Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Chapter 3 Solutions Theories of Employment and Income
Students can Download Economics Chapter 3 Theories of Employment and Income Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Solutions Chapter 3 Theories of Employment and Income
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Theories of Employment and Income Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part – A
Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1.
Every able bodied person who is willing to work at the prevailing wage rate is employed called as –
(a) Full employment
(b) Under employment
(c) Unemployment
(d) Employment opportunity
Answer:
(a) Full employment
Question 2.
Structural unemployment is a feature in a –
(a) Static society
(b) Socialist society
(c) Dynamic society
(d) Mixed economy
Answer:
(c) Dynamic society
![]()
Question 3.
In disguised unemployment, the marginal productivity of labour is –
(a) Zero
(b) One
(c) Two
(d) Positive
Answer:
(a) Zero
Question 4.
The main concention of the Classical Economic Theory is –
(a) Under employment
(b) Economy is always in the state of equilibrium
(c) Demand creates its supply
(d) Imperfect competition
Answer:
(b) Economy is always in the state of equilibrium
Question 5.
J.B. Say is a –
(a) Neo Classical Economist
(b) Classical Economist
(c) Modem Economist
(d) New Economist
Answer:
(b) Classical Economist
![]()
Question 6.
According to Keynes, which type of unemployment prevails in capitalist economy?
(a) Full employment
(b) Voluntary unemployment
(c) Involuntary unemployment
(d) Under employment
Answer:
(d) Under employment
Question 7.
The core of the classical theory of employment is –
(a) Law of Diminishing Return
(b) Law of Demand
(c) Law of Markets
(d) Law of Consumption
Answer:
(c) Law of Markets
![]()
Question 8.
Keynes attributes unemployment to –
(a) A lack of effective supply
(b) A lock of effective demand
(c) Alack of both
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) A lock of effective demand
Question 9.
…………………… Flexibility brings equality between saving and investment.
(a) Demand
(b) Supply
(c) Capital
(d) Interest
Answer:
(d) Interest
Question 10.
……………………. theory is a turning point in the development of modem economic theory.
(a) Keynes’
(b) Say’s
(c) Classical
(d) Employment.
Answer:
(a) Keynes’
Question 11.
The basic concept used in Keynes Theory of Employment and Income is –
(a) Aggregate demand
(b) Aggregate supply
(c) Effective demand
(d) Marginal Propensity Consume
Answer:
(c) Effective demand
![]()
Question 12.
The component of aggregate demand is –
(a) Personal demand
(b) Government expenditure
(c) Only export
(d) Omli import
Answer:
(b) Government expenditure
Question 13.
Aggregate supply is equal to –
(a) C +1 + G
(b) C + S + G + (x – m)
(c) C + S + T + (x-m)
(d) C + S + T + Rf
Answer:
(d) C + S + T + Rf
Question 14.
Keynes theory pursues to replace laissez faire by –
(a) No government intervention
(b) Maximum intervention
(c) State intervention in certain situation
(d) Private sector intervention
Answer:
(c) State intervention in certain situation
Question 15.
In Keynes theory of employment and income, ……………………… is the basic cause of economic depression.
(a) Less production
(b) More demand
(c) Inelastic supply
(d) Less aggregate demand in relation to productive capacity.
Answer:
(d) Less aggregate demand in relation to productive capacity.
![]()
Question 16.
Classical theory advocates –
(a) Balanced budget
(b) Unbalanced budget
(c) Surplus budget
(d) Deficit budget
Answer:
(a) Balanced budget
Question 17.
Keynes theory emphasized on ……………………….. equilibrium.
(a) Very short run
(b) Short run
(c) Very long run
(d) Long run
Answer:
(b) Short run
Question 18.
According to classical theory, rate of interest is a reward for –
(a) Investment
(b) Demand
(c) Capital
(d) Saving
Answer:
(d) Saving
Question 19.
In Keynes theory, the demand for and supply of money are determined by –
(a) Rate of interest
(b) Effective demand
(c) Aggregate demand
(d) Aggregate supply
Answer:
(a) Rate of interest
![]()
Question 20.
Say’s law stressed the operation of ……………………… in the economy.
(a) Induced price mechanism
(b) Automatic price mechanism
(c) Induced demand
(d) Induced investment
Answer:
(b) Automatic price mechanism
Part – B
Answer The Following Questions In One or Two Sentences.
Question 21.
Define full employment?
Answer:
Full employment refers to a situation in which every able bodied person who is willing to work at the prevailing wage rate, is employed. In other words full employment means that persons who are willing to work and able to work must have employment or a job.
Question 22.
What is the main feature of rural unemployment?
Answer:
- India’s rural economy has both unemployment and underemployment.
- The major feature of rural unemployment is the existence of unemployment in the form of disguised unemployment and seasonal unemployment.
- In agriculture and agro based industries like sugar, production activities are carried out only in some seasons.
![]()
Question 23.
Give short note on frictional unemployment?
Answer:
Frictional Unemployment (Temporary Unemployment):
- Frictional unemployment arises due to imbalance between supply of labour and demand for labour.
- This is because of immobility of labour, lack of necessary skills, break down of machinery, shortage of raw materials etc.
- The persons who lose jobs and in search of jobs are also included under frictional unemployment.
Question 24.
Give reasons for labour retrenchment at present situation?
Answer:
- Modem technology being capital intensive requires less labourers and contributes to ’ technological unemployment.
- Now a days, invention and innovations lead to the adoption of new techniques there by the existing workers are retrenched.
- Labour saving devices are responsible for technological unemployment.
Question 25.
List out the assumptions of Say’s law?
Answer:
The Say’s Law of market is based on the following assumptions:
- No single buyer or seller of commodity or an input can affect price.
- Full employment.
- People are motivated by self interest and self – interest determines economic decisions.
- The laissez faire policy is essential for an automatic and self adjusting process of full employment equilibrium. Market forces determine everything right.
- There will be a perfect competition in labour and product market.
- There is wage-price flexibility.
- Money acts only as a medium of exchange.
- Long – run analysis.
- There is no possibility for over production or unemployment.
![]()
Question 26.
What is effective demand?
Answer:
- The starting point of Keynes theory of employment and income is the principle of effective demand.
- Effective demand denotes money actually spent by the people on products of industry.
- The money which entrepreneurs receive is paid in the form of rent, wages, interest and profit.
- Therefore effective demand equals national income.
Question 27.
What are the components of aggregate supply?
Answer:
Aggregate demand has the following four components:
- Consumption demand
- Investment demand
- Government expenditure and
- Net Export (export – import)
Part – C
Answer The Following Questions In A Paragraph.
Question 28.
Explain the following in short:
- Seasonal unemployment
- Frictional unemployment
- Educated unemployment
Answer:
Seasonal Unemployment:
- This type of unemployment occurs during certain seasons of the year.
- In agriculture and agro based industries like sugar,production activities are carried out only in some seasons.
- These industries offer employment only during that season in a year. Therefore people may remain unemployed during the off season.
- Seasonal unemployment happens from demand side also; for example ice cream industry, holiday resorts etc.
Frictional Unemployment (Temporary Unemployment):
- Frictional unemployment arises due to imbalance between supply of labour and demand for labour.
- This is because of immobility of labour, lack of necessary skills, break down of machinery, shortage of raw materials etc.
- The persons who lose jobs and in search of jobs are also included under frictional unemployment.
Educated Unemployment:
- Sometimes educated people are underemployed or unemployed when qualification does not match the job.
- Faulty education system, lack of employable skills, mass student turnout and preference for white collar jobs are highly responsible for educated unemployment in India.
![]()
Question 29.
According to classical theory of employment, how wage reduction solves the problem of unemployment? Diagrammatically explain?
Answer:
The classical theory of employment assumes that the economy operates at the level of full employment without inflation in the long period. It also assumes that wages and prices of goods are flexible and the competitive market exists in the economy (laissez – faire economy). According to the classical theory of employment, full employment condition can be achieved by cutting down the wage rate. Unemployment would be eliminated when wages are determined by the mechanism of economy itself. The following figure shows the relationship between wage rate and employment:
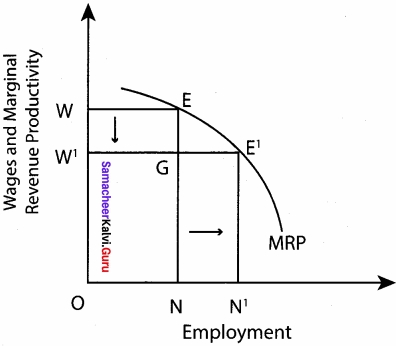
In the figure, when the wage rate is OW, then the employment is ON. As the wage rate is reduced to OW1, then the employment has increased to ON1. Prof. Pigou has taken this theory as base for developing the solution of unemployment problem.
Question 30.
Write short note on the implications of Say’s law?
Answer:
Implications of Say’s Law:
- There is no possibility for over production or unemployment.
- If there exist unutilized resources in the economy, it is profitable to employ them up to the point of full employment. This is true under the condition that factors are willing to accept rewards on a par with their productivity.
- As automatic price mechanism operates in the economy, there is no need for government intervention. (However, J.M. Keynes emphasized the role of the State)
- Interest flexibility brings about equality between saving and investment.
- Money performs only the medium of exchange function in the economy, as people will not hold idle money.
![]()
Question 31.
Explain Keynes’ theory in the form of flow chart?
Answer:
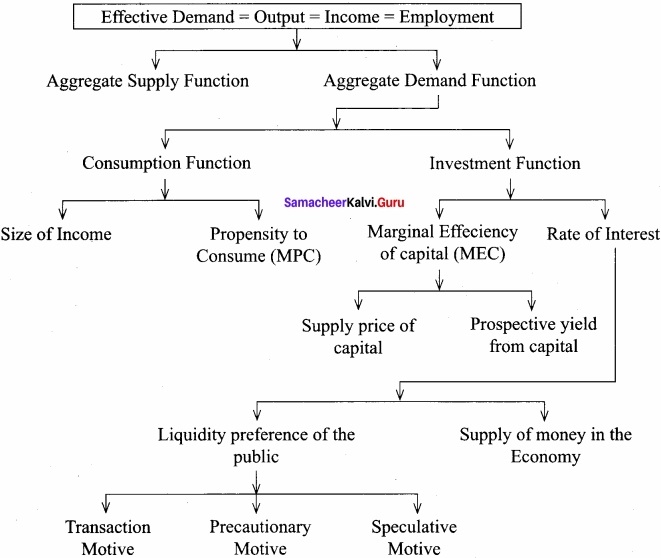
Question 32.
What do you mean by aggregate demand? Mention its components?
Answer:
- The aggregate demand is the amount of money which entrepreneurs expect to get by selling the output produced by the number of labourers employed.
- Therefore, it is the expected income or revenue from the sale of output at different levels of employment.
- Aggregate demand has the following four components:
- Consumption demand
- InvestmenTdemand
- Government expenditure and
- Net Export (export – import)
![]()
Question 33.
Explain about aggregate supply with the help of diagram?
Answer:
- Aggregate supply function is an increasing function of the level of employment.
- Aggregate supply refers to the value of total output of goods and services produced in an economy in a year.
- In other words, aggregate supply is equal to the value of national product, i.e., national income.
- Aggregate Supply = C + S + T + Rf = Aggregate income generated in the economy.
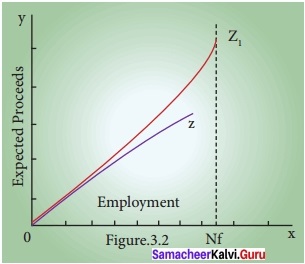
- The following figure shows the shape of the two aggregate supply curves drawn for the assumption of fixed money wages and variable wages.
Aggregate Supply Curve
- Z curve is linear where money wages remains fixed; Z<sub>1</sub> curve is non – linear since wage rate increases with employment.
- When full employment level of Nf is reached it is impossible to increase output by employing more men.
- So aggregate supply curve becomes inelastic (Vertical straight line).
- The slope of the aggregate supply curve depends on the relation between the employment and productivity.
- Based upon this relation, the aggregate supply curve can be expected to slope upwards.
- In reality the aggregate supply curve will be like Z1
- Therefore, the aggregate supply depends on the relationship between price and wages.
Question 34.
Write any five differences between classism and Keynesianism?
Answer:
Comparison of Classicism and Keynesianism
Keynesianism:
- Short – run equilibrium Saving is a vice
- The function of money is a medium of exchange on the one side and a store of value on the other side.
- Macro approach to national problems
- State intervention is advocated
Classicism:
- Long – run equilibrium
- Saving is a social virtue
- The function of money is to act as a medium of exchange.
- Micro foundation to macro problems
- Champions of Laissez – fair policy
Part – D
Answer The Following Questions In One Page.
Question 35.
Describe the types of unemployment?
Answer:
The following are the types of unemployment.
Types of unemployment:
- Cyclical Unemployment
- Frictional Unemployment
- Technical Unemployment
- Disguised Unemployment
- Seasonal Unemployment
- Educated Unemployment
- Structural Unemployment
1. Cyclical Unemployment:
- This unemployment exists during the downturn phase of trade cycle in the economy.
- In a business cycle during the period of recession and depression, income and output fall leading to widespread unemployment.
- It is caused by deficiency of effective demand.
- Cyclical unemployment can be cured by public investment or expansionary monetary policy.
2. Seasonal Unemployment:
- This type of unemployment occurs during certain seasons of the year.
- In agriculture and agro based industries like sugar, production activities are carried out only in some seasons.
- These industries offer employment only during that season in a year. Therefore people may remain unemployed during the off season.
- Seasonal unemployment happens from demand side also; for example ice cream industry, holiday resorts etc.
3. Frictional Unemployment (Temporary Unemployment):
- Frictional unemployment arises due to imbalance between supply of labour and demand for labour.
- This is because of immobility of labour, lack of necessary skills, break down of machinery, shortage of raw materials etc.
- The persons who lose jobs and in search of jobs are also included under frictional unemployment.
4. Educated Unemployment:
- Sometimes educated people are underemployed or unemployed when qualification does not match the job.
- Faulty education system, lack of employable skills, mass student turnout and preference for white collar jobs are highly responsible for educated unemployment in India.
5. Technical Unemployment:
- Modem technology being capital intensive requires less labourers and contributes to technological unemployment.
- Now a days, invention and innovations lead to the adoption of new techniques there by the existing workers are retrenched.
- Labour saving devices are responsible for technological unemployment.
6. Structural Unemployment:
- Structural unemployment is due to drastic change in the structure of the society.
- Lack of demand for the product or shift in demand to other products cause this type of unemployment.
- For example rise in demand for mobile phones has adversely affected the demand for cameras, tape recorders etc.
- So this kind of unemployment results from massive and deep rooted changes in economic structure.
7. Disguised Unemployment:
- Disguised unemployment occurs when more people are than what is actually required.
- Even if some workers are withdrawn, production does not suffer.
- This type of unemployment is found in agriculture.
- A person is said to be disguisedly by unemployed if his contribution to output is less than what he can produce by working for normal hours per day.
- In this situation, marginal productivity of labour is zero or less or negative.
![]()
Question 36.
Critically explain Say’s law of market?
Answer:
Criticisms of Say’s Law:
The following are the criticisms against Say’s law:
- According to Keynes, supply does not create its demand. It is not applicable where demand does not increase as much as production increases.
- Automatic adjustment process will not remove unemployment. Unemployment can be removed by increase in the rate of investment.
- Money is not neutral. Individuals hold money for unforeseen contingencies while businessmen keep cash reserve for future activities.
- Say’s law is based on the proposition that supply creates its own demand and there is no over production. Keynes said that over production is possible.
- Keynes regards full employment as a special case because there is under – employment in capitalist economies.
- The need for state intervention arises in the case of general over production and mass unemployment.
Question 37.
Narrate the equilibrium between ADF and ASF with diagram? Equilibrium between ADF and ASF?
Answer:
- Under the Keynes theory of employment, a simple two sector economy consisting of the household sector and the business sector is taken to understand the equilibrium between ADF and ASF.
- All the decisions concerning consumption expenditure are taken by the individual households, while the business firms take decisions concerning investment.
- It is also assumed that consumption function is linear and planned investment is autonomous.
- There are two approaches to determination of the equilibrium level of income in Keynesian theory. These are:
- Aggregate demand – Aggregate supply approach
- Saving – Investment approach –
- In this chapter, out of these two, aggregate demand and aggregate supply approach is alone explained to understand the determination of equilibrium level of income and employment.
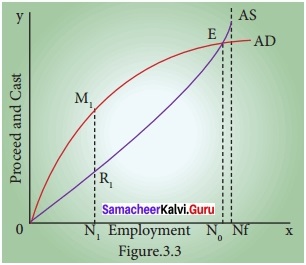
- The concept of effective demand is more clearly shown in the figure.
- In the figure, the aggregate demand and aggregate supply reach equilibrium at point E. The employment level is N0 at that point.
- At ON1 employment, the aggregate supply is N, Rr But they are able to produce M1 N1 The expected level of profit is M1, R1
- To attain this level of profit, entrepreneurs will employ more labourers.
- The tendency to employ more labour will stop once they reach point E.
- At all levels of employment beyond, ON0, the aggregate demand curve is below the aggregate supply curve indicating loss to the producers.
- Hence they will never employ more than ON0 labour.
- Thus effective demand concept becomes a crucial point in determining the equilibrium level of output in the capitalist economy or a free market economy in the Keynesian system.
- It is important to note that the equilibrium level of employment need not be the full employment level (N<sub>1</sub>) from the Figure, it is understood that the difference between N0 – N0 is the level of unemployment.
- Thus the concept of effective demand becomes significant in explaining the under employment equilibrium.
Question 38.
Explain the differences between classical theory and Keynes theory?
Answer:
Keynesianism:
- Short – run equilibrium
- Saving is a vice
- The function of money is a medium of exchange on the one side and a store of value on the other side.
- Macro approach to national problems
- State intervention is advocated.
- Applicable to all situations – full employment and less than full employment.
- Capitalism has inherent contradictions
- Budgeting should be adjusted to the requirements of economy.
- The equality between saving and investment is advanced through changes in income.
- Rate of interest is determined by the demand for and supply of money.
- Rate of interest is a flow.
- Demand creates its own supply.
- Rate of interest is a reward for parting with liquidity.
Classicism:
- Long – run equilibrium
- Saving is a social virtue.
- The function of money is to act as a medium of exchange
- Micro foundation to macro problems
- Champions of Laissez – fair policy
- Applicable only to the full employment situation.
- Capitalism is well and good.
- Balanced budget
- The equality between saving and investment is achieved through changes of rate of interest.
- Rate of interest is determined by saving and investment.
- Rate of interest is a stock.
- Supply creates its own demand.
- Rate of interest is a reward for saving.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Theories of Employment and Income Addtional Questions and Answers
Part – A
I. Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1.
Who is one of the greatest and most influential economist?
(a) J.M. Keynes
(b) Adam Smith
(c) Marshall
(d) Simon Kuznets
Answer:
(a) J.M. Keynes
Question 2.
Keynes book “The General theory of Employment, Interest and Money” published in –
(a) 1926
(b) 1936
(c) 1946
(d) 1956
Answer:
(b) 1936
![]()
Question 3.
The total stock of money circulating in an Economy is called –
(a) Money
(b) Capital
(c) Money Supply
(d) Finance
Answer:
(c) Money Supply
Question 4.
The …………………… function depends upon Income of the people and marginal propensity to consume?
(a) demand
(b) consumption
(c) supply
(d) marginal
Answer:
(b) consumption
Question 5.
Every economy in the world aims at attaining the level of –
(a) full employment
(b) under employment
(c) un employment
(d) employment opportunity
Answer:
(a) full employment
Question 6.
…………………… is an increasing function of the level of employment –
(a) Aggregate supply function
(b) Aggregate demand function
(c) Aggregate consumption function
(d) Aggregate consumption expenditure
Answer:
(a) Aggregate supply function
![]()
Question 7.
Effective demand signifies the money spent on consumption of goods and services and on –
(a) capital
(b) investment
(c) profit
(d) finance
Answer:
(b) investment
Question 8.
Who has given importance to the concept of liquidity preference?
(a) Kuznet
(b) Marshall
(c) Keynes
(d) Adam Smith
Answer:
(c) Keynes
Question 9.
…………………….. was a French Economist and an Industrialist?
(a) J.B. Say
(b) Keynes
(c) Adam Smith
(d) David Ricardo
Answer:
(a) J.B. Say
Question 10.
Frictional unemployment another name is called –
(a) Educated unemployment
(b) Seasonal unemployment
(c) Temporary unemployment
(d) Technical unemployment
Answer:
(c) Temporary unemployment
![]()
Question 11.
Discussed unemployment is mostly found in –
(a) agriculture
(b) sericulture
(c) industry
(d) architecture
Answer:
(a) agriculture
Question 12.
The main reason for massive unemployment is poor –
(a) economic planning
(b) educational planning
(c) military planning
(d) man power planning
Answer:
(d) man power planning
Question 13.
The Employment Assurance Scheme was launched in the year –
(a) 1983
(b) 1993
(c) 2003
(d) 2013
Answer:
(b) 1993
Question 14.
Cyclical unemployment is caused by …………………………. cycles.
(a) business
(b) money
(c) trade
(d) finance
Answer:
(c) trade
![]()
Question 15.
The problem of rural unemployment can be solved only by ………………………….. agriculture.
(a) modernising
(b) agro based
(c) innovative
(d) new method followed
Answer:
(a) modernising
Question 16.
Unemployment is classified as voluntary unemployment and –
(a) involuntary unemployment
(b) cyclical unemployment
(c) rural unemployment
(d) seasonal unemployment
Answer:
(b) cyclical unemployment
Question 17.
Existence of Joint Family System in India promotes –
(a) educational unemployment
(b) disguised unemployment
(c) seasonal unemployment
(d) voluntary unemployment
Answer:
(b) disguised unemployment
![]()
Question 18.
Educated and skilled persons who may not accept casual work. This is called ………………………. unemployment.
(a) closed
(b) open
(c) seasonal
(d) disguised unemployment
Answer:
(b) open
Question 19.
………………………. law of market was the basis for assuming the situation of full employment.
(a) J.B. Say
(b) Keynes
(c) Marshall
(d) Lemer
Answer:
(a) J.B. Say
Question 20.
The aggregate effective demand would increase the level of –
(a) unemployment
(b) employment
(c) cyclical unemployment
(d) open unemployment
Answer:
(b) employment
Question 21.
…………………. refers to the labour force of a country.
(a) Employment
(b) Unemployment
(c) Full employment
(d) Open employment
Answer:
(c) Full employment
![]()
Question 22.
…………………. means that persons who are willing to work and able to work must have employment or a job?
(a) Full employment
(b) Unemployment
(c) Educational unemployment
(d) Seasonal unemployment
Answer:
(a) Full employment
Question 23.
………………….. is the principle of effective demand?
(a) Profit
(b) Income
(c) Money
(d) Interest
Answer:
(a) Profit
Question 24.
When goods are produced by firms in the economy, they pay reward to the factors of the production is called –
(a) J.M. Keynes
(b) Adam Smith
(c) J.B. Say
(d) Ricardo
Answer:
(c) J.B. Say
![]()
Question 25.
…………………….. defines “Full employment as that level of employment at which any further increase in spending would resort in an inflationary spiral of wages and prices”
(a) Lemer
(b) J.M. Keynes
(c) J.B. Say
(d) Adam Smith
Answer:
(a) Lemer
II. Match the following and choose the correct answer by using codes given below
Question 1.
A. Full employment – (i) Qualified job
B. Educated unemployment – (ii) Deficiency of effective demand
C. Cyclical unemployment – (iii) During season of the year
D. Seasonal unemployment – (iv) Learner
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (ii) B (iv) C (i) D (iii)
(c) A (iv) B (i) C (ii) D (iii)
(d) A (iii) B (iv) C (i) D (ii)
Answer:
(c) A (iv) B (i) C (ii) D (iii)
Question 2.
A. Public Investment – (i) Temporary unemployment
B. Production activities only in Some seasons – (ii) Deficiency of effective demand
C. Frictional unemployment – (iii) During season of the year
D. Educated unemployment – (iv) Learner
Codes:
(a) A (ii) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (iii) B (ii) C (iv) D (i)
(c) A (i) B (iii) C (ii) D (iv)
(d) A (iv) B (i) C (iii) D (ii)
Answer:
(a) A (ii) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
![]()
Question 3.
A. ED – (i) Income of the people
B. ADF – (ii) Y = C + I = Output = Employment
C. ASF – (iii) C + I + G + (X – M)
D. CF – (iv) C + S + T + Rf = Aggregate Income generated in the economy
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (iii) B (i) C (iv) D (i)
(c) A (iv) B (ii) C (i) D (iii)
(d) A (iv) B (iii) C (iv) D (i)
Answer:
(d) A (iv) B (iii) C (iv) D (i)
![]()
Question 4.
A. Keynes concept – (i) Aggregate spending
B. Demand – (ii) Liquidity preference
C. Aggregate supply – (iii) To spend on domestic output
D. Aggregate demand – (iv) The value of national product
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (ii) B (i) C (iv) D (iii)
(c) A (iii) B (iv) C (ii) D (i)
(d) A (iv) B (iii) C (i) D (ii)
Answer:
(b) A (ii) B (i) C (iv) D (iii)
![]()
Question 5.
A. Keynesianism – (i) Long run – equilibrium
B. Classicism – (ii) Short run – equilibrium
C. Keynesianism – (iii) State intervention is advocated
D. Classicism – (iv) Saving is a vice
Codes:
(a) A (ii) B (i) C (iv) D (iii)
(b) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(c) A (iii) B (iv) C (ii) D(i)
(d) A (iv) B (iii) C (i) D (ii)
Answer:
(a) A (ii) B (i) C (iv) D (iii)
III. State whether the statements are true or false
Question 1.
(i) The function of money is a medium of exchange on the one side and a store of value on the other side is called Keynesianism.
(ii) Macro approach to national problems.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
Question 2.
(i) Aggregate demand has the four components are consumption demand, investment demand, Government expenditure and Net export.
(ii) Aggregate demand refers to the required amount of labourers and materials to produce the neccessary output.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
![]()
Question 3.
(i) Keynesian theory is – Aggregate demand – Aggregate supply approach. Saving – Investment approach.
(ii) This approach explained the determination level of Income and employment.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
Question 4.
(i) Effective demand denotes money actually spent by the people on products of Industry and agriculture.
(ii) Effective demand equals to State Income.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
![]()
Question 5.
(i) “Supply creates its own Demand”.
(ii) The aggregate demand and aggregate supply reach equilibrium at point ‘E’.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
IV. Which of the following is correctly matched
Question 1.
(a) Seasonal unemployment – Type of unemployment
(b) Technical unemployment – Some season only
(c) Cyclical unemployment – Public capital
(d) Full employment – Not willing to job
Answer:
(a) Seasonal unemployment – Type of unemployment
Question 2.
(a) Frictional unemployment – Permanant
(b) Educated unemployment – White collar jobs
(c) Structural unemployment – In search job
(d) Disguised unemployment – Found in industry
Answer:
(b) Educated unemployment – White collar jobs
![]()
Question 3.
(a) Keynes – A general theory
(b) Aggregate supply – A level of money
(c) Keynesianism – Champions of Laissez – Faire
(d) Effective demand – Classical Economy
Answer:
(a) Keynes – A general theory
Question 4.
(a) Effective demand – Income Effective
(b) Aggregate demand – Money demand
(c) Say’s law – Supply creates own demand
(d) Aggregate supply – Money supply
Answer:
(c) Say’s law – Supply creates own demand
Question 5.
(a) J.B. Say – Industrialist
(b) Adam Smith – Classical Economist
(c) David Ricardo – Capitalist Economist
(d) Lemer – Socialist
Answer:
(a) J.B. Say – Industrialist
![]()
V. Which of the following is not correctly matched
Question 1.
(a) Say’s law of Market – Classical theory of Employment
(b) Adam Smith – Wealth of nations
(c) Keynes – The General theory of Employment, Interest and Money
(d) A.C. Pigou – French Economist
Answer:
(d) A.C. Pigou – French Economist
Question 2.
(a) Full Employment – Willing to work and able to work
(b) Unemployment – Cannot find suitable job
(c) Underemployment – Not fully utilized
(d) Disguised unemployment – More people not working
Answer:
(d) Disguised unemployment – More people not working
![]()
Question 3.
(a) Keynes – Liquidity preference
(b) Aggregate demand – Consumption demand
(c) Consumption function – Money supply
(d) Marginal effeciency of capital – Investment level
Answer:
(c) Consumption function – Money supply
Question 4.
(a) Effective demand – Y = C + I = Output = Employment
(b) Aggregate supply – C + S + T + Rf = Aggregate Income
(c) Aggregate demand – C + I + G + (X – M)
(d) Aggregate private saving – C + S + T
Answer:
(d) Aggregate private saving – C + S + T
![]()
Question 5.
(a) Keynesianism – Capitalism has inherant contradictions
(b) Classism – Capitalism well and good
(c) Keynesian theory – Saving – Investment approach
(d) Frictional – Full employment
Answer:
(d) Frictional – Full employment
VI. Pick the odd one out
Question 1.
Types of unemployment
(a) Cyclical unemployment
(b) Seasonal unemployment
(c) Frictional unemployment
(d) nature unemployment
Answer:
(d) nature unemployment
Question 2.
Classical theory was developed by –
(a) David Ricardo
(b) Adam Smith
(c) J.S. Mill
(d) J.B. Say
Answer:
(b) Adam Smith
![]()
Question 3.
The Say’s law of Market Assumptions are –
(a) No single buyer
(b) Full employment
(c) Money is not neutral
(d) Wage flexibility
Answer:
(c) Money is not neutral
Question 4.
Keynesianism is called –
(a) Short run equilibrium
(b) saving is social virtue
(c) Macro approach to national problems
(d) State intervention is advocated
Answer:
(b) Saving is social virtue
![]()
Question 5.
Classicism is called –
(a) Capatalism is well and good
(b) Balanced Budget
(c) savinf is vice
(d) Micro foundation to Macro problems
Answer:
(c) Saving is vice
VII. Assertion and Reason
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Modem technology being capital intensive requires less labourers, and contributes to technological unemployment.
Reason (R): Now – a – days invention and innovations lead to the adoption of new techniques there by the existing workers are retrenched.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are tme and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are tme but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is tme but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is tme .
Answer:
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are tme and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A): According to say, “when goods are produced by firms in the Economy”.
Reason (R): There was no single theory which could be labeled as classical theory of employment.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are tme and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Keynes book “The General theory of Employment, Interest and Money” published in 1916.
Reason (R): A turning point in the development of modem economic theory – Keynes.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Question 4.
Assertion (A): Aggregate supply function is increasing function of the level of employment.
Reason (R): Aggregate supply is only state product.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
![]()
Question 5.
Assertion (A): Keynesianism is Macro approach to national problems.
Reason (R): Keynesianism is state intervention is advocated.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are tme and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(.b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are tme but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is tme but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is tme
Answer:
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is tme
Part – B
Answer The Following Questions In One or Two Sentences
Question 1.
Write two approaches of the equilibrium level of Income in Keynesian theory?
Answer:
There are two approaches te determination of the equilibrium level of income in Keynesian theory. These are:
- Aggregate demand – Aggregate supply approach
- Saving – Investment approach
![]()
Question 2.
Define “Unemployment”?
Answer:
Unemployment:
When there are people, who are willing to work and able to work but cannot find suitable jobs.
Question 3.
Define “Marginal propensity to consume”?
Answer:
Marginal Propensity to Consume is the additional consumption due to an additional unit of income.
![]()
Question 4.
Write the types of unemployment?
Answer:
Types of unemployment:
- Cyclical Unemployment
- Frictional Unemployment
- Technical Unemployment
- Disguised Unemployment
- Seasonal Unemployment
- Educated Unemployment
- Structural Unemployment
Part – C
Answer The Following Questions In One Paragraph.
Question 1.
Explain the Aggregate Demand Function with Diagram?
Answer:
- In the Keynesian model, output is determined mainly by aggregate demand.
- The aggregate demand is the amount of money which entrepreneurs expect to get by selling the output produced by the number of labourers employed.
- Therefore, it is the expected income or revenue from the sale of output at different levels of employment.
- Aggregate demand has the following four components:
- Consumption demand
- Investment demand
- Government expenditure and
- Net Export (export – import)
- Aggregate demand has the following four components:
- The desired or planned demand (spending) is the amount that households, firms, the governments and the foreign purchasers would like to spend on domestic output.
- In other words, desired demand in the economy is the sum total of desired private consumption expenditure, desired investment expenditure, desired government spending and desired net exports (difference between exports and imports).
- Thus, the desired spending is called aggregate spending (demand), and can be expressed as:
AD = C + I + G + (X – M) - The diagram explains that aggregate demand price increases or decreases with an increase or decrease in the volume of employment.
- Aggregate demand curve increases at an increasing rate in the beginning and then increases at a decreasing rate.
- This shows that as income increases owing to increase in employment, expenditure of the economy increases at a decreasing rate.
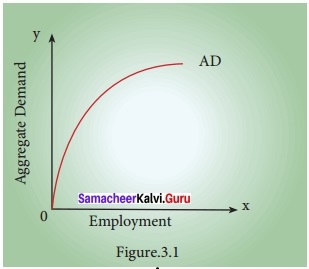
Question 2.
Aggregate Supply Function meaning and components?
Answer:
- Aggregate supply function is an increasing function of the level of employment.
- Aggregate supply refers to the value of total output of goods and services produced in an economy in a year.
- In other words, aggregate supply is equal to the value of national product, i.e., national income.
The components of aggregate supply are:
- Aggregate (desired) consumption expenditure (C)
- Aggregate (desired) private savings (S)
- Net tax payments (T) (Total tax payment to be received by the government minus transfer payments, subsidy and interest payments to be incurred by the government) and (iv) Personal (desired) transfer payments to the foreigners (Rf) (e.g. Donations to international relief efforts)
![]()
Question 3.
Describe the features of classicism?
Answer:
- Long – run equilibrium
- Saving is a social virtue.
- The function of money is to act as a medium of exchange
- Micro foundation to macro problems
- Champions of Laissez-fair policy
- Applicable only to the full employment situation.
- Capitalism is well and good.
- Balanced budget
- The equality between saving and investment is achieved through changes of rate of interest.
- Rate of interest is determined by saving and investment.
- Rate of interest is a stock.
- Supply creates its own demand.
- Rate of interest is a reward for saving.
Part – D
Answer The Following Questions In One Page.
Question 1.
Describe the Say’s Law of Market?
Answer:
- Say’s law of markets is the core of the classical theory of employment.
- J.B.Say (1776 – 1832) was a French Economist and an industrialist.
- He was influenced by the writings of Adam Smith and David Ricardo.
- J.B. Say enunciated the proposition that “Supply creates its own demand”.
- Hence there cannot be general over production or the problem of unemployment in the economy.
- According to Say, “When goods are produced by firms in the economy, they pay reward to the factors of production.
- The households after receiving rewards of the factors of production spend the amount on the purchase of goods and services produced by them.
- Therefore, each product produced in the economy creates demand equal to its value in the market.
- In short, this classical theory explains that “A person receives his income from production which is spent on the purchase of goods and services produced by others.
- For the economy as a whole, therefore, total production equals total income.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the features of Keynesianism?
Answer:
- Short – run equilibrium
- Saving is a vice
- The function of money is a medium of exchange on the one side and a store of value on the other side.
- Macro approach to national problems
- State intervention is advocated.
- Applicable to all situations – full employment and less than full employment.
- Capitalism has inherent contradictions.
- Budgeting should be adjusted to the requirements of economy.
- The equality between saving and investment is advanced through changes in income.
- Rate of interest is determined by the demand for and supply of money.
- Rate of interest is a flow.
- Demand creates its own supply.
- Rate of interest is a reward for parting with liquidity.
![]()
Question 3.
Describe the Effective demand?
Answer:
- The starting point of Keynes theory of employment and income is the principle of effective demand.
- Effective demand denotes money actually spent by the people on products of industry.
- The money which entrepreneurs receive is paid in the form of rent, wages, interest and profit.
- Therefore effective demand equals national income.
- An increase in the aggregate effective demand would increase the level of employment.
- A decline in total effective demand would lead to unemployment.
- Therefore, total employment of a country can be determined with the help of total demand ‘ of a country.
- According to the Keynes theory of employment, “Effective demand signifies the money spent on consumption of goods and services and on investment.
- The total expenditure is equal to the national income, which is equivalent to the national output”.
- The relationship between employment and output of an economy depends upon the level of effective demand which is determined by the forces of aggregate supply and aggregate demand.
ED = Y = C + I = Output = Employment - Effective demand determines the level of employment in the economy.
- When effective demand increases, employment will increase.
- When effective demand decreases, the level employment will decline.
- The effective demand will be determined by two determinants namely consumption and investment expenditures.
- The consumption function depends upon income of the people and marginal propensity to consume.
- According to Keynes, if income increases, consumption will also increase but by less than the increase in income.