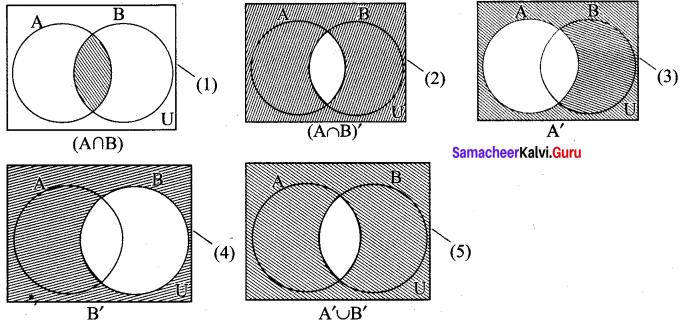
(2) = (5)
∴ (A ∩ B)’ = A’ ∪ B’