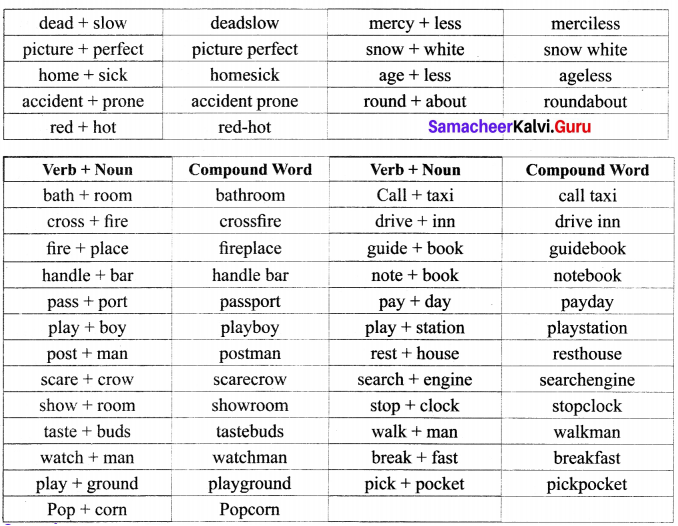
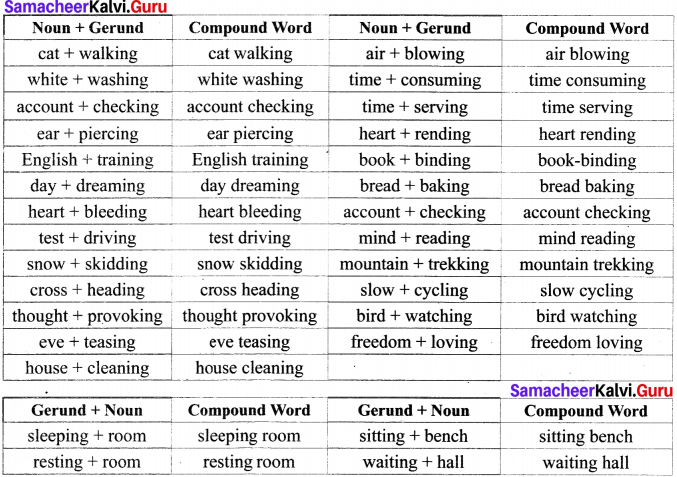
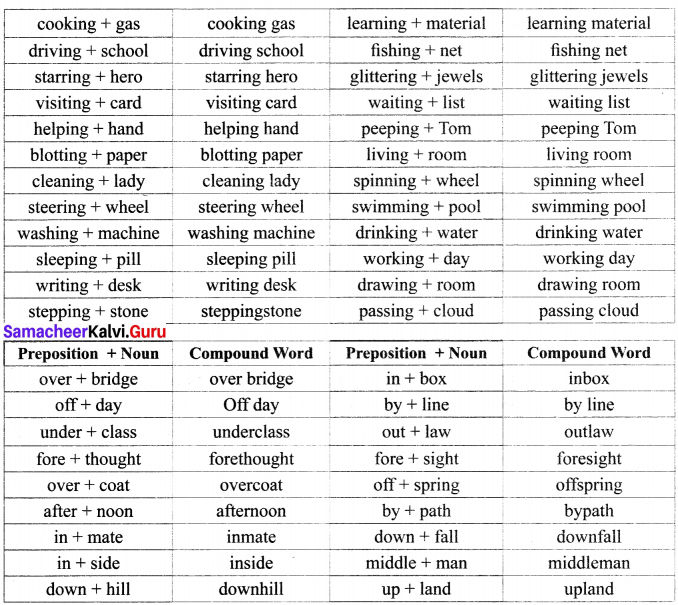
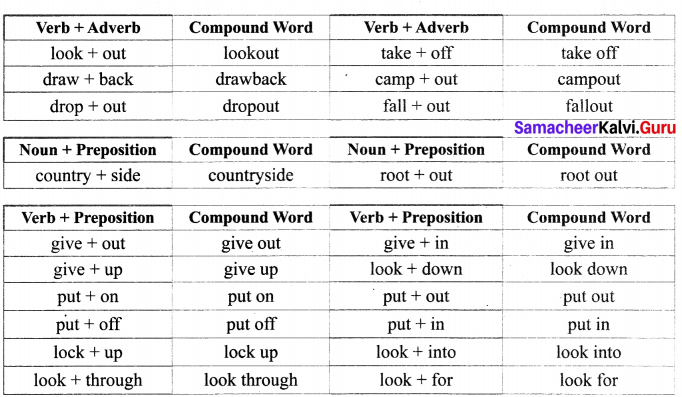
Students can Download Economics Chapter 2 National Income Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Solutions Chapter 2 National Income
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics National Income Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part – A
Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1.
Net National product at factor cost is also known as –
(a) National Income
(b) Domestic Income
(c) Per capita Income
(d) Salary
Answer:
(a) National Income
Question 2.
Primary sector is –
(a) Industry
(b) Trade
(c) Agriculture
(d) Construction
Answer:
(c) Agriculture

Question 3.
National income is measured by using ………………. methods.
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) Five
(d) Four
Answer:
(b) Three
Question 4.
Income method is measured by summing up of all forms of –
(a) Revenue
(b) Taxes
(c) Expenditure
(d) Income
Answer:
(d) Income
Question 5.
Which is the largest figure?
(a) Disposable income
(b) Personal Income
(c) NNP
(d) GNP
Answer:
(d) GNP

Question 6.
Expenditure method is used to estimate national income in –
(a) Construction sector
(b) Agricultural Sector
(c) Service sector
(d) Banking sector
Answer:
(a) Construction sector
Question 7.
Tertiary sector is also called as ……………………….. sector.
(a) Service
(b) Income
(c) Industrial
(d) Production
Answer:
(a) Service
Question 8.
National income is a measure of the performance of an economy.
(a) Industrial
(b) Agricultural
(c) Economic
(d) Consumption
Answer:
(c) Economic

Question 9.
Per capita income is obtained by dividing the National income by –
(a) Production
(b) Population of a country
(c) Expenditure
(d) GNP
Answer:
(b) Population of a country
Question 10.
GNP = ……………………… + Net factor income from abroad.
(a) NNP
(b) NDP
(c) GDP
(d) Personal income
Answer:
(c) GDP
Question 11.
NNP stands for ………………………
(a) Net National Product
(b) National Net product
(c) National Net Provident
(d) Net National Provident
Answer:
(a) Net National Product

Question 12.
…………………… is deducted from gross value to get the net value.
(a) Income
(b) Depreciation
(c) Expenditure
(d) Value of final goods
Answer:
(b) Depreciation
Question 13.
The financial year in India is –
(a) April 1 to March 31
(b) March 1 to April 30
(c) March 1 to March 16
(d) January 1 to December 31
Answer:
(a) April 1 to March 31
Question 14.
When net factor income from abroad is deducted from NNP, the net value is –
(a) Gross National Product
(b) Disposable Income
(c) Net Domestic Product
(d) Personal Income
Answer:
(c) Net Domestic Product

Question 15.
The value of NNP at production point is called –
(a) NNP at factor cost
(b) NNP at market cost
(c) GNP at factor cost
(d) Per capita income
Answer:
(a) NNP at factor cost
Question 16.
The average income of the country is –
(a) Personal Income
(b) Per capita income
(c) Inflation Rate
(d) Disposal Income
Answer:
(b) Per capita income
Question 17.
The value of national income adjusted for inflation is called –
(a) Inflation Rate
(b) Disposal Income
(c) GNP
(d) Real national income
Answer:
(d) Real national income

Question 18.
Which is a flow concept?
(a) Number of shirts
(b) Total wealth
(c) Monthly income
(d) Money supply
Answer:
(c) Monthly income
Question 19.
PQLI is the indicator of –
(a) Economic growth
(b) Economic welfare
(c) Economic progress
(d) Economic development
Answer:
(b) Economic welfare
Question 20.
The largest proportion of national income comes from –
(a) Private sector
(b) Local sector
(c) Public sector
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Private sector

Part – B
Answer The Following Questions In One or Two Sentences.
Question 21.
Define National Income?
Answer:
National Income means the total money value of all final goods and services produced in a country during a particular period of time (one year).
Question 22.
Write the formula for calculating GNP?
Answer:
GNP at market prices means the gross value of final goods and services produced annually in a country plus net factor income from abroad
(C + I + G + (X – M) + (R – P)).
Question 23.
What is the difference between NNP and NDP?
Answer:
NNP:
- NNP refers to the market value of output.
- NNP at factor cost is the total of income payment made to factors of production.
NDP:
- NDP is the value of net output of the economy during the year
- The country’s capital equipment wears out of becomes outdated each year during the production process.

Question 24.
Trace the relationship between GNP and NNP?
Answer:
GNP:
1. Total money value of final goods and services produced in a country during a particular year (one year).
NNP:
1. Total money value of final goos and services produced in a country in a country during a particular year (one year).
Question 25.
What do you mean by the term ‘Personal Income’?
Answer:
Personal income is the total income received by the individuals of a country from all sources before payment of direct taxes in a year.
Question 26.
Define GDP deflator?
Answer:
GDP is the total market value of final goods and services produced within the country during a year. This is calculated at market prices and is known as GDP at market prices. Thus GDP by expenditure method at market prices = C + I + G + (X – M)
Where C – consumption goods;
I – Investment goods;
G – Government purchases;
(X – M) is net export which can be positive or negative.

Question 27.
Why is self consumption difficult in measuring national income?
Answer:
- Farmers keep a large portion of food and other goods produced on the farm for self consumption.
- The problem is whether that part of the produce which is not sold in the market can be included in national income or not.
Part – C
Answer The Following Questions In One Paragraph.
Question 28.
Write a short note on per capita income?
Answer:
Per Capita Income:
- The average income of a person of a country in a particular year is called Per Capita Income.
- Per capita income is obtained by dividing national income by population.
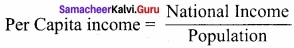
Question 29.
Differentiate between personal and disposable income?
Answer:
Personal income:
Personal income is the total income received by the individuals of a country from all sources before payment of direct taxes in a year.
Disposable income:
Disposable Income is also known as Disposable personal income. It is the individuals income after the payment of income tax. This is the amount available for households for consumption.

Question 30.
Explain briefly NNP at factor cost?
Answer:
Net National Product refers to the value of the net output of the economy during the year. NNP is obtained by deducting the value of depreciation, or replacement allowance of the capital assets from the GNP. It is expressed as, NNP = GNP – depreciation allowance.
Question 31.
Give short note on Expenditure method?
The Expenditure Method (Outlay method):
Answer:
- The total expenditure incurred by the society in a particular year is added together.
- To calculate the expenditure of a society, it includes personal consumption expenditure, net domestic investment, government expenditure on consumption as well as capital goods and net exports.
Question 32.
What is the solution to the problem of double counting in the estimation of national income?
Answer:
- The value obtained is actually the GNP at market prices. Care must be taken to avoid double counting.
- The value of the final product is derived by the summation of all the values added in the productive process.
- To avoid double counting, either the value of the final output should be taken into the estimate of GNP or the sum of values added should be taken.
- Double counting is to be avoided under value added method.
- Any commodity which is either raw material or intermediate good for the final production should not be included.
- For example, value of cotton enters value of yam as cost, and value of yam in cloth and
that of cloth in garments.
- At every stage value added only should be calculated.

Question 33.
Write briefly about national income and welfare?
Answer:
National Income and Welfare:
National Income is considered as an indicator of the economic wellbeing of a country. The per capita income as an index of economic welfare suffers from limitations which are stated below:
- The economic welfare depends upon the composition of goods and services provided. The greater the proportion of capital goods over consumer goods, the improvement in economic welfare will be lesser.
- Higher GDP with greater environmental hazards such as air, water and soil pollution will be little economic welfare.
- The production of war goods will show the increase in national output but not welfare.
- An increase in per capita income may be due to employment of women and children or forcing workers to work for long hours. But it will not promote economic welfare.
Question 34.
List out the uses of national income?
Answer:
The following are some of the concepts used in measuring national income?
GDP:
- GDP is the total market value of final goods and services produced within the country during a year.
- This is calculated at market prices and is known as GDP at market prices. Thus GDP by expenditure method at market
prices = C + I + G + (X-M)
Where C – Consumption goods;
I – Investment goods;
G – Government purchases;
(X – M) is net export which can be positive or negative.
Net National Product (NNP) (at Market price):
- Net National Product refers to the value of the net output of the economy during the year.
- NNP is obtained by deducting the value of depreciation, or replacement allowance of the capital assets from the GNP. It is expressed as,
- NNP = GNP – depreciation allowance.
NNP at Factor cost:
- NNP refers to the market value of output.
- NNP at factor cost is the total of income payment made to factors of production.
Personal Income:
- Personal income is the total income received by the individuals of a country’ from all sources before payment of direct taxes in a year.
Per Capita Income:
- The average income of a person of a country in a particular year is called Per Capita Income.
- Per capita income is obtained by dividing national income by population.
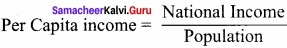
Disposable Income:
- Disposable Income is also known as Disposable personal income.
- It is the individuals income after the payment of income tax.
- This is the amount available for households for consumption.
Real Income:
- Nominal income is national income expressed in terms of a general price level of a particular year in other words, real income is the buying power of nominal income.
GDP deflator:
- GDP deflator is an index of price changes of goods and services included in GDP.
- It is a price index which is calculated by dividing the nominal GDP in a given year by the real GDP for the same year and multiplying it by 100.

Part – D
Answer The Following Questions In One Page.
Question 35.
Explain the importance of national income
Importance of National Income Analysis
Answer:
National income is of great importance for the economy of a country. Nowadays the national income is regarded as accounts of the economy, which are known as social accounts. It enables us:
1. To know the relative importance of the various sectors of the economy and their contribution towards national income; from the calculation of national income, we could find how income is produced, how it is distributed, how much is spent, saved or taxed.
2. To formulate the national policies such as monetary policy, fiscal policy and other policies; the proper measures can be adopted to bring the economy to the right path with the help of collecting national income data.
3. To formulate planning and evaluate plan progress; it is essential that the data pertaining to a country’s gross income, output, saving and consumption from different sources should be available for economic planning.
4. To build economic models both in short – run and long – run.
5. To make international comparison, inter – regional comparison and inter – temporal comparison of growth of the economy during different periods.
6. To know a country’s per capita income which reflects the economic welfare of the country (Provided income is equally distributed)
7. To know the distribution of income for various factors of production in the country.
8. To arrive at many macro economic variables namely, Tax – GDP ratio, Current Account Deficit – GDP ratio, Fiscal Deficit – GDP ratio, Debt – GDP ratio etc.

Question 36.
Discuss the various methods of estimating the national income of a country?
Answer:
There are three methods that are used to measure national income.
- Production or value added method
- Income method or factor earning method
- Expenditure method
And if these methods are done correctly, the following equation must hold
Output = Income = Expenditure
This is because the three methods are circular in nature. It begins as production, through recruitments of factors of production, generating income and going as incomes to factors of production.
Product Method:
Product method measures the output of the country. It is also called inventory method. Under this method, the gross value of output from different sectors like agriculture, industry, trade and commerce, etc., is obtained for the entire economy during a year. The value obtained is actually the GNP at market prices. Care must be taken to avoid double counting.
Income Method (Factor Earning Method):
This method approaches national income from the distribution side. Under this method, national income is calculated by adding up all the incomes generated in the course of producing national product.
National income is calculated as domestic factor income plus net factor incomes from abroad. In short,
Y = w + r + i + π + (R – P)
w = wages, r = rent, i = interest, n = profits,
This method is adopted for estimating the contributions of the remaining sectors, viz., small enterprises, banking and insurance, commerce and transport, professions, liberal arts and domestic service, public authorities, house property and foreign sector transaction.
The Expenditure Method (Outlay method): \
The total expenditure incurred by the society in a particular year is added together. To calculate the expenditure of a society, it includes personal consumption expenditure, net domestic investment, government expenditure on • consumption as well as capital goods and net exports. Symbolically,
GNP = C + I + G + (X – M)
C – Private consumption expenditure
I – Private Investment Expenditure
G – Government expenditure
X – M = Net exports

Question 37.
What are the difficulties involved in the measurement of national income?
Answer:
Difficulties in Measuring National Income:
- In India, a special conceptual problem is posed by the existence of a large, unorganised and non-monetised subsistence sector where the barter system still prevails for transacting goods and services.
- Here, a proper valuation of output is very difficult.
Transfer payments:
- Government makes payments in the form of pensions, unemployment allowance, subsidies, etc. These are government expenditure.
- But they are not included in the national income.
- Because they are paid without adding anything to the production processes.
- During a year, Interest on national debt is also considered transfer payments because it is paid by the government to individuals and firms on their past savings without any productive work.
Difficulties in assessing depreciation allowance:
- The deduction of depreciation allowances, accidental damages, repair and replacement charges from the national income is not an easy task.
- It requires high degree of judgment to assess the depreciation allowance and other charges.
Unpaid services:
- A housewife renders a number of useful services like preparation of meals, serving, tailoring, mending, washing, cleaning, bringing up children, etc.
- She is not paid for them and her services are not directly included in national income.
Income from illegal activities:
- Income earned through illegal activities like gambling, smuggling, illicit extraction of liquor, etc., is not included in national income.
- Such activities have value and satisfy the wants of the people but they are not considered as productive from the point of view of society.
Production for self-consumption and changing price:
- Farmers keep a large portion of food and other goods produced on the farm for self consumption.
- The problem is whether that part of the produce which is not sold in the market can be included in national income or not.
Capital Gains:
- The problem also arises with regard to capital gains.
- Capital gains arise when a capital asset such as a house, other property, stocks or shares, etc. is sold at higher price than was paid for it at the time of purchase.
- Capital gains are excluded from national income.
Statistical problems:
- There are statistical problems, too. Great care is required to avoid double counting. Statistical data may not be perfectly reliable, when they are compiled from numerous sources.
- Skill and efficiency of the statistical staff and cooperation of people at large are also equally important in estimating national income.

Question 38.
Discuss the importance of social accounting in economic analysis?
Answer:
National Income and Social Accounting:
- National income is also being measured by the social accounting method.
- Under this method, the transactions among various sectors such as firms, households, government, etc., are recorded and their interrelationships traced.
- The social accounting framework is useful for economists as well as policy makers, because it represents the major economic flows and statistical relationships among various sectors of the economic system.
- It becomes possible to forecast the trends of economy more accurately.
Social Accounting and Sector:
- Under this method, the economy is divided into several sectors.
- A sector is a group of individuals or institutions having common interrelated economic transactions.
- The economy is divided into the following sectors:
- Firms
- Households
- Government
- Rest of the world and
- Capital sector.
- “Firms” undertake productive activities. Thus, they are all organizations which employ the factors of production to produce goods and services.
- “Households” are consuming entities and represent the factors of production, who receive payment for services rendered by them to firms. Households consume the goods and services that are produced by the firms.
- “The Government sector” refers to the economic transactions of public bodies at all levels, centre, state and local.
- The main function of the government is to provide social goods like defence, public health, education, etc.
- “Rest of the world sector” relates to international economic transactions of the country. It contains income, export and import transactions, external loan transaction, and allied overseas investment income and payments.
- “Capital sector” refers to saving and investment activities. It includes the transactions of banks, insurance corporations, financial houses, and other agencies of the money market.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics National Income Additional Questions
Part – A
I. Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1.
Who first introduced the concept of national Income?
Answer:
(a) Simon Kuznets
(b) Karl Marx
(c) Marshall
(d) Adam Smith
Answer:
(a) Simon Kuznets
Question 2.
………………. is the total market value of final goods and services produced with in the country during a year?
(a) GNP
(b) NDP
(c) GDP
(d) NNP
Answer:
(c) GDP

Question 3.
……………………. is also known as Disposable Personal Income?
(a) Personal Income
(b) Disposable Income
(c) Consumer Income
(d) Product Income
Answer:
(b) Disposable Income
Question 4.
………………………. is great importance for the economy of a country?
(a) Personal Income
(b) National Income
(c) Industry Income
(d) Village Income
Answer:
(b) National Income
Question 5.
…………………….. helps to build economic models both in short run and long run?
(a) National Income
(b) Personal Income
(c) Per Capita Income
(d) State Income
Answer:
(a) National Income

Question 6.
……………….. Sector refer to Saving and Investment activities?
(a) Government
(b) World
(c) Capital
(d) Accounting
Answer:
(c) Capital
Question 7.
The Economy is divided into the ………………….. sectors?
(a) two
(b) three
(c) four
(d) five
Answer:
(d) five
Question 8.
…………………….. is considered as a better Indicator of economic welfare?
(a) PQLI
(b) NNP
(c) GDP
(d) NNP
Answer:
(a) PQLI

Question 9.
……………………. means the total money value of all final goods and services produced in a country?
(a) Personal Income
(b) Disposable Income
(c) National Income
(d) Per Capita Income
Answer:
(c) National Income
Question 10.
While assessing sectoral contribution to GDP, the economy is Sectors?
(a) two
(b) three
(c) four
(d) five
Answer:
(b) three
Question 11.
The growth of an economy is indicated by an –
(a) increase in general price level
(b) increase in National Income
(c) increase in contribution of agriculture
(d) increase in Investment
Answer:
(b) increase in National Income

Question 12.
Per Capital Income of an economy can be established by –
(a) Dividing GDP by population
(b) dividing GNP by population
(c) multiplying GNP by population
(d) Multiplying GDP by population
Answer:
(b) dividing GNP by population
Question 13.
Write the Four Sector Model of National Income?
(а) Y = C + I + G + (X – M)
(b) Y = C + I + G + X
(c) Y = C + I + G + M
(d) Y – C + I + G (M – X)
Answer:
(а) Y = C + I + G + (X – M)

Question 14.
Which includes profits earned from Capital Invested abroad?
(a) GNP
(b) GDP
(c) NNP
(d) NDP
Answer:
(a) GNP
Question 15.
Write two components of National Income?
(a) Consumers and producers
(b) Consumers and Industries
(c) Consumers and agricultures
(d) Agricultures and Industries
Answer:
(a) Consumers and producers
Question 16.
The country’s economic performance has been measured by Indicators of –
(a) per Capita Income
(b) national Income
(c) per People’s Income
(d) state Income
Answer:
(b) national Income
Question 17.
NNP is arrived by deducting value of depreciation from –
(a) NDP
(b) GDP
(c) GNP
(d) NNP
Answer:
(c) GNP

Question 18.
Income Method of National Income is the side of our National Income?
(a) Production
(b) Agriculture
(c) Income
(d) Distribution
Answer:
(d) Distribution
Question 19.
The difference between NNP and NDP is –
(a) net Factor Income from abroad
(b) depreciation
(c) current transfer
(d) direct taxes
Answer:
(a) net Factor Income from abroad
Question 20.
In …………………… method, the measures of GDP?
(a) Income
(b) Expenditure
(c) Product
(d) Capital
Answer:
(c) Product
Question 21.
………………… is measure of Income flow from production.
(a) Per Capita Income
(b) National Income
(c) Personal Income
(d) Income method
Answer:
(b) National Income

Question 22.
In estimating national Income, Net value added method is also known as –
(a) income Method
(b) expenditure Method
(c) product Method
(d) investment Method
Answer:
(c) product Method
Question 23.
National Income as commonly understood by everyone refers to –
(a) GNP
(b) GDP
(c) NDP
(d) NNP
Answer:
(d) NNP
Question 24.
Economic growth is determined by changes in ……………………… National income of the country.
(a) Real
(b) Total
(c) True
(d) GDP
Answer:
(c) True
Question 25.
GDP is measure of an economy’s total ………………………..
(a) inflation
(b) deflation
(c) product
(d) output
Answer:
(d) output

II. Match the following and choose the correct answer by using codes given below:
Question 1.
A. Nominal Income – (i) Facrtor earninig method
B. Production – (ii) National Income
C. Income Method – (iii) Final value of goods
D. Expenditure Method – (iv) Value added method
Codes:
(a) A (ii) B (iv) C (i) D (iii)
(b) A (iii) B(ii) C (iv) D (i)
(c) A (ii) B (iv) C (iii) D (i)
(d) A (iv) B (iii) C (i) D (ii)
Answer:
(a) A (ii) B (iv) C (i) D (iii)
Question 2.
A. GDP – (i) NNP
B. Net Income Abroad – (ii) Foreign trade excluded
C. GNP – Depreciation – (iii) X – M
D. Net National Product – (iv) GNP – Depreciation
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (ii) B (iii) C (i) D (iv)
(c) A (iv) B (i) C (ii) D (iii)
(d) A (iii) B (ii) C (iv) D (i)
Answer:
(b) A (ii) B (iii) C (i) D (iv)

Question 3.
A. Per Capita Income – (i) Half of our National Income
B. Purchasing power of Income – (ii) C + I + G + (X – M)
C. Service Sector – (iii) Standard of Living
D. Expenditure method – (iv) National Income
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (iv) B (iii) C (i) D (ii)
(c) A (ii) B (i) C (iii) D (iv)
(d) A (iii) B (iv) C (i) D (ii)
Answer:
(d) A (iii) B (iv) C (i) D (ii)
Question 4.
A. Labour Income – (i) Profit and Interest
B. Capital Income – (ii) Domestic Factor Income
C. Mixed Income – (iii) Wages and Salaries
D. National Income – (iv) Farming, Sole proprietorship
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (ii) C (iv) D (iv)
(b) A (i) B (iii) C (ii) D (i)
(c) A (iii) B (i) C (iv) D (ii)
(d) A (iv) B (ii) C (ii) D (iii)
Answer:
(c) A (iii) B (i) C (iv) D (ii)

Question 5.
A. Income Method – (i) Outlay Method
B. Expenditure Method – (ii) Y = w + r + π + 7t + (R – P)
C. Income Method – (iii) GNP = C + I + G + (X-M)
D. Expenditure Method – (iv) Factor Earning Method
Codes:
(a) A (ii) B (i) C (iv) D (iii)
(b) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(c) A (iii) B (ii) C (i) D (iv)
(d) A (i) B (iv) C (iii) D (ii)
Answer:
(a) A (ii) B (i) C (iv) D (iii)
III. State whether the statements are true or false.
Question 1.
(i) Net Factor Income earned abroad is always positive.
(ii) Per Capita Income is influenced vastly by population growth.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Question 2.
(i) Income Method estimates National Income from the production side.
(ii) The value added method is also known as output method.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (0 and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true

Question 3.
(i) National Income at current prices is vastly influenced by a rise in general price levels.
(ii) Percentage share of agriculture sector in the national income is increasing.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
Question 4.
(i) GNP is Crude Indicator for living standard.
(ii) The non – resident Indian income will be added to GDP to arrive at our GNP.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
Question 5.
(i) Secondary Sector is Agriculture.
(ii) Tertiary Sector is Industry.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false

IV. Which of the following is correctly matched:
Question 1.
(a) Disposable Income – Gross National Product
(b) Three Method – Domestic Income
(c) Parallel Economy – Industries
(d) Transfer Earnings – Medical payments
Answer:
(a) Disposable Income – Gross National Product
Question 2.
(a) National Income – Employment
(b) GDP Indicates – Productive capacity
(c) Output = Income = – Price
(d) Primary Sector – Banking
Answer:
(b) GDP Indicates – Productive capacity
Question 3.
(a) Expenditure Method – Per Capita Income
(b) Product Method – Self consumption
(c) Income Method – Factor Earning Method
(d) Revenue Method – Outlay Method
Answer:
(c) Income Method – Factor Earning Method

Question 4.
(a) Labour Income – Farming, Sole proprietorship
(b) Capital Income – Profit, Interest, Dividend & Royalty
(c) Mixed Income – Domestic Factor Income
(d) National Income – Wages and Salaries
Answer:
(b) Capital Income – Profit, Interest, Dividend & Royalty
Question 5.
(a) PQLI – Physical Quantity of Life Index
(b) PQLI – Personal Quantity of Life Index
(c) PQLI – Personal Quality of Life Index
(d) PQLI – Physical Quality of Life Index
Answer:
(d) PQLI – Physical Quality of Life Index
V. Which of the following is not correctly matched:
Question 1.
(a) Simon Kuznets introduced – National Income
(b) Illegal activities are – Gambling and Smuggling
(c) Product Method, the measures – GDP
(d) Income Method – Expenditure Method
Answer:
(a) Income Method – Expenditure Method
Question 2.
(a) Disposable Income – Disposable Personal Income
(b) Per Capita Income – The average income of a person
(c) Real Income – Production
(d) Nominal Income – National Income
Answer:
(c) Real Income – Production

Question 3.
(a) Product Method – Inventory Method
(b) Income Method – Factor Earning Method
(c) Expenditure Method – Outlay Method
(d) Value added Method – Transfer Payments
Answer:
(d) Value added Method – Transfer Payments
Question 4.
(a) Two Sector Model – Households, firms
(b) Four Sector Economy – Foreign Earning Method
(c) Four Sector Model – outlay Method
(d) Major Problem – Transfer Payments
Answer:
(a) Two Sector Model – Households, firms
Question 5.
(a) Transfer payments – Pensions, unemployement
(b) Unpaid services – House Wife
(c) Illegal activities – Smuggling
(d) The Government Sector – Private Enterprises
Answer:
(d) The Government Sector – Private Enterprises
VI. Pick the odd one out.
Question 1.
The concepts used in Measuring National Income?
(a) GDP
(b) NNP
(c) NNP at factor cost
(d) Personal Expenditure
Answer:
(d) Personal Expenditure
Question 2.
GNP – Includes these types of final goods and services?
(a) Consumption
(b) Investment
(c) Government
(d) Capital
Answer:
(d) Capital

Question 3.
The Expenditure Method precautions are –
(a) Second hand goods should not be included
(b) Purchase of shares and bonds are not be included
(c) Transfer payments of old age pension added
(d) Avoid double counting
Answer:
(c) Transfer payments of old age pension added
Question 4.
The Economy is divided into the following sectors –
(a) Investment Sector
(b) Firms
(c) Households
(d) Government Sector
Answer:
(a) Investment Sector

Question 5.
Dispsoable Income is the individuals Income after the payment of Income tax?
(a) Disposable Income = Personal Income – Direct tax
(b) Disposable Income = Consumption + Saving
(c) Disposable Income = Agriculture + Industry
(d) Disposable Income = Individual Income + Income Tax
Answer:
(c) Disposable Income = Agriculture + Industry
VII. Assertion and Reason.
Question 1.
Assertion (A): National Income is a measure of the total value of the goods and services produced in an economy for a year.
Reason (R): GNP – is the total value of output produced and income received in a year by domestic residence of a country.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false (id) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Product method measures the output of the country.
Reason (R): Product method measures the agriculture field only.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(c) ‘A’ is – true but ‘R’ is false

Question 3.
Assertion (A): Deflation is the common feature in almost all the economies.
Reason (R): Inflation is the common feature in almost all the economies.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Question 4.
Assertion (A): The Income method is called Factor Earning Method.
Reason (R): This method approaches National Income from the distribution side.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
Question 5.
Assertion (A): The Expenditure method is called outlay method.
Reason (R): This method is used only private sector.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false

Part – B
Answer The Following Questions In One or Two Sentences.
Question 1.
Write the Factor Incomes group?
Answer:
Factor incomes are grouped under labour income, capital income and mixed income.
- Labour income – Wages and salaries, fringe benefits, employer’s contribution to social security.
- Capital income – Profit, interest, dividend and royalty
- Mixed income – Farming, sole proprietorship and other professions.
Question 2.
Write the headlines of difficulties in Measuring National Income?
Answer:
Difficulties in Measuring National Income:
- Transfer payments:
- Difficulties in assessing depreciation allowance:
- Unpaid services:
- Income from illegal activities:
- Production for self-consumption and changing price:
- Capital Gains:
- Statistical problems

Question 3.
Define “Capital Gains”?
Answer:
The problem also arises with regard to capital gains. Capital gains arise when a capital asset such as a house, other property, stocks or shares, etc. is sold at higher price than was paid for it at the time of purchase. Capital gains are excluded from national income.
Question 4.
Define “Social and Environmental Cost”?
Answer:
Social and Environmental Cost: While producing economic goods, many environmental and social bads are also generated. Hence, they also must be considered while enumerating National income.

Question 5.
Define “National Income & Erosion of National Wealth”?
Answer:
For achieving higher GDP, larger natural resources are being depleted or damaged. This means reduction of potential for future growth. Hence, it is suggested that while assessing national income, loss of natural resources should be subtracted from national income.
Part – C
Answer The Following Questions In One Paragraph.
Question 1.
Write the statistical problems?
Answer:
The following are the some of the statistical problems:
- Accurate and reliable data are not adequate, as farm output in the subsistence sector is not completely informed. In animal husbandry, there are no authentic production data available.
- Different languages, customs, etc., also create problems in computing estimates.
- People in India are indifferent to the official inquiries. They are in most cases non – cooperative also.
- Most of the statistical staff are untrained and inefficient.

Question 2.
Discuss the estimating the national income through the Income Method precautions?
Answer:
- Transfer payments are not to be included in estimation of national income as these payments are not received for any services provided in the current year such as pension, social insurance etc.
- The receipts from the sale of second hand goods should not be treated as part of national income as they do not create new flow of goods or services in the current year.
- Windfall gains such as lotteries are also not to be included as they do not represent receipts from any current productive activity.
- Corporate profit tax should not be separately included as it has been already included as a part of company profit.
Question 3.
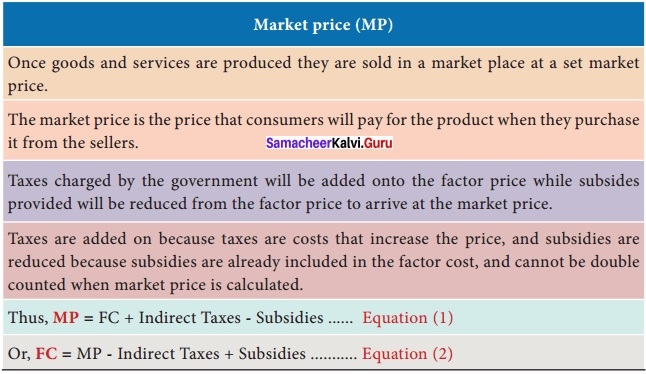
What is Market price and Equations?
Answer:
Part – D
Answer The Following Questions In One Page.
Question 1.
Write the gross value of the farm output in India?
Answer:
In India, the gross value of the farm output is obtained as follows:
- Total production of 64 agriculture commodities is estimated. The output of each crop is measured by multiplying the area sown by the average yield per hectare.
- The total output of each commodity is valued at market prices.
- The aggregate value of total output of these 64 commodities is taken to measure the gross value of agricultural output.
- The net value of the agricultural output is measured by making deductions for the cost of seed, manures and fertilisers, market charges, repairs and depreciation from the gross value.

Question 2.
Explain the Expenditure Method (Outlay Method) precautions?
Answer:
Precautions:
- Second hand goods:
The expenditure made on second hand goods should not be included.
- Purchase of shares and bonds:
Expenditures on purchase of old shares and bonds in the secondary market should not be included.
- Transfer payments:
Expenditures towards payment incurred by the government like old age pension should not be included.
- Expenditure on intermediate goods:
Expenditure on seeds and fertilizers by farmers, cotton and yam by textile industries are not to be included to avoid double counting. That is only expenditure on final products are to be included.

Question 3.
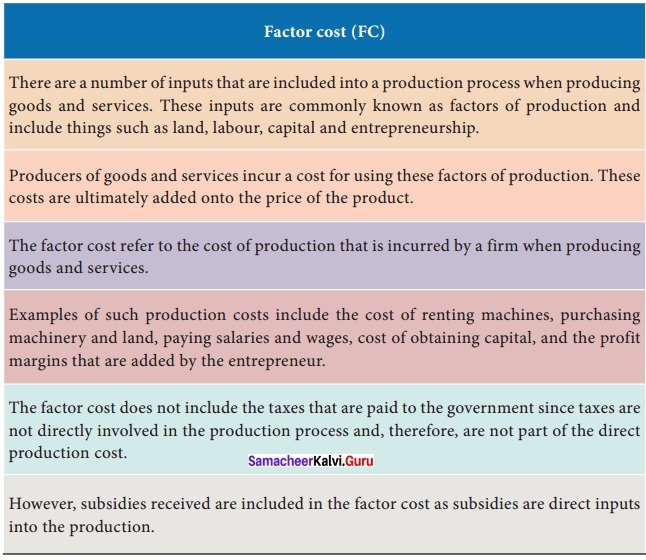
Explain the Importance of Factor Cost?
Answer:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()